-
Články
Top novinky
Reklama- Vzdělávání
- Časopisy
Top články
Nové číslo
- Témata
Top novinky
Reklama- Videa
- Podcasty
Nové podcasty
Reklama- Kariéra
Doporučené pozice
Reklama- Praxe
Top novinky
ReklamaCell-Cycle Dependent Expression of a Translocation-Mediated Fusion Oncogene Mediates Checkpoint Adaptation in Rhabdomyosarcoma
Rhabdomyosarcoma is the most commonly occurring soft-tissue sarcoma in childhood. Most rhabdomyosarcoma falls into one of two biologically distinct subgroups represented by alveolar or embryonal histology. The alveolar subtype harbors a translocation-mediated PAX3:FOXO1A fusion gene and has an extremely poor prognosis. However, tumor cells have heterogeneous expression for the fusion gene. Using a conditional genetic mouse model as well as human tumor cell lines, we show that that Pax3:Foxo1a expression is enriched in G2 and triggers a transcriptional program conducive to checkpoint adaptation under stress conditions such as irradiation in vitro and in vivo. Pax3:Foxo1a also tolerizes tumor cells to clinically-established chemotherapy agents and emerging molecularly-targeted agents. Thus, the surprisingly dynamic regulation of the Pax3:Foxo1a locus is a paradigm that has important implications for the way in which oncogenes are modeled in cancer cells.
Published in the journal: . PLoS Genet 10(1): e32767. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1004107
Category: Research Article
doi: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1004107Summary
Rhabdomyosarcoma is the most commonly occurring soft-tissue sarcoma in childhood. Most rhabdomyosarcoma falls into one of two biologically distinct subgroups represented by alveolar or embryonal histology. The alveolar subtype harbors a translocation-mediated PAX3:FOXO1A fusion gene and has an extremely poor prognosis. However, tumor cells have heterogeneous expression for the fusion gene. Using a conditional genetic mouse model as well as human tumor cell lines, we show that that Pax3:Foxo1a expression is enriched in G2 and triggers a transcriptional program conducive to checkpoint adaptation under stress conditions such as irradiation in vitro and in vivo. Pax3:Foxo1a also tolerizes tumor cells to clinically-established chemotherapy agents and emerging molecularly-targeted agents. Thus, the surprisingly dynamic regulation of the Pax3:Foxo1a locus is a paradigm that has important implications for the way in which oncogenes are modeled in cancer cells.
Introduction
Rhabdomyosarcoma (RMS) is the most common childhood soft tissue sarcoma. Historically, RMS has been thought to arise from muscle because of the expression of myogenic markers. Most childhood RMS falls into one of two biologically distinct subgroups: alveolar (aRMS) or embryonal (eRMS). aRMS is the more aggressive variant with a survival rate of less than 20% when metastatic due to chemotherapy and radiation resistance [1]. aRMS is characterized by a frequent t(2;13) chromosomal translocation, which results in the PAX3:FOXO1A fusion gene, or less frequently by a t(1;13) mediated PAX7:FOXO1A fusion oncogene [1]. Clinically, the aggressive behavior of aRMS has been attributed to PAX3:FOXO1A transcriptional reprograming because fusion negative aRMS have a more favorable outcome similar to eRMS [2], [3], [4].
We previously developed a mouse model of aRMS employing a conditional knock-in approach that expresses Pax3:Foxo1a from the native Pax3 locus in fetal and postnatal myoblasts [5], [6], [7]. In this model, Pax3:Foxo1a was necessary but not sufficient for aRMS tumor initiation. Interestingly, cells expressing high levels of Pax3:Foxo1a were more prevalent in metastatic tumors [7]. The heterogeneity of Pax3:Foxo1a expression in primary and metastatic tumors, and enrichment in the latter, suggested that Pax3:Foxo1a might be selectively expressed in a subset of aRMS cells; alternatively, Pax3:Foxo1a expression might be temporally regulated. In the current study we present striking evidence that Pax3:Foxo1a is expressed in a dynamic manner and mediates a G2-specific program enabling checkpoint adaptation and refractoriness to therapy.
Results
Pax3:Foxo1a expression is dynamic in mouse aRMS cells
In our genetically-engineered conditional knock-in mouse model of aRMS, eYFP is expressed as a second cistron on the same mRNA as Pax3:Foxo1a (Figure 1A). We have observed heterogeneity of eYFP expression among tumor cells in situ (Figure 1B). To first examine Pax3:Foxo1a expression as a function of time, we flow sorted Pax3:Foxo1alow and Pax3:Foxo1ahigh cells using eYFP signal in two independent murine aRMS primary cultures (Figure 1C and 1D; Figure S1A and S1B). Comparison of Pax3:Foxo1a protein levels for sorted populations showed Pax3:Foxo1alow cells possessed much reduced levels of Pax3:Foxo1a protein (Figure 1E and Figure S1C). However, FACS analysis over time revealed that the eYFP signal of Pax3:Foxo1alow and Pax3:Foxo1ahigh tended towards the mean eYFP fluorescence intensity of unsorted tumor cells with time and/or cell divisions (Figure 1C and 1D; Figure S1A and S1B). Thus, Pax3:Foxo1ahigh cell could dynamically reduce expression of eYFP from the Pax3:Foxo1a locus, and Pax3:Foxo1alow cells could dynamically increase expression of eYFP from the Pax3:Foxo1a locus. We further confirmed that eYFP expression was indeed reflective of Pax3:Foxo1a expression in terms of protein half-life. Figure S1E and S1F shows levels of eYFP signal and Pax3:Foxo1a protein stability after translation inhibition by cycloheximide (CHX). Akin to the strong correlation between eYFP and Pax3:Foxo1a expression at the protein level (Figure 1 and Figure S1C), the protein half-lives of Pax3:Foxo1a and eYFP were roughly similar at 31.6 and 44.7 hours (Figure S1E and S1F), thereby affirming that eYFP is a reasonable surrogate for transcription of Pax3:Foxo1a from the Pax3 locus (we do however acknowledge that eYFP is a better marker of the start of Pax3:Foxo1a transcription than the end of Pax3:Foxo1a transcription or protein expression (i.e., since eYFP is expressed on the same mRNA as Pax3:Foxo1a, the beginning of fluorescence should coincide with the initial presence of the Pax3:Foxo1a transcript). Thereafter, eYFP is susceptible to photo-bleaching and possible proteasomal degradation sooner than the 44 hours observed under conditions of cyclohexamide treatment (Figure S1F)).
Fig. 1. eYFP activity and Pax3:Foxo1a expression is cell cycle specific. 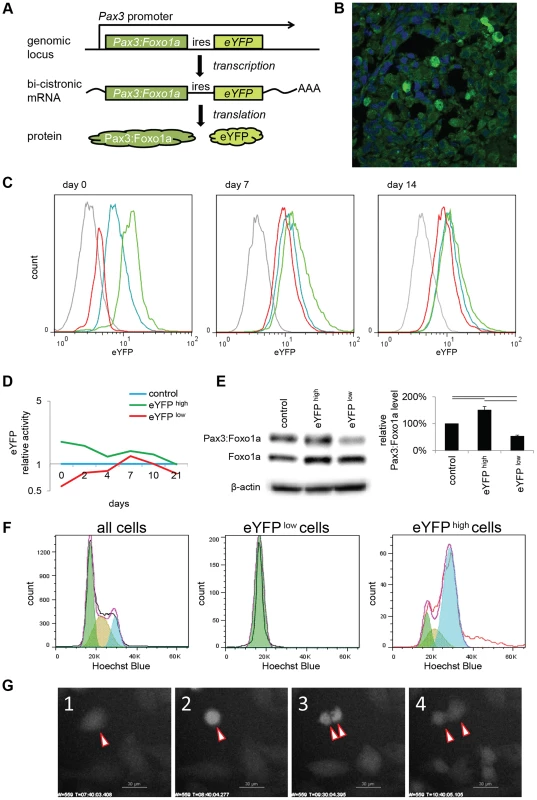
(A) Diagrammatic representation of the conditional Pax3:Foxo1a knock-in allele by which eYFP is expressed as a second cistron on the same mRNA as Pax3:Foxo1a at the native Pax3 promoter. (B) Heterogeneity of eYFP expression in a murine aRMS tumor by immunofluorescence. (C) eYFP fluorescence of eYFP sorted cells overtime as measured by FACS. Grey: C2C12 (negative control), blue: no sorted cells, green: eYFP activity high cells, red: eYFP activity low cells. (D) Mean of relative eYFP activity in panel 1C measured by FACS. (E) Western blot analysis using eYFP sorted cells. Plotted are relative protein levels of Pax3:Foxo1a/β-Actin. Mean ± SE were obtained from three independent immunoblottings. Black line shows significant difference (p<0.05). (F) eYFP activity and cell cycle analysis using Hochest33342 staining for mouse primary cell culture U23674. Green shows G0/G1 phase, brown shows S phase, and blue shows G2/M phase. (G) Time-lapse experiment of eYFP activity (select frames over 16 hours). See also corresponding Movie S1. Pax3:Foxo1a expression is dynamically regulated during the cell cycle
To investigate what conditions affect the dynamic alteration of Pax3:Foxo1a expression in aRMS cells, we compared eYFP fluorescence to cell cycle phase as determined by staining with the DNA dye Hoechst33342. Almost all Pax3:Foxo1alow cells existed in G0/G1 (2N) stage, while to our surprise Pax3:Foxo1ahigh cells were G2/M or hyperdiploid/multinuclear (≥4N) cells (Figure 1F and Figure S1D). We next performed time-lapse experiments of eYFP activity by confocal microscopy. Figure 1G shows in time-lapse images that eYFP activity during cell division is transiently but markedly increased, particularly in pre-mitotic cells. Interestingly, the level of eYFP in some multinuclear cells remained at a high level in cells that appeared to be unable to undergo telophase/cytokinesis (Movie S1).
We next performed QPCR of Pax3:Foxo1a and PAX3:FOXO1A using cell cycle specific sorted mouse and human aRMS cells, respectively. Both mouse and human aRMS cells showed significant differences in the mRNA expression of Pax3:Foxo1a and PAX3:FOXO1A in the transition from 2N (G1) to 3N (S phase) and 4N (G2/M) cells (Figure 2A and 2B) affirming cross-species relevance of the cell cycle dependent mRNA regulation of Pax3:Foxo1a expression.
Fig. 2. Pax3:Foxo1a activity is cell cycle dependent. 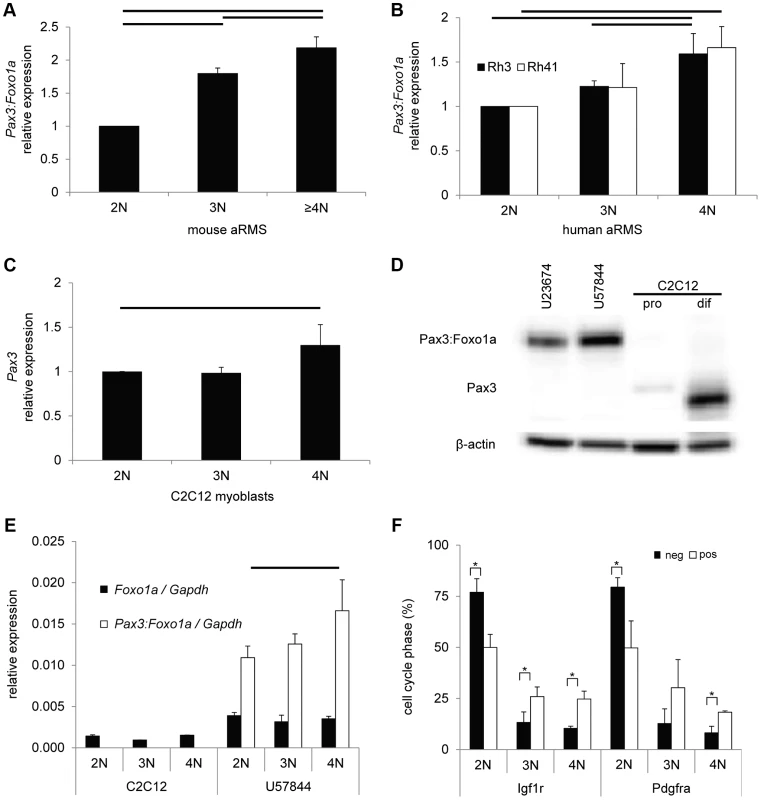
(A) mRNA expression of Pax3:Foxo1a normalized by Gapdh in U23674 mouse aRMS primary cell culture sorted by DNA content. Black lines show significant differences (p<0.05). (B) mRNA expression of PAX3:FOXO1A normalized by GAPDH in Rh3 and Rh41 human aRMS cell lines sorted by DNA content. (C) mRNA expression of Pax3 normalized by Gapdh in C2C12 murine myoblasts sorted by DNA content. (D) Western blot analysis of Pax3 and Pax3:Foxo1a in unsorted murine U23674 aRMS cells (genotype Pax3 (Pax3:Foxo1a activated/Pax3:Foxo1a activated)), murine U57844 aRMS cells (genotype Pax3 (wt/Pax3:Foxo1a activated)), proliferative C2C12 myoblasts (pro) and differentiating C2C12 myoblasts (dif). (E) mRNA expression of Foxo1 and Pax3:Foxo1a normalized to Gapdh in C2C12 myoblasts and the U57844 mouse aRMS primary cell culture. (F) Cell cycle analysis after sorting for Pax3:Foxo1a targets Igf1r or Pdgfra in mouse aRMS tumor cells. Nearly twice as many 4N cells are Igf1r (or Pdgfra) positive versus Igf1r (or Pdgfra negative), suggesting these Pax3:Foxo1a targets may have a functional role late in the cell cycle (* P<0.05). pos, positive. Neg, negative. To investigate the transcriptional basis of this Pax3:Foxo1a dynamic expression, we performed QPCR of Pax3 and Foxo1 using cell cycle specific sorted C2C12 mouse myoblast cells of the genotype Pax3(wt/wt) and mouse aRMS primary tumor cells of the genotype Pax3(wt/Pax3:Foxo1a). C2C12 myoblasts showed significant increases in Pax3 mRNA levels for 4N cells when compared with 2N cells (Figure 2C). Pax3 was not detectable in aRMS cells at the mRNA level (data not shown), which was also reflected in the absence of expression of Pax3 protein in aRMS cells by western blotting (Figure 2D). This result is consistent with our prior studies suggesting that Pax3:Foxo1a causes decreased expression of the wildtype Pax3 locus [5], [6]. By contrast, Foxo1 mRNA expression did not differ between 2N and 4N in either C2C12 myoblasts or aRMS tumor cells (Figure 2E). Thus, the cell cycle dependence of Pax3:Foxo1a may in some part be attributable to increased Pax3 promoter activity at G2/M versus G1 in C2C12 myoblasts, but Pax3:Foxo1a transcript level is so significantly increased over Pax3 in aRMS cells that other factors related to the chromosomal fusion are likely responsible, e.g. gain of a Foxo1a 3′ cis-enhancer, or loss of a Pax3 3′ cis-repressor repressor. From the design of the conditional knock-in allele [5], this element(s) can be inferred to exist in the 9.3 kB of the Foxo1a 3′ region containing exons 2 and 3 and untranslated region (6.5 kb), or exons 8–10 of Pax3. We also cannot exclude that stabilization of the Pax3:Foxo1a transcript may to some degree play a role, and this stabilization may or may not be related to the Foxo1a cis-elements on the chimeric mRNA.
Because Pdgfra [8] and Igf1r [9] are well known direct downstream targets of Pax3:Foxo1a, we determined whether these targets were expressed to any degree in 4N (G2/M) cells. We first sorted aRMS tumor cells for Pdgfra or Igf1r positivity versus negativity, then performed DNA content analysis. For both receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs), the majority of cells with positive RTK surface expression were 2N (Figure 2F). However, nearly twice as many 4N cells are Igf1r (or Pdgfra) positive versus Igf1r (or Pdgfra) negative, suggesting these Pax3:Foxo1a targets may have a functional role late in the cell cycle, such as the Igf1r-mediated radioresistance seen for other forms of cancer [10].
Pax3:Foxo1a expression is specific to G2 and acts in G2/M checkpoint adaptation
To determine the role of Pax3:Foxo1a in G2, M or G2/M checkpoint, we examined markers of each cell cycle phase under non-stress or stress conditions. Immunocytochemistry is presented in Figure 3 is a for Pax3:Foxo1a (Pax3) with phospho-histone H3 (pHH3), a marker of mitosis, or CDC2-Y15 (pCDC2), a negative marker of entry into mitosis that is commonly expressed in G2 (CDC2-Y15 is phosphorylated by Wee1 kinase, which then negatively regulates Cdc2 kinase [11]; CDC2-Y15 is present starting in late G1 then also in S, and G2 phases, but absent in M [12]). In murine aRMS primary cultures U23674 and U42369, pHH3 positive metaphase cells did not express Pax3:Foxo1a protein and yet most pCDC2 positive cells expressed Pax3:Foxo1a very highly (Figure 3). These results suggest that Pax3:Foxo1a is expressed in the G2 cell cycle phase but not M phase. Human aRMS cell lines Rh3 and Rh41 showed identical results (Figure 3). Next, we sought to understand the function of Pax3:Foxo1a in G2. For this purpose we performed genome-wide expression analysis using cells sorted at specific stages of the cell cycle (2N vs. 4N) with or without Pax3:Foxo1a siRNA knockdown (Figure 4A). Because eYFP is expressed as a second cistron in the targeted Pax3:Foxo1a-ires-eYFP allele, we anticipated that siRNA for eYFP would knock down not only eYFP but also Pax3:Foxo1a. Western blotting of Pax3:Foxo1a and native Foxo1a protein 48 hours after siRNA transfection showed that eYFP siRNA efficiently and specifically knocked down Pax3:Foxo1a protein (Figure 4B). Protein expression of the Pax3:Foxo1a transcriptional target Pdgfra was also reduced (Figure 4B).
Fig. 3. Pax3:Foxo1a is expressed in G2 for mouse and human aRMS. 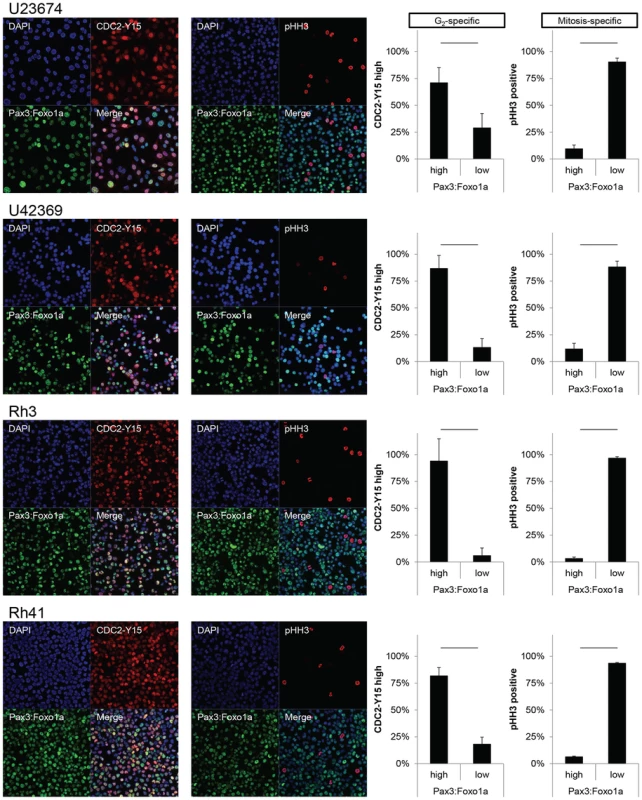
Immunocytochemistry for Pax3 (green), pHH3 (red) and DAPI (blue) or Pax3 (green), pCDC2 (red) and DAPI (blue). Numbers are relative rate of Pax3:Foxo1a high or low cells/pHH3 positive cells and Pax3:Foxo1a high or low cells/CDC2-Y15 high cells. Black line shows significant difference (p<0.05). Fig. 4. Pax3:Foxo1a induces G2/M checkpoint adaptation gene in G2/M. 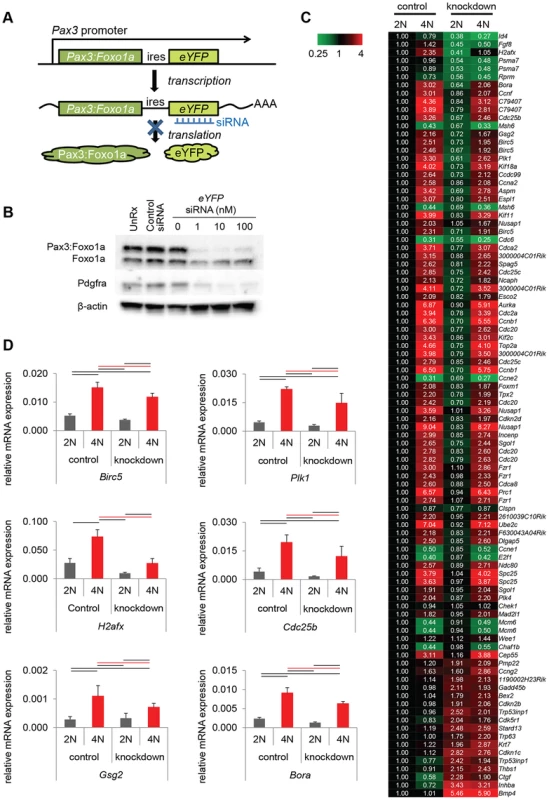
(A) Diagrammatic representation of Pax3:Foxo1a knockdown strategy using eYFP siRNA. (B) Knockdown of the Pax3:Foxo1a protein by siYFP. Total cell lysates were isolated 48 h after transfection. Pax3:Foxo1a was detected with an antibody targeting the C-terminus of Foxo1a. (C) Differential expression of 60 of cell cycle genes (as annotated by Gene Ontology) for DNA content with or without Pax3:Foxo1a knockdown. (D) mRNA expression by QPCR of Plk1, Cdc25b, H2afx and Birc5 normalized to Gapdh in DNA content-sorted U23674 mouse aRMS primary tumor cells with or without Pax3:Foxo1a knockdown. Black and red line shows significant difference (p<0.05). From genome-wide expression analysis of 2N vs. 4N sorted cells with or without Pax3:Foxo1a siRNA knockdown, we found several genes implicated in the process of G2/M checkpoint adaptation to be down-regulated in G2/M (4N cells) when Pax3:Foxo1a was knocked down (Figure 4C; Table S1 shows all data analyzed by ANOVA (<0.05) using the multiple comparison correction method of Benjamini and Hochberg). Checkpoint adaptation is the process by which unicellular organisms or cancer cells progress through a delayed cell cycle checkpoint (G2 or by analogy the mitotic spindle assembly checkpoint) in lieu of programmed cell death, but before DNA damage is completely repaired [13], [14], [15]. Factors implicated in checkpoint adaptation are similar to those involved in checkpoint recovery (after complete repair of DNA damage), but additionally require anti-apoptotic signals [14]. Select G2/M checkpoint adaptation genes implicated in this experiment, the DNA damage sensing/checkpoint progression factors Plk1, Cdc25b, H2afx and the cell survival factor Birc5 (Survivin), were validated for differential expression by QPCR (Figure 4D). Whether these genes are direct transcriptional targets of Pax3:Foxo1a was investigated by interrogating loci for reported nearby Pax3:Foxo1a binding sites [16]. Most potential regulatory sites were greater than 60 kB away (Table S2). While regulatory sequences can be hundreds of kBs away from the target gene, it remains possible that these genes may also be regulated indirectly by other Pax3:Foxo1a target genes or miRNAs.
As a test of checkpoint adaptation and the permissiveness of aRMS cells to transit from G2 to mitosis despite single - and double-stranded DNA damage, we irradiated tumor cells with or without Pax3:Foxo1a knockdown. Radiation resulted in a higher fraction of DNA breaks amongst mitotic cells (as represented by dual pHH3 positive, H2AX positive cells) under conditions of Pax3:Foxo1a expression than its knockdown (Figure 5A and Figure S2A), suggesting that Pax3:Foxo1a does facilitate G2 to M transition, consistent with checkpoint adaptation. Moreover, we performed cell cycle and Annexin V apoptosis detection assay after treatment with 10 Gy radiation for two independent eYFP shRNA knockdown clones compared to two other independent shRNA controls (as stated early, eYFP knockdown also achieves Pax3:Foxo1a knockdown) (Figure S2). Cell cycle analysis of the shRNA clones treated with radiation revealed increasing percentage of cells in cells having ≥4N DNA content after radiation for Pax3:Foxo1a knockdown cells compared to radiated controls (p<0.05)(Figure 5B). This result is consistent with a role of Pax3:Foxo1a in overcoming G2 arrest or M checkpoint arrest after radiation. Similarly, the Annexin V apoptosis detection assay showed a lower induction of apoptosis following radiation when Pax3:Foxo1a expression was preserved in shControl clones than shYFP cells (Figure 5C).
Fig. 5. Pax3:Foxo1a facilitates G2/M checkpoint adaptation. 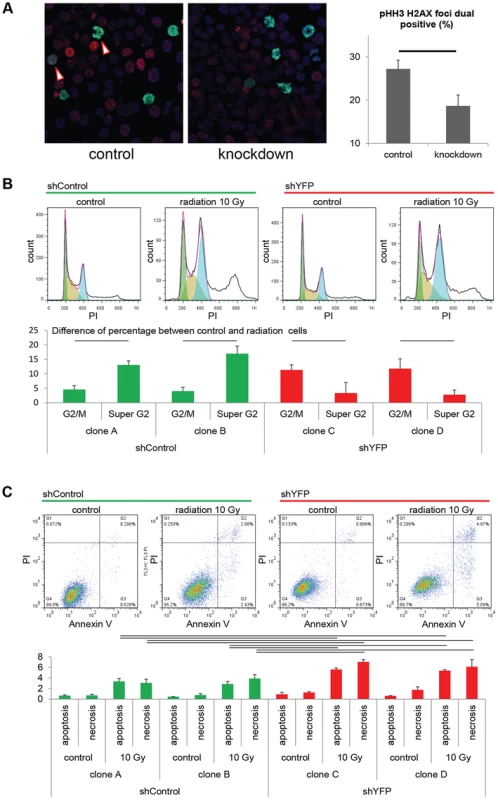
(A) Immunocytochemistry for pHH3 (green), pH2AX (red) and DAPI (Blue) using U23674 mouse aRMS primary cell culture with or without Pax3:Foxo1a knockdown treated with 6 Gy irradiation. Black line shows significant difference (p<0.05). See Figure S2A for representative single-channel ICC images corresponding to Figure 5A. Arrowheads indicate pHH3 and pH2AX double positive cells. (B) Representative cell cycle analysis for U23674 transfected by shControl (Clone A) or shYFP (Clone C) with or without 10 Gy irradiation. The graph shows the differences of percentage between control and radiated cells in shControl and shYFP clones in 3 independent experiments. Black line shows significant difference (p<0.05). (C) Annexin V apoptosis detection assay for U23674 transfected by shControl or shYFP clones with or without 10 Gy irradiation. Black line shows significant difference (p<0.05). To test the acute role of Pax3:Foxo1a in tolerization to treatment-related DNA damage in vivo, we used eYFP siRNA to transiently knock down Pax3:Foxo1a in aRMS tumor cells treated with radiation versus non-irradiated controls that were then orthotopically injected into unirradiated host mice. Pax3:Foxo1a mediated a cell survival and tumor re-establishment advantage under the stress condition of irradiation, but not under homeostatic conditions (p = 0.02, Figure 6A and 6B).
Fig. 6. Treatment-related implications for dynamic oncogene expression in rhabdomyosarcoma in vivo. 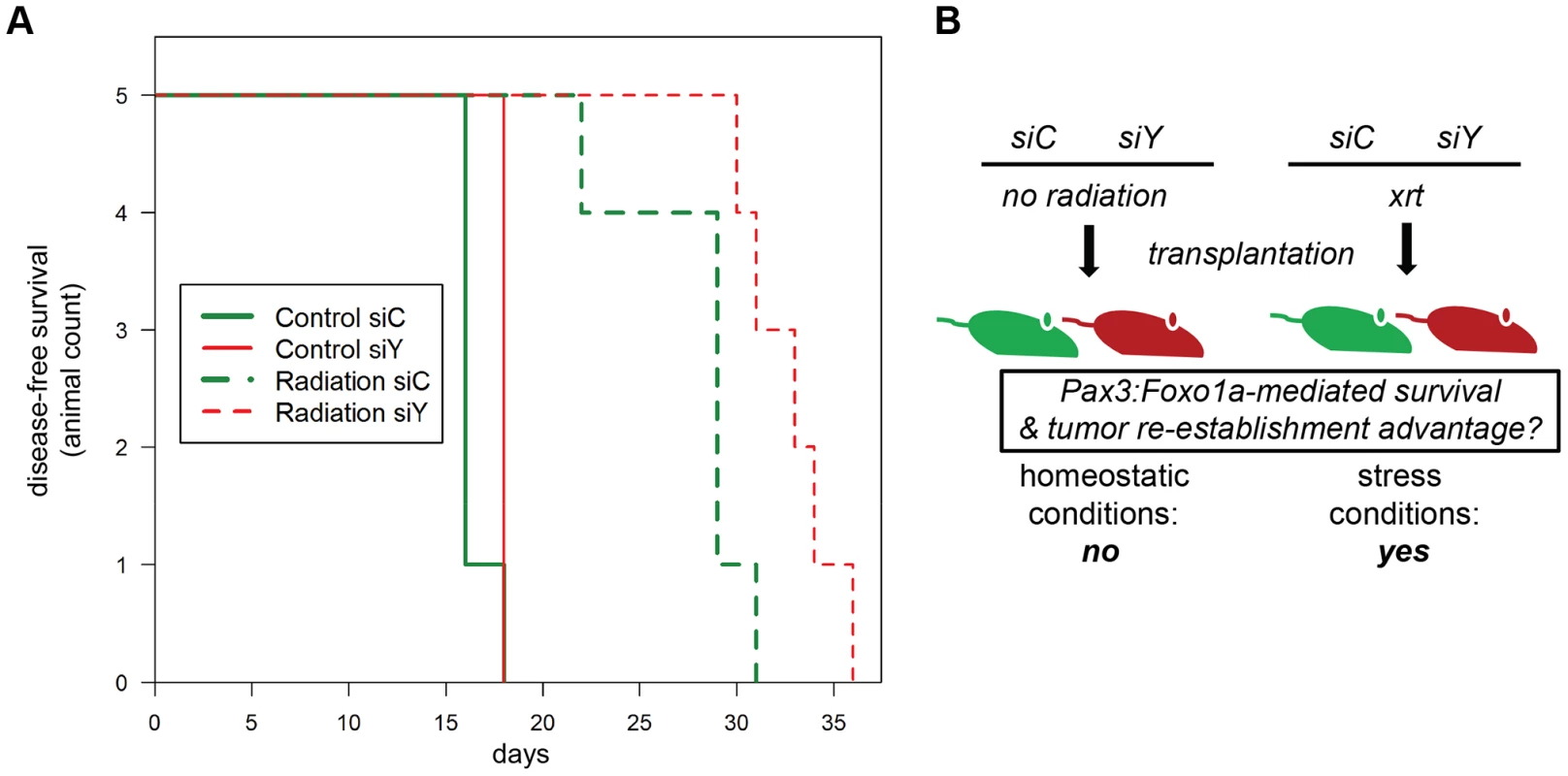
(A) Kaplan-Meier survival analysis for disease-free survival of mice implanted with pre-irradiated (10Gy) primary murine aRMS tumor cells treated with Pax3:Foxo1a siRNA (siY) or control siRNA (siC), n = 5 animals per cohort. The p value for the difference between siY and siC groups receiving radiation was 0.02. (B) Diagrammatic representation of results in (A). To assess the extent to which the fusion gene mediates refractoriness to chemotherapy agents, we observed Pax3:Foxo1a to facilitate 2–4 fold refractoriness to clinical agents capable of causing double-stranded DNA breaks and mitotic arrest (vincristine, actinomycin-D, topotecan) more so than agent inducing single-strand breaks (mafosfamide, the active metabolite of cyclophosphamide) (Figure S3A–E). That a similar role of Pax3:Foxo1a may apply to targeted agents was previously suggested by enriched G2 expression of Pdgfra (Figure 2F) and then demonstrated by increased sensitivity to prototypic Pdgfr inhibitor, imatinib, after Pax3:Foxo1a knockdown (Figure S3F). Similarly, Pax3:Foxo1a knockdown sensitized tumor cells to siRNA inhibition of downstream signaling mediators of acquired imatinib resistance (Figure S3G) [17]. Thus, these in vitro and in vivo results are consistent with a function of Pax3:Foxo1a in mediating checkpoint adaptation and refractoriness to the established clinical therapies of radiation and chemotherapy, or more contemporary molecularly-targeted agents.
Discussion
A key finding of this study is that Pax3:Foxo1a expression is dynamic and varies during the cell cycle. To our knowledge this is first report of a translocation-mediated chimeric transcription factor oncogene that is expressed in a cell cycle-specific manner – much less, one that is expressed specifically during G2. The master transcription factor MYOD is expressed strongly during G1 [18] but is inactivated by phosphorylation during mitosis, which results in deportation from the nucleus [19]. MYF5 is also expressed in a cell cycle-dependent manner, but neither MYOD nor MYF5 expression is increased during G2/M as observed in our study of Pax3:Foxo1a in aRMS. Our findings reveal that Pax3 expression in wildtype C2C12 myoblasts is dynamic and increased during G2/M, but that to account for the dramatic increase in Pax3:Foxo1a expression an additional enhancer effect of Foxo1a 3′ region DNA is likely to be present. This result opens the possibility that co-factors assembled at the Pax3 promoter or fusion gene specific cis-elements might be targeted to suppress Pax3:Foxo1a expression.
Cell cycle progression after DNA damage is regulated by checkpoint controls, which prevent continued transit through the cycle until the damage has been repaired, hence protecting the integrity of the genome. Arrest in G1 permits repair prior to replication, whereas arrest in G2 allows repair prior to mitotic chromosome segregation. The p53 tumor suppressor, which is mutated in roughly half of human aRMS, has been shown to be integral to both G1 and G2 damage checkpoint machinery, but some reports found p53 dispensable for the G2 checkpoint [13], [20].
Checkpoint adaptation is defined as the ability to divide and survive following a sustained checkpoint arrest despite the presence of unrepairable DNA breaks [14]. Cells undergoing checkpoint adaptation will frequently die in subsequent cell cycles if DNA damage goes unrepaired, yet, some cells may be able to survive and proliferate in an aneuploid state [14]. Furthermore, in unicellular eukaryotes and tumor cells, DNA repair can occur at G1 [21]. Here, we reveal that the G2/M adaptation genes (H2afx, Cdc25b and Plk1) were suppressed by Pax3:Foxo1a knockdown in G2 and M cell cycle phases and that fewer cells transited from G2 to M without initiating apoptosis under conditions of Pax3:Foxo1a knockdown in the context of radiation-induced stress. These results suggested that not only cell cycle dependent expression but also a clinically-relevant biology underlying Pax3:Foxo1a expression at the G2-M checkpoint, a critical cell cycle checkpoint following radiation or DNA double strand break inducing-chemotherapy.
That a myogenic cancer might utilize genomic instability, aneuploidy or multinucleation as a mechanism of cell survival or tumor cell evolution/progression may not be so unexpected, in retrospect. Normal myofibers are typically multi-nuclear by definition, and genetic conditions predisposing to mitotic disjunction such as Mosaic Variegated Aneuploidy (MVA) are strongly associated with the development of RMS [22]. Both aRMS and eRMS have also been documented to be hyperdiploid, tetraploid, polyploid or to even have mixed aneuploid populations [23], [24], [25]. At a cellular level, the heterogeneity of cells in rhabdomyosarcoma is notable for the subpopulation of multi-nucleated rhabdomyoblasts which appears with giant nuclei or as multi-nucleated giant cells, often with cross-striations – yet highly mitotic [26]. These rhabdomyoblasts might be compared to the multinucleated stemloid cells in fibrosarcoma, which have a tumor-repopulating ability [27]. Our recent study of aRMS and the PKC iota inhibitor, aurothiomalate, reveals that aRMS cells have a remarkable tolerance to polyploidy, which induces neither apoptosis or senescence [28]. This intrinsic capacity to tolerate aneuploidy as well as this report's observed Pax3:Foxo1a-mediated increase in checkpoint adaptation gene expression may be directly relevant to clinical care, given that decreased expression of these same factors (i.e., PLK1, CCCNB1, BIRC5, AURKB) have been reported to improve sensitivity to mitotic inhibitors [29]. Therefore, the interest generated from chemical screens identifying PLK1 as a potential therapeutic target in RMS [30] is likely warranted.
When considering the differences in treatment-related outcomes in RMS subtypes, the role of Pax3:Fox01a in checkpoint adaptation may be our most important clue yet as to how to improve outcome for fusion positive patients: while aRMS are certainly sensitive to standard chemotherapy and radiation, it is the survival of resistant clones which is the cause of disease progression and relapse – which occur to a greater extent in Pax:Foxo1a positive aRMS than fusion negative aRMS or eRMS [31], [32], and which we believe to be a result of Pax3:Foxo1a-mediated checkpoint adaptation. These effects on tumor cell sensitivity to radiation, chemotherapy and targeted therapeutics are likely to be cumulative and possibly critically important in defining the otherwise very narrow therapeutic window for fusion positive aRMS, for which the toxicity of chemotherapy and radiation is now dose-limiting [33].
Perhaps the most interesting aspect of this genetically-engineered conditional mouse model of a deadly but rare childhood cancer is that a labor-intensive knock-in approach to modeling the molecular pathophysiology of a fusion gene was beneficial. Successful transgenic tumor models have been generated by constitutive, ectopic expression of translocation-related fusion oncogenes for synovial sarcoma [34] as well as other “driver” oncogene related tumors [35]; similarly, retroviral transfection of oncogenes into hematopoietic cells has enabled this study of translocation-associated leukemia for many years [36], [37]. However, are these systems driven by non-native or partial-native promoters to be the definitive preclinical platforms for interrogating molecular physiology – or are distal native cis - and trans-regulation temporally critical? Every experimental system has its advantages and limitations, yet for cell and animal models where translocation-mediated fusion genes have yet to be modeled at the native promoter, we may have an entirely new spectrum of cancer genetics to explore.
Materials and Methods
Ethics statement
All animal procedures were conducted in accordance with the Guidelines for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals and were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC) at the University of Oregon Health & Science University (OHSU) or the Joslin Diabetes Center (Boston, MA). Every effort was made to minimize suffering.
Mice
The Myf6Cre,Pax3:Foxo1a,p53 conditional aRMS mouse model has been described previously [5], [6], [7], is described as caMOD Model 150064393, and is publically available through the NCI MMHCC Repository (MMHCC Strain Codes 01XBL B6; 129-Myf6<tm2(Cre)Mrc> and 01XBM B6; 129-Pax3<tm1Mrc>). SHO-PrkdcscidHrhr mice were purchased from Charles River Laboratories (Wilmington, MA) and bred/maintained at OHSU.
Primary tumor cell cultures and cell lines
Mouse primary cell cultures (U23674, U42369, U57844) were established from tumor samples. Tumors were minced into small pieces and digested with collagenase (10 mg/ml) overnight at 37°C. The dissociated cells were then incubated in Dulbecco's modified eagle's media supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS) and 1% penicillin-streptomycin in 5% CO2 at 37°C. C2C12 mouse myoblast cells were purchased from ATCC (Manassas, VA). Human aRMS cell lines were a gift from Peter Houghton (Rh3; Nationwide Children's Hospital, Columbus, OH) or Patrick Reynolds (Rh41; COG Cell Culture and Xenograft Repository). These cells lines were maintained in the same culture conditions as primary tumor cell cultures: DMEM supplemented with 10% Fetal Bovine Serum (FBS) and 1% Penicillin-Streptomycin. All primary cell cultures experiments using cells were carried out at passage 3–7.
Confocal imaging
For immunofluorescence staining of frozen sections, the polyclonal antibody for green fluorescent protein (1∶1000, AB16901, Chemicon) was used with DAPI counterstain.
RNA interference studies
siRNA transfections were carried out using Lipofectamine2000 (Invitrogen, Grand Island, NY) according to manufacturer's recommended protocol. siRNA's were diluted between 0.1 and 10 nM, and the final concentration of Lipofectamine2000 was 0.2%. siYFP Stealth RNAi siRNA Reporter Controls (cat. 12935-145; Invitrogen) were used as the eYFP siRNA to knockdown the Pax3:Foxo1a-ires-eYFP bi-cistronic mRNA, whereas Stealth RNAi siRNA Negative Control Med GC #3 (cat. 12935-113; Invitrogen) was used as the siRNA control (siCont).
Generation of shRNA tumor cell culture clones
To establish shRNA knockdown clones of primary tumor cell cultures, we used MISSION pLKO.1-puro eGFP shRNA Control Transduction Particles (cat. SHC005V; Sigma Aldrich) for Pax3:Foxo1a knockdown and MISSION pLKO.1-puro Non-Mammalian shRNA Control Transduction Particles (cat. SHC002V; Sigma Aldrich) as the control, respectively. shRNA transfections and clonal selection were carried out according to manufacturer's recommended procedures. Mouse RMS primary cell cultures were plated at 1.8×106 cells per 150 mm dish. After 24 h, hexadimethrine bromide was added (8 µg/ml, cat. H9268; Sigma Aldrich), followed by each particle solution (MOI 0.5). After another 24 h, media were removed and fresh media were added. The following day, puromycin was added (5 µg/ml, cat. P8833; Sigma Aldrich). Puromycin-resistant clones were selected cloning rings at day 14 (shControl) and day 17 (shYFP), with continuous puromycin selection at all times.
Radiation
Cells were irradiated on a Trilogy linear accelerator (Varian, Palo Alto, CA) with a 10×10 cm AP field. Two centimeter of bolus material was placed on top of the 2 chamber slide or 6 cm dish and the target surface distance to the bolus was at 97 cm. Monitor units on the linear accelerator were then set to deliver 6 Gy or 10 Gy of dose to the cells.
Immunoblotting
Tumors were lysed in radioimmunoprecipitation assay (RIPA) buffer or NP40 buffer containing both protease and phosphatase inhibitor (Sigma). The lysates were homogenized and centrifuged at 8000 g for 10 minutes. The resulting supernatants were used for immunoblot analysis. Goat anti-FOXO1A antibody (cat. Sc-9808; Santa Cruz, Santa Cruz, CA), goat anti-GFP antibody (cat. 600-101-215, Rockland; Gilbertsville, PA) or rabbit anti-PDGFRa antibody (cat. #3164; Cell signaling Technology, Danvers, MA).
Immunocytochemistry
Cells were plated on 8-well CultureSlides (cat. 354118; BD Falcon, Franklin Lakes, NJ), fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde, permeabilized with 0.1% or 0.25% TritonX100, washed and incubated with mouse monoclonal anti-skeletal myosin (FAST) (cat. M4276; Sigma), rabbit anti-Ki67 (cat. RM-9106-F; Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA), mouse anti-Pax3 (cat. MAB2457; R&D Systems), mouse anti-phospho Histone H3 (cat. #9706; Cell Signaling Technology), rabbit anti-phospho Histone H3 (cat. #3377; Cell Signaling Technology), mouse anti-phospho Histone H3 (cat. #9706; Cell Signaling Technology), rabbit anti-CDC2-Y15 (cat. #4539; Cell Signaling Technology) or rabbit anti-phospho H2AX antibody (cat. #9718; Cell Signaling Technology), overnight, rinsed with PBS, incubated with fluorescein isothiocyanate-conjugated anti-mouse and rabbit IgG (1∶200) for 1 h, and examined by confocal microscopy with a Zeiss LSM700 instrument. For immunocytochemistry experiments, at least 100 positive cells were scored per specimen.
FACS sorting
Cells were suspended in Hank's balanced salt solution (HBSS) with 2% FBS and 2 mM EDTA. Antibody staining was performed for 20 minutes on ice. Prior to FACS sorting, cells were suspended in 1 µg/ml propidium iodide (Pi) and 10 µM calcein blue (Invitrogen) to identify viable cells (Pi−Ca+). Purity checks were performed to confirm that the sorted eYFP+ and eYFP - cell subsets had a purity of >98% using a eYFP expression threshold determined by the background fluorescence of eYFP - C2C12 cells. The following antibodies were used to evaluate receptor tyrosine kinase surface expression: APC-conjugated Pdgfrα antibody (#17-1401-81, eBiosciences) or anti-IGF1 Receptor antibody (cat. Ab32823; Abcam, Cambridge, MA; 1 in 25).
Cell cycle analysis
Mouse RMS primary cell cultures were trypsinized and incubated with Hoechst33342 (final concentration 15 µg/ml) and Reserpine (final concentration 5 µM). Cells were incubated in the dark for 30 min at 37°C, and analyzed and sorted by flow cytometry using an Influx FACS instrument (Becton Dickinson, Franklin Lakes, NJ). Cell cycle was determined with the FlowJo software (Tree Star, Inc., Ashland, OR).
Annexin V apoptosis detection assay
Mouse primary cell cultures were stained with Annexin V and Propidium iodide using Annexin-V-FLUOS Staining Kit (cat. 11 858 777 001; Roche) following the protocol provided by the manufacturer. Briefly, 48 hour after irradiation, 106 mouse primary cell cultures were trypsinized, washed by PBS and resuspended in 100 µl of Annexin-VFLUOS labeling solution, incubated 10–15 min at 15–25°C, and analyzed by FACS Calibur.
Quantitative RT PCR (QPCR)
U23674 cells were subfractionated by FACS sorting as described above. mRNA was isolated using RNeasy spin columns (Qiagen, Valencia, CA) and reverse transcribed using Superscript III First-Strand Synthesis System for RT-PCR (Invitrogen). QPCR was performed using an AV7900 PCR system (Applied Biosystem) with SYBR-green PCR reagents. Pax3:Foxo1a was detected using the following primer sequences: 5′-AGACAGCTTTGTGCCTCCAT-3′ and 5′-CTCTTGCCTCCCTCTGGATT-3′. Other primers are Taqman Gene Expression assay, H2afx (Mm00515990_s1), Cdc25b (Mm00499136_m1), Birc5 (Mm00599749_m1), Plk1 (Mm00440924_g1) and Gapdh (Mm99999915_g1) by Invitrogen. RT-PCR data were quantified using the standard curve method, and relative expression of Pax3:Foxo1a per sample was determined by normalization against the quantity of 18 s rRNA and Gapdh within each sample. For each sample, QPCR was performed in technical duplicates and results were averaged.
In vitro growth inhibition assays
Mouse RMS primary cell cultures were plated at 1×103 cells of each cohort per well in a 96-well plate. After cell incubations, cytotoxic effects were assayed using CellTiter 96 AQueous One Solution Cell Proliferation Assay system (Promega, Madison, WI) and SpectraMax M5 luminometer (Molecular Devices, Sunnyvale, CA). IC50 and C.I. were determined with CalcuSyn software (BIOSOFT, United Kingdom).Drugs: Vincristine sulfate salt (cat. V8879; Sigma), Actinomycin-D (cat. A9415; Sigma), Mafosfamide (cat. sc-211761; Santa Cruz), Topotecan hydrochloride (cat. S1231; Selleck), Eribulin mesylate (NDC 62856-389-01; Eisai) or Imatinib Mesylate (cat. S1026; Selleck).
RNAi-assisted protein target identification (RAPID) screen
For these studies, individual siRNA were obtained from Dharmacon (Lafayette, CO), including the mouse siRNA library targeting the tyrosine kinome (siGENOME). These experiments are performed at 100 nM concentration and include non-specific pooled siRNA as a control purchased from Dharmacon. Transfection of siRNA was carried out using Lipofectamine 2000 in Opti-MEM Reduced Serum Media (Invitrogen). After cells were plated in 96-well plates in the presence of inhibitor or siRNA, and incubated for 96 hours, respectively, 20 µL CellTiter 96 AQueous One solution (MTS) was added to each well and absorbance values assessed by the BioTek Synergy 2 plate reader (BioTek, Winooski, VT).
Genome-wide expression analysis
Labeled target cRNA was prepared from 12 mouse total RNA samples (3 independent experiments×4 samples). Samples were amplified and labeled using the Ambion MessageAmp Premier RNA Amplification Kit following the manufacturer's protocol. Sample order was randomized. Each sample target was hybridized to an Illumina MouseRef 8 v 2 Expression BeadChip Array. Image processing and expression analysis were performed using Illumina BeadArray Reader and GenomeStudio (v. 2010.1) Gene Expression module (v. 1.6.0) software. Microarray data have been accessioned with the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) under series GSE41675. The following link has been created to allow review of record GSE41675 while it remains in in review/under private status: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/query/acc.cgi?token=xdajbqeisomcyhq&acc=GSE41675.
In vivo studies with Pax3:Foxo1a knockdown and radiation
aRMS primary cultures (passage 5) were plated in 6 cm dishes. The next day cells were transfected with siYFP Stealth RNAi siRNA Reporter Controls or Stealth RNAi siRNA Negative Control Med GC #3. Two days later cells were irradiated on a Trilogy linear accelerator with a 10×10 cm AP field with two centimeter of bolus material was placed on top of the 6 cm dish. The target surface distance to the bolus was at 97 cm and monitor units on the linear accelerator were then set to deliver 10 Gy of dose to the cells. Subsequently, cells were trypsinized and 500,000 cells were injected into the gastrocnemius muscle of SHO mice that had been pre-injured 24 hours prior with 0.85 µg/mouse cardiotoxin intramuscularly. Tumor volumes (cm3) were measured 3-dimensionally with electronic calipers and calculated from formula (π/6)×length×width×height, assuming tumors to be spheroid. For statistical analysis of disease-free survival, a tumor volume threshold of 0.25 cc was applied. The log-rank test was used to contrast treatments. All analyses were performed using R 3.0.0 (The R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria).
Supporting Information
Zdroje
1. BrenemanJC, LydenE, PappoAS, LinkMP, AndersonJR, et al. (2003) Prognostic factors and clinical outcomes in children and adolescents with metastatic rhabdomyosarcoma–a report from the Intergroup Rhabdomyosarcoma Study IV. J Clin Oncol 21 : 78–84.
2. AndersonJR, BarrFG, HawkinsDS, ParhamDM, SkapekSX, et al. (2010) Fusion-negative alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma: modification of risk stratification is premature. J Clin Oncol 28: e587–588; author reply e589–590.
3. WilliamsonD, MissiagliaE, de ReyniesA, PierronG, ThuilleB, et al. (2010) Fusion gene-negative alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma is clinically and molecularly indistinguishable from embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma. J Clin Oncol 28 : 2151–2158.
4. WexlerLH, LadanyiM (2010) Diagnosing alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma: morphology must be coupled with fusion confirmation. J Clin Oncol 28 : 2126–2128.
5. KellerC, ArenkielBR, CoffinCM, El-BardeesyN, DePinhoRA, et al. (2004) Alveolar rhabdomyosarcomas in conditional Pax3:Fkhr mice: cooperativity of Ink4a/ARF and Trp53 loss of function. Genes Dev 18 : 2614–2626.
6. KellerC, HansenMS, CoffinCM, CapecchiMR (2004) Pax3:Fkhr interferes with embryonic Pax3 and Pax7 function: implications for alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma cell of origin. Genes Dev 18 : 2608–2613.
7. NishijoK, ChenQR, ZhangL, McCleishAT, RodriguezA, et al. (2009) Credentialing a preclinical mouse model of alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma. Cancer Res 69 : 2902–2911.
8. TaniguchiE, NishijoK, McCleishAT, MichalekJE, GraysonMH, et al. (2008) PDGFR-A is a therapeutic target in alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma. Oncogene 27 : 6550–6560.
9. CaoL, YuY, BilkeS, WalkerRL, MayeenuddinLH, et al. (2010) Genome-Wide Identification of PAX3-FKHR Binding Sites in Rhabdomyosarcoma Reveals Candidate Target Genes Important for Development and Cancer. Cancer Res 70 : 6497–508.
10. OsukaS, SampetreanO, ShimizuT, SagaI, OnishiN, et al. (2013) IGF1 receptor signaling regulates adaptive radioprotection in glioma stem cells. Stem cells 31 : 627–640.
11. NurseP (1994) Ordering S phase and M phase in the cell cycle. Cell 79 : 547–550.
12. BerryLD, GouldKL (1996) Regulation of Cdc2 activity by phosphorylation at T14/Y15. Progress in cell cycle research 2 : 99–105.
13. SyljuasenRG, JensenS, BartekJ, LukasJ (2006) Adaptation to the ionizing radiation-induced G2 checkpoint occurs in human cells and depends on checkpoint kinase 1 and Polo-like kinase 1 kinases. Cancer Res 66 : 10253–10257.
14. SyljuasenRG (2007) Checkpoint adaptation in human cells. Oncogene 26 : 5833–5839.
15. YooHY, KumagaiA, ShevchenkoA, ShevchenkoA, DunphyWG (2004) Adaptation of a DNA replication checkpoint response depends upon inactivation of Claspin by the Polo-like kinase. Cell 117 : 575–588.
16. CaoL, YuY, BilkeS, WalkerRL, MayeenuddinLH, et al. (2010) Genome-wide identification of PAX3-FKHR binding sites in rhabdomyosarcoma reveals candidate target genes important for development and cancer. Cancer Res 70 : 6497–6508.
17. AbrahamJ, ChuaYX, GloverJM, TynerJW, LoriauxMM, et al. (2012) An adaptive Src-PDGFRA-Raf axis in rhabdomyosarcoma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 426 : 363–368.
18. KitzmannM, CarnacG, VandrommeM, PrimigM, LambNJ, et al. (1998) The muscle regulatory factors MyoD and myf-5 undergo distinct cell cycle-specific expression in muscle cells. J Cell Biol 142 : 1447–1459.
19. Batonnet-PichonS, TintignacLJ, CastroA, SirriV, LeibovitchMP, et al. (2006) MyoD undergoes a distinct G2/M-specific regulation in muscle cells. Exp Cell Res 312 : 3999–4010.
20. KoniarasK, CuddihyAR, ChristopoulosH, HoggA, O'ConnellMJ (2001) Inhibition of Chk1-dependent G2 DNA damage checkpoint radiosensitizes p53 mutant human cells. Oncogene 20 : 7453–7463.
21. ClemensonC, Marsolier-KergoatMC (2009) DNA damage checkpoint inactivation: adaptation and recovery. DNA Repair (Amst) 8 : 1101–1109.
22. HanksS, ColemanK, ReidS, PlajaA, FirthH, et al. (2004) Constitutional aneuploidy and cancer predisposition caused by biallelic mutations in BUB1B. Nat Genet 36 : 1159–1161.
23. Kowal-VernA, Gonzalez-CrussiF, TurnerJ, TrujilloYP, ChouP, et al. (1990) Flow and image cytometric DNA analysis in rhabdomyosarcoma. Cancer Res 50 : 6023–6027.
24. San Miguel-FraileP, Carrillo-GijonR, Rodriguez-PeraltoJL, BadiolaIA (2004) Prognostic significance of DNA ploidy and proliferative index (MIB-1 index) in childhood rhabdomyosarcoma. Am J Clin Pathol 121 : 358–365.
25. ShapiroDN, ParhamDM, DouglassEC, AshmunR, WebberBL, et al. (1991) Relationship of tumor-cell ploidy to histologic subtype and treatment outcome in children and adolescents with unresectable rhabdomyosarcoma. J Clin Oncol 9 : 159–166.
26. LiG, KikuchiK, RadkaM, AbrahamJ, RubinBP, et al. (2013) IL-4 receptor blockade abrogates satellite cell - rhabdomyosarcoma fusion and prevents tumor establishment. Stem cells 31 : 2304–12.
27. WeihuaZ, LinQ, RamothAJ, FanD, FidlerIJ (2011) Formation of solid tumors by a single multinucleated cancer cell. Cancer 117 : 4092–4099.
28. KikuchiK, SoundararajanA, ZarzabalLA, WeemsCR, NelonLD, et al. (2012) Protein kinase C iota as a therapeutic target in alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma. Oncogene 32 : 286–95.
29. YamadaHY, RaoCV (2010) Genes that modulate the sensitivity for anti-microtubule drug-mediated chemotherapy. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 10 : 623–633.
30. HuK, LeeC, QiuD, FotovatiA, DaviesA, et al. (2009) Small interfering RNA library screen of human kinases and phosphatases identifies polo-like kinase 1 as a promising new target for the treatment of pediatric rhabdomyosarcomas. Mol Cancer Ther 8 : 3024–3035.
31. SkapekSX, AndersonJ, BarrFG, BridgeJA, Gastier-FosterJM, et al. (2013) PAX-FOXO1 Fusion Status Drives Unfavorable Outcome for Children With Rhabdomyosarcoma: A Children's Oncology Group Report. Pediatr Blood Cancer 60 : 1411–7.
32. MissiagliaE, WilliamsonD, ChisholmJ, WirapatiP, PierronG, et al. (2012) PAX3/FOXO1 fusion gene status is the key prognostic molecular marker in rhabdomyosarcoma and significantly improves current risk stratification. J Clin Oncol 30 : 1670–1677.
33. GuptaAA, AndersonJR, PappoAS, SpuntSL, DasguptaR, et al. (2012) Patterns of chemotherapy-induced toxicities in younger children and adolescents with rhabdomyosarcoma: a report from the Children's Oncology Group Soft Tissue Sarcoma Committee. Cancer 118 : 1130–1137.
34. HaldarM, HancockJD, CoffinCM, LessnickSL, CapecchiMR (2007) A conditional mouse model of synovial sarcoma: insights into a myogenic origin. Cancer Cell 11 : 375–388.
35. ZhuH, AcquavivaJ, RamachandranP, BoskovitzA, WoolfendenS, et al. (2009) Oncogenic EGFR signaling cooperates with loss of tumor suppressor gene functions in gliomagenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106 : 2712–2716.
36. BerntKM, ZhuN, SinhaAU, VempatiS, FaberJ, et al. (2011) MLL-rearranged leukemia is dependent on aberrant H3K79 methylation by DOT1L. Cancer Cell 20 : 66–78.
37. DiMartinoJF, MillerT, AytonPM, LandeweT, HessJL, et al. (2000) A carboxy-terminal domain of ELL is required and sufficient for immortalization of myeloid progenitors by MLL-ELL. Blood 96 : 3887–3893.
38. TynerJW, WaltersDK, WillisSG, LuttroppM, OostJ, et al. (2008) RNAi screening of the tyrosine kinome identifies therapeutic targets in acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 111 : 2238–2245.
Štítky
Genetika Reprodukční medicína
Článek Unwrapping BacteriaČlánek A Chaperone-Assisted Degradation Pathway Targets Kinetochore Proteins to Ensure Genome StabilityČlánek The Candidate Splicing Factor Sfswap Regulates Growth and Patterning of Inner Ear Sensory OrgansČlánek The SPF27 Homologue Num1 Connects Splicing and Kinesin 1-Dependent Cytoplasmic Trafficking inČlánek Down-Regulation of eIF4GII by miR-520c-3p Represses Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma DevelopmentČlánek Meta-Analysis Identifies Gene-by-Environment Interactions as Demonstrated in a Study of 4,965 MiceČlánek High Risk Population Isolate Reveals Low Frequency Variants Predisposing to Intracranial Aneurysms
Článek vyšel v časopisePLOS Genetics
Nejčtenější tento týden
2014 Číslo 1
-
Všechny články tohoto čísla
- How Much Is That in Dog Years? The Advent of Canine Population Genomics
- The Sense and Sensibility of Strand Exchange in Recombination Homeostasis
- Unwrapping Bacteria
- DNA Methylation Changes Separate Allergic Patients from Healthy Controls and May Reflect Altered CD4 T-Cell Population Structure
- Evidence for Mito-Nuclear and Sex-Linked Reproductive Barriers between the Hybrid Italian Sparrow and Its Parent Species
- Translation Enhancing ACA Motifs and Their Silencing by a Bacterial Small Regulatory RNA
- Relationship Estimation from Whole-Genome Sequence Data
- Genetic Models of Apoptosis-Induced Proliferation Decipher Activation of JNK and Identify a Requirement of EGFR Signaling for Tissue Regenerative Responses in
- ComEA Is Essential for the Transfer of External DNA into the Periplasm in Naturally Transformable Cells
- Loss and Recovery of Genetic Diversity in Adapting Populations of HIV
- Bioelectric Signaling Regulates Size in Zebrafish Fins
- Defining NELF-E RNA Binding in HIV-1 and Promoter-Proximal Pause Regions
- Loss of Histone H3 Methylation at Lysine 4 Triggers Apoptosis in
- Cell-Cycle Dependent Expression of a Translocation-Mediated Fusion Oncogene Mediates Checkpoint Adaptation in Rhabdomyosarcoma
- How a Retrotransposon Exploits the Plant's Heat Stress Response for Its Activation
- A Nonsense Mutation in Encoding a Nondescript Transmembrane Protein Causes Idiopathic Male Subfertility in Cattle
- Deletion of a Conserved -Element in the Locus Highlights the Role of Acute Histone Acetylation in Modulating Inducible Gene Transcription
- Developmental Link between Sex and Nutrition; Regulates Sex-Specific Mandible Growth via Juvenile Hormone Signaling in Stag Beetles
- PP2A/B55 and Fcp1 Regulate Greatwall and Ensa Dephosphorylation during Mitotic Exit
- Differential Effects of Collagen Prolyl 3-Hydroxylation on Skeletal Tissues
- Comprehensive Functional Annotation of 77 Prostate Cancer Risk Loci
- Evolution of Chloroplast Transcript Processing in and Its Chromerid Algal Relatives
- A Chaperone-Assisted Degradation Pathway Targets Kinetochore Proteins to Ensure Genome Stability
- New MicroRNAs in —Birth, Death and Cycles of Adaptive Evolution
- A Genome-Wide Screen for Bacterial Envelope Biogenesis Mutants Identifies a Novel Factor Involved in Cell Wall Precursor Metabolism
- FGFR1-Frs2/3 Signalling Maintains Sensory Progenitors during Inner Ear Hair Cell Formation
- Regulation of Synaptic /Neuroligin Abundance by the /Nrf Stress Response Pathway Protects against Oxidative Stress
- Intrasubtype Reassortments Cause Adaptive Amino Acid Replacements in H3N2 Influenza Genes
- Molecular Specificity, Convergence and Constraint Shape Adaptive Evolution in Nutrient-Poor Environments
- WNT7B Promotes Bone Formation in part through mTORC1
- Natural Selection Reduced Diversity on Human Y Chromosomes
- In-Vivo Quantitative Proteomics Reveals a Key Contribution of Post-Transcriptional Mechanisms to the Circadian Regulation of Liver Metabolism
- The Candidate Splicing Factor Sfswap Regulates Growth and Patterning of Inner Ear Sensory Organs
- The Acid Phosphatase-Encoding Gene Contributes to Soybean Tolerance to Low-Phosphorus Stress
- p53 and TAp63 Promote Keratinocyte Proliferation and Differentiation in Breeding Tubercles of the Zebrafish
- Affects Plant Architecture by Regulating Local Auxin Biosynthesis
- The SET Domain Proteins SUVH2 and SUVH9 Are Required for Pol V Occupancy at RNA-Directed DNA Methylation Loci
- Down-Regulation of Rad51 Activity during Meiosis in Yeast Prevents Competition with Dmc1 for Repair of Double-Strand Breaks
- Multi-tissue Analysis of Co-expression Networks by Higher-Order Generalized Singular Value Decomposition Identifies Functionally Coherent Transcriptional Modules
- A Neurotoxic Glycerophosphocholine Impacts PtdIns-4, 5-Bisphosphate and TORC2 Signaling by Altering Ceramide Biosynthesis in Yeast
- Subtle Changes in Motif Positioning Cause Tissue-Specific Effects on Robustness of an Enhancer's Activity
- C/EBPα Is Required for Long-Term Self-Renewal and Lineage Priming of Hematopoietic Stem Cells and for the Maintenance of Epigenetic Configurations in Multipotent Progenitors
- The SPF27 Homologue Num1 Connects Splicing and Kinesin 1-Dependent Cytoplasmic Trafficking in
- Down-Regulation of eIF4GII by miR-520c-3p Represses Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma Development
- Genome Sequencing Highlights the Dynamic Early History of Dogs
- Re-sequencing Expands Our Understanding of the Phenotypic Impact of Variants at GWAS Loci
- Meta-Analysis Identifies Gene-by-Environment Interactions as Demonstrated in a Study of 4,965 Mice
- , a -Antisense Gene of , Encodes a Evolved Protein That Inhibits GSK3β Resulting in the Stabilization of MYCN in Human Neuroblastomas
- A Transcription Factor Is Wound-Induced at the Planarian Midline and Required for Anterior Pole Regeneration
- A Comprehensive tRNA Deletion Library Unravels the Genetic Architecture of the tRNA Pool
- A PNPase Dependent CRISPR System in
- Genomic Confirmation of Hybridisation and Recent Inbreeding in a Vector-Isolated Population
- Zinc Finger Transcription Factors Displaced SREBP Proteins as the Major Sterol Regulators during Saccharomycotina Evolution
- GATA6 Is a Crucial Regulator of Shh in the Limb Bud
- Tissue Specific Roles for the Ribosome Biogenesis Factor Wdr43 in Zebrafish Development
- A Cell Cycle and Nutritional Checkpoint Controlling Bacterial Surface Adhesion
- High Risk Population Isolate Reveals Low Frequency Variants Predisposing to Intracranial Aneurysms
- E3 Ubiquitin Ligase CHIP and NBR1-Mediated Selective Autophagy Protect Additively against Proteotoxicity in Plant Stress Responses
- Evolutionary Rate Covariation Identifies New Members of a Protein Network Required for Female Post-Mating Responses
- 3′ Untranslated Regions Mediate Transcriptional Interference between Convergent Genes Both Locally and Ectopically in
- Single Nucleus Genome Sequencing Reveals High Similarity among Nuclei of an Endomycorrhizal Fungus
- Metabolic QTL Analysis Links Chloroquine Resistance in to Impaired Hemoglobin Catabolism
- Notch Controls Cell Adhesion in the Drosophila Eye
- AL PHD-PRC1 Complexes Promote Seed Germination through H3K4me3-to-H3K27me3 Chromatin State Switch in Repression of Seed Developmental Genes
- Genomes Reveal Evolution of Microalgal Oleaginous Traits
- Large Inverted Duplications in the Human Genome Form via a Fold-Back Mechanism
- Variation in Genome-Wide Levels of Meiotic Recombination Is Established at the Onset of Prophase in Mammalian Males
- Age, Gender, and Cancer but Not Neurodegenerative and Cardiovascular Diseases Strongly Modulate Systemic Effect of the Apolipoprotein E4 Allele on Lifespan
- Lifespan Extension Conferred by Endoplasmic Reticulum Secretory Pathway Deficiency Requires Induction of the Unfolded Protein Response
- Is Non-Homologous End-Joining Really an Inherently Error-Prone Process?
- Vestigialization of an Allosteric Switch: Genetic and Structural Mechanisms for the Evolution of Constitutive Activity in a Steroid Hormone Receptor
- Functional Divergence and Evolutionary Turnover in Mammalian Phosphoproteomes
- A 660-Kb Deletion with Antagonistic Effects on Fertility and Milk Production Segregates at High Frequency in Nordic Red Cattle: Additional Evidence for the Common Occurrence of Balancing Selection in Livestock
- Comparative Evolutionary and Developmental Dynamics of the Cotton () Fiber Transcriptome
- The Transcription Factor BcLTF1 Regulates Virulence and Light Responses in the Necrotrophic Plant Pathogen
- Crossover Patterning by the Beam-Film Model: Analysis and Implications
- Single Cell Genomics: Advances and Future Perspectives
- PLOS Genetics
- Archiv čísel
- Aktuální číslo
- Informace o časopisu
Nejčtenější v tomto čísle- GATA6 Is a Crucial Regulator of Shh in the Limb Bud
- Large Inverted Duplications in the Human Genome Form via a Fold-Back Mechanism
- Differential Effects of Collagen Prolyl 3-Hydroxylation on Skeletal Tissues
- Affects Plant Architecture by Regulating Local Auxin Biosynthesis
Kurzy
Zvyšte si kvalifikaci online z pohodlí domova
Současné možnosti léčby obezity
nový kurzAutoři: MUDr. Martin Hrubý
Všechny kurzyPřihlášení#ADS_BOTTOM_SCRIPTS#Zapomenuté hesloZadejte e-mailovou adresu, se kterou jste vytvářel(a) účet, budou Vám na ni zaslány informace k nastavení nového hesla.
- Vzdělávání



