-
Články
Top novinky
Reklama- Vzdělávání
- Časopisy
Top články
Nové číslo
- Témata
Top novinky
Reklama- Videa
- Podcasty
Nové podcasty
Reklama- Kariéra
Doporučené pozice
Reklama- Praxe
Top novinky
ReklamaA Mutation in the Mouse Gene Leads to Impaired Hedgehog Signaling
The Hedgehog (Hh) signaling pathway determines pattern formation in many developing tissues, e.g., during digit formation in the limbs, by regulating proteins of the Gli family. Activation of these proteins requires their transport to the tip of the primary cilium (an antenna-like sensory structure of the cell), and subsequent dissociation from their negative regulator, Sufu. Little is known about the mechanism underlying this dissociation. To gain new insights into Hh signaling, we analyzed the mutant mouse hop-sterile (hop), whose developmental defects suggest that the primary cilia are dysfunctional. We discovered that the hop mutation lies in the Ttc26 gene, and that levels of the encoded protein are low in hop mice. Normal Ttc26 was found to bind to Intraflagellar Transport (IFT) complex B, a structure essential for building the cilium and moving proteins towards its tip. Nevertheless, unlike previously characterized mutations that affect IFT complex B, hop did not interfere with either the formation of primary cilia or the accumulation of Gli at their tips, but rather with dissociation of Gli from Sufu. Our results provide novel insights into Hh signaling, demonstrating that efficient coupling between Gli's accumulation at the ciliary tip and its dissociation from Sufu depends on Ttc26.
Published in the journal: . PLoS Genet 10(10): e32767. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1004689
Category: Research Article
doi: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1004689Summary
The Hedgehog (Hh) signaling pathway determines pattern formation in many developing tissues, e.g., during digit formation in the limbs, by regulating proteins of the Gli family. Activation of these proteins requires their transport to the tip of the primary cilium (an antenna-like sensory structure of the cell), and subsequent dissociation from their negative regulator, Sufu. Little is known about the mechanism underlying this dissociation. To gain new insights into Hh signaling, we analyzed the mutant mouse hop-sterile (hop), whose developmental defects suggest that the primary cilia are dysfunctional. We discovered that the hop mutation lies in the Ttc26 gene, and that levels of the encoded protein are low in hop mice. Normal Ttc26 was found to bind to Intraflagellar Transport (IFT) complex B, a structure essential for building the cilium and moving proteins towards its tip. Nevertheless, unlike previously characterized mutations that affect IFT complex B, hop did not interfere with either the formation of primary cilia or the accumulation of Gli at their tips, but rather with dissociation of Gli from Sufu. Our results provide novel insights into Hh signaling, demonstrating that efficient coupling between Gli's accumulation at the ciliary tip and its dissociation from Sufu depends on Ttc26.
Introduction
The Hedgehog (Hh) signaling pathway plays critical roles in embryonic development, wound healing, and tumorigenesis [1]–[4]. It is activated when the receptor protein Patched-1 (Ptch1) binds to one of the secreted Hh lipoproteins, Sonic Hh (Shh), Indian Hh, or Desert Hh [5], [6]. The Hh-Ptch1 interaction affects cell proliferation, differentiation, and patterning by regulating three Gli transcription factors (Gli1-3) [7], [8], and the extent of Gli activation is dictated by the ratio of the activator and repressor forms of Gli proteins in the cell. When Hh is absent, the full-length Gli3 protein (Gli3-F) is processed into a shorter repressor form (Gli3-R), which strongly suppresses the expression of target genes [9]. The repressor form of Gli2 (Gli2-R), in contrast, has only a minimal effect on transcription, and is formed inefficiently from full-length Gli2 (Gli2-F) [10]. Gli1 has no repressor form; it is regulated transcriptionally through activation of the other two Gli proteins [11]. Hh signaling activates both Gli2-F and Gli3-F and blocks their processing into repressors [9], [10]. Although data on the full range and importance of various posttranscriptional modifications of Gli are still emerging [12]–[16], it is clear that a crucial step in the activation of Gli2-F and Gli3-F is their dissociation from Sufu [17], [18].
The primary cilium is the Hh signaling center of the mammalian cell. In the absence of Hh proteins, Patch1 is localized to this structure, where it inhibits the activity of the seven-span transmembrane protein Smoothened (Smo) [19]. Activation of the Hh pathway causes Ptch1 to exit the cilium and Smo to enter [19], [20]. Smo enhances the ciliary import of Gli-F proteins (Gli-Fs) by inhibiting protein kinase A [21], [22], after which Gli-Fs are transported to the tip. This trafficking of Gli-Fs to the ciliary tip is required for their dissociation from Sufu [17], [18], and thus for activation of the Gli transcription factors [23]–[25].
Ciliary trafficking is facilitated by IFT particles, whose core proteins are organized into complexes A and B [26]. Complex B interacts physically with the kinesin-2 motor to mediate anterograde transport (towards the ciliary tip) [27], [28]. Complex A and cytoplasmic dynein 2 are necessary for retrograde transport. Mutations in the gene that encodes cytoplasmic dynein 2 lead to the production of shortened cilia and reduced Hh signaling [29], [30]. The complete absence of subunit Ift144 of IFT complex A likewise results in stumpy cilia and decreased Hh signaling, whereas a hypomorphic Ift144 allele and the null alleles of two other genes encoding components of complex A (Ift122, Ift139) are associated with the formation of swollen cilia and enhanced Hh signaling [31]–[33]. With regard to mutations affecting complex B, depending on the subunit involved, defects can include a lack of ciliogenesis, the formation of short cilia, or the dysregulation of Ptch1 and Smo trafficking [24], [34]–[39]. All pathogenic mutations in complex B genes analyzed to date prevent or reduce Gli trafficking to the ciliary tip and inhibit Hh pathway activation. Two mechanisms by which complex B defects impair Hh signaling have been identified: indiscriminate interference with ciliary trafficking due to structural changes in the axoneme [40], or selectively dysregulation of re-localization of the Hh signaling proteins Ptch1 and Smo [34].
In an effort to gain additional insight into Hh signaling, we searched publicly available mouse lines with unidentified gene mutations for phenotypic signs of reduced Hh signaling. We selected the hop mouse for further analysis based on its preaxial polydactyly, hopping gait, hydrocephalus, and male sterility [41]–[47]; preaxial polydactyly also occurs in Gli3+/− mice [48], and a hopping gait has been described in Gli1−/−; Gli2+/− mice [49]. Furthermore, although Hh signaling and primary cilia had not been examined in hop mice previously, their motile cilia had been reported to be abnormal. Firstly, their sperms lack flagella, explaining the male sterility phenotype [43]. Secondly, although their epithelia in the trachea, oviduct, and ependyma form motile cilia, approximately 40% of these lack outer dynein arms [43]. Because ciliary beating at the apical side of ependymal cells is critical for the normal flow of cerebrospinal fluid [50], the partial lack of outer dynein arms in ependymal cilia likely explains the hydrocephalus of hop mice.
The hop mutation (also known as hydrocephalic-polydactyly, hpy [51]) arose spontaneously in an unirradiated mouse colony of the Radiobiology Unit of the Medical Research Council at Harwell more than 40 years ago [42]. Nevertheless, the gene harboring this mutation remained unidentified prior to our study. We used positional cloning to localize the hop mutation to the Ttc26 gene, which encodes a component [52] of IFT complex B. Based on the association of Ttc26 with IFT complex B, we expected to find that the Ttc26 mutation leads to the formation of abnormally short primary cilia, and to below-normal levels of Hh-triggered Gli accumulation at the ciliary tip. Surprisingly, neither proved true. Instead, Ttc26 was required for effective dissociation of Gli from Sufu. This finding suggests that Ttc26 protein is necessary for at least one step in the Hh pathway that lies downstream of Gli trafficking to the ciliary tip.
Results
The hop mouse harbors a nonsense mutation in the Ttc26 gene
Although the gene affected by the hop mutation was not identified in previous studies, it had been localized to mouse chromosome 6 [47]. We hypothesized that the breeding history of the hop mouse line could facilitate further genetic mapping because the hop mutation had been transferred from an undefined genetic background onto the BALB/c background at The Jackson Laboratory, through repeated backcrosses. We analyzed chromosome 6 of hop mice for 15 SNPs that are almost completely BALB/c specific, as they have been detected in very few other strains (see Table S1). This approach identified a non-BALB/c region on chromosome 6 between SNPs rs36592952 and rs30852324 (Figure 1A), encompassing 142 protein-coding RefSeq genes. We selected 3 of these genes for testing (Figure 1A), based on their known association with the ciliome [53], [54]. Sequence analysis of the candidate genes from the hop line showed that one, Ttc26, contained a C-to-A point mutation that changes a tyrosine-encoding codon to a stop codon in exon 15 (Figure 1B). This nonsense mutation is predicted to truncate the Ttc26 protein 125 amino acids from its C-terminus (Figure 1C). We used Western blotting to examine expression of the wild-type Ttc26 protein (Ttc26wt) as well as the hop genome-encoded Ttc26 (Ttc26hop). Each was readily detected in HEK293 cells transfected with the corresponding construct, and Ttc26hop was ∼13 kDa smaller (Figure 1D). Immunoblotting also revealed the presence of endogenous Ttc26wt in airway epithelial cells and the testes of wild-type mice, but Ttc26hop was not detected in the equivalent samples from hop mice (Figure 1D). We hypothesized that the premature stop codon in the endogenous Ttc26hop mRNA may trigger nonsense-mediated decay (NMD), but that the transfected and intronless Ttc26hop evades degradation because NMD is not activated by a premature stop codon in the absence of downstream exon-exon junctions [55]. Real-time RT-PCR experiments revealed that, in mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) from the hop line, expression of the endogenous Ttc26hop mRNA was reduced 5.7-fold compared to that of the Ttc26wt mRNA in control MEFs (Figure S1). These results strongly suggest that the hop mutation is located within the Ttc26 gene, and that it leads to reduced expression of the Ttc26 protein.
Fig. 1. The Ttc26 gene of the hop mouse contains a nonsense mutation. 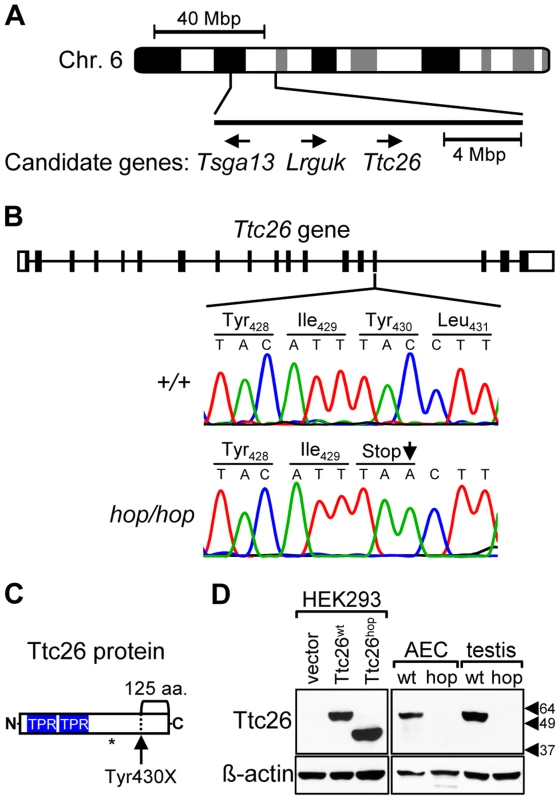
(A) Schematic representation of genomic positions of genes that both fall within the 16-mega base pair (Mbp) interval to which the hop mutation was mapped and had a known association with the ciliome. (B) Comparison of the 15th exon of the Ttc26 gene in wild-type and hop/hop mice. Horizontal lines represent introns, and black and white rectangles represent the coding and non-coding regions of exons, respectively. A deoxycytidine nucleotide (C) of wild-type Ttc26 (upper chromatogram) is replaced with a deoxyadenosine (A) in the hop mouse, as indicated by an arrow in the lower chromatogram. The point mutation changes the tyrosine (Tyr) at position 430 of Ttc26 to a stop codon (Stop), as shown in the amino-acid sequence lines. (C) Schematic representation of the Ttc26 protein. Blue boxes indicate the predicted TPR motifs. The bracket indicates the C-terminal 125-amino acid region of the protein that is predicted to be missing in hop/hop cells. The asterisk indicates the position of the epitope that is recognized by the anti-Ttc26 antibody. (D) Immunoblot analysis of Ttc26 expression in transfected HEK293 cells, airway epithelial cells (AEC) and testis of wild type (wt) and hop/hop (hop) mice. HEK293 cells were transfected with the indicated Ttc26-encoding construct or an empty expression vector. Arrowheads indicate the positions of the 64, 49, and 37 kDa standards. The antibodies used for immunoblotting are indicated next to the upper and lower panels. The hop mutation is associated with partial embryonic lethality and patterning defects
We found that each homozygous Ttc26 mutant mouse (n = 82) in our hop colony had preaxial polydactyly (Figure 2B). Thus, the previously reported polydactyly phenotype [44], [47] was fully penetrant in this line. However, we observed that most litters included fewer hop/hop mice than expected based on Mendelian ratios. The genotyping of 126 newborn mice from heterozygous breeding pairs confirmed that the ratio of hop/hop mice was significantly lower than the expected 25% (33 wild-type [26.2%], 75 heterozygous [59.5%], and 18 homozygous mutant [14.3%]; χ2 test p = 0.017). In contrast, when embryos were harvested from heterozygous breeding pairs on embryonic day (E) 10.5, the ratio of hop/hop mice was close to 25% (27 wild-type [26.2%], 51 heterozygous [49.5%], and 25 homozygous mutant [25.7%]; χ2 test p = 0.96). Thus, homozygosity for the Ttc26 mutation is associated with partial lethality between E10.5 and birth. The surviving homozygous Ttc26 mutant mice were smaller than control littermates (Figure 2A), consistent with a previous characterization of the hop mouse line [44].
Fig. 2. The hop mouse exhibits patterning defects and hearing impairment. 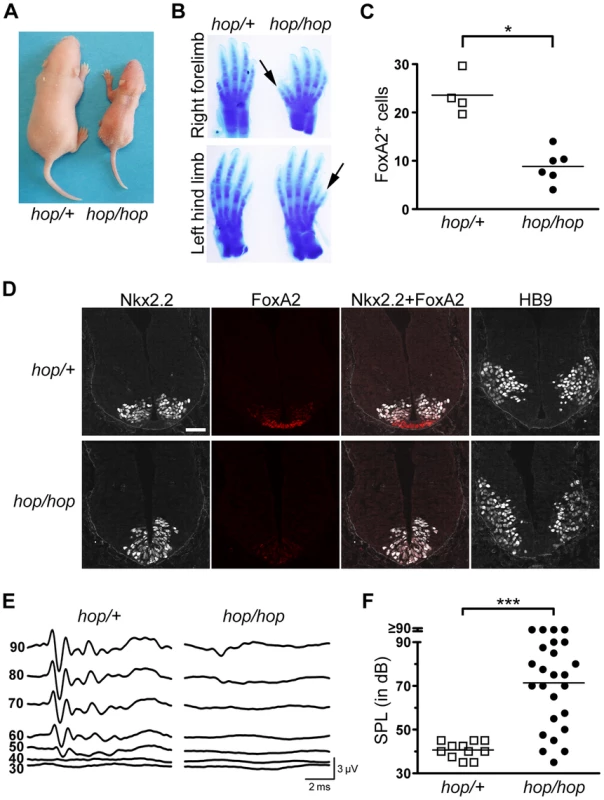
(A) Representative images of hop/+ and hop/hop mice at postnatal day 4. (B) Comparison of Alcian Blue-stained fore and hind limbs of hop/+ and hop/hop mice. Extra digits are indicated by arrows. (C) Statistical analysis of FoxA2-positive cells in the lumbar neural tubes of hop/+ and hop/hop mice (E10.5). Each symbol represents the average number of FoxA2+ cells per focal plane in a single embryo (for each embryo, 12 focal planes in 4 sections were analyzed, Mann-Whitney test: *P = 0.01). (D) Immunostaining of the lumbar neural tube of hop/+ and hop/hop mice (E10.5) with antibodies against the V3 progenitor marker Nkx2.2 (white contrast), the floor plate marker FoxA2 (red), and the motor neuron protein HB9 (white contrast). The hop/hop genotype is associated with reduced FoxA2 expression and ventralization of the Nkx2.2- and HB9-expressing cells. Scale bar: 50 µm. (E) Representative ABR waveforms for 3–4 week-old hop/+ and hop/hop mice. Broadband click stimuli were applied at the indicated sound pressure levels (in dB). (F) Statistical analysis of ABR thresholds measured in 3–4 week-old hop/+ and hop/hop mice. Broadband click stimuli between 30 and 90 dB sound pressure level (SPL) were used. Each symbol represents the value for a single mouse (Mann-Whitney test: ***P<0.0001). One of the best-studied examples of Shh-regulated patterning besides digit formation in the limb is cell-type specification in the neural tube. In this structure, neuronal fates are dictated by the local concentration of Shh, which decreases gradually from its source in the notochord and floor plate [28], [56], [57]. We examined the pattern of neuronal specification in the ventral neural tubes of hop/hop and control mice based on the expression of three markers of neuronal cell types: FoxA2, Nkx2.2, and HB9. Immunofluorescence detection of FoxA2 at E10.5 revealed that the number of FoxA2-positive cells (which require the highest Shh concentration for their specification) was reduced in the neural tubes of hop/hop mice compared to that in their heterozygous littermates (Figures 2C and 2D). Furthermore, in the hop/hop mice the Nkx2.2-expressing V3 interneurons were shifted to the ventromedial region (Figure 2D), and the ventral edge of the HB9-expressing motoneuron area was located abnormally close to the ventral border of the neural tube (Figure 2D). Thus, the Ttc26 mutation is associated with patterning defects that are characteristic of reduced Hh signaling.
Defects in the primary cilium often lead to hearing loss, polycystic kidney disease, and retinopathy [58]. Testing of the auditory brainstem responses (ABR) of hop/hop and heterozygous control mice to broad-band sound stimuli of various intensities revealed that the homozygous animals were hearing impaired (Figure 2E and 2F); however, the severity of the hearing impairment was variable. Histological examination of the cochlear cross sections of hearing impaired hop/hop mice did not identify pathological changes other than reduced thickness of the bony labyrinth (Figure S2). Furthermore, visualization of the bundles of stereocilia in whole-mount preparations of organ of Corti samples from hop/hop mice showed that the planar orientation of hair cells was not altered (Figure S3). Thus, unlike the lack of several other ciliary proteins [59], [60], the Ttc26 defect of hop mice impairs hearing through mechanisms other than the dysregulation of planar polarity in hair cells. Histological examination of the kidneys and retinas of 1 year old hop/hop mice also did not reveal abnormalities (Figure S4). Collectively, these results indicate that the Ttc26 mutation is associated with some – but not all – of the pathological changes that are typically linked to dysfunction of the primary cilium.
Full-length Ttc26 interacts directly with the Ift46 subunit of IFT complex B
Although Ttc26 had been co-purified with IFT complex B and was recently classified as a subunit of this complex [52], [61], [62], its ability to interact directly with proteins had not been examined. To gain insight into Ttc26 function, we screened mouse and human cDNA libraries for Ttc26wt-binding proteins, using the yeast two-hybrid method. These screens identified a single Ttc26-interacting protein: the IFT complex B subunit Ift46. Next, we tested whether the C-terminus of Ttc26 is required for this protein-protein interaction, using the two-hybrid assay in yeast co-transformed with Ift46 and Ttc26wt or Ift46 and Ttc26hop. Because Ift46 was fused to a Gal4 activator domain and the Ttc26 proteins were fused to a Gal4 DNA-binding domain, the Ift46-Ttc26 interaction was predicted to reconstitute the active Gal4 transcription factor. We visualized Gal4 activity by supplementing the yeast plates with X-α-Gal, which is metabolized into a blue product by a Gal4-induced enzyme. This test showed Gal4 activation in yeast co-transformed with Ift46 and Ttc26wt, but not in yeast co-transformed with Ift46 and Ttc26hop (Figure 3A). Thus, the Ttc26 C-terminus is required for binding to Ift46.
Fig. 3. The hop mutation does not impair ciliogenesis or ciliary localization of the Ttc26-interacting protein Ift46. 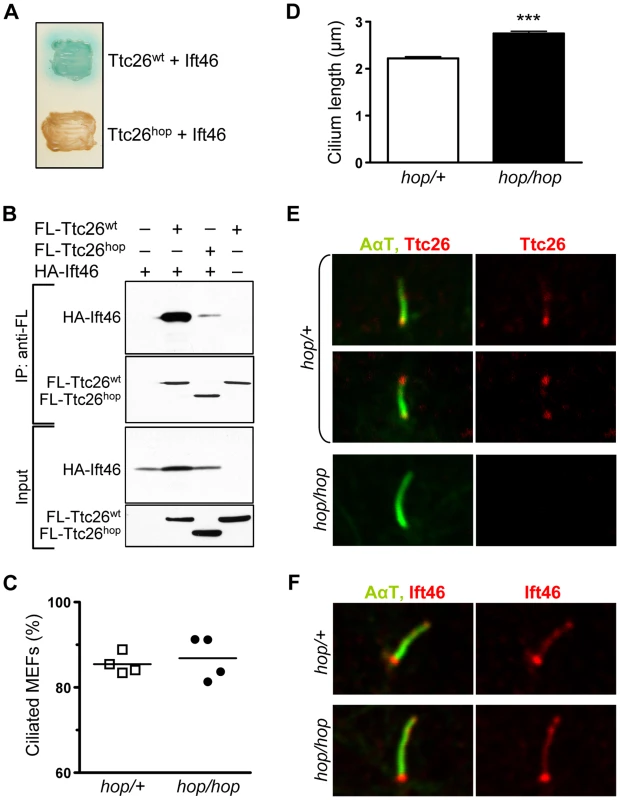
(A) Color test of protein-protein interactions in yeast transformed with the indicated combination of Ift46 and Ttc26wt or Ttc26hop. Blue staining of the yeast colony (upper patch) is indicative of a protein-protein interaction; a lack thereof indicates the absence of a protein-protein interaction (lower patch). (B) Immunoprecipitation analysis of the Ttc26wt-Ift46 interaction. HEK293 cells were transfected with the indicated combinations of HA-tagged Ift46 and flag (FL)-tagged Ttc26wt or Ttc26hop. The two upper panels show immunoblot analysis of tagged proteins pulled down with an anti-flag antibody, and the two lower panels show immunoblot analysis of input controls. (C) Percentages of ciliated hop/+ and hop/hop MEFs following 2 days of serum starvation. MEFs were isolated from 4 embryos per genotype, and 150 MEFs per embryo were analyzed. (D) Statistical analysis of cilium length in the primary cultures of serum-starved hop/+ and hop/hop MEFs (mean ± SEM, n = 200 cilia per genotype, unpaired t-test with Welch correction, ***P<0.0001). (E,F) Immunofluorescence analysis of (E) Ttc26 and (F) Ift46 expression in the cilia of hop/+ and hop/hop MEFs. The axoneme was visualized by immunolabeling of acetylated-α-tubulin (AαT). We used immunoprecipitation to test whether Ift46 and Ttc26 can interact in mammalian cells. HEK293 cells were transfected with HA-tagged Ift46 and either flag-tagged Ttc26wt or flag-tagged Ttc26hop. The cells were lysed, and Ttc26 and the interacting proteins were pulled down from the lysates using an anti-flag antibody. Immunoblot analyses of the proteins in these samples confirmed that Ift46 interacted efficiently with Ttc26wt (Figure 3B) but not with Ttc26hop, supporting the idea that the Ttc26 C-terminus is important for this interaction (Figure 3B, see quantification in Figure S5). Thus, even if the endogenous Ttc26hop protein is expressed in the hop mice at levels below the detection limit of our Western blots, its ability to interact with Ift46 is severely impaired.
The hop mutation does not lead to the shortening of cilia in embryonic fibroblasts
Defects in most subunits of IFT complex B cause either a complete lack of ciliogenesis or the formation of short cilia, depending on the affected subunit [27]. We therefore evaluated cilium formation in the MEFs of hop/hop and wild-type mice, visualizing the ciliary marker proteins acetylated-α-tubulin (AαT) and Arl13b by immunofluorescence. We normalized the number of visualized cilia to the number of ToPro-3-stained nuclei. These experiments revealed that the hop mutation did not affect the percentage of ciliated MEFs (Figure 3C). Furthermore, it did not result in the production of short cilia, in either MEF cultures (Figure 3D) or the mesenchyme of hop/hop embryos (Figure S6). In fact, the hop mutation was associated with a slight increase in cilium length (Figure 3D and Figure S6). Next, we evaluated the expression of Ttc26 and Ift46 in the cilia of control and hop/hop MEFs by immunofluorescence. In control MEFs, Ttc26 was detected at the base of most cilia and at the tip of ∼20% of cilia (Figure 3E); the specificity of the immunostaining was confirmed by the lack of Ttc26 signal in the cilia of hop/hop MEFs. The expression of Ift46 was not different in the cilia of control and hop/hop cells (Figure 3F). Collectively, these results show that the Ttc26 mutation of hop mice does not inhibit the formation of primary cilia or the ciliary localization of Ift46.
Gli activation is reduced in the embryonic fibroblasts of hop mice
The patterning defects in the limbs and neural tube of hop/hop mice suggested that the Ttc26 mutation impairs Hh signaling. To evaluate the functionality of the Hh pathway, we transduced control and hop/hop MEFs with an adenovirus that encodes a previously described Gli-responsive reporter gene [63]–[65], and measured reporter expression following 48-h treatment with Shh-conditioned medium. Gli reporter signal was normalized to the expression of GFP from a separate expression cassette in the adenoviral vector. This experiment revealed that Shh-induced expression of the Gli reporter was dramatically reduced in the hop/hop MEFs compared to wild-type controls (Figure 4A). Next, we tested the response of control and hop/hop MEFs to the chemical agonist SAG, which activates Smo directly and induces Shh signaling independently of Ptch1 [66]. Again, induction of the Gli reporter was much lower in hop/hop MEFs than in their control counterparts (Figure 4A). Thus, the hop mutation impairs Hh signaling downstream of Ptch1.
Fig. 4. The Ttc26 mutation in the hop mouse impairs Shh signaling. 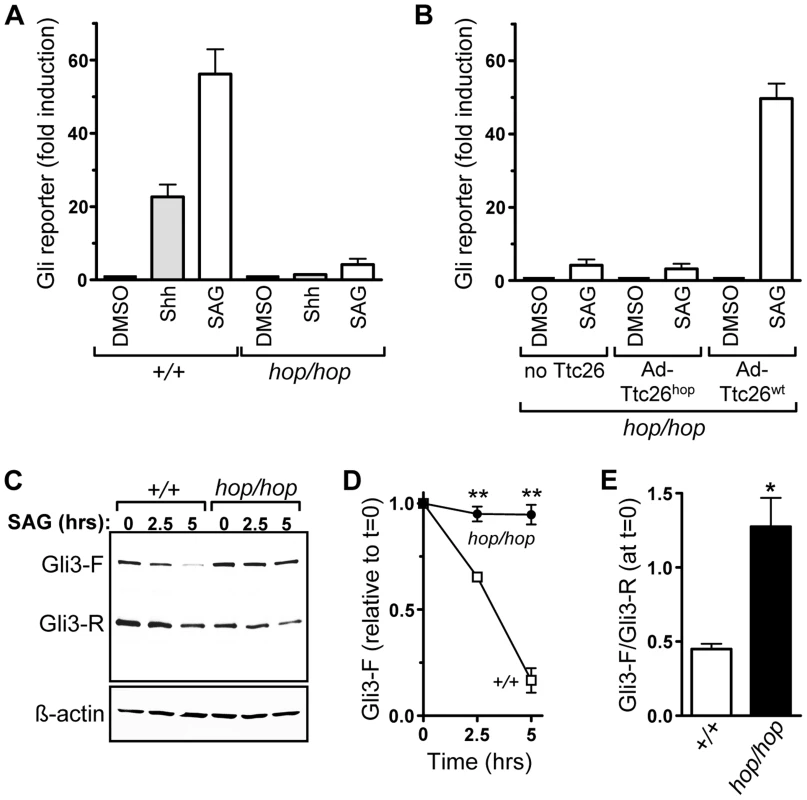
(A) Induction of an adenovirus-delivered Glix8-luciferase reporter gene in wild-type (+/+) and hop/hop MEFs following 2-day incubation with DMSO (0.02%), Shh-conditioned medium, or SAG (400 nM) as indicated (mean ± SEM, n = 3–7). The increase in luciferase expression is shown relative to that in the DMSO control. Constitutive GFP expression from the Glix8-luciferase-encoding viral vector was used for normalization. (B) SAG-dependent induction of the Glix8-luciferase gene in hop/hop MEFs following adenoviral delivery of Ttc26hop or Ttc26wt (mean ± SEM, n = 3–7). The control group of MEFs was not transduced with a Ttc26-encoding virus (no Ttc26). The luciferase signal was normalized to GFP expression as described in panel A. (C) Immunoblot analyses of expression of Gli3-F and Gli3-R in wild-type and hop/hop MEFs, following SAG treatment (400 nM) for the indicated times. ß-actin serves as a loading control (lower panel). (D) Statistical analysis of Gli3-F band intensities in the immunoblot experiments described in panel C (mean ± SEM, n = 3; two-way ANOVA, P<0.006 for the genotype variable; post-hoc Bonferroni test, **P<0.01). (E) Statistical analysis of the ratio of the Gli3-F and Gli3-R bands at the 0 time point in the experiments described in panel C (mean ± SEM, n = 3; unpaired t-test, *P = 0.014). We also used the Gli reporter assay to assess whether the Ttc26 mutation was the cause of the Hh signaling defect in hop/hop cells. MEFs from hop/hop mice were co-transduced with the Gli reporter-encoding virus and either a Ttc26wt - or Ttc26hop-encoding adenovirus, and hop/hop MEFs transduced with only the Gli reporter-encoding virus served as a negative control. Western blot analysis confirmed that the Ttc26 constructs were expressed in the transduced cells (Figure S7A), and immunofluorescence microscopy showed that the heterologously expressed Ttc26wt and Ttc26hop were imported into the cilium (Figure S7B). Results of the reporter assay demonstrated that heterologous expression of Ttc26wt restored the SAG-dependent induction of the Gli reporter to nearly wild-type levels (Figure 4B), but that overexpression of Ttc26hop had no significant effect (Figure 4B). These data indicate that the Ttc26 mutation is the cause of the Hh signaling defect in the hop mouse line.
Activation of Gli3-F is followed rapidly by its proteasomal degradation [17], [18]. We therefore used Western blotting to examine whether the Ttc26 mutation was associated with a defect in Gli3 processing. In hop/hop MEFs, the Gli3-F levels changed only minimally following SAG treatment, whereas in wild-type MEFs they declined significantly (Figure 4C and 4D). In addition, we found that the ratio of Gli3-F to Gli3-R was high in non-stimulated hop/hop MEFs (Figure 4C and 4E), suggesting that the Ttc26 mutation also impaired the processing of Gli3-F into Gli3-R. These data are consistent with a cilium-dependent Hh signaling defect in hop/hop cells, because Gli3-F transport through the cilium is required for both the activation of Gli3-F and efficient production of Gli3-R [23], [67].
The hop mutation does not affect accumulation of Gli at the ciliary tip but impairs its dissociation from Sufu
We next probed the Hh pathway upstream of Gli3 processing in hop/hop cells by assessing the ciliary localization of Smo. Immunofluorescence experiments showed that SAG treatment led to an increase in the amount of Smo in the cilia of both hop/hop and wild-type MEFs (Figure 5A). Thus, the Ttc26 mutation of hop mice did not block entry of Smo into the cilium. Next we used immunofluorescence to evaluate accumulation of the Gli protein at the ciliary tips of wild-type and hop/hop MEFs. Because Gli3 is degraded soon after stimulation with SAG (Figure 4C), its accumulation was measured after short treatments (i.e. 1 and 2 h, Figure 5B and 5C). In the case of the more stable Gli2 protein, accumulation was measured after both short (i.e. 2 h, Figure S8) and long (i.e. 48 h, Figure 5D and 5E) incubations with SAG. The results revealed that the Ttc26 mutation did not block the SAG-induced transport of either Gli2 or Gli3 to the ciliary tip. To evaluate whether our immunofluorescence approach was suitable for detecting intermediate changes in the quantity of ciliary Gli2, we measured its accumulation at the ciliary tip after treating control and hop/hop MEFs with low and high concentrations of SAG. We found that high concentration of SAG (400 nM) led to a greater increase of the Gli2 signal at the tip than low concentration of SAG (1 nM), in both control and hop/hop MEFs (Figure 5E). Moreover, the Gli2 signal at the ciliary tip was stronger in hop/hop MEFs treated with 400 nM SAG than in wild-type MEFs treated with 1 nM SAG (Figure 5E), yet Gli reporter induction was milder in the former (Figure S9). Thus, the Ttc26 mutation disrupts the correlation between the amount of Gli2 accumulated at the ciliary tip and the transcriptional output of the Hh pathway.
Fig. 5. The hop mutation inhibits Gli-Sufu dissociation without altering Gli accumulation at the ciliary tip. 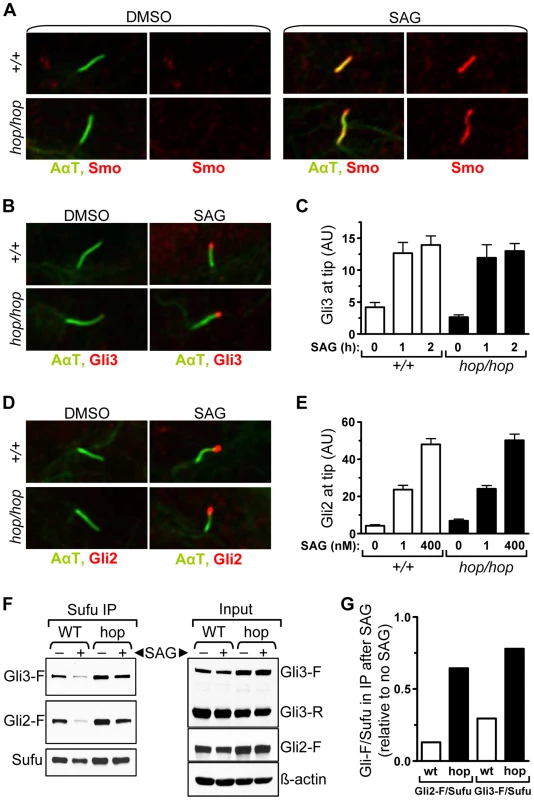
(A) Immunofluorescence analysis of Smo (red) localization to primary cilium (AαT-labeled, green) in wild-type (+/+) and hop/hop MEFs following 4-h treatment with DMSO (0.02%) or SAG (400 nM) as indicated. (B) Immunofluorescence analysis of Gli3 (red) localization to primary cilium tip in wild-type (+/+) and hop/hop MEFs following 2-h treatment with DMSO (0.02%) or SAG (400 nM). (C) Quantitative analysis of Gli3 immunofluorescence signal intensities at the primary cilium tip in +/+ and hop/hop MEFs following SAG treatment (400 nM) for the indicated times (mean ± SEM, n = 40–50). AU: arbitrary units. (D) Immunofluorescence analysis of Gli2 (red) localization to primary cilium tip in +/+ and hop/hop MEFs following 2-day treatment with DMSO (0.02%) or SAG (400 nM). (E) Quantitative analysis of Gli2 immunofluorescence signal intensities at the primary cilium tip in +/+ and hop/hop MEFs following 2-day treatment with the indicated concentrations of SAG (mean ± SEM, n = 45–55). AU: arbitrary units. (F) Gli-Sufu dissociation in +/+ and hop/hop MEFs following 5-h incubation with SAG (400 nM) and the proteasome inhibitor bortezomib (2 µM) or with DMSO (0.02% negative control). Left panels show the relative amounts of Gli3-F, Gli2-F, and Sufu pulled down from the cell lysates using an anti-Sufu antibody. Right panels show the relative amounts of Gli3-F, Gli3-R, Gli2-F, Sufu and ß-actin (loading control) in the total cell lysates. (G) Ratios of band intensities of Gli-F and Sufu were calculated based on the immunoprecipitation results in the left column of panel F, and the Gli-F/Sufu ratios in the immunoprecipitated fractions of SAG-treated +/+ (wt) and hop/hop (hop) cells are shown relative to the Gli-F/Sufu ratios in the immunoprecipitated fractions of non-treated cells. A subset of the cellular pool of Sufu protein that forms complexes with Gli is also transported to the ciliary tip following activation of the Hh pathway [7]. To evaluate whether the hop mutation affected Sufu accumulation in the cilium, we measured the intensity of Sufu immunofluorescence at the ciliary tip of hop/hop and control MEFs after treating them with SAG and DMSO (control) for 2 days (Figure S10). Our results showed that the SAG-induced accumulation of Sufu at the ciliary tip was not affected by the hop mutation, supporting the notion that the transport of Gli-Sufu complexes in the cilium was unimpaired.
Since the transport of Gli-Sufu complexes to the ciliary tip is followed by their dissociation [17], [18], we evaluated this signaling step in hop/hop and wild-type cells using an immunoprecipitation approach. MEFs were treated with SAG or DMSO (control) for 5 hours, at which point the Sufu-associated proteins were pulled down from the cell lysates using an anti-Sufu antibody. To prevent the degradation of Gli3 following its dissociation from Sufu, we treated the SAG-stimulated cells with the proteasome inhibitor bortezomib. Western blot analysis of the immunoprecipitated fractions revealed that, in the cases of both Gli3 and Gli2, dissociation from Sufu was reduced in the SAG-treated hop/hop vs. wild-type MEFs (Figure 5F and 5G). Thus, the Ttc26 deficiency in hop mice led to a general decrease in the dissociation of Gli proteins from Sufu.
Discussion
In the present study, we show that the Hh signaling defect of hop mice is caused by a nonsense mutation in the Ttc26 gene, which encodes a component of IFT complex B. Our analysis of the Hh pathway in hop/hop cells indicates that the signaling defect lies downstream of the accumulation of Gli at the ciliary tip, but upstream of its dissociation from Sufu.
How does the deficiency for Ttc26 function lead to impaired dissociation of the Gli-Sufu complex? Although the simplest interpretation of our data is that Ttc26 is an organizer of molecular interactions that lead to the dissociation of Gli from Sufu, this seems unlikely because neither our yeast two-hybrid screen nor previous high-throughput screens detected physical interactions between Ttc26 and Gli or Ttc26 and Sufu [68]–[70]. We therefore posit that Ttc26 facilitates Gli-Sufu dissociation indirectly, potentially by affecting the localization of other ciliary proteins. This hypothesis is supported, albeit indirectly, by the known role of Ttc26 in the motile cilium. Specifically, Ttc26 appears to be required for the correct localization of a group of proteins that form the inner dynein arm in the motile cilium; this is suggested by the fact that in hop mice approximately 40% of cilia in the trachea, ependyma, and oviduct lack inner dynein arms [43], and by the recent discovery of an association between the Ttc26 mutation and a reduction in the levels of inner dynein-arm proteins in the flagella of the green alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii [52]. Alternatively, it is possible that the hop mutation slows both the anterograde and retrograde transport of Gli proteins, because a balanced defect in the bidirectional transport would potentially temper the dissociation of Gli from Sufu without altering the amount of Gli at the ciliary tip. Although this alternative hypothesis cannot be ruled out, tracings of IFT particles in the flagella of the Ttc26 mutant C. reinhardtii indicate that the velocity of IFT is not affected by the lack of Ttc26 [52]. Thus, the absence of Ttc26 is not likely to alter the structure of the primary cilium to the extent that the movement of motor proteins along the axoneme is impaired.
Some of the phenotypic features of hop mice have been described in various animal models of Gli protein deficiency. For example, Gli1−/−; Gli2+/− mice have a hopping gait [49], and Gli3+/− mice have preaxial polydactyly [48]. Thus, defective regulation of Gli proteins is the most likely cause of the hopping gait and polydactyly in the hop mouse. Nevertheless, the phenotype of hop mice is milder than that of Gli2−/− and Gli3−/− mice, which do not survive after birth [48], [49]. Our detection of residual induction of the Gli reporter gene in SAG-treated hop/hop MEFs (Figure 4A) is consistent with the relatively mild phenotype of hop mice. The residual Hh pathway activation in hop/hop cells suggests that Ttc26 is not absolutely necessary for Hh signaling. Alternatively, hop could be a hypomorphic mutation. The “modest” (5.7-fold) downregulation of the Ttc26 mRNA in hop/hop MEFs supports the notion that hop could be hypomorphic; however, the expression of the encoded Ttc26hop protein was reduced much more dramatically (Figure 1D). This difference in the extent of downregulation of Ttc26hop transcript and protein is compatible with NMD-dependent inhibition of Ttc26hop expression. During NMD, the premature stop codon-containing mRNAs are not degraded immediately after the completion of pre-mRNA splicing; rather, their degradation occurs after a single round of pioneering translation. The temporal lag between splicing and degradation leads to the steady-state abundance of aberrant mRNAs at levels which are “only” 3 - to 10-fold below the expression of their wild-type counterparts [55], [71]. Our inability to detect truncated Ttc26 protein in hop/hop cells could reflect the very low protein output of the pioneering translations of Ttc26hop mRNA molecules.
Among the various mouse models that involve deficiencies in complex B subunits, the orpk and gt mice exhibit the most hop-like phenotypes. These mice carry hypomorphic alleles of two complex B protein-encoding genes, Ift88 and Ift80, respectively. Homozygosity for the Ift88Orpk and Ift80gt alleles leads to postnatal growth retardation, preaxial polydactyly and incomplete pre-weaning lethality [37], [72], [73]. In the hop and Ift80gt/gt mice, the Hh signaling defects are not accompanied by pathological changes in the kidney. In the Ift88Orpk/Orpk mice, by contrast, the Hh signaling defect is accompanied by polycystic kidney disease. Cyst formation correlates with deformities in the cilia of Ift88Orpk/Orpk and Ift80gt/gt mice, with the Ift88Orpk/Orpk genotype – but not the Ift80gt/gt genotype – being associated with the shortening of primary cilia. Thus, the absence of polycystic kidney disease in the hop mouse is consistent with the lack of cilium shortening in hop/hop MEFs. Although ciliary trafficking of Gli has not been examined in the Ift88Orpk/Orpk and Ift80gt/gt cells, the ciliary localization of Smo has been found to be dysregulated in Ift88Orpk/Orpk MEFs [74]. Thus, the orpk mutation appears to affect the Hh pathway further upstream than the hop mutation.
The Ttc26 mutation led to an elevated hearing threshold in the hop mice; however, unlike the absence of many other ciliary proteins, the Ttc26 defect did not disrupt the planar polarity of outer hair cells (Figure S3). Furthermore, histological analysis of the middle ear of hop/hop mice did not reveal signs of inflammation (Figure S11), a frequent consequence of defects in the motile cilia. Because a complete lack of Hh signaling has been shown to cause agenesis of the middle ear ossicles and the cochlear duct [75], [76], we speculate that reduced Hh signaling in hop mice could potentially impair hearing through as yet undetected alterations in the structures of the middle ear ossicles or the expression of cochlear genes.
The biological relevance of Ttc26 was recently evaluated in zebrafish [52], [77], and comparison of the zebrafish and mouse models of Tc26 deficiency reveals both similarities and differences in Ttc26 function. In both species the motile cilia are defective, as indicated by reduced ciliary beating in Ttc26 knockdown zebrafish [52], [77] and the partial loss of inner dynein arms in the hop mouse [43]. However, abnormal patterning has not been reported in the Ttc26 knockdown zebrafish, and thus Ttc26 may not be necessary for Hh signaling in fish. This notion is supported by the recent finding that the morpholino-dependent knockdown of various subunits of the IFT complexes in zebrafish leads to minimal Hh signaling defects but severely deformed cilia [78], [79]. Another difference between the two animal models is the impact of the Ttc26 deficiency on the length of cilia. In the Ttc26 knock-down zebrafish the motile cilia are shorter than normal [52], [77], whereas in the hop mouse the lengths of neither the motile [43] nor the primary cilia (Figure 3) are generally decreased – the only exception being the sperm flagellum [42]. This discrepancy in cilium length cannot be explained simply by species differences in ciliogenesis, because the shRNA-mediated knockdown of Ttc26 in mouse cell lines also leads to the formation of short cilia [77], [80]. The unique feature of the hop cells is the presence of a premature stop codon towards the end of the coding region in the Ttc26 mRNA. Therefore, we suggest that very low expression of the truncated Ttc26 protein could be responsible for the lack of cilium shortening in the hop mouse.
Models describing IFT function in Hh signaling have developed rapidly over the past 10 years. After key Hh signaling molecules were detected in the primary cilium, IFT defects were proposed to affect the Hh pathway by causing structural changes in the axoneme, a model supported by the finding that a combination of anterograde and retrograde trafficking defects results in milder structural and signaling anomalies in the cilium than does either in isolation [40]. This model was further developed with the discovery that, in mice deficient for the IFT complex B subunit Ift25, the ciliary structure is intact but ciliary trafficking of Ptch1 and Smo is dysregulated [34]. This indicated that the contribution of complex B to Hh signaling is not limited to maintenance of the ciliary microtubule track. The detailed analysis of a series of mouse lines carrying various hypomorphic and null alleles of the complex A subunit Ift144 has also suggested that changes in the ciliary structure alone do not fully explain the Hh signaling defects of the mutant mice [31]. The results we present here show that the Ttc26 component of IFT complex B is necessary for efficient coupling between the ciliary accumulation of Gli and its activation. We thus propose that the Ttc26 defect of hop mice reveals a novel role for IFT complex B in Hh signaling, downstream of the maintenance of ciliary structure and the facilitation of Smo trafficking.
Materials and Methods
Ethics statement
Mice were euthanized according to the current AVMA guidelines. Experimental procedures were approved by the Animal Care and Use Committee of the University of Iowa (protocol#: ACURF 1303050).
Genetic, histological, and ABR analysis of hop mice
Hop mice (BALB/cByJ genetic background) were obtained from The Jackson Laboratory. The hop allele was mapped by sequencing 15 PCR-amplified genomic regions that contain BALB/c specific SNPs (SNP accession numbers and PCR primers are listed in Table S1). The transcripts of candidate genes were RT-PCR amplified from testis RNA, using the PCR primers listed in Table S2, and sequenced without subcloning. Our routine genotyping procedure detected the single nucleotide difference between the hop and WT alleles based on the elimination of a Bpu10I restriction site from Ttc26 by the hop mutation. In brief, a 618-bp long genomic segment containing the hop mutation site was PCR amplified using the PCR primers 5′-dTACTGCTTTTGAGGAGACTAGGG-3′ and 5′-dGGATGATGGAACTAGTCACGGG-3′, the reactions were digested with Bpu10I (New England BioLabs), and the digestion products were resolved on 1% agarose gels (Figure S12). Kidneys and eyes from ∼1 year old mice were fixed, paraffin-embedded, sectioned, and stained with hematoxylin and eosin. Fore and hind limbs from newborn mice were stained with Alcian Blue and Alizarin Red S as previously described [81]. Hematoxylin and eosin stained cochlear sections and phalloidin-Alexa Fluor 488 stained organ of Corti samples were prepared as previously described [82]. The ABR thresholds of mice were measured at postnatal day 21–28, using a previously described open-field system and broadband click stimuli [83].
Constructs, viral vectors, and HEK293 cell culture
The Glix8-luciferase reporter cassette was kindly provided by Dr. Michael K. Cooper (Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, TN); all other constructs were generated from mouse RNA. The Pfu DNA polymerase was used under standard reaction conditions, with primers listed in Table S3, to amplify the entire coding regions of the Ift46, Ttc26wt, and Ttc26hop transcripts, the 5′ coding region of the Shh mRNA (1–594 nucleotides), and the entire Glix8-luciferase reporter cassette. The amplified DNA fragments were subcloned into yeast expression vectors (pGBKT7 and pGADT7), the mammalian expression vector pcDNA3.1, and two adenoviral shuttle vectors (pacAd5-CMV and the promoterless pacAd5). Adenoviral particles were generated by the Gene Transfer Vector Core of the University of Iowa and by ViraQuest Inc. (North Liberty, IA). The Glix8-luciferase encoding adenovirus contained a PGK-EGFP expression cassette; all other viral vectors lacked GFP. HEK293 cultures were maintained and transfected as previously described [84]. Shh-conditioned medium was harvested from HEK293 cells 3 days after transfecting them with the Shh-encoding plasmid. The harvested medium contained 2% FBS (Hyclone), and it was used in MEF cultures after 5-fold dilution with DMEM.
Yeast two-hybrid screens
The Matchmaker Gold Yeast Two-Hybrid system was used, according to the manufacturer's instructions (Clontech), to screen human testis, mouse embryo, and universal mouse cDNA libraries (Clontech) for genes whose products interact with Ttc26wt. Verification of the Ift46-Ttc26wt interaction was carried out in Y2HGold yeast (Clontech) co-transformed with plasmids encoding Ift46 (in pGADT7 vector) and either the WT or mutant form of Ttc26 (in pGBKT7), using the Yeastmaker Yeast Transformation System (Clontech). Following transformation, the yeast was spread on X-α-Gal-supplemented double dropout medium lacking leucine and tryptophan.
Immunofluorescence on mouse embryo sections
Pregnant mice were euthanized at E10.5. Embryos were removed from the amniotic cavity, fixed in 4% PFA for 4 h at 4°C, cryoprotected in 30% sucrose solution, and embedded in Optimal Cutting Temperature compound. Transverse cryosections through the lumbar region were re-fixed with pre-chilled 4% PFA for 10 min at RT, permeabilized with 0.1% Triton X-100 for 10 min, blocked with 5% normal goat serum (Sigma) and incubated with antibodies against FoxA2 (Abcam; 1∶250 dilution), HB9 (Developmental Studies Hybridoma Bank, University of IA; 1∶30 dilution), Nkx2.2 (Developmental Studies Hybridoma Bank, University of IA; 1∶10), acetylated α-tubulin (1∶1000, Sigma), or Arl13b (1∶500, Protein Tech). Secondary antibodies were labeled with Alexa fluor 488 and Alexa fluor 568 (Invitrogen, 1∶500), and fluorescence was visualized using a confocal microscope (LSM-510, Carl Zeiss Inc.).
MEF culture, immunostaining of cilia, and cilium length measurement
MEFs were isolated from E10.5 embryos as described previously [85]. In brief, decapitated and eviscerated embryos were pressed through 18-gauge needles twice, and pipetted onto 0.2% gelatin-coated plates in high-glucose DMEM containing 10% FBS, penicillin (100 units/ml), streptomycin (100 µg/ml), and 4 mM L-glutamine. MEF cultures were maintained for 4–6 passages. For immunofluorescence experiments, MEFs were seeded onto glass coverslips and cultured to near confluency. Cilium formation was induced by serum starvation (0.4% FBS in DMEM) for 48 h. When SAG treatment was used, cells were serum starved for 16–24 h prior to addition of the SAG-containing medium. Cultures were fixed in 4% PFA for 15 min, permeabilized with 0.2% Triton X-100 for 7 min, and blocked in 5% normal donkey serum (Sigma), 5% normal goat serum (Sigma), or 1% BSA, depending on the primary antibody used (see Table S4). The sources, catalogue numbers, and dilutions of the primary antibodies against acetylated α-tubulin, Arl13b, Ttc26, Ift46, Smo, Gli2, Gli3, and Sufu are also listed in Table S4. The secondary anti-mouse, anti-rabbit, and anti-goat antibodies (1∶500, Invitrogen) were labeled with Alexa fluor 488 or Alexa fluor 568. For analysis of the percentage of ciliated MEFs, cells were incubated with the nuclear stain ToPro-3 (1∶2000; Invitrogen) for 10 min immediately before the slides were mounted. Images were obtained using a confocal microscope (LCM-510, Carl Zeiss Inc.). Intensity of the Gli signal at the ciliary tip (400-pixel area) was measured using the ZEN software (Carl Zeiss Inc.). Cilium length was measured in 4% PFA-fixed and acetylated α-tubulin-stained samples at 63× magnification (0.03 µm×0.03 µm pixel size), by line segment tracing and spline fitting in Image J.
Adenoviral transduction of MEFs
MEFs were seeded onto glass coverslips and plastic dishes in DMEM containing 10% FBS. Approximately 16 h after seeding, the indicated adenoviral particles were added to MEFs at 40 multiplicity of infection (MOI), in DMEM containing 1.8% FBS and polybrene (2.75 µg/ml). Cells were incubated with adenoviruses for 4 h and then allowed to recover for 4 h in 10% FBS-containing DMEM. The Hh pathway was activated by incubating MEFs with SAG (1–400 nM) in 0.4% FBS-containing DMEM for 48 h. Control cultures were incubated with DMSO (0.02%) instead of SAG. The transduced MEFs were used for immunostaining, protein extraction, and luciferase assay.
Luciferase assay
Control and adenovirus transduced MEFs were incubated with SAG (1–400 nM) or DMSO (0.02%) in 0.4% FBS-containing DMEM for 48 h before lysis with Reporter Lysis Buffer (Promega) according to the manufacturer's protocol. Cell lysates were cleared by brief centrifugation, and luciferase activity in the supernatants was measured using the Luciferase Assay System (Promega) following the manufacturer's instructions. Luminescence was quantified with a Victor3 1420 Multilabel Plate Counter (Perkin Elmer). To facilitate the evaluation of relative transduction efficiency, the Gli reporter-encoding adenovirus was engineered to contain a PGK-EGFP expression cassette. GFP fluorescence in the supernatants of cell lysates was measured with the Victor3 1420 Multilabel Plate Counter and was used for normalization of luciferase activity.
Co-immunoprecipitation and Western blotting
MEFs were serum starved for 24 hours before treatment with 400 nM SAG or 0.02% DMSO (control) for 0–5 h in DMEM plus 0.4% FBS. Cells were lysed in a previously described buffer [18] containing 50 mM Tris (pH 7.5), 300 mM NaCl, 2% NP-40, 0.25% deoxycholate, 10 mM N-ethylmaleimide, 1 mM DTT, 10 µL/mL P8340 (Sigma), 1 mM PMSF, 10 µg/mL chymostatin, and PhosSTOP Phosphatase Inhibitor Cocktail (Roche). When bortezomib (2 µM) was added to the cell culture medium, its concentration was maintained in the lysis buffer. The cell lysates were passed through insulin needles ∼5 times and cleared by centrifugation. Aliquots from the supernatant were used directly for Western blotting, or were used for immunoprecipitation. In the latter case, the samples were incubated with 7 µg of an anti-Sufu antibody (Santa Cruz, sc-28847) overnight at 4°C, and immunocomplexes were pulled down using the Dynabeads Protein G Immunoprecipitation kit (Invitrogen). The pulled-down and input fractions were immunoblotted using the following antibodies: anti-Gli3 (R&D, AF3690), anti-Gli2 [86] (kindly provided by Dr. Jonathan T. Eggenschwiler, University of Georgia, Athens, GA), anti-Sufu (Santa Cruz, sc-10933), and anti-ß-actin (Santa Cruz, sc-1616).
For the FL-Ttc26 and HA-Ift46 co-immunoprecipitation experiments, lysis buffer (Buffer A) consisted of PBS (pH 7.2), 5 mM EDTA, 0.5% Triton X-100, 10 µL/mL P8340, 1 mM PMSF, and 10 µg/mL chymostatin. Transfected HEK293 cells were scraped into ice-cold Buffer A and sonicated (40% amplitude, 2×6 s at 4°C). The lysates were cleared by centrifugation, and aliquots of the supernatant were used directly as “input control” during Western blotting, or were used for immunoprecipitation. In the latter case, the samples were incubated with 7 µg of a monoclonal anti-flag antibody (Sigma, M2 clone) and immunocomplexes were pulled down using protein G agarose beads as previously described [84]. The pulled-down and input fractions were immunoblotted using the following antibodies: anti-HA (Abcam, ab9134) and anti-flag (Abcam, ab1162). Airway epithelial cells were harvested from 5–6 mouse tracheas by pronase digestion, as described previously [87]. Protein was extracted from airway epithelial cells, testes, Ttc26-transfected HEK293 cells, and Ttc26-transduced MEFs using Buffer A. Protein extracts were immunoblotted with anti-Ttc26 (Novus Biologicals, NBP1-84034) and anti-ß-actin (Santa Cruz, sc-1616) antibodies.
Real-time PCR
Total RNA from serum-starved MEFs was isolated using the TRIzol reagent (Invitrogen), and reverse transcribed using SuperScriptIII (Invitrogen). Real-time PCR was performed using PerfeCTa SYBR Green Fastmix (VWR), a Mastercycler ep realplex PCR machine (Eppendorf), and the following primers: Ttc26 forward 5′-dTGGCCAGGAAATGGGTTCAAGG-3′ and reverse 5′-dACTAGCTGATCCTCCTACCAACTG -3′, Gapdh forward 5′-dCGTCCCGTAGACAAAATGGT-3′ and reverse 5′-dGAATTTGCCGTGAGTGGAGT-3′. The relative mRNA expression values were determined using the ΔΔCT method [88].
Supporting Information
Zdroje
1. HuiCC, AngersS (2011) Gli proteins in development and disease. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 27 : 513–537.
2. InghamPW, McMahonAP (2001) Hedgehog signaling in animal development: paradigms and principles. Genes Dev 15 : 3059–3087.
3. TaipaleJ, BeachyPA (2001) The Hedgehog and Wnt signalling pathways in cancer. Nature 411 : 349–354.
4. BriscoeJ, ThérondPP (2013) The mechanisms of Hedgehog signalling and its roles in development and disease. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 14 : 416–429.
5. BeachyPA, HymowitzSG, LazarusRA, LeahyDJ, SieboldC (2010) Interactions between Hedgehog proteins and their binding partners come into view. Genes Dev 24 : 2001–2012.
6. GoetzSC, AndersonKV (2010) The primary cilium: a signalling centre during vertebrate development. Nat Rev Genet 11 : 331–344.
7. Mariani LE, Caspary T (2013) Primary cilia, sonic hedgehog signaling, and spinal cord development. In: Tucker KL, Caspary T, editors. Cilia and nervous system development and function. New York: Springer Netherlands. pp. 55–82.
8. EggenschwilerJT, AndersonKV (2007) Cilia and developmental signaling. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 23 : 345–373.
9. WangB, FallonJF, BeachyPA (2000) Hedgehog-regulated processing of Gli3 produces an anterior/posterior repressor gradient in the developing vertebrate limb. Cell 100 : 423–434.
10. PanY, BaiCB, JoynerAL, WangB (2006) Sonic hedgehog signaling regulates Gli2 transcriptional activity by suppressing its processing and degradation. Mol Cell Biol 26 : 3365–3377.
11. SasakiH, NishizakiY, HuiC, NakafukuM, KondohH (1999) Regulation of Gli2 and Gli3 activities by an amino-terminal repression domain: implication of Gli2 and Gli3 as primary mediators of Shh signaling. Development 126 : 3915–3924.
12. MarksSA, KalderonD (2011) Regulation of mammalian Gli proteins by Costal 2 and PKA in Drosophila reveals Hedgehog pathway conservation. Development 138 : 2533–2542.
13. NiewiadomskiPK, J.H., AhrendsR, MaY, HumkeEW, KhanS, et al. (2014) Gli protein activity is controlled by multisite phosphorylation in vertebrate Hedgehog signaling. Cell Rep 6 : 168–181.
14. CanettieriG, Di MarcotullioL, GrecoA, ConiS, AntonucciL, et al. (2010) Histone deacetylase and Cullin3-REN(KCTD11) ubiquitin ligase interplay regulates Hedgehog signalling through Gli acetylation. Nat Cell Biol 12 : 132–142.
15. CoxB, BriscoeJ, UlloaF (2010) SUMOylation by Pias1 regulates the activity of the Hedgehog dependent Gli transcription factors. PLoS One 5: e11996.
16. PanY, WangC, WangB (2009) Phosphorylation of Gli2 by protein kinase A is required for Gli2 processing and degradation and the Sonic Hedgehog-regulated mouse development. Dev Biol 326 : 177–189.
17. TukachinskyH, LopezLV, SalicA (2010) A mechanism for vertebrate Hedgehog signaling: recruitment to cilia and dissociation of SuFu-Gli protein complexes. J Cell Biol 191 : 415–428.
18. HumkeEW, DornKV, MilenkovicL, ScottMP, RohatgiR (2010) The output of Hedgehog signaling is controlled by the dynamic association between Suppressor of Fused and the Gli proteins. Genes Dev 24 : 670–682.
19. RohatgiR, MilenkovicL, ScottMP (2007) Patched1 regulates hedgehog signaling at the primary cilium. Science 317 : 372–376.
20. CorbitKC, AanstadP, SinglaV, NormanAR, StainierDY, et al. (2005) Vertebrate Smoothened functions at the primary cilium. Nature 437 : 1018–1021.
21. TusonM, HeM, AndersonKV (2011) Protein kinase A acts at the basal body of the primary cilium to prevent Gli2 activation and ventralization of the mouse neural tube. Development 138 : 4921–4930.
22. DornKV, HughesCE, RohatgiR (2012) A Smoothened-Evc2 complex transduces the Hedgehog signal at primary cilia. Dev Cell 23 : 823–835.
23. HaycraftCJB, B., Aydin-SonY, ZhangQ, MichaudEJ, YoderBK (2005) Gli2 and Gli3 localize to cilia and require the intraflagellar transport protein polaris for processing and function. PLoS Genet 1: e53.
24. HuangfuD, LiuA, RakemanAS, MurciaNS, NiswanderL, et al. (2003) Hedgehog signalling in the mouse requires intraflagellar transport proteins. Nature 426 : 83–87.
25. KimJ, KatoM, BeachyPA (2009) Gli2 trafficking links Hedgehog-dependent activation of Smoothened in the primary cilium to transcriptional activation in the nucleus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106 : 21666–21671.
26. RosenbaumJL, WitmanGB (2002) Intraflagellar transport. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 3 : 813–825.
27. IshikawaH, MarshallWF (2011) Ciliogenesis: building the cell's antenna. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 12 : 222–234.
28. SasaiN, BriscoeJ (2012) Primary cilia and graded Sonic Hedgehog signaling. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Dev Biol 1 : 753–772.
29. MaySR, AshiqueAM, KarlenM, WangB, ShenY, et al. (2005) Loss of the retrograde motor for IFT disrupts localization of Smo to cilia and prevents the expression of both activator and repressor functions of Gli. Dev Biol 287 : 378–389.
30. HuangfuD, AndersonKV (2005) Cilia and Hedgehog responsiveness in the mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102 : 11325–11330.
31. LiemKFJA, A., HeM, SatirP, MoranJ, BeierD, et al. (2012) The IFT-A complex regulates Shh signaling through cilia structure and membrane protein trafficking. J Cell Biol 197 : 789–800.
32. QinJ, LinY, NormanRX, KoHW, EggenschwilerJT (2011) Intraflagellar transport protein 122 antagonizes Sonic Hedgehog signaling and controls ciliary localization of pathway components. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108 : 1456–1461.
33. TranPV, HaycraftCJ, BesschetnovaTY, Turbe-DoanA, StottmannRW, et al. (2008) THM1 negatively modulates mouse sonic hedgehog signal transduction and affects retrograde intraflagellar transport in cilia. Nat Genet 40 : 403–410.
34. KeadyBT, SamtaniR, TobitaK, TsuchyaM, San AgustinJT, et al. (2012) IFT25 links the signal-dependent movement of Hedgehog components to intraflagellar transport. Dev Cell 22 : 940–951.
35. JonassenJA, San AgustinJ, FollitJA, PazourGJ (2008) Deletion of IFT20 in the mouse kidney causes misorientation of the mitotic spindle and cystic kidney disease. J Cell Biol 183 : 377–384.
36. BerbariNF, KinNW, SharmaN, MichaudEJ, KestersonRA, et al. (2011) Mutations in Traf3ip1 reveal defects in ciliogenesis, embryonic development, and altered cell size regulation. Dev Biol 360 : 66–76.
37. MoyerJH, Lee-TischlerMJ, KwonHY, SchrickJJ, AvnerED, et al. (1994) Candidate gene associated with a mutation causing recessive polycystic kidney disease in mice. Science 264 : 1329–1333.
38. HoudeC, DickinsonRJ, HoutzagerVM, CullumR, MontpetitR, et al. (2006) Hippi is essential for node cilia assembly and Sonic hedgehog signaling. Dev Biol 300 : 523–533.
39. HaycraftCJ, ZhangQ, SongB, JacksonWS, DetloffPJ, et al. (2007) Intraflagellar transport is essential for endochondral bone formation. Development 134 : 307–316.
40. OcbinaPJ, EggenschwilerJT, MoskowitzI, AndersonKV (2011) Complex interactions between genes controlling trafficking in primary cilia. Nat Genet 43 : 547–553.
41. SchumacherJM, ArtztK, BraunRE (1998) Spermatid perinuclear ribonucleic acid-binding protein binds microtubules in vitro and associates with abnormal manchettes in vivo in mice. Biol Reprod 59 : 69–76.
42. JohnsonDR, HuntDM (1971) Hop-sterile, a mutant gene affecting sperm tail development in the mouse. J Embryol Exp Morphol 25 : 223–236.
43. BryanJH (1983) Abnormal cilia in a male-sterile mutant mouse. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histopathol 400 : 77–86.
44. BryanJH, HughesRL, BatesTJ (1977) Brain development in hydrocephalic-polydactyl, a recessive pleiotropic mutant in the mouse. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histol 374 : 205–214.
45. BryanJH (1981) Spermatogenesis revisited. V. Spermiogenesis in mice homozygous for two different male-sterile mutations (ps and hpy). Cell Tissue Res 221 : 169–180.
46. BryanJH (1977) Spermatogenesis revisited. IV. Abnormal spermiogenesis in mice homozygous for another male-sterility-inducing mutation, hpy (hydrocephalic-polydactyl). Cell Tissue Res 180 : 187–201.
47. HollanderWF (1976) Hydrocephalic-polydactyl, a recessive pleiotropic mutant in the mouse and its location in chromosome 6. Iowa State Journal of Research 51 : 13–24.
48. HuiCC, JoynerAL (1998) A mouse model of greig cephalopolysyndactyly syndrome: the extra-toesJ mutation contains an intragenic deletion of the Gli3 gene. Nat Genet 3 : 241–246.
49. ParkHL, BaiC, PlattKA, MatiseMP, BeeghlyA, et al. (2000) Mouse Gli1 mutants are viable but have defects in SHH signaling in combination with a Gli2 mutation. Development 127 : 1593–1605.
50. Ibañez-TallonI, PagenstecherA, FliegaufM, OlbrichH, KispertA, et al. (2004) Dysfunction of axonemal dynein heavy chain Mdnah5 inhibits ependymal flow and reveals a novel mechanism for hydrocephalus formation. Hum Mol Genet 13 : 2133–2141.
51. HollanderWF (1967) Hop - hydrocephalic-polydactyly. Mouse News Lett 36 : 37.
52. IshikawaH, IdeT, YagiT, JiangX, HironoM, et al. (2014) TTC26/DYF13 is an intraflagellar transport protein required for transport of motility-related proteins into flagella. Elife 3: e01566.
53. McClintockTS, GlasserCE, BoseSC, BergmanDA (2008) Tissue expression patterns identify mouse cilia genes. Physiol Genomics 32 : 198–206.
54. InglisPN, BoroevichKA, LerouxMR (2006) Piecing together a ciliome. Trends Genet 22 : 491–500.
55. Neu-YilikG, GehringNH, HentzeMW, KulozikAE (2004) Nonsense-mediated mRNA decay: from vacuum cleaner to Swiss army knife. Genome Biol 5 : 218.
56. CasparyT, AndersonKV (2003) Patterning cell types in the dorsal spinal cord: what the mouse mutants say. Nat Rev Neurosci 4 : 289–297.
57. WongSY, ReiterJF (2008) The primary cilium at the crossroads of mammalian hedgehog signaling. Curr Top Dev Biol 85 : 225–260.
58. ZaghloulNA, KatsanisN (2009) Mechanistic insights into Bardet-Biedl syndrome, a model ciliopathy. J Clin Invest 119 : 428–437.
59. RossAJ, May-SimeraH, EichersER, KaiM, HillJ, et al. (2005) Disruption of Bardet-Biedl syndrome ciliary proteins perturbs planar cell polarity in vertebrates. Nat Genet 37 : 1135–1140.
60. JonesC, RoperVC, FoucherI, QianD, BanizsB, et al. (2008) Ciliary proteins link basal body polarization to planar cell polarity regulation. Nat Genet 40 : 69–77.
61. BlacqueOE, PerensEA, BoroevichKA, InglisPN, LiC, et al. (2005) Functional genomics of the cilium, a sensory organelle. Curr Biol 15 : 935–941.
62. FollitJA, XuF, KeadyBT, PazourGJ (2009) Characterization of mouse IFT complex B. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton 66 : 457–468.
63. SasakiH, HuiC, NakafukuM, KondohH (1997) A binding site for Gli proteins is essential for HNF-3beta floor plate enhancer activity in transgenics and can respond to Shh in vitro. Development 124 : 1313–1322.
64. CooperMK, WassifCA, KrakowiakPA, TaipaleJ, GongR, et al. (2003) A defective response to Hedgehog signaling in disorders of cholesterol biosynthesis. Nat Genet 33 : 508–513.
65. GroverVK, ValadezJG, BowmanAB, CooperMK (2011) Lipid modifications of Sonic hedgehog ligand dictate cellular reception and signal response. PLoS One 6: e21353.
66. ChenJK, TaipaleJ, YoungKE, MaitiT, BeachyPA (2002) Small molecule modulation of Smoothened activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 99 : 14071–14076.
67. LiuA, WangB, NiswanderLA (2005) Mouse intraflagellar transport proteins regulate both the activator and repressor functions of Gli transcription factors. Development 132 : 3103–3111.
68. Paces-FessyM, BoucherD, PetitE, Paute-BriandS, Blanchet-TournierMF (2004) The negative regulator of Gli, Suppressor of fused (Sufu), interacts with SAP18, Galectin3 and other nuclear proteins. Biochem J 378 : 353–362.
69. RualJF, VenkatesanK, HaoT, Hirozane-KishikawaT, DricotA, et al. (2005) Towards a proteome-scale map of the human protein-protein interaction network. Nature 437 : 1173–1178.
70. DaiP, ShinagawaT, NomuraT, HaradaJ, KaulSC, et al. (2002) Ski is involved in transcriptional regulation by the repressor and full-length forms of Gli3. Genes Dev 16 : 2843–2848.
71. LareauLF, BrooksAN, SoergelDA, MengQ, BrennerSE (2007) The coupling of alternative splicing and nonsense-mediated mRNA decay. Adv Exp Med Biol 623 : 190–211.
72. LehmanJM, MichaudEJ, SchoebTR, Aydin-SonY, MillerM, et al. (2008) The Oak Ridge Polycystic Kidney mouse: modeling ciliopathies of mice and men. Dev Dyn 237 : 1960–1971.
73. RixS, CalmontA, ScamblerPJ, BealesPL (2011) An Ift80 mouse model of short rib polydactyly syndromes shows defects in hedgehog signalling without loss or malformation of cilia. Hum Mol Genet 20 : 1306–1314.
74. ZhangQ, SeoS, BuggeK, StoneEM, SheffieldVC (2012) BBS proteins interact genetically with the IFT pathway to influence SHH-related phenotypes. Hum Mol Genet 21 : 1945–1953.
75. BrownAS, EpsteinDJ (2011) Otic ablation of smoothened reveals direct and indirect requirements for Hedgehog signaling in inner ear development. Development 138 : 3967–3976.
76. Kolpakova-HartE, JinninM, HouB, FukaiN, OlsenBR (2007) Kinesin-2 controls development and patterning of the vertebrate skeleton by Hedgehog - and Gli3-dependent mechanisms. Dev Biol 309 : 273–284.
77. ZhangQ, LiuQ, AustinC, DrummondI, PierceEA (2012) Knockdown of ttc26 disrupts ciliogenesis of the photoreceptor cells and the pronephros in zebrafish. Mol Biol Cell 23 : 3069–3078.
78. HuangP, SchierAF (2009) Dampened Hedgehog signaling but normal Wnt signaling in zebrafish without cilia. Development 136 : 3089–3098.
79. LuntSC, HaynesT, PerkinsBD (2009) Zebrafish ift57, ift88, and ift172 intraflagellar transport mutants disrupt cilia but do not affect hedgehog signaling. Dev Dyn 238 : 1744–1759.
80. LaiCK, GuptaN, WenX, RangellL, ChihB, et al. (2011) Functional characterization of putative cilia genes by high-content analysis. Mol Biol Cell 22 : 1104–1119.
81. McLeodMJ (1980) Differential staining of cartilage and bone in whole mouse fetuses by alcian blue and alizarin red S. Teratology 22 : 299–301.
82. NakanoY, KimSH, KimHM, SannemanJD, ZhangY, et al. (2009) A claudin-9-based ion permeability barrier is essential for hearing. PLoS Genet 5: e1000610.
83. NakanoY, JahanI, BondeG, SunX, HildebrandMS, et al. (2012) A mutation in the Srrm4 gene causes alternative splicing defects and deafness in the Bronx waltzer mouse. PLoS Genet 8: e1002966.
84. NakanoY, BanfiB, JesaitisAJ, DinauerMC, AllenLA, et al. (2007) Critical roles for p22phox in the structural maturation and subcellular targeting of Nox3. Biochem J 403 : 97–108.
85. LarkinsCE, AvilesGD, EastMP, KahnRA, CasparyT (2011) Arl13b regulates ciliogenesis and the dynamic localization of Shh signaling proteins. Mol Biol Cell 22 : 4694–4703.
86. ChoA, KoHW, EggenschwilerJT (2008) FKBP8 cell-autonomously controls neural tube patterning through a Gli2 - and Kif3a-dependent mechanism. Dev Biol 321 : 27–39.
87. MoskwaP, LorentzenD, ExcoffonKJ, ZabnerJ, McCrayPBJ, et al. (2007) A novel host defense system of airways is defective in cystic fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 175 : 174–183.
88. LivakKJ, SchmittgenTD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 25 : 402–408.
Štítky
Genetika Reprodukční medicína
Článek Oligoasthenoteratozoospermia and Infertility in Mice Deficient for miR-34b/c and miR-449 LociČlánek The Kinesin AtPSS1 Promotes Synapsis and is Required for Proper Crossover Distribution in MeiosisČlánek Payoffs, Not Tradeoffs, in the Adaptation of a Virus to Ostensibly Conflicting Selective PressuresČlánek Examination of Prokaryotic Multipartite Genome Evolution through Experimental Genome ReductionČlánek BMP-FGF Signaling Axis Mediates Wnt-Induced Epidermal Stratification in Developing Mammalian SkinČlánek Role of STN1 and DNA Polymerase α in Telomere Stability and Genome-Wide Replication in ArabidopsisČlánek RNA-Processing Protein TDP-43 Regulates FOXO-Dependent Protein Quality Control in Stress ResponseČlánek Integrating Functional Data to Prioritize Causal Variants in Statistical Fine-Mapping StudiesČlánek Salt-Induced Stabilization of EIN3/EIL1 Confers Salinity Tolerance by Deterring ROS Accumulation inČlánek Ethylene-Induced Inhibition of Root Growth Requires Abscisic Acid Function in Rice ( L.) SeedlingsČlánek Metabolic Respiration Induces AMPK- and Ire1p-Dependent Activation of the p38-Type HOG MAPK PathwayČlánek Signature Gene Expression Reveals Novel Clues to the Molecular Mechanisms of Dimorphic Transition inČlánek A Mouse Model Uncovers LKB1 as an UVB-Induced DNA Damage Sensor Mediating CDKN1A (p21) DegradationČlánek Dominant Sequences of Human Major Histocompatibility Complex Conserved Extended Haplotypes from to
Článek vyšel v časopisePLOS Genetics
Nejčtenější tento týden
2014 Číslo 10
-
Všechny články tohoto čísla
- An Deletion Is Highly Associated with a Juvenile-Onset Inherited Polyneuropathy in Leonberger and Saint Bernard Dogs
- Licensing of Yeast Centrosome Duplication Requires Phosphoregulation of Sfi1
- Oligoasthenoteratozoospermia and Infertility in Mice Deficient for miR-34b/c and miR-449 Loci
- Basement Membrane and Cell Integrity of Self-Tissues in Maintaining Immunological Tolerance
- The Kinesin AtPSS1 Promotes Synapsis and is Required for Proper Crossover Distribution in Meiosis
- Germline Mutations in Are Associated with Familial Gastric Cancer
- POT1a and Components of CST Engage Telomerase and Regulate Its Activity in
- Controlling Meiotic Recombinational Repair – Specifying the Roles of ZMMs, Sgs1 and Mus81/Mms4 in Crossover Formation
- Payoffs, Not Tradeoffs, in the Adaptation of a Virus to Ostensibly Conflicting Selective Pressures
- FHIT Suppresses Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition (EMT) and Metastasis in Lung Cancer through Modulation of MicroRNAs
- Genome-Wide Mapping of Yeast RNA Polymerase II Termination
- Examination of Prokaryotic Multipartite Genome Evolution through Experimental Genome Reduction
- White Cells Facilitate Opposite- and Same-Sex Mating of Opaque Cells in
- BMP-FGF Signaling Axis Mediates Wnt-Induced Epidermal Stratification in Developing Mammalian Skin
- Genome-Wide Association Study of CSF Levels of 59 Alzheimer's Disease Candidate Proteins: Significant Associations with Proteins Involved in Amyloid Processing and Inflammation
- COE Loss-of-Function Analysis Reveals a Genetic Program Underlying Maintenance and Regeneration of the Nervous System in Planarians
- Fat-Dachsous Signaling Coordinates Cartilage Differentiation and Polarity during Craniofacial Development
- Identification of Genes Important for Cutaneous Function Revealed by a Large Scale Reverse Genetic Screen in the Mouse
- Sensors at Centrosomes Reveal Determinants of Local Separase Activity
- Genes Integrate and Hedgehog Pathways in the Second Heart Field for Cardiac Septation
- Systematic Dissection of Coding Exons at Single Nucleotide Resolution Supports an Additional Role in Cell-Specific Transcriptional Regulation
- Recovery from an Acute Infection in Requires the GATA Transcription Factor ELT-2
- HIPPO Pathway Members Restrict SOX2 to the Inner Cell Mass Where It Promotes ICM Fates in the Mouse Blastocyst
- Role of and in Development of Abdominal Epithelia Breaks Posterior Prevalence Rule
- The Formation of Endoderm-Derived Taste Sensory Organs Requires a -Dependent Expansion of Embryonic Taste Bud Progenitor Cells
- Role of STN1 and DNA Polymerase α in Telomere Stability and Genome-Wide Replication in Arabidopsis
- Keratin 76 Is Required for Tight Junction Function and Maintenance of the Skin Barrier
- Encodes the Catalytic Subunit of N Alpha-Acetyltransferase that Regulates Development, Metabolism and Adult Lifespan
- Disruption of SUMO-Specific Protease 2 Induces Mitochondria Mediated Neurodegeneration
- Caudal Regulates the Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Pair-Rule Waves in
- It's All in Your Mind: Determining Germ Cell Fate by Neuronal IRE-1 in
- A Conserved Role for Homologs in Protecting Dopaminergic Neurons from Oxidative Stress
- The Master Activator of IncA/C Conjugative Plasmids Stimulates Genomic Islands and Multidrug Resistance Dissemination
- An AGEF-1/Arf GTPase/AP-1 Ensemble Antagonizes LET-23 EGFR Basolateral Localization and Signaling during Vulva Induction
- The Proteomic Landscape of the Suprachiasmatic Nucleus Clock Reveals Large-Scale Coordination of Key Biological Processes
- RNA-Processing Protein TDP-43 Regulates FOXO-Dependent Protein Quality Control in Stress Response
- A Complex Genetic Switch Involving Overlapping Divergent Promoters and DNA Looping Regulates Expression of Conjugation Genes of a Gram-positive Plasmid
- ZTF-8 Interacts with the 9-1-1 Complex and Is Required for DNA Damage Response and Double-Strand Break Repair in the Germline
- Integrating Functional Data to Prioritize Causal Variants in Statistical Fine-Mapping Studies
- Tpz1-Ccq1 and Tpz1-Poz1 Interactions within Fission Yeast Shelterin Modulate Ccq1 Thr93 Phosphorylation and Telomerase Recruitment
- Salt-Induced Stabilization of EIN3/EIL1 Confers Salinity Tolerance by Deterring ROS Accumulation in
- Telomeric (s) in spp. Encode Mediator Subunits That Regulate Distinct Virulence Traits
- Ethylene-Induced Inhibition of Root Growth Requires Abscisic Acid Function in Rice ( L.) Seedlings
- Ancient Expansion of the Hox Cluster in Lepidoptera Generated Four Homeobox Genes Implicated in Extra-Embryonic Tissue Formation
- Mechanism of Suppression of Chromosomal Instability by DNA Polymerase POLQ
- A Mutation in the Mouse Gene Leads to Impaired Hedgehog Signaling
- Keeping mtDNA in Shape between Generations
- Targeted Exon Capture and Sequencing in Sporadic Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
- TIF-IA-Dependent Regulation of Ribosome Synthesis in Muscle Is Required to Maintain Systemic Insulin Signaling and Larval Growth
- At Short Telomeres Tel1 Directs Early Replication and Phosphorylates Rif1
- Evidence of a Bacterial Receptor for Lysozyme: Binding of Lysozyme to the Anti-σ Factor RsiV Controls Activation of the ECF σ Factor σ
- Hsp40s Specify Functions of Hsp104 and Hsp90 Protein Chaperone Machines
- Feeding State, Insulin and NPR-1 Modulate Chemoreceptor Gene Expression via Integration of Sensory and Circuit Inputs
- Functional Interaction between Ribosomal Protein L6 and RbgA during Ribosome Assembly
- Multiple Regulatory Systems Coordinate DNA Replication with Cell Growth in
- Fast Evolution from Precast Bricks: Genomics of Young Freshwater Populations of Threespine Stickleback
- Mmp1 Processing of the PDF Neuropeptide Regulates Circadian Structural Plasticity of Pacemaker Neurons
- The Nuclear Immune Receptor Is Required for -Dependent Constitutive Defense Activation in
- Genetic Modifiers of Neurofibromatosis Type 1-Associated Café-au-Lait Macule Count Identified Using Multi-platform Analysis
- Juvenile Hormone-Receptor Complex Acts on and to Promote Polyploidy and Vitellogenesis in the Migratory Locust
- Uncovering Enhancer Functions Using the α-Globin Locus
- The Analysis of Mutant Alleles of Different Strength Reveals Multiple Functions of Topoisomerase 2 in Regulation of Chromosome Structure
- Metabolic Respiration Induces AMPK- and Ire1p-Dependent Activation of the p38-Type HOG MAPK Pathway
- The Specification and Global Reprogramming of Histone Epigenetic Marks during Gamete Formation and Early Embryo Development in
- The DAF-16 FOXO Transcription Factor Regulates to Modulate Stress Resistance in , Linking Insulin/IGF-1 Signaling to Protein N-Terminal Acetylation
- Genetic Influences on Translation in Yeast
- Analysis of Mutants Defective in the Cdk8 Module of Mediator Reveal Links between Metabolism and Biofilm Formation
- Ribosomal Readthrough at a Short UGA Stop Codon Context Triggers Dual Localization of Metabolic Enzymes in Fungi and Animals
- Gene Duplication Restores the Viability of Δ and Δ Mutants
- Selection on a Variant Associated with Improved Viral Clearance Drives Local, Adaptive Pseudogenization of Interferon Lambda 4 ()
- Break-Induced Replication Requires DNA Damage-Induced Phosphorylation of Pif1 and Leads to Telomere Lengthening
- Dynamic Partnership between TFIIH, PGC-1α and SIRT1 Is Impaired in Trichothiodystrophy
- Signature Gene Expression Reveals Novel Clues to the Molecular Mechanisms of Dimorphic Transition in
- Mutations in Moderate or Severe Intellectual Disability
- Multifaceted Genome Control by Set1 Dependent and Independent of H3K4 Methylation and the Set1C/COMPASS Complex
- A Role for Taiman in Insect Metamorphosis
- The Small RNA Rli27 Regulates a Cell Wall Protein inside Eukaryotic Cells by Targeting a Long 5′-UTR Variant
- MMS Exposure Promotes Increased MtDNA Mutagenesis in the Presence of Replication-Defective Disease-Associated DNA Polymerase γ Variants
- Coexistence and Within-Host Evolution of Diversified Lineages of Hypermutable in Long-term Cystic Fibrosis Infections
- Comprehensive Mapping of the Flagellar Regulatory Network
- Topoisomerase II Is Required for the Proper Separation of Heterochromatic Regions during Female Meiosis
- A Splice Mutation in the Gene Causes High Glycogen Content and Low Meat Quality in Pig Skeletal Muscle
- KDM5 Interacts with Foxo to Modulate Cellular Levels of Oxidative Stress
- H2B Mono-ubiquitylation Facilitates Fork Stalling and Recovery during Replication Stress by Coordinating Rad53 Activation and Chromatin Assembly
- Copy Number Variation in the Horse Genome
- Unifying Genetic Canalization, Genetic Constraint, and Genotype-by-Environment Interaction: QTL by Genomic Background by Environment Interaction of Flowering Time in
- Spinster Homolog 2 () Deficiency Causes Early Onset Progressive Hearing Loss
- Genome-Wide Discovery of Drug-Dependent Human Liver Regulatory Elements
- Developmentally-Regulated Excision of the SPβ Prophage Reconstitutes a Gene Required for Spore Envelope Maturation in
- Protein Phosphatase 4 Promotes Chromosome Pairing and Synapsis, and Contributes to Maintaining Crossover Competence with Increasing Age
- The bHLH-PAS Transcription Factor Dysfusion Regulates Tarsal Joint Formation in Response to Notch Activity during Leg Development
- A Mouse Model Uncovers LKB1 as an UVB-Induced DNA Damage Sensor Mediating CDKN1A (p21) Degradation
- Notch3 Interactome Analysis Identified WWP2 as a Negative Regulator of Notch3 Signaling in Ovarian Cancer
- An Integrated Cell Purification and Genomics Strategy Reveals Multiple Regulators of Pancreas Development
- Dominant Sequences of Human Major Histocompatibility Complex Conserved Extended Haplotypes from to
- The Vesicle Protein SAM-4 Regulates the Processivity of Synaptic Vesicle Transport
- A Gain-of-Function Mutation in Impeded Bone Development through Increasing Expression in DA2B Mice
- Nephronophthisis-Associated Regulates Cell Cycle Progression, Apoptosis and Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition
- Beclin 1 Is Required for Neuron Viability and Regulates Endosome Pathways via the UVRAG-VPS34 Complex
- The Not5 Subunit of the Ccr4-Not Complex Connects Transcription and Translation
- Abnormal Dosage of Ultraconserved Elements Is Highly Disfavored in Healthy Cells but Not Cancer Cells
- Genome-Wide Distribution of RNA-DNA Hybrids Identifies RNase H Targets in tRNA Genes, Retrotransposons and Mitochondria
- The Chromosomal Association of the Smc5/6 Complex Depends on Cohesion and Predicts the Level of Sister Chromatid Entanglement
- Cell-Autonomous Progeroid Changes in Conditional Mouse Models for Repair Endonuclease XPG Deficiency
- PLOS Genetics
- Archiv čísel
- Aktuální číslo
- Informace o časopisu
Nejčtenější v tomto čísle- The Master Activator of IncA/C Conjugative Plasmids Stimulates Genomic Islands and Multidrug Resistance Dissemination
- A Splice Mutation in the Gene Causes High Glycogen Content and Low Meat Quality in Pig Skeletal Muscle
- Keratin 76 Is Required for Tight Junction Function and Maintenance of the Skin Barrier
- A Role for Taiman in Insect Metamorphosis
Kurzy
Zvyšte si kvalifikaci online z pohodlí domova
Současné možnosti léčby obezity
nový kurzAutoři: MUDr. Martin Hrubý
Všechny kurzyPřihlášení#ADS_BOTTOM_SCRIPTS#Zapomenuté hesloZadejte e-mailovou adresu, se kterou jste vytvářel(a) účet, budou Vám na ni zaslány informace k nastavení nového hesla.
- Vzdělávání



