-
Články
Top novinky
Reklama- Vzdělávání
- Časopisy
Top články
Nové číslo
- Témata
Top novinky
Reklama- Videa
- Podcasty
Nové podcasty
Reklama- Kariéra
Doporučené pozice
Reklama- Praxe
Top novinky
ReklamaSynergistic Interaction of Rnf8 and p53 in the Protection against Genomic Instability and Tumorigenesis
Rnf8 is an E3 ubiquitin ligase that plays a key role in the DNA damage response as well as in the maintenance of telomeres and chromatin remodeling. Rnf8−/− mice exhibit developmental defects and increased susceptibility to tumorigenesis. We observed that levels of p53, a central regulator of the cellular response to DNA damage, increased in Rnf8−/− mice in a tissue - and cell type–specific manner. To investigate the role of the p53-pathway inactivation on the phenotype observed in Rnf8−/− mice, we have generated Rnf8−/−p53−/− mice. Double-knockout mice showed similar growth retardation defects and impaired class switch recombination compared to Rnf8−/− mice. In contrast, loss of p53 fully rescued the increased apoptosis and reduced number of thymocytes and splenocytes in Rnf8−/− mice. Similarly, the senescence phenotype of Rnf8−/− mouse embryonic fibroblasts was rescued in p53 null background. Rnf8−/−p53−/− cells displayed defective cell cycle checkpoints and DNA double-strand break repair. In addition, Rnf8−/−p53−/− mice had increased levels of genomic instability and a remarkably elevated tumor incidence compared to either Rnf8−/− or p53−/− mice. Altogether, the data in this study highlight the importance of p53-pathway activation upon loss of Rnf8, suggesting that Rnf8 and p53 functionally interact to protect against genomic instability and tumorigenesis.
Published in the journal: . PLoS Genet 9(1): e32767. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1003259
Category: Research Article
doi: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1003259Summary
Rnf8 is an E3 ubiquitin ligase that plays a key role in the DNA damage response as well as in the maintenance of telomeres and chromatin remodeling. Rnf8−/− mice exhibit developmental defects and increased susceptibility to tumorigenesis. We observed that levels of p53, a central regulator of the cellular response to DNA damage, increased in Rnf8−/− mice in a tissue - and cell type–specific manner. To investigate the role of the p53-pathway inactivation on the phenotype observed in Rnf8−/− mice, we have generated Rnf8−/−p53−/− mice. Double-knockout mice showed similar growth retardation defects and impaired class switch recombination compared to Rnf8−/− mice. In contrast, loss of p53 fully rescued the increased apoptosis and reduced number of thymocytes and splenocytes in Rnf8−/− mice. Similarly, the senescence phenotype of Rnf8−/− mouse embryonic fibroblasts was rescued in p53 null background. Rnf8−/−p53−/− cells displayed defective cell cycle checkpoints and DNA double-strand break repair. In addition, Rnf8−/−p53−/− mice had increased levels of genomic instability and a remarkably elevated tumor incidence compared to either Rnf8−/− or p53−/− mice. Altogether, the data in this study highlight the importance of p53-pathway activation upon loss of Rnf8, suggesting that Rnf8 and p53 functionally interact to protect against genomic instability and tumorigenesis.
Introduction
DNA double strand breaks (DSBs) are among the most deleterious type of DNA lesions. They can be generated either by extrinsic factors such as ionizing radiation (IR) or during normal physiological processes such as class switch recombination (CSR) and meiosis [1], [2]. DSBs are highly toxic for cells and failure in the signaling or repair of these breaks can also increase the risk for genomic instability and promote development of diseases including cancer [1], [2]. In response to DSBs, eukaryotic cells have evolved a DNA damage response (DDR) process that involves a network of signaling, repair and checkpoint proteins that lead to either the repair of the damaged DNA or elimination of the damaged cells by inducing their death or entry into senescence [1]. Phosphorylation of H2ax on Ser139 (γ-H2ax) elicited by the sensors of DSBs, Atm and DNA-PK, is an essential event in the initiation of the DDR signaling cascade [1], [2]. This phosphorylation of H2ax prompts the recruitment of Mdc1 to the site of DNA damage where it then undergoes phosphorylation by Atm. Phospho-Mdc1 is then recognized by the E3 ubiquitin ligase Rnf8 via its FHA domain [3]. At the DSB sites, Rnf8 cooperates with the E2 ligase Ubc13 to attach K63-linked ubiquitin moieties to chromatin components H2a, H2b and γ-H2ax [4], [5], [6]. This in turn leads to the recruitment of another E3 ligase, Rnf168 which polyubiquitylates H2a-type histones on sites flanking the DSB [7], [8]. Polyubiquitylation of histones leads to the recruitment of DNA damage signaling and repair proteins including 53bp1 and Brca1 [3], [4], [5], [7], [8], [9], [10]. In addition to K63-linked ubiquitylation, in response to DSBs, Rnf8 mediates K48-linked ubiquitylation of JMJD2A leading to its proteasomal degradation and the facilitation of 53bp1 recruitment to DSB sites [11]. Rnf8 also adds K48-linked ubiquitin chains to the non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) protein Ku80, also leading to its proteasomal degradation and facilitating NHEJ mediated DNA damage repair [12]. In addition to its central role in the response to DSBs, Rnf8 was also found to play a role in telomere protection by ubiquitylating and stabilizing the shelterin component Tpp1 at telomere ends [13].
To investigate Rnf8 physiological role, Rnf8-null (Rnf8−/−) mice have recently been generated. These mice harbor various developmental defects as exemplified by their smaller size and male sterility [14], [15], [16]. Cells derived from Rnf8−/− mice were observed to have increased radiosensitivity, class switch recombination (CSR) defects, and elevated genomic instability [14], [16]. Interestingly, Rnf8−/− mice also demonstrated an increased risk for tumor development, suggesting that Rnf8 is a bona fide tumor suppressor [14].
p53, an essential effector of the DNA damage response [17], [18] is also the most frequently inactivated tumor suppressor in human cancer [19], [20]. Through its transcriptional activity, p53 activates the expression of a number of genes important for diverse cellular processes including cell cycle arrest and apoptosis [17], [18]. p53 mutant mice have an increased risk of spontaneous tumor development, with most p53−/− mice succumbing by 6 months of age mainly due to lymphomas and sarcomas [21]. p53 deficiency also accelerates tumorigenesis in mutant mice lacking DNA damage repair proteins. For example, mice deficient for both p53 and either Xrcc4 or Lig4, two NHEJ factors, rapidly succumb to B-cell lymphomas that present chromosomal translocations resulting in c-Myc amplification [22], [23]. Similarly, loss of p53 also exacerbates tumorigenesis in mice lacking proteins important for homologous recombination (HR)-mediated repair such as Brca1 and Brca2 [17], [24], [25], [26], [27]. Furthermore, dual loss of p53 and the DSB signaling protein Rnf168 increases the frequency and shortens the latency of tumors [28].
In this study, we have generated Rnf8−/−p53−/− mice and examined the consequences of Rnf8 and p53 loss on development, DNA damage responses and cancer. We observed that loss of p53 reversed the increased radiosensitivity and premature senescence associated with the loss of Rnf8. Moreover, loss of p53 rescued the homeostasis defect observed in Rnf8−/− thymocytes and splenocytes, yet it failed to rescue the defects in the growth and CSR of Rnf8−/− mice. Concomitant loss of Rnf8 and p53 resulted in defects of both G1/S and G2/M checkpoints. Overall, loss of p53 potentiated genomic instability and dramatically accelerated tumor development in the absence of Rnf8, suggesting that an important functional interaction between p53 and Rnf8 exists, and is relevant for DDR and related mechanisms.
Results
Rnf8−/−p53−/− mice are viable
While Rnf8 plays important roles in DSB signaling and genomic integrity [3], [4], [5], [9], [14], p53 is known for its central role in the DDR as the “guardian of the genome” [29]. To examine functional interactions of Rnf8 and p53, we crossed Rnf8−/− mice (AS0574 strain) with p53−/− mice to ultimately generate Rnf8−/−p53−/− mice. These double mutant mice were born with a normal Mendelian ratio indicating that double-knockout of Rnf8 and p53 does not lead to embryonic lethality.
p53 loss rescues some but not all of the growth defects of Rnf8−/− mice
Rnf8−/− mice have been previously shown to display growth defects as demonstrated by their smaller size compared to Wild-Type (WT) littermates [14]. Accordingly, we examined the consequence of p53 loss on the observed growth defects associated with Rnf8 deficiency. As expected, Rnf8−/− male mice weighed significantly less than their WT counterparts (22.8 g±1.4 vs. 32.1 g±2.5, P<0.0001; Figure S1A). Rnf8−/−p53−/− male mice were significantly smaller than their age matched WT littermates (20.6 g±1.3, P<0.0001), however they were no different in size compared to Rnf8−/− littermates (Figure S1A). A similar trend was observed for female mice where both Rnf8−/− and Rnf8−/−p53−/− weighted significantly less than matched WT female littermates (15.6 g±1.7 for Rnf8−/−, P = 0.0002 and 16 g±0.8 for Rnf8−/−p53−/−, P<0.0001 vs. 25 g±1.7 for WT; Figure S1B). No difference in weight was observed between Rnf8−/− and Rnf8−/−p53−/− females (Figure S1B). These data indicate that p53 loss does not rescue growth defects observed in Rnf8−/− mice.
Rnf8 loss was also reported to result in reduced number of thymocytes, splenocytes and bone marrow cells [14], [16]. In order to investigate whether the impaired homeostasis of Rnf8-null immune cells was p53-dependent, we examined the numbers and subpopulations of splenocytes, thymocytes and bone marrow cells from 6-week-old Rnf8−/−p53−/−mice and their Rnf8−/−, p53−/− and WT littermates. Splenocyte, thymocyte and bone marrow cell numbers was significantly lower in Rnf8−/− mice compared to WT littermates (P = 0.0004, P = 0.001 and P = 0.0007 respectively; Figure 1A–1C). Interestingly, Rnf8−/−p53−/− mice and their WT and p53−/− littermates had similar numbers of splenocytes and thymocytes, indicating that loss of p53 rescues the reduced number of Rnf8−/− cells in these compartments (Figure 1A and 1B). In contrast, the reduced number of bone marrow cells in Rnf8−/− mice was also observed in Rnf8−/−p53−/− mice (Figure 1C). These data indicate that p53 loss rescues the number of thymocytes and splenocytes, but not bone marrow cells, in Rnf8−/− mice.
Fig. 1. p53 loss rescues homeostasis of thymocytes and splenocytes, but not bone marrow populations deficient for Rnf8. 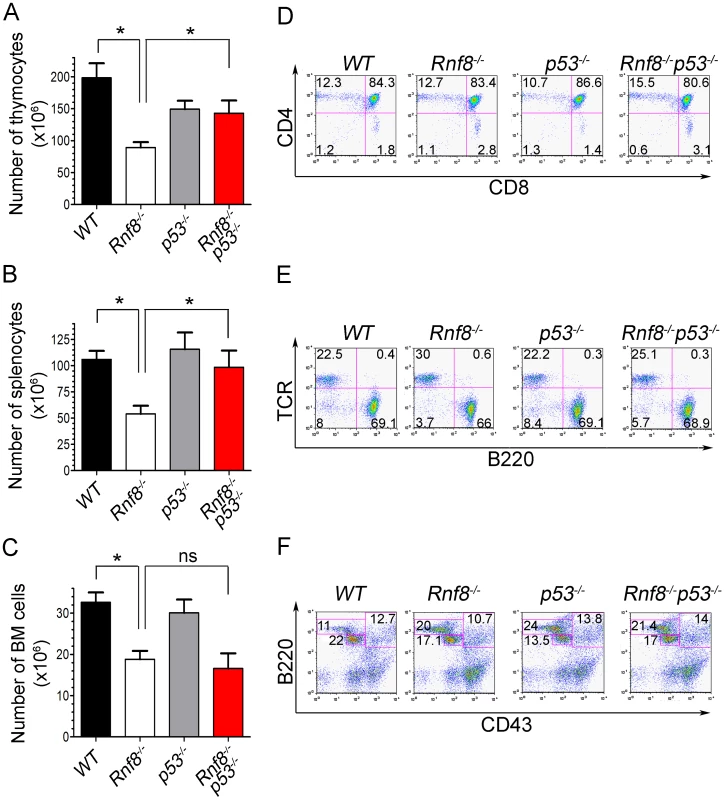
(A) Thymus cell count in Rnf8−/−p53−/− mice. Total number of thymocytes was counted using trypan blue dye exclusion assay from 6-week old Rnf8−/−p53−/− and control mice. Data are presented as the means SD of at least 5 independent experiments. * represents P<0.05. Statistical analysis was performed using a student t-test. (B) Splenocyte cell count in Rnf8−/−p53−/− mice. Total number of cells was counted from freshly isolated spleen from 6-week-old Rnf8−/−p53−/− and control mice. Data are presented as the means SD of at least 5 independent experiments. * represents P<0.05. Statistical analysis was performed using a student t-test. (C) Bone marrow cell count in Rnf8−/−p53−/− mice. Cells isolated from one femur of 6-week old Rnf8−/−p53−/− mice and their controls were counted. Data are presented as the means SD of at least 5 independent experiments. Statistical analysis using student t-test indicated no significant difference between cells counts in Rnf8−/−p53−/− and Rnf8−/− mice. ns: Not significant. (D) Cell population profile in Rnf8−/−p53−/− thymus. Thymocytes from Rnf8−/−p53−/− and control 6 week-old mice were stained with anti-CD4 and anti-CD8 antibodies and the proportion of each thymocyte subpopulation was determined by flow cytometry. No difference was observed between Single positive (CD4+CD8−, CD4−CD8+), double positive (CD4+CD8+) or double negative (CD4−CD8−) subpopulation in Rnf8−/−p53−/− mice as compared to control mice. (E) Proportion of B- and T-cells in spleen from Rnf8−/−p53−/− mice and controls. Freshly isolated splenocytes from 6 week-old Rnf8−/−p53−/− mice and its controls were stained with anti-TCR and anti-B220 antibodies and the proportion of B-cells (B220+TCR−) and T-cells (B220−TCR+) were determined by flow cytometry. (F) Rnf8−/−p53−/− B-cell progenitor profile. Bone marrow cells from 6 week-old Rnf8−/−p53−/− and control mice were stained with anti-B220 and anti-CD43 antibodies and the frequency of each subpopulation was determined by flow cytometry. We next examined thymocytes, splenocytes and bone marrow cells by flow cytometry to characterize defects in immune cell subpopulations in Rnf8−/−p53−/− mice. The proportions of double positive (CD4+CD8+), single positive (CD4+ and CD8+), and T-cell receptor β (TCRβ) positive thymocytes were similar in all four genotypes (Figure 1D and Figure S2A). Representation of B - and T-cell populations in the spleen as well as proportions of recirculating (B220highCD43−IgM+), pre - (CD43−B220+IgM−) and pro-B (CD43+B220+IgM−) cells in the bone marrow were not affected by dual loss of Rnf8 and p53 (Figure 1E and 1F; and Figure S2A and S2B). Collectively these data illustrate that the impaired homeostasis of immune cells deficient for Rnf8 is dependent on p53 in the case of thymocytes and splenocytes but p53-independent in the case of bone marrow cells.
Increased p53 and cleaved caspase-3 expression in Rnf8−/− thymus and spleen
Because loss of p53 rescued the reduced cell numbers in the thymus and spleen we wanted to determine whether p53-dependent apoptosis could be the cause behind the reduced cell numbers in these organs. Immunohistochemistry on tissues derived from WT and Rnf8−/− mice showed a tissue specific increase in p53 expression in Rnf8−/− mice. We observed a significant increase in the number p53-positive thymocytes in Rnf8−/− mice compared to WT littermates (18%±8.1 vs. 0.27%±0.3 respectively, P<0.0001; Figure 2A and 2B). Similarly, there was an increase in the number of p53-positive cells in the spleen of Rnf8−/− mice compared to WT littermates (17%±5.4 vs. 0.64%±0.49 respectively, P<0.0001; Figure S3A and S3B). In addition, immunohistochemistry was also performed on these tissues using cleaved caspase-3 antibody to detect apoptotic cells. We observed a dramatic increase in cleaved caspase-3 staining in the thymus of Rnf8−/− mice compared to WT controls (16.5%±4.6 for Rnf8−/− vs. 1%±0.9 for WT, P<0.0001; Figure 2C and 2D). However, the staining of cleaved caspase-3 was significantly reduced in the thymus of Rnf8−/−p53−/− mice compared to Rnf8−/− littermates (3.1%±1 vs. 16.5%±4.6, P<0.0001; Figure 2C and 2D). Similarly, levels of cleaved caspase-3 were also increased in Rnf8−/− splenocytes as compared to WT and Rnf8−/−p53−/− splenocytes (8.3%±3.5 for Rnf8−/− vs. 0.61%±0.49 for WT, P<0.0001 and 1.3%±0.99 for Rnf8−/−p53−/− P<0.0001; Figure S3C and S3D).
Fig. 2. Increased p53 expression and cleaved caspase-3 levels in Rnf8−/− thymocytes. 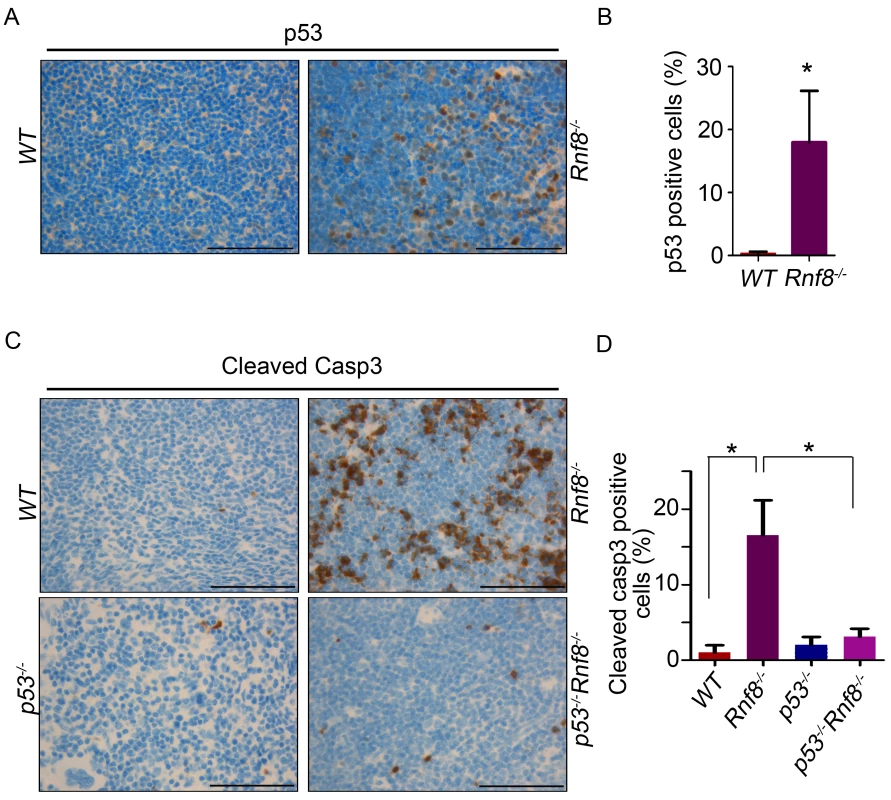
(A) p53 IHC staining of thymus sections of Rnf8−/− mice and WT littermates. (B) Quantification of p53 positive cells in thymus. An average of 20 randomly chosen fields was counted at 63× magnifications. (C) Cleaved caspase-3 levels in the thymus of Rnf8−/−p53−/− mice and control littermates. Anti-cleaved caspase-3 IHC staining of thymus of Rnf8−/−p53−/−, Rnf8−/−, p53−/− and WT mice. (D) Quantification of cleaved caspase-3 positive cells in the thymus. An average of 20 fields counted at 63× magnification. Data is representative of 3 different experiments. * indicates statistical significance (P<0.05). Bar: 50 µm. In order to determine if p53 is also activated in other Rnf8−/− tissues, we stained liver, kidney, lung, heart and intestine of Rnf8−/− mice and WT controls with anti-p53 antibodies. With the exception of the intestinal crypts of Rnf8−/− mice that showed increased frequency of p53 positive basal cells compared to WT controls (P<0.0001), p53 staining remained low and similar to WT mice in other tissues (Figure S4A and S4B).
These results suggest the activation of p53 in Rnf8−/− mice is tissue specific and that lower cellularity in the thymus and spleen of Rnf8−/− mice is caused by increased p53 activation and cell death in these tissues.
Rnf8−/−p53−/− mice display class switch recombination defects
Rnf8−/− mice are immunodeficient and display CSR defects similar to what was observed with H2ax−/− and Rnf168−/− mice, yet less prominent than that observed in 53bp1−/− mice [14], [16], [28], [30], [31], [32]. We examined whether p53 plays a role in the defective CSR associated with Rnf8 deficiency. The ability of B-cells purified from the spleens of Rnf8−/−p53−/− mice and littermate controls to undergo IgG1 CSR was examined in response to anti-CD40 and IL-4. Rnf8−/− B-cells presented a reduced ability to switch to IgG1 in response to anti-CD40 plus IL-4 compared to WT B-cells (7.1%±0.7 vs. 25%±6.1; P = 0.0004); and as reported [33], p53−/− B-cells showed similar level of CSR (22.1%±5.9) compared to WT controls (25%±6.1) (Figure 3A and 3B). Interestingly, the level of IgG1 CSR in Rnf8−/−p53−/− B-cells was significantly reduced compared to WT controls (8.9%±5.5 vs. 25%±6.1; P = 0.0029) and remained similar to that observed in Rnf8−/− B-cells (P>0.05; Figure 3A and 3B). This reduced ability to undergo class switch to IgG1 in the absence of Rnf8 was not caused by a defect in cell proliferation as B-cells of all four genotypes showed similar Carboxyfluorescein Diacetate Succinimidyl Ester (CFSE) profiles 96 hours following anti-CD40+IL4 stimulation (Figure 3C). Therefore, inactivation of p53 does not rescue or exacerbate CSR defects associated with the loss of Rnf8.
Fig. 3. Loss of p53 does not rescue class switch recombination defects observed in Rnf8−/− mice. 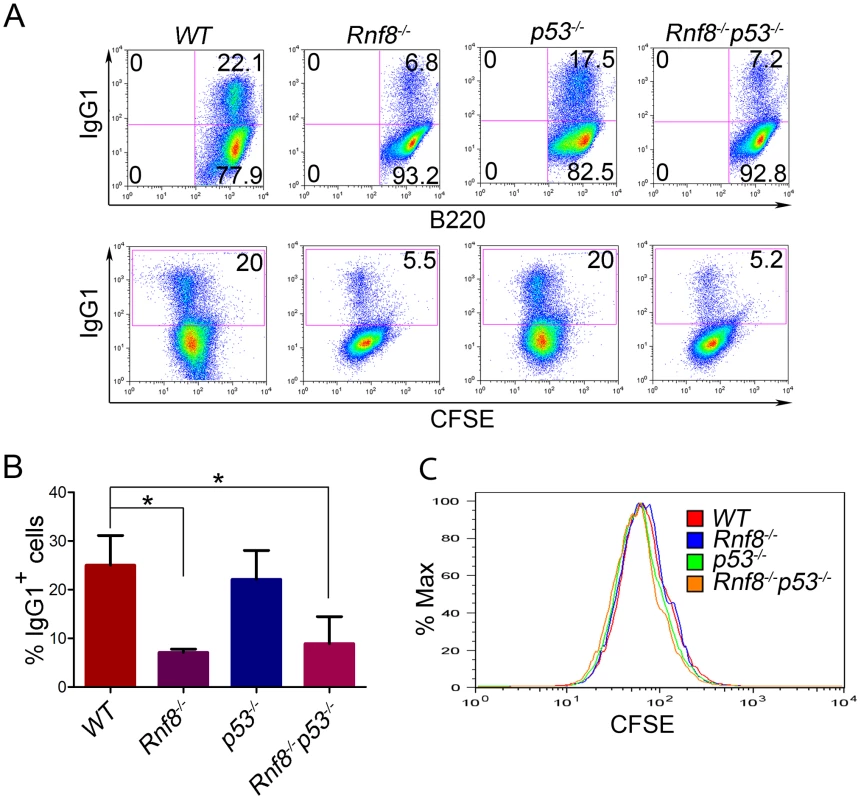
(A) B-cells were purified from the spleen of 6-week old Rnf8−/−p53−/− and control mice and class switch recombination was examined. B-cells were treated with anti-CD40 and IL-4 for 4 days, then the percentage of B-cells that have switched to IgG1 expression was determined by flow cytometry. Data presented are representative of at least 4 different experiments. (B) Quantification of Ig switching to IgG1. Percentage of B-cells that were IgG1+ after 4 days of stimulation in vitro in the presence of anti-CD40 and IL-4. Data are presented as the means SD of at least 4 independent experiments. * represents statistical significance (P<0.05) using a student t-test. (C) Cell division profiles of Rnf8−/−p53−/− B-cells and their controls. Cells were stained with CFSE and allowed to proliferate for 4 days in the presence of CD40 and Il-4. CFSE dilution profiles were examined using flow cytometry. Loss of p53 rescues radiosensitivity of Rnf8−/− mice and the growth defect of Rnf8−/− cells
Our previous findings demonstrated increased radiosensitivity of Rnf8−/− thymocytes and bone marrow cells and sensitivity to whole body irradiation was also increased in Rnf8−/− mice compared to WT littermates [14]. In addition, p53 levels were increased in both untreated and gamma irradiated thymocytes from Rnf8−/− mice as compared to those of WT littermates [14]. In order to define whether the increased radiosensitivity of Rnf8−/− mice was dependent on p53, we examined cell death rates of Rnf8−/−p53−/−, Rnf8−/−, p53−/−, and WT thymocytes and splenocytes following IR-treatment. Freshly collected thymocytes from littermates with the four genotypes were subjected to IR (2 Gy) and cell death was examined 12 hours later using propidium iodide (PI) staining. As expected [14], Rnf8−/− thymocytes were significantly more radiosensitive compared to WT controls (P = 0.03; Figure 4A). However, in contrast to thymocytes from Rnf8−/− mice (P<0.0001) and WT mice (P = 0.034), but similar to p53−/− thymocytes (P>0.05), Rnf8−/−p53−/− thymocytes were highly radioresistant (Figure 4A). These results demonstrate that radiosensitivity of Rnf8−/− thymocytes was indeed p53-dependent.
Fig. 4. Radioresistance and increased proliferation of Rnf8−/− cells in the absence of p53. 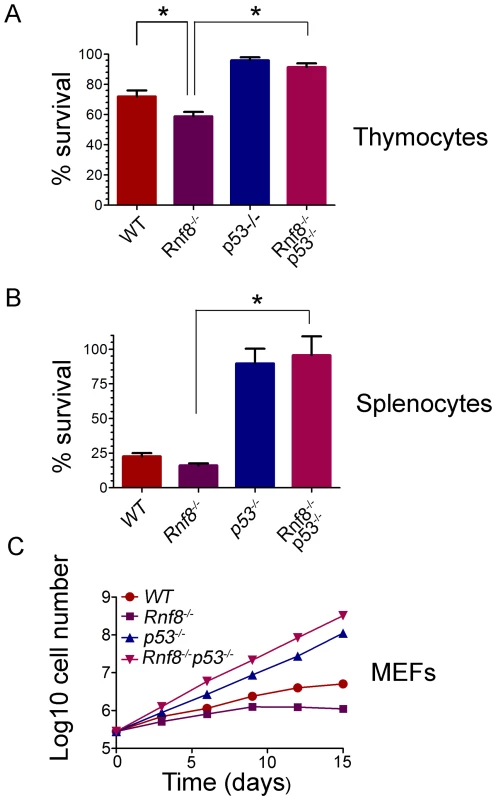
(A) Freshly isolated thymocytes from Rnf8−/−p53−/− mice and control littermates were irradiated with 2 Gy and cell death was determined 12 hours later. Data are presented as the means SD of at least 5 independent experiments. * represents significant difference (P<0.05; student t-test) compared to WT and Rnf8−/− controls. No difference was observed between p53−/− and Rnf8−/−p53−/− thymoctes. (B) Freshly isolated splenocytes were irradiated (2 Gy) and cell death was determined 24 hours later. Data are presented as the means SD of at least 5 independent experiments. * represents statistical significance (P<0.05; student t-test) compared to WT and Rnf8−/− controls. No significant difference was observed between p53−/− and Rnf8−/−p53−/− splenocytes. (C) Cumulative growth curve of Rnf8−/−p53−/− MEFs. Passage 2 Rnf8−/−p53−/− MEFs and controls were plated in 60 mm plates at a density of 3×105 cells/plate. Cells were replated at the same density every 3 days and cumulative cell growth was calculated. Data are presented as the log10 of means ± SD of at least 5 independent experiments. We next examined responses to irradiation of splenocytes from Rnf8−/−p53−/− mice and littermates. Increased radiosensitivity was observed 24 hours post-irradiation (2 Gy) of Rnf8−/− splenocytes compared to splenocytes from WT littermates (P = 0.037, Figure 4B). However, in contrast to Rnf8−/− and WT splenocytes (P<0.0001), and similar to p53−/− splenocytes (P>0.05), Rnf8−/−p53−/− splenocytes were completely radioresistant (Figure 4B). These data suggest that like thymocytes, increased irradiation-induced cell death of Rnf8−/− splenocytes was p53-dependent.
It has been reported that Rnf8−/− mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) exhibited growth defects [14]. Thus, we addressed the effect of p53 on the growth defect of Rnf8−/− MEFs by performing 3T3 passaging of Rnf8−/−p53−/− MEFs and their Rnf8−/−, p53−/− and WT controls. We found that Rnf8−/− MEFs grew slower than WT MEFs, However, loss of p53 completely rescued this growth defect such that Rnf8−/−p53−/− MEFs grew significantly faster than Rnf8−/− MEFs (P = 0.0006 at day 3, P = 0.0015 at day 6, P = 0.0015 at day 9, P = 0.0118 at day 12 and P = 0.0195 at day 15; Figure 4C and Table S1). The growth rate of Rnf8−/−p53−/− MEFs was similar to that of p53−/− mutant controls (Figure 4C and Table S1).
Senescence of Rnf8−/− MEFs is p53-dependent
Because Rnf8−/− MEFs display severe growth defects that are completely abrogated in the absence of p53 we wanted to test whether these cells undergo p53-induced senescence. Primary MEFs can undergo a limited number of replications before they enter a senescence state. Senescence in MEFs is usually associated with increased levels of p53 and its downstream target p21 as well as increased levels of p19ARF [34]. We therefore examined levels of p21, p19ARF and p53 under both untreated conditions and following γ-irradiation in passage 3 MEFs. We found that p21 levels were higher in Rnf8−/− MEFs compared to WT, p53−/− and Rnf8−/−p53−/− MEFs under both basal and irradiated conditions (Figure 5A). In contrast, levels of p19ARF were similar and very low in both WT and Rnf8−/− MEFs (Figure 5A). Consistent with previous studies of p53−/− MEFs [35], levels of p19ARF were elevated in both p53−/− and Rnf8−/−p53−/− MEFs, (Figure 5A). Examination of p53 indicated increased levels of total p53 and its phosphorylated Ser-15 form in Rnf8−/− MEFs compared to WT controls under both untreated and irradiated conditions (Figure 5B). As p21 is a transcriptional target of p53, its increased expression levels in Rnf8−/− MEFs is most likely caused by the increased activation of p53 in these cells (Figure 5A and 5B).
Fig. 5. p53 deficiency rescues the senescence of Rnf8−/− MEFs. 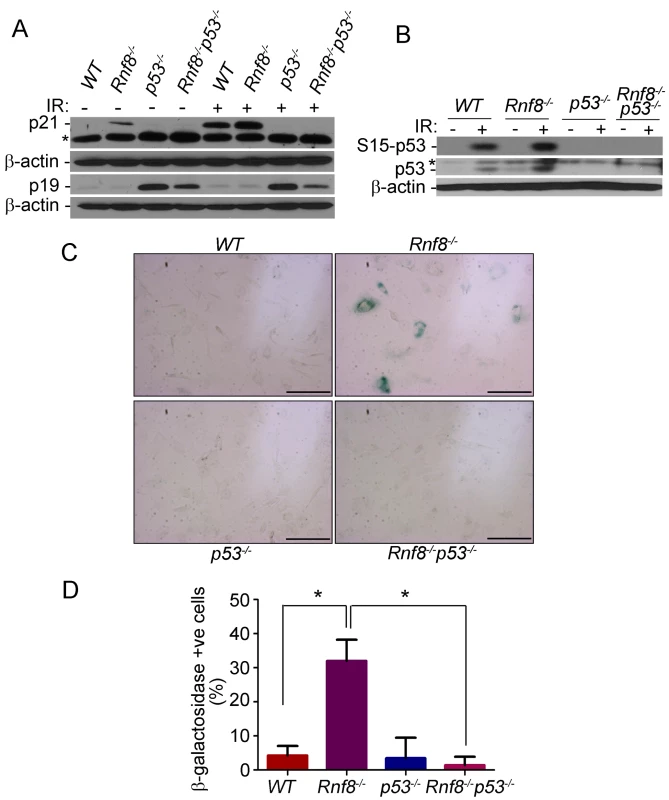
(A) Western blot analysis of Rnf8−/−p53−/− and control MEFs for p21 and p19ARF under untreated conditions and following 8 Gy ionizing radiation. β-actin is used as a loading control. * indicates a non specific band. (B) Western blot analysis of phosphorylated Ser-p53 and total p53 in untreated or γ-irradiated Rnf8−/−p53−/− and control MEFs. β-actin was used as a loading control. * indicates a non specific band. (C) Senescence-associated β-galactosidase staining of Rnf8−/− MEFs and controls. MEFs were fixed and stained with X-gal solutions. The cells were then visualized using a brightfield microscope. These images are representative of three different experiments. (D) Quantification of the percentages of β-galactosidase-positive cells for 3 different experiments. * indicates P<0.05. Bar: 500 µm. Increased levels of senescence associated β-galactosidase have been used as a biomarker for senescence [34]. We therefore used this method to determine whether the reduced growth in Rnf8−/− MEFs was caused by senescence. We found that there was a significantly higher percentage of Rnf8−/− MEFs that stained positive for the senescence associated β-galactosidase compared to WT (P = 0.0022), p53−/− (P = 0.0047) and Rnf8−/−p53−/− (P<0.0001) MEFs respectively (Figure 5C and 5D). These results point to increased senescence of Rnf8−/− MEFs in a manner dependent on p53 and p21 but independent of p19ARF.
Rnf8−/−p53−/− MEFs display both G1/S and G2/M DNA damage checkpoint defects
Cell cycle checkpoints are activated in response to DSBs, thereby preventing cells from progressing to the next phase of the cell cycle before the repair of damaged DNA. The two main cell cycle checkpoints are the G1/S and the G2/M checkpoints [36]. While p53 plays roles in both G1/S and G2/M checkpoints [36], [37], defective G2/M checkpoint activation has been observed in Rnf8 deficient cells [5], [38]. We examined the effect of combined loss of Rnf8 and p53 on cell cycle checkpoints following IR-induced DNA damage. Our data indicated that only 41.3%±3.8% of WT MEFs and 23%±4.5% of Rnf8−/− MEFs were in the S phase following treatment with IR (10 Gy) as compared to untreated MEFs (Figure 6A and 6B). These results suggest that Rnf8 is dispensable for the execution of the G1/S checkpoint. Our data also indicated that in contrast to WT and Rnf8−/− MEFs, 80.7%±10.3% of p53−/− MEFs and 107%±13.2% of Rnf8−/−p53−/− MEFs were in the S phase of the cell cycle 22 hours post exposure to 10 Gy of irradiation (Figure 6A and 6B). The percentage of cells in S phase post-irradiation compared to untreated controls was significantly higher in Rnf8−/−p53−/− MEFs compared to both WT and Rnf8−/− MEFs (P = 0.0085 and P = 0.0037 respectively; Figure 6B).
Fig. 6. Loss of Rnf8 and p53 results in defective cell cycle checkpoints. 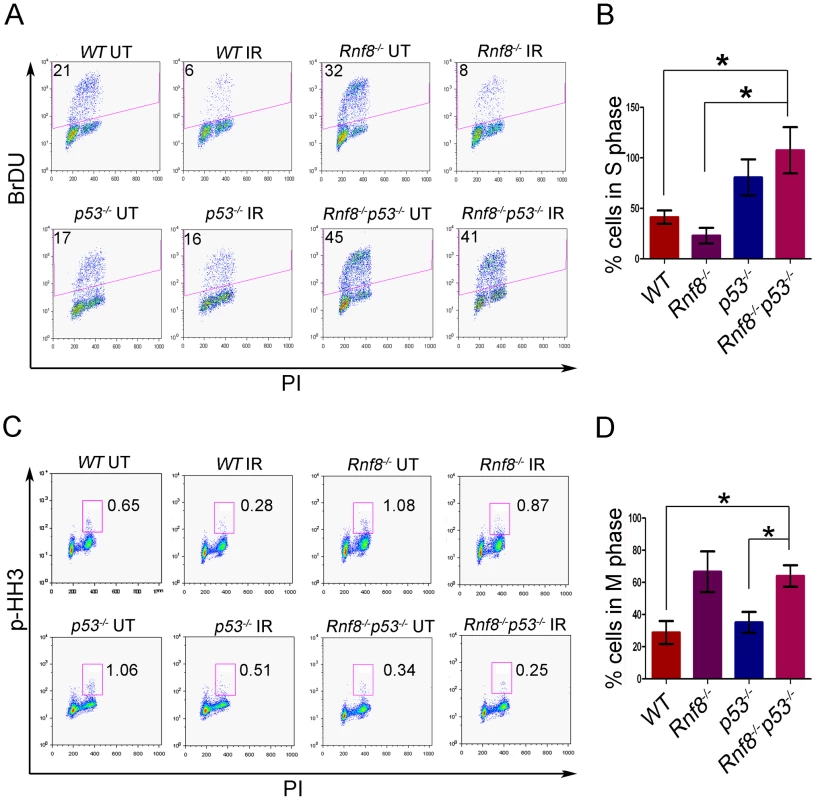
(A) G1-S checkpoint analysis. Rnf8−/−p53−/− early passage primary MEFs and their controls were left untreated or irradiated with 10 Gy and 18 hours later, cells were pulsed with BrDU for 4 hours. The percentage of cells in S-phase was determined by flow cytometry. A representative of 3 independent experiments is shown. (B) Quantification of the percentage of cells remaining in S phase after irradiation relative to untreated controls. Data are presented as the means SD of at least 3 independent experiments. * denotes statistical significance (P<0.05, student t-test). There is no statistical difference between p53−/− and Rnf8−/−p53−/− MEFs. (C) G2-M checkpoint analysis. Rnf8−/−p53−/− early passage primary MEFs and their controls were irradiated with 2 Gy or left untreated, then allowed to recover for 1 hour. Cells in M phase were determined by staining with PI and p-HH3. A representative of 3 independent experiments is shown. (D) Quantification of the percentage of cells in M phase following irradiation relative to untreated. Data are presented as the means SD of at least 3 independent experiments. * denotes statistical significance (P<0.05; student t-test). We next examined the consequence of p53 loss on G2/M checkpoint defects associated with Rnf8 deficiency [5], [38]. Rnf8−/−p53−/− MEFs and their controls were either untreated or irradiated (2 Gy) and their activation of G2/M checkpoint was examined 1 hour later. Combined loss of Rnf8 and p53 resulted in G2/M checkpoint defects similar to Rnf8−/− MEFs (P>0.05; Figure 6C and 6D). The percentage of irradiated cells in mitosis compared to untreated controls was significantly higher in Rnf8−/−p53−/− MEFs (64%±6.7%) compared to WT (28.9%±7.2%; P = 0.0235) and p53−/− MEFs (35.2±6.5; P = 0.0367); but it remained similar to Rnf8−/− MEFs (66.7%±12.6%). Therefore, Rnf8−/−p53−/− MEFs displayed both the G1/S and G2/M checkpoint defects observed in p53−/− and Rnf8−/− single mutant MEFs respectively.
Rnf8−/−p53−/− MEFs display increased spontaneous and residual γ-H2ax and Mdc1 foci but have defective 53bp1 and Brca1 foci formation
Rnf8−/− MEFs were reported to display transient, but not sustained, Irradiation Induced Foci (IRIF) for 53bp1 indicating a defect in DSB signaling [14], [39]. We examined the effect of p53 loss on the ability of Rnf8−/− MEFs to recruit and retain 53bp1 at DSB flanking sites. Similar to Rnf8−/− MEFs, and in contrast to p53−/− and WT MEFs, Rnf8−/−p53−/− MEFs displayed only small transient 53bp1 foci at early time point (0.5 hour) post-IR (8 Gy) and were unable to retain 53bp1 proteins at DSB sites (Figure S5).
Cell cycle checkpoints are crucial for preventing accumulation of damaged DNA in cells [36]. Because Rnf8−/−p53−/− MEFs have defective cell cycle checkpoints and defective DSB signaling as indicated by the impaired recruitment of 53bp1 to DSB sites, we examined whether these double mutant cells might also exhibit increased spontaneous DSBs compared to Rnf8−/−, p53−/− and WT control MEFs. In response to DSBs, γ-H2ax accumulates at the sites of the breaks and forms distinct nuclear foci that can be used to quantify DSBs [1]. Examination of γ-H2ax foci indicated that untreated Rnf8−/−p53−/− MEFs had significantly higher frequency of spontaneous γ-H2ax foci compared to Rnf8−/− (P = 0.0117), p53−/− (P = 0.0185) and WT (P = 0.0048) MEFs (Figure 7A and 7B).
Fig. 7. Increased basal and residual γ-H2ax foci in Rnf8−/−p53−/− MEFs. 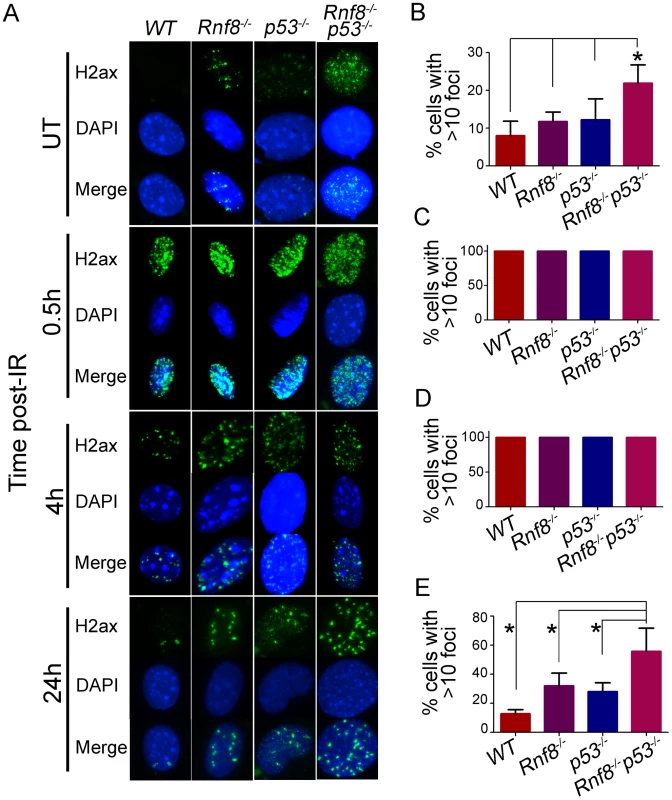
(A) γ-H2ax staining for Rnf8−/−p53−/− MEFs and controls. Rnf8−/−p53−/−, Rnf8−/−, p53−/− and WT early passage primary MEFs were either mock-treated (UT) or irradiated (8 Gy) and allowed to recover for 0.5, 4 and 24 hours. Cells were then fixed, stained using anti-γ-H2ax antibody and counterstained with DAPI. (B) Percentage of untreated cells that contained 10 or more γ-H2ax foci. Data are presented as the means SD of at least 3 independent experiments. At least 100 cells were quantified per experiment. * denotes statistical significance (P<0.05; student t-test). (C, D) Percentage of cells that showed more than 10 γ-H2ax foci at 0.5 and 4 hours post-irradiation respectively. At least 100 cells were quantified for each experiment. (E) Percentage of cells showing 10 or more γ-H2ax foci 24 hours after irradiation. Data are presented as the means SD of at least 3 independent experiments. At least 100 cells were quantified per experiment. * indicates statistical significance (P<0.05; student t-test). No differences were observed between the four genotypes when cells were examined at early time points (0.5 and 4 hours) post-IR (8 Gy) for the presence of 10 or more γ-H2ax foci. In contrast, at the 24 hours time point post-IR, where most DSBs have been repaired in WT cells, the percentage of Rnf8−/−p53−/− MEFs that displayed 10 or more γ-H2ax foci was significantly higher compared to Rnf8−/− (P = 0.0403), p53−/− (P = 0.0175) and WT (P = 0.0018) MEFs (Figure 7A and 7C–7E).
We next examined Mdc1 foci as its phosphorylation is required for binding of Rnf8 to DSBs [5]. Similar to what we have observed with γ-H2ax, Rnf8−/−p53−/− MEFs displayed higher numbers of Mdc1 foci under both untreated conditions and during later time points following γ-irradiation (Figure S6). The increased number of Rnf8−/−p53−/− MEFs with more than 10 Mdc1 foci was statistically significant compared to WT (P = 0.0026), Rnf8−/− (P = 0.042) and p53−/− (P = 0.002) under untreated conditions (Figure S6). 24 hrs following irradiation, we also observed increased number of Rnf8−/−p53−/− MEFs displaying more than 10 residual Mdc1 foci compared to WT (P = 0.0006), Rnf8−/− (P = 0.0031) and p53−/− (P = 0.0008) (Figure S6). The same number of foci was observed in all genotypes 30 minutes following irradiation (Figure S6).
In addition to 53bp1, loss of Rnf8 also impairs the recruitment of Brca1 to the sites of DSBs [5]. Brca1 is involved in cell cycle checkpoint and in the promotion of DSB repair through homologous recombination [40], [41]. We found that there was a significant decrease in the number of MEFs with more that 10 Brca1 foci in Rnf8−/− and Rnf8−/−p53−/− backgrounds compared to WT MEFs at 6 and 24 hrs post-irradiation (P<0.0001) (Figure S7).
Collectively, the increased foci formation of γ-H2ax and Mdc1, that function upstream of Rnf8 in DSB, and the defective recruitment and retention at DSB sites of the downstream cell cycle checkpoint and DNA repair proteins 53bp1 and Brca1 respectively suggest defective DSB signaling and repair in the Rnf8−/−p53−/− MEFs.
Dual loss of Rnf8 and p53 leads to increased levels of genomic instability
Defects in DSB signaling or cell cycle checkpoints have been associated with increased genomic instability [42]. We previously reported increased genomic instability in B-cells lacking Rnf8 [14]. In addition, due to its major functions in DDR, loss of p53 also impairs genomic integrity [29]. To examine the effect of dual loss of Rnf8 and p53 on genomic integrity, we examined metaphase spreads from untreated and irradiated (2 Gy) LPS-activated B-cells from Rnf8−/−p53−/− mice and their Rnf8−/−, p53−/− and WT littermate controls. Under untreated conditions, the frequency of total aberrations in Rnf8−/−p53−/− B-cells was significantly higher compared to WT (P = 0.001), Rnf8−/− (P = 0.021) and p53−/− (P = 0.004) B-cells (Table 1). In response to IR (2 Gy), total aberrations were significantly higher in Rnf8−/−p53−/− B-cells compared to WT (P = 1.5×10−6), Rnf8−/− (P = 0.0025) and p53−/− (P = 8.6×10−6) (Table 1 and Figure 8). These data were consistent with the radioresistance and the defects in DSB signaling and checkpoints activation observed in Rnf8−/−p53−/− cells, and suggested that Rnf8 and p53 cooperate to maintain genomic integrity.
Fig. 8. Representative chromosomal abnormalities observed in activated B-cells from Rnf8−/−p53−/− mice and control littermates. 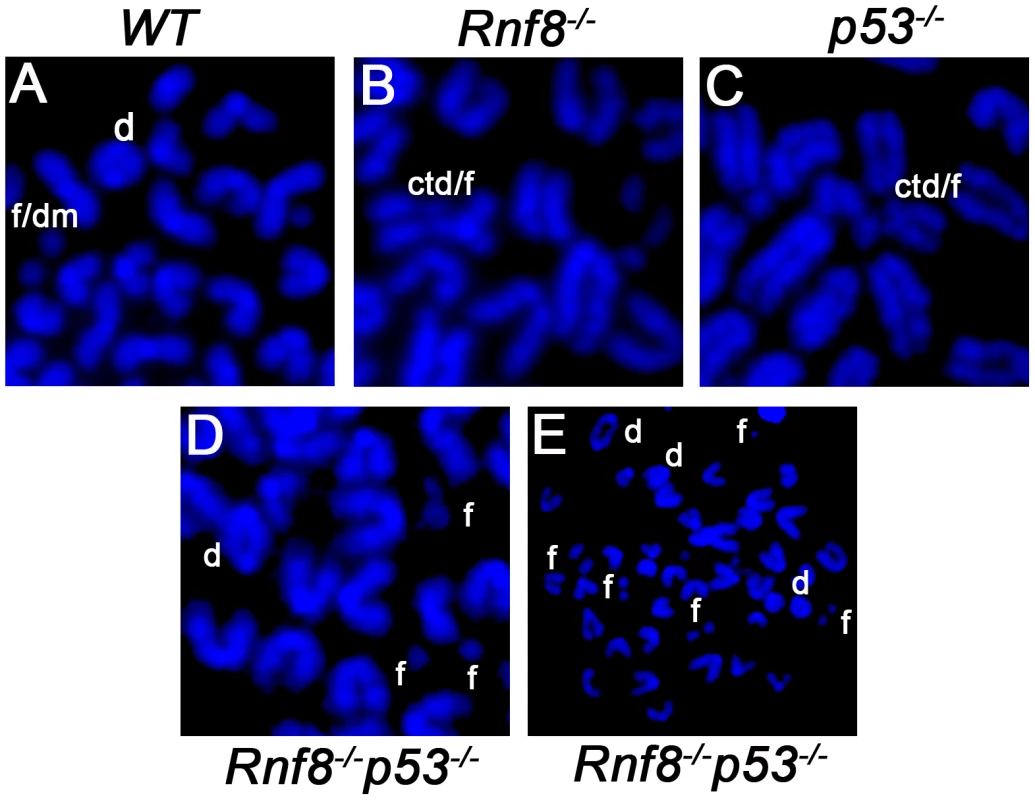
Representative metaphase spreads of irradiated (2 Gy) WT (A), Rnf8−/− (B), p53−/− (C) and Rnf8−/−p53−/− (D and E) LPS-activated B-cells. d: dicentric chromosome, f: chromosome fragments, dm: double minute chromosomes, ctd: chromatid type exchange/breaks. Tab. 1. Dual loss of Rnf8 and p53 leads to increased aneuploidy and genomic instability. 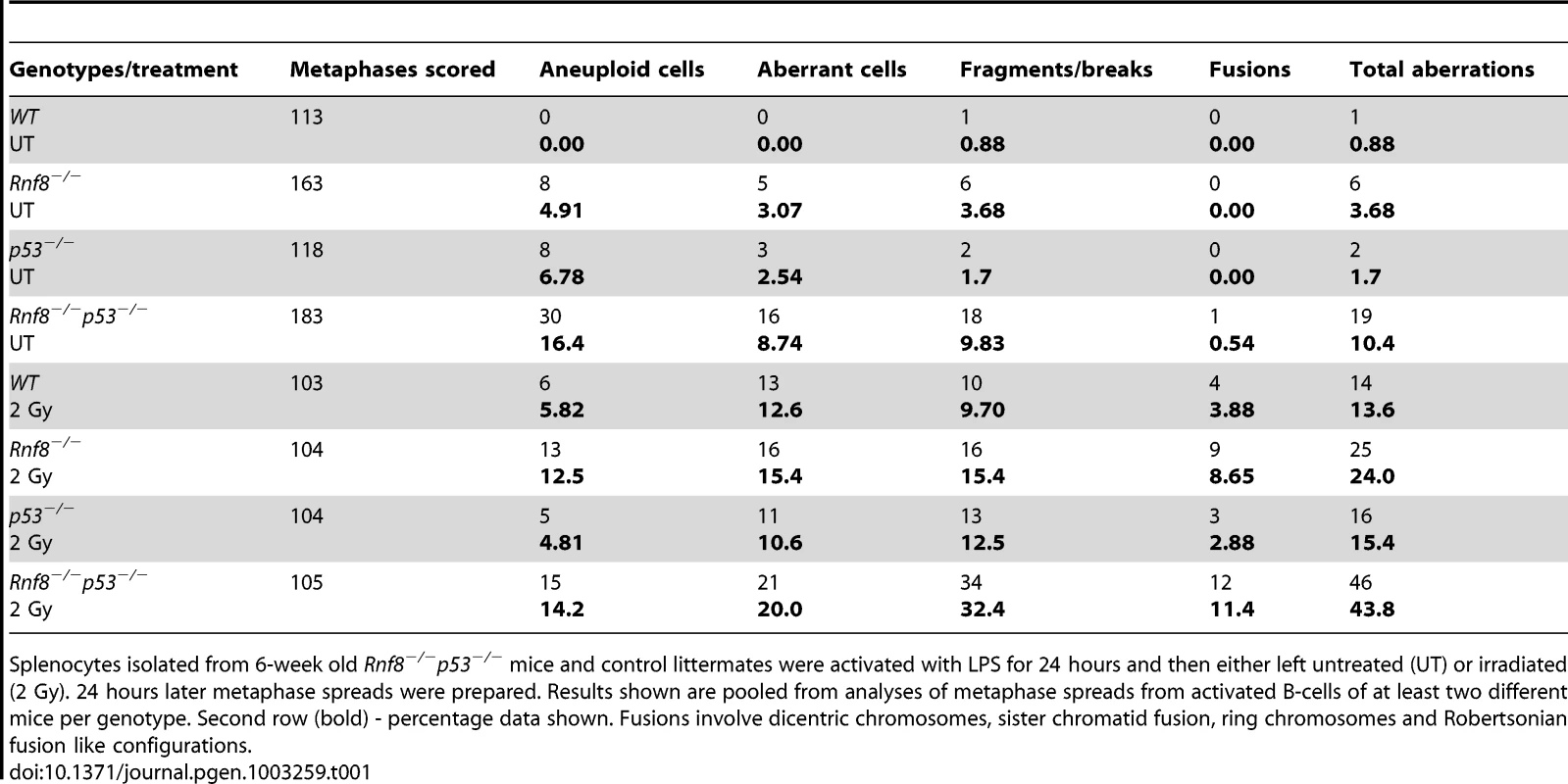
Splenocytes isolated from 6-week old Rnf8−/−p53−/− mice and control littermates were activated with LPS for 24 hours and then either left untreated (UT) or irradiated (2 Gy). 24 hours later metaphase spreads were prepared. Results shown are pooled from analyses of metaphase spreads from activated B-cells of at least two different mice per genotype. Second row (bold) - percentage data shown. Fusions involve dicentric chromosomes, sister chromatid fusion, ring chromosomes and Robertsonian fusion like configurations. Rnf8 cooperates with p53 in tumor suppression
p53 is the most frequently inactivated tumor suppressor in human cancer [18]. Recent data has indicated that Rnf8 also functions as a tumor suppressor, and that about 40% of Rnf8-deficient mice develop tumors, mostly thymic and B-cell lymphomas [14]. To examine the functional interactions of p53 and Rnf8 in suppressing cancer; we first monitored cohorts of Rnf8−/−p53+/−, Rnf8−/− ¸ p53+/− and WT mice for one and a half years for tumor development and Kaplan-Meier tumor free survival analysis was performed. Tumor-free survival of Rnf8−/−p53+/− mice was significantly reduced compared to WT (P = 0.0029), p53+/− (P = 0.0115) and Rnf8−/− (P = 0.0188) controls (Figure 9A). Rnf8−/−p53+/− mice developed a wide range of tumors. 20% of the Rnf8−/−p53+/− mice (3 out of 15) developed hindlimb paralysis and in one of these mice the cause of the hindlimb paralysis was determined to be a benign osteiod osteoma in the spinal cord (Figure 9B). In addition, 7% of Rnf8−/−p53+/− mice (1 out of 15) developed rhabdomyosarcoma (Figure 9C) and lung adenocarcinoma (Figure 9D). By 485 days, 40% of the Rnf8−/−p53+/− mice had developed invasive lymphomas that disseminated into organs including the lung, spleen and liver (Figure 9E and 9F). Therefore, loss of one allele of p53 in the absence of Rnf8 can accelerate tumorigenesis without significantly affecting the tumor spectrum of Rnf8−/− mice (which develop mainly lymphomas) or p53+/− mice (which develop primarily sarcomas and lymphomas) [14], [43].
Fig. 9. Increased tumor incidence and modification of the tumor spectrum in Rnf8−/−p53+/− mice. 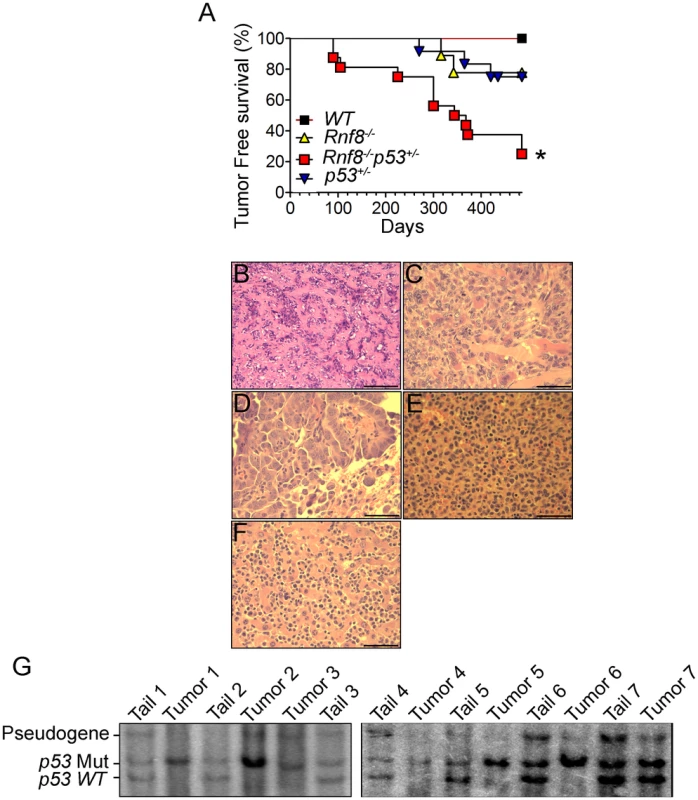
(A) Kaplan-Meir tumor free survival curve for Rnf8−/−p53+/− mice and control littermates. Survival of Rnf8−/−p53+/− mice (n = 15) is significantly decreased compared to Rnf8−/− (n = 9), p53+/− (n = 12) and WT (n = 7) littermates (P<0.05; Log rank test). (B) Osteoid osteoma that is composed of extracellular matrix resembling osteoid interspersed with groups of osteoblastic cells. These cells do not display any cytological features suggesting malignancy. The tumor is very homogeneous in nature, well vascularized and lacking any necrotic foci. (C) Rhabdomyosarcoma showing good vascularization, a high mitotic index and the absence of necrosis. (D) Lung adenocarcinoma compressing adjacent alveoli (lower right corner). (E) Spleen tissue that has been completely invaded by lymphoma. (F) The same lymphoma has also invaded liver tissue. Bars: B: 200 µm, C: 100 µm, D–G: 50 µm. (G) Southern blot showing loss of WT p53 allele in Rnf8−/−p53+/− tumors (tumor 1: rhabdomyosarcoma; tumors 2 & 3: thymomas, tumor 4 & 5 lymphomas, tumors 6 & 7 thymomas). Tail DNA of the same mouse was used as a control. It has been previously reported that less than 50% of tumors that spontaneously develop in p53+/− mice exhibit loss of heterozygocity (LOH) [44]. In addition, the level of p53 LOH in tumors from p53+/− mice exposed to mutagenic carcinogens was found to vary depending on the tumor types [45]. We therefore used Southern blot analysis to determine the status of the WT p53 allele in 8 different tumors (4 thymic lymphomas, 1 rhabdomyosarcoma and 3 B-cell lymphomas) derived from Rnf8−/−p53+/− mice. Our data indicated that the WT p53 allele was lost in the majority (75%) of the Rnf8−/−p53+/− tumors examined (Figure 9G). These data suggest a selective pressure for the loss of the remaining WT p53 allele is behind the accelerated tumor development in Rnf8−/−p53+/− mice.
p53−/− mice are highly prone to development of spontaneous tumors which are mostly thymomas. These mice have a median tumor incidence of about 4.5 months and they all succumb to tumors by the age of 10 months [21]. To examine the effect of dual loss Rnf8 and p53 on tumor development, we monitored cohorts of Rnf8−/−p53−/−mice and their Rnf8−/− ¸ p53−/− and WT controls for one year, and Kaplan-Meier tumor free survival analysis was performed. While as expected tumors were observed in Rnf8−/− and p53−/− mice, double mutants displayed higher cancer risk compared to single mutant littermates (Log-rank test, P<0.0001 compared to Rnf8−/− mice and P = 0.0004 compared to p53−/− mice; Figure 10A). Double mutant mice developed tumors with a remarkably short latency compared to single mutants. While the median tumor free survival was 185 days for our p53−/− cohort of mice, it was significantly reduced to 80 days for Rnf8−/−p53−/− mice. By 12 weeks of age all of Rnf8−/−p53−/− mice had succumbed to thymic lymphomas and/or B-cell lymphomas. One Rnf8−/−p53−/− mouse in the survival cohort developed both a B-cell lymphoma (B220+IgM+) (Figure S8A) and a thymic lymphoma (CD4+CD8+) (Figure S8B), whereas the rest of the cohort developed thymic lymphomas exclusively (Figure S8C). These lymphomas had very high mitotic index (Figure 10B), and were able to invade the liver (Figure 10C), kidney (Figure 10D), and skeletal muscle tissues (Figure 10E). Histopathological analysis of two Rnf8−/−p53−/− mice that had developed ataxia and an unsteady gait indicated that these mice suffered lymphoma that had crossed the meninges and disseminated into the cerebellum and the cerebrum which could explain the observed neurological defects (Figure 10F and 10G). Collectively, these data indicate that dual loss of Rnf8 and p53 exacerbated the risks for cancer development.
Fig. 10. Cooperation of Rnf8 and p53 in the prevention of tumorigenesis. 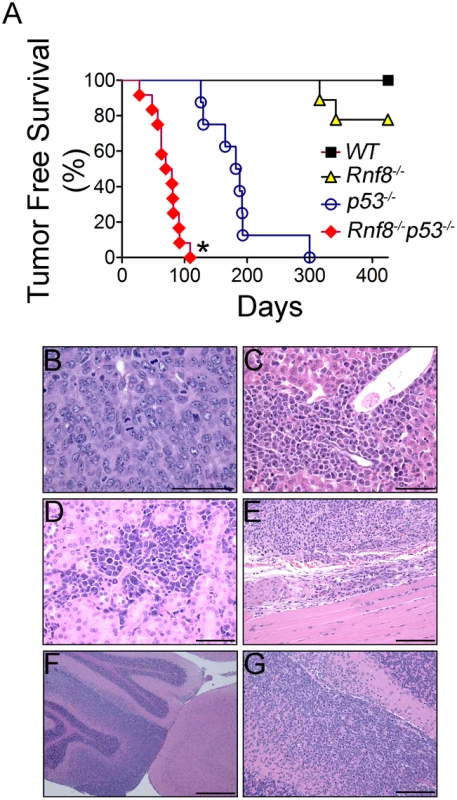
(A) Kaplan-Meier tumor free survival analysis of cohorts of Rnf8−/−p53−/− (n = 12), Rnf8−/− (n = 9), p53−/− (n = 9), and WT (n = 7) mice. Mice were monitored for one year and their tumor free survival curves were established. * indicates statistical significance compared to p53−/− and Rnf8−/− mice (P<0.05; log-rank test). (B) H&E staining of Rnf8−/−p53−/− thymoma. This tumor is composed of large and pleomorphic lymphocytes displaying sparse chromatin, prominent nucleoli and high mitotic index. (C) Rnf8−/−p53−/− lymphoma invading the liver. Liver infiltration is particularly evident around periportal areas. (D) Rnf8−/−p53−/− lymphoma invading the kidneys. Multiple tumor infiltrates are present in the interstitial peritubular spaces and display very high mitotic activity. (E) Rnf8−/−p53−/− lymphoma invading skeletal muscle tissue. (F) Rnf8−/−p53−/− lymphoma infiltrating the cerebellum. This figure shows a normal cerebellar cortex adjacent to cortex that has been mostly infiltrated by lymphoma. (G) Compromised cerebellum infiltrated by Rnf8−/−p53−/− lymphoma. Bars: B–D 50 µm, E and G 100 µm and F 500 µm. Discussion
Post-translational modification by ubiquitin plays a critical role in the signaling and repair of DSBs [1], [2], [46]. In response to these DNA breaks, the E3 ubiquitin ligase Rnf8 ubiquitylates chromatin components H2a, H2ax and H2b at the flanking regions of DSBs [3], [4], [5], [6]. This ubiquitylation facilitates the recruitment to DNA break sites of a number of DNA damage response proteins (e.g. 53bp1 and Brca1) which are required for the activation of cell cycle checkpoints and effective DNA damage repair [2], [10].
Loss of Rnf8 in mice results in many defects including reduced growth, radiosensitivity, male sterility and immunodeficiency [14], [15], [16]. We have previously reported increased levels of p53 expression and activation in untreated and irradiated Rnf8−/− cells compared to WT controls [14]. We hypothesized that elevated levels of p53 occurs in response to defective repair of DNA damage in Rnf8 deficient cells and that this is the underlying cause for the increased radiosensitivity and the growth defects observed in Rnf8−/− mice.
p53 is crucial for the response to DSBs as it eliminates cells unable to repair damaged DNA, thus preventing increased genomic instability and suppressing cancer development [20]. Due to its important functions, loss of p53 has been reported to fully or partially rescue the growth and the embryonic and postnatal developmental defects associated with impaired DNA damage signaling and repair. For example, mice deficient for Brca1, Xrcc4 or Lig4 die during embryonic development, and loss of p53 either prolongs their embryonic development in the case of Brca1 null mutants [47] or fully restores the viability of these mice in the case of Xrcc4 and Lig4 mutants [22], [23].
Our data indicate that loss of p53 completely restrained the elevated radiosensitivity of Rnf8−/− thymus and spleen, reflecting a complete dependence of this radiosensitivity on the p53 pathway. In these two organs specifically, p53 and cleaved caspase-3 levels were elevated, which might indicate that p53 and caspase-3-dependent apoptosis occurs in these organs but not in others such as heart, lung, kidney and liver. Interestingly, basal cells of the intestinal crypts are the only non-hematopoietic cells that displayed increased p53 levels in the absence of Rnf8. It is possible that Rnf8−/− cell types that do not generate programmed DSBs during development or that are less prone to generate spontaneous DSBs due to low rate of proliferation associated stalled replication would not display increased p53 levels.
Rnf8 is required for efficient recruitment of Brca1 to DSB flanking sites [4], [9], and our data indicate that as in Brca1−/− MEFs [25], [26], loss of p53 fully rescued the growth defect of Rnf8−/− MEFs. Interestingly, primary Rnf8−/− MEFs display similar characteristics to those observed with Brca1−/− MEFs, mainly a senescent phenotype, increased basal levels of p21 and p53 but no increase of p19ARF [48]. These results suggest that rescue of the senescent phenotype in Rnf8−/−p53−/− MEFs is caused by an abrogation of the p53-p21 pathway.
Our studies of Rnf8−/−p53−/− mice characterized p53-dependent and independent roles for defective homeostasis of Rnf8−/− immune cells and the post-natal growth defects of Rnf8−/− mice [14]. In contrast to 53bp1−/− thymocytes [49], but similar to Brca1 null thymocytes [25], loss of p53 fully rescued thymocyte numbers in Rnf8−/− mice. These data are consistent with the higher steady state level of p53 in Rnf8−/− thymocytes compared to WT controls [14], and suggest that impaired homeostasis of thymocytes in Rnf8−/− mice is p53-dependent. In addition, as in Brca1 deficient splenocytes [25], loss of p53 rescued the lymphopenia associated with Rnf8 deficiency [14], [16]. Notably, loss of p53 failed to rescue the growth defects of Rnf8−/− mice and the reduced bone marrow cellularity, suggesting that they occur in p53-independent manner. Previous studies have shown that defects in B and T-cell progenitors did not necessarily affect cellularity of the thymus and the spleen. In Foxo3−/− knockout mice the number of pre B-cells and recirculating B-cells were diminished in the bone marrow but the number of B-cells in the spleen remained the same [50]. In addition, it was shown that although T-cell progenitors were unable to settle in the thymus of Ccr7−/−Ccr9−/− double knockout mice, thymocyte numbers of these mutants remained close to those found in WT mice [51]. Therefore, it is possible that while B-cell progenitors are reduced in the bone marrow of Rnf8−/−p53−/− mice, there is increased expansion and a rescue of the B-cell population in spleen of these mice due to absence of p53-dependent apoptosis.
While CSR has been reported to be defective in the presence of impaired DSB signaling as in the case of the absence of Rnf8 [14], [16], Rnf168 [28], [52], H2ax [30] or 53bp1 [31], [32]; loss of p53 does not affect B-cell class switching to IgG1 [33]. Our data indicate that Rnf8−/−p53−/− B-cells display similarly reduced CSR level to what was observed with Rnf8−/− B-cells. These data suggest that the impaired CSR associated with Rnf8 loss is p53-independent. The inability of p53 to rescue CSR defects suggests that even if Rnf8−/−p53−/− B-cells escape the apoptosis associated with Rnf8 deficiency, they are still unable to undergo CSR. This might be because Rnf8 plays a direct role in the repair of the DSBs at switch junctions as was previously suggested [14], [16]. This is similar to what has been observed for other mutations of DNA repair proteins involved in CSR such as DNA-PKcs and Artemis [53], [54].
The repair of DSBs is mediated by the HR or the NHEJ repair pathways [55]. Previous studies indicated that loss of Rnf8 impairs both repair pathways [12], [56]. Rnf8 has also been reported to mediate ubiquitylation and proteasomal degradation of the NHEJ protein Ku80 and this function has been proposed to be important for the role Rnf8 plays in NHEJ [12]. While defects of HR or NHEJ increase cancer risks, additional loss of p53 further exacerbates these risks [55], [57]. Consistent with its role in DSB signaling and repair, loss of Rnf8 leads to increased genomic instability and cancer risks [14]. Rnf8−/−p53−/− B-cells display a considerable increase in genomic instability compared to either Rnf8−/− or p53−/− B-cells under both untreated and irradiated conditions. This could be explained by the fact that cells with elevated levels of genomic instability, caused by unrepaired DSBs, are not eliminated in the absence of p53 and are allowed to accumulate genomic lesions without undergoing programmed cell death. The very high levels of genomic instability in Rnf8−/−p53−/− mice led us to hypothesize that they will develop tumors with shorter latency compared to single mutant mice. Indeed, Rnf8−/−p53−/− mice developed thymic and B-cell lymphomas and very rapidly succumb to their tumors.
Interestingly, even though Rnf8 and Rnf168 have been proposed to function in the same DNA damage signaling pathway, the tumor spectrum of Rnf8−/−p53−/− mice was different from what was observed in Rnf168−/−p53−/− mice which develop primarily B-cell lymphomas, followed by thymomas and sarcomas [28]. In addition, consistent with the increased cancer risk in Rnf8 but not Rnf168 deficient background [14], [28], Rnf8−/−p53−/− mice developed tumors with a significantly shorter latency compared to Rnf168−/−p53−/− mice. The impaired checkpoints in Rnf8−/−p53−/− cells and their elevated levels of spontaneous and IR-induced genomic instability compared to p53−/− and Rnf8−/− cells are likely to play important role in the increased propensity of these cells to undergo tumorigenic transformation.
The tumor spectrum observed with Rnf8−/−p53+/− mice, which included thymomas, lymphomas, rhabdomyosarcoma, adenocarcinoma and osteoma, was different from what we observed for Rnf8−/−p53−/− mice. In addition, while Rnf8−/−p53+/− mice started to die at 90 days of age with 80% dead by 485 days, consistent with previous studies [43], p53+/− mice started to die at around 9 months of age and only 50% of them were dead by 18 months of age. Thus, loss of Rnf8 in a p53 heterozygous background also leads to decreased latency period and increased penetrance of tumors. LOH of p53 is likely to play an important role in tumorigenesis in Rnf8−/−p53+/− mice as the majority of tumors from these mice showed loss of the WT p53 allele.
Collectively, our data indicate that Rnf8 and p53 work synergistically to activate checkpoints, maintain genomic integrity and suppress cancer development. While p53-independent mechanisms contribute to some of the defects associated with Rnf8 deficiency, the accumulation of DNA double strand breaks in the absence of Rnf8, and the subsequent activation of p53, likely play a major role in the mechanisms that eliminate damaged cells through cell cycle arrest, blunted growth or increased cell death. Thus, when p53 is deficient, uncontrolled growth and proliferation of damaged Rnf8−/− cells and their dramatic increase of genomic instability drive the remarkably high tumor incidence in these mice.
Materials and Methods
Mice
Rnf8−/− mice generated using the AS0574 ES clone [14] and p53−/− mice [58] (Taconic), both in a mixed 129/J×C57BL/6 genetic background, were crossed to generate Rnf8+/−p53+/− mice. These mice were then bred to obtain Rnf8−/−p53−/− mutants. Mice were genotyped by PCR using the following primers: forward WT Rnf8 5′-TGATGACACCTGGGCATGT-3′; reverse WT Rnf8 5′-TCTTTGAGACAGCGCCTGG-3′; forward mutant Rnf8 5′-TCAAAGGTTTGCCCTCTCTGAT-3′; reverse mutant Rnf8 5′-CGGAGCGGATCTCAAACTCT-3′; forward WT p53 5′-GTGTTTCATTAGTTCCCCACCTTGAC-3′; reverse WT p53 5′-ATGGGAGGCTGCCAGTCCTAACCC-3′; forward p53 mutant 5′-TTTACGGAGCCCTGGCGCTCGATGT-3′; reverse p53 mutant 5′-GTGGGAGGGACAAAAGTTCGAGGCC -3′. All animal experiments were done in compliance with the Ontario Cancer Institute animal care committee guidelines. Animal protocols were approved by the Animal Resource Center of Ontario Cancer Institute.
Western blot analysis
Equal amounts of cell lysates were loaded onto 7.5% or 10% polyacrylamide gels and were transferred onto PVDF membrane. Detection of protein was done using primary antibodies against phosphorylated p53-Ser15 (Cell Signaling), p53 (FL393, Santa Cruz Biotechnology), p21 (M-19, Santa Cruz Biotechnology), p19 (Novus), β-actin (Santa Cruz Biotechnology) and HRP-conjugated secondary antibodies against rabbit or rat.
Senescence-associated β-galactosidase assay
Passage 3 primary MEFs were fixed and stained using the Senescence β-galactosidase staining kit from Cell Signaling according to Manufacturer's instructions. The cells were visualized using a brightfield Olympus CKX41 microscope using the 10× objective and images were taken using the Infinity 2 camera and Infinity Capture software.
Immune cell counts and flow cytometry
Thymocytes, splenocytes and bone marrow cells were isolated from 6 weeks old mice. Red blood cells collected with splenocytes and bone marrow cells were lysed using red blood cell lysis buffer (Sigma). Cells were counted and stained with anti-B220, anti-TCRβ, anti-CD4, anti-CD8, anti-IgM, anti-IgD and anti-CD43 antibodies (eBioscience) and were examined using a FACSCalibur flow cytometer (Becton Dickinson). The data was analyzed using the FlowJo software (Tree Star, Inc.).
Cell death assays
Freshly isolated thymocytes and splenocytes from 6 weeks old mice were irradiated with 2 Gy ionizing radiation and allowed to recover for 12 and 24 hours respectively. Cells were stained with PI (Sigma) and flow cytometry analysis was performed using a FACSCalibur flow cytometer. The data was analyzed using the FlowJo software.
In vitro proliferation assays
WT, Rnf8−/−, p53−/− and Rnf8−/−p53−/− MEFs were generated from E13.5 embryos. Passage 2 MEFs were used to generate growth curves by 3T3 passaging. Briefly, 3×105 cells were seeded in a 60 mm dish and allowed to grow for 3 days. The cells were trypsinized and the same number of cells was reseeded on the plate. This was repeated until cells became senescent.
Class switch recombination
Negative selection, using the mouse B-cell negative isolation kit (Invitrogen), was used to purify B-cells from freshly isolated splenocytes of 6–8 week old mice. Cells were stained with CFSE (Invitrogen) and allowed to proliferate for 4 days in RPMI medium in the presence of anti-CD40 (eBioscience) and IL-4 (eBioscience). Cells were then stained with anti-B220 (eBioscience) and IgG1 (eBioscience) antibodies and analyzed by flow cytometry.
G1-S checkpoint assay
Passage 1 or 2 primary MEFs were either untreated or irradiated (10 Gy) and left to recover for 16 hours before pulsing with 10 µM BrDU for 4 hours. Cells were then fixed overnight with 70% ethanol before staining with FITC-conjugated anti-BrDU antibody (e-Bioscience) and PI as previously described [59].
G2-M checkpoint assay
Passage 1–3 MEFs were irradiated with 2 Gy ionizing radiation (IR) or left untreated. 1 hour after the irradiation cells were fixed with 70% ethanol overnight and were then stained with FITC - conjugated anti-phospho histone H3 (Ser10) antibody (Cell Signaling) and PI and analysed by flow cytometry as previously described [59].
Immunofluorescence
Early passage primary MEFs were plated on glass coverslips. The cells were then left untreated or irradiated with 8 Gy IR. Cells were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde for 20 minutes and incubated overnight with anti-γ-H2ax (07-164, Millipore; 1∶500 dilution), anti-Mdc1 (A300-757A, Bethyl, 1∶500 dilution), anti-Brca1 (1∶500 dilution) and anti-53bp1 (A300-272A, Bethyl; 1∶500 dilution) in dilution buffer (5% FBS, 3% BSA, 0.05% Triton X-100 in PBS). Following washes with 10% dilution buffer and PBS, cells were incubated with a goat anti-rabbit Alexa fluor 488-conjugated antibody (A11008, Molecular Probes; 1∶1000 dilution). After washing, cells were stained with DAPI (Invitrogen) and mounted on slides using Mowiol (Sigma). Cells were visualized and quantified for their foci using a Leica DM 4000 B microscope with a 100× oil immersion objective. Image acquisition and overlay was performed using the Leica Application Suite V 4.0 software (Leica Microsystems, Switzerland).
Chromosomal aberration analysis
Freshly isolated splenocytes from 6-week-old tumor-free mice were stimulated to proliferate for 24 hours in RPMI medium containing 10 µg/ml LPS (Sigma). Cells were then either left untreated or irradiated with 2 Gy IR. 24 hours post-irradiation, cells were incubated in hypotonic buffer (75 mM potassium chloride solution) at 37°C and then fixed with ice-cold 3∶1 methanol-acetic acid solution. Chromosome numbers and aberrations were scored for at least 50 metaphases from two separate sets of samples.
Tumor analysis
Cohorts of Rnf8−/−p53−/−, Rnf8−/−p53+/−, Rnf8−/−, p53−/−, p53+/− and WT mice were monitored for a period of one year. Moribund mice were sacrificed and examined for the presence of tumors. Tumors of lymphoid origin were characterized using flow cytometry. Histopathological examination of H&E stained sections of tumors embedded in paraffin was performed using a Leica DM 4000 B microscope and images were acquired using the Leica Application Suite software. Kaplan-Meier plots for tumor free survival of mice were charted. Log-Rank test statistical analysis was performed using Prism 5 (GraphPad Software, Inc.).
Immunohistochemistry
Tissues fixed in buffered formalin and embedded in paraffin and sectioned at 5 µm were stained using anti-p53 antibody (FL393, Santa Cruz Biotechnology) or anti - cleaved caspase-3 antibody (Cell Signaling). Slides were viewed using a Leica DM 4000 B microscope and images were acquired using the Leica Application Suite software.
Southern blot analysis of p53 loss of heterozygosity
Genomic DNA isolated from tails and tumors of Rnf8−/−p53+/− mice were digested overnight with the restriction enzyme BamH1 and run on a 0.8% agarose gel. DNA were then transferred to a Hybond N+ membrane (GE healthcare) and hybridized with a 32P-labeled p53 specific probe. The bands were visualized using a phosphoimager (Typhoon 9410, Amersham Biosciences).
Statistical analysis
The data is presented as the mean ± SD. Statistical analysis of experimental data was performed using student t-test and statistical significance was determined at P<0.05. The log-rank test was used to generate tumor-free survival curves for mouse cohorts. Two-sided Fisher exact test using the Mstat software was used to determine statistical significance for analysis of chromosomal aberrations.
Supporting Information
Zdroje
1. CicciaA, ElledgeSJ (2010) The DNA damage response: making it safe to play with knives. Mol Cell 40 : 179–204.
2. BohgakiT, BohgakiM, HakemR (2010) DNA double-strand break signaling and human disorders. Genome Integr 1 : 15.
3. KolasNK, ChapmanJR, NakadaS, YlankoJ, ChahwanR, et al. (2007) Orchestration of the DNA-damage response by the RNF8 ubiquitin ligase. Science 318 : 1637–1640.
4. MailandN, Bekker-JensenS, FaustrupH, MelanderF, BartekJ, et al. (2007) RNF8 ubiquitylates histones at DNA double-strand breaks and promotes assembly of repair proteins. Cell 131 : 887–900.
5. HuenMS, GrantR, MankeI, MinnK, YuX, et al. (2007) RNF8 transduces the DNA-damage signal via histone ubiquitylation and checkpoint protein assembly. Cell 131 : 901–914.
6. WuJ, HuenMS, LuLY, YeL, DouY, et al. (2009) Histone ubiquitination associates with BRCA1-dependent DNA damage response. Mol Cell Biol 29 : 849–860.
7. DoilC, MailandN, Bekker-JensenS, MenardP, LarsenDH, et al. (2009) RNF168 binds and amplifies ubiquitin conjugates on damaged chromosomes to allow accumulation of repair proteins. Cell 136 : 435–446.
8. StewartGS, PanierS, TownsendK, Al-HakimAK, KolasNK, et al. (2009) The RIDDLE syndrome protein mediates a ubiquitin-dependent signaling cascade at sites of DNA damage. Cell 136 : 420–434.
9. WangB, ElledgeSJ (2007) Ubc13/Rnf8 ubiquitin ligases control foci formation of the Rap80/Abraxas/Brca1/Brcc36 complex in response to DNA damage. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104 : 20759–20763.
10. Bekker-JensenS, MailandN (2011) The ubiquitin - and SUMO-dependent signaling response to DNA double-strand breaks. FEBS Lett 585 : 2914–2919.
11. MalletteFA, MattiroliF, CuiG, YoungLC, HendzelMJ, et al. (2012) RNF8 - and RNF168-dependent degradation of KDM4A/JMJD2A triggers 53BP1 recruitment to DNA damage sites. EMBO J 31 : 1865–1878.
12. FengL, ChenJ (2012) The E3 ligase RNF8 regulates KU80 removal and NHEJ repair. Nat Struct Mol Biol 19 : 201–206.
13. RaiR, LiJM, ZhengH, LokGT, DengY, et al. (2011) The E3 ubiquitin ligase Rnf8 stabilizes Tpp1 to promote telomere end protection. Nat Struct Mol Biol 18 : 1400–1407.
14. LiL, HalabyMJ, HakemA, CardosoR, El GhamrasniS, et al. (2010) Rnf8 deficiency impairs class switch recombination, spermatogenesis, and genomic integrity and predisposes for cancer. J Exp Med 207 : 983–997.
15. LuLY, WuJ, YeL, GavrilinaGB, SaundersTL, et al. (2010) RNF8-dependent histone modifications regulate nucleosome removal during spermatogenesis. Dev Cell 18 : 371–384.
16. SantosMA, HuenMS, JankovicM, ChenHT, Lopez-ContrerasAJ, et al. (2010) Class switching and meiotic defects in mice lacking the E3 ubiquitin ligase RNF8. J Exp Med 207 : 973–981.
17. LevineAJ, OrenM (2009) The first 30 years of p53: growing ever more complex. Nat Rev Cancer 9 : 749–758.
18. BradyCA, AttardiLD (2010) p53 at a glance. J Cell Sci 123 : 2527–2532.
19. GreenblattMS, BennettWP, HollsteinM, HarrisCC (1994) Mutations in the p53 tumor suppressor gene: clues to cancer etiology and molecular pathogenesis. Cancer Res 54 : 4855–4878.
20. BiegingKT, AttardiLD (2012) Deconstructing p53 transcriptional networks in tumor suppression. Trends Cell Biol 22 : 97–106.
21. DonehowerLA, LozanoG (2009) 20 years studying p53 functions in genetically engineered mice. Nat Rev Cancer 9 : 831–841.
22. FrankKM, SharplessNE, GaoY, SekiguchiJM, FergusonDO, et al. (2000) DNA ligase IV deficiency in mice leads to defective neurogenesis and embryonic lethality via the p53 pathway. Mol Cell 5 : 993–1002.
23. GaoY, FergusonDO, XieW, ManisJP, SekiguchiJ, et al. (2000) Interplay of p53 and DNA-repair protein XRCC4 in tumorigenesis, genomic stability and development. Nature 404 : 897–900.
24. XuX, WagnerKU, LarsonD, WeaverZ, LiC, et al. (1999) Conditional mutation of Brca1 in mammary epithelial cells results in blunted ductal morphogenesis and tumour formation. Nat Genet 22 : 37–43.
25. MakTW, HakemA, McPhersonJP, ShehabeldinA, ZablockiE, et al. (2000) Brca1 required for T cell lineage development but not TCR loci rearrangement. Nat Immunol 1 : 77–82.
26. McPhersonJP, LemmersB, HiraoA, HakemA, AbrahamJ, et al. (2004) Collaboration of Brca1 and Chk2 in tumorigenesis. Genes Dev 18 : 1144–1153.
27. JonkersJ, MeuwissenR, van der GuldenH, PeterseH, van der ValkM, et al. (2001) Synergistic tumor suppressor activity of BRCA2 and p53 in a conditional mouse model for breast cancer. Nat Genet 29 : 418–425.
28. BohgakiT, BohgakiM, CardosoR, PanierS, ZeegersD, et al. (2011) Genomic instability, defective spermatogenesis, immunodeficiency, and cancer in a mouse model of the RIDDLE syndrome. PLoS Genet 7: e1001381 doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1001381.
29. MeekDW (2009) Tumour suppression by p53: a role for the DNA damage response? Nat Rev Cancer 9 : 714–723.
30. Reina-San-MartinB, DifilippantonioS, HanitschL, MasilamaniRF, NussenzweigA, et al. (2003) H2AX is required for recombination between immunoglobulin switch regions but not for intra-switch region recombination or somatic hypermutation. J Exp Med 197 : 1767–1778.
31. WardIM, Reina-San-MartinB, OlaruA, MinnK, TamadaK, et al. (2004) 53BP1 is required for class switch recombination. J Cell Biol 165 : 459–464.
32. ManisJP, MoralesJC, XiaZ, KutokJL, AltFW, et al. (2004) 53BP1 links DNA damage-response pathways to immunoglobulin heavy chain class-switch recombination. Nat Immunol 5 : 481–487.
33. GuikemaJE, SchraderCE, BrodskyMH, LinehanEK, RichardsA, et al. (2010) p53 represses class switch recombination to IgG2a through its antioxidant function. J Immunol 184 : 6177–6187.
34. KuilmanT, MichaloglouC, MooiWJ, PeeperDS (2010) The essence of senescence. Genes Dev 24 : 2463–2479.
35. ZindyF, EischenCM, RandleDH, KamijoT, ClevelandJL, et al. (1998) Myc signaling via the ARF tumor suppressor regulates p53-dependent apoptosis and immortalization. Genes Dev 12 : 2424–2433.
36. KastanMB, BartekJ (2004) Cell-cycle checkpoints and cancer. Nature 432 : 316–323.
37. BoldersonE, RichardDJ, ZhouBB, KhannaKK (2009) Recent advances in cancer therapy targeting proteins involved in DNA double-strand break repair. Clin Cancer Res 15 : 6314–6320.
38. WuJ, ChenY, LuLY, WuY, PaulsenMT, et al. (2011) Chfr and RNF8 synergistically regulate ATM activation. Nat Struct Mol Biol 18 : 761–768.
39. YuanJ, ChenJ (2010) MRE11-RAD50-NBS1 complex dictates DNA repair independent of H2AX. J Biol Chem 285 : 1097–1104.
40. MoynahanME, ChiuJW, KollerBH, JasinM (1999) Brca1 controls homology-directed DNA repair. Mol Cell 4 : 511–518.
41. RoyR, ChunJ, PowellSN (2011) BRCA1 and BRCA2: different roles in a common pathway of genome protection. Nat Rev Cancer 12 : 68–78.
42. BartekJ, LukasJ (2007) DNA damage checkpoints: from initiation to recovery or adaptation. Curr Opin Cell Biol 19 : 238–245.
43. AttardiLD, JacksT (1999) The role of p53 in tumour suppression: lessons from mouse models. Cell Mol Life Sci 55 : 48–63.
44. VenkatachalamS, ShiYP, JonesSN, VogelH, BradleyA, et al. (1998) Retention of wild-type p53 in tumors from p53 heterozygous mice: reduction of p53 dosage can promote cancer formation. EMBO J 17 : 4657–4667.
45. FrenchJE, LacksGD, TrempusC, DunnickJK, FoleyJ, et al. (2001) Loss of heterozygosity frequency at the Trp53 locus in p53-deficient (+/−) mouse tumors is carcinogen-and tissue-dependent. Carcinogenesis 22 : 99–106.
46. HuangTT, D'AndreaAD (2006) Regulation of DNA repair by ubiquitylation. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 7 : 323–334.
47. HakemR, de la PompaJL, EliaA, PotterJ, MakTW (1997) Partial rescue of Brca1 (5–6) early embryonic lethality by p53 or p21 null mutation. Nat Genet 16 : 298–302.
48. CaoL, LiW, KimS, BrodieSG, DengCX (2003) Senescence, aging, and malignant transformation mediated by p53 in mice lacking the Brca1 full-length isoform. Genes Dev 17 : 201–213.
49. DifilippantonioS, GapudE, WongN, HuangCY, MahowaldG, et al. (2008) 53BP1 facilitates long-range DNA end-joining during V(D)J recombination. Nature 456 : 529–533.
50. HinmanRM, NicholsWA, DiazTM, GallardoTD, CastrillonDH, et al. (2009) Foxo3−/ − mice demonstrate reduced numbers of pre-B and recirculating B cells but normal splenic B cell sub-population distribution. Int Immunol 21 : 831–842.
51. ZlotoffDA, SambandamA, LoganTD, BellJJ, SchwarzBA, et al. (2010) CCR7 and CCR9 together recruit hematopoietic progenitors to the adult thymus. Blood 115 : 1897–1905.
52. StewartGS, StankovicT, ByrdPJ, WechslerT, MillerES, et al. (2007) RIDDLE immunodeficiency syndrome is linked to defects in 53BP1-mediated DNA damage signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104 : 16910–16915.
53. ManisJP, DudleyD, KaylorL, AltFW (2002) IgH class switch recombination to IgG1 in DNA-PKcs-deficient B cells. Immunity 16 : 607–617.
54. FrancoS, MurphyMM, LiG, BorjesonT, BoboilaC, et al. (2008) DNA-PKcs and Artemis function in the end-joining phase of immunoglobulin heavy chain class switch recombination. J Exp Med 205 : 557–564.
55. HakemR (2008) DNA-damage repair; the good, the bad, and the ugly. EMBO J 27 : 589–605.
56. MeerangM, RitzD, PaliwalS, GarajovaZ, BosshardM, et al. (2011) The ubiquitin-selective segregase VCP/p97 orchestrates the response to DNA double-strand breaks. Nat Cell Biol 13 : 1376–1382.
57. AttardiLD, DonehowerLA (2005) Probing p53 biological functions through the use of genetically engineered mouse models. Mutat Res 576 : 4–21.
58. DonehowerLA, HarveyM, SlagleBL, McArthurMJ, MontgomeryCAJr, et al. (1992) Mice deficient for p53 are developmentally normal but susceptible to spontaneous tumors. Nature 356 : 215–221.
59. TheunissenJW, PetriniJH (2006) Methods for studying the cellular response to DNA damage: influence of the Mre11 complex on chromosome metabolism. Methods Enzymol 409 : 251–284.
Štítky
Genetika Reprodukční medicína
Článek Comparative Genome Structure, Secondary Metabolite, and Effector Coding Capacity across PathogensČlánek TATES: Efficient Multivariate Genotype-Phenotype Analysis for Genome-Wide Association StudiesČlánek Secondary Metabolism and Development Is Mediated by LlmF Control of VeA Subcellular Localization inČlánek Human Disease-Associated Genetic Variation Impacts Large Intergenic Non-Coding RNA ExpressionČlánek The Roles of Whole-Genome and Small-Scale Duplications in the Functional Specialization of GenesČlánek The Role of Autophagy in Genome Stability through Suppression of Abnormal Mitosis under Starvation
Článek vyšel v časopisePLOS Genetics
Nejčtenější tento týden
2013 Číslo 1
-
Všechny články tohoto čísla
- A Model of High Sugar Diet-Induced Cardiomyopathy
- Comparative Genome Structure, Secondary Metabolite, and Effector Coding Capacity across Pathogens
- Emerging Function of Fat Mass and Obesity-Associated Protein (Fto)
- Positional Cloning Reveals Strain-Dependent Expression of to Alter Susceptibility to Bleomycin-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis in Mice
- Genetics of Ribosomal Proteins: “Curiouser and Curiouser”
- Transposable Elements Re-Wire and Fine-Tune the Transcriptome
- Function and Regulation of , a Gene Implicated in Autism and Human Evolution
- MAML1 Enhances the Transcriptional Activity of Runx2 and Plays a Role in Bone Development
- Predicting Mendelian Disease-Causing Non-Synonymous Single Nucleotide Variants in Exome Sequencing Studies
- A Systematic Mapping Approach of 16q12.2/ and BMI in More Than 20,000 African Americans Narrows in on the Underlying Functional Variation: Results from the Population Architecture using Genomics and Epidemiology (PAGE) Study
- Transcription of the Major microRNA–Like Small RNAs Relies on RNA Polymerase III
- Histone H3K56 Acetylation, Rad52, and Non-DNA Repair Factors Control Double-Strand Break Repair Choice with the Sister Chromatid
- Genome-Wide Association Study Identifies a Novel Susceptibility Locus at 12q23.1 for Lung Squamous Cell Carcinoma in Han Chinese
- Genetic Disruption of the Copulatory Plug in Mice Leads to Severely Reduced Fertility
- The [] Prion Exists as a Dynamic Cloud of Variants
- Adult Onset Global Loss of the Gene Alters Body Composition and Metabolism in the Mouse
- Fis Protein Insulates the Gene from Uncontrolled Transcription
- The Meiotic Nuclear Lamina Regulates Chromosome Dynamics and Promotes Efficient Homologous Recombination in the Mouse
- Genome-Wide Haplotype Analysis of Expression Quantitative Trait Loci in Monocytes
- TATES: Efficient Multivariate Genotype-Phenotype Analysis for Genome-Wide Association Studies
- Structural Basis of a Histone H3 Lysine 4 Demethylase Required for Stem Elongation in Rice
- The Ecm11-Gmc2 Complex Promotes Synaptonemal Complex Formation through Assembly of Transverse Filaments in Budding Yeast
- MCM8 Is Required for a Pathway of Meiotic Double-Strand Break Repair Independent of DMC1 in
- Comparative Genomic Analysis of the Endosymbionts of Herbivorous Insects Reveals Eco-Environmental Adaptations: Biotechnology Applications
- Integration of Nodal and BMP Signals in the Heart Requires FoxH1 to Create Left–Right Differences in Cell Migration Rates That Direct Cardiac Asymmetry
- Pharmacodynamics, Population Dynamics, and the Evolution of Persistence in
- A Hybrid Likelihood Model for Sequence-Based Disease Association Studies
- Aberration in DNA Methylation in B-Cell Lymphomas Has a Complex Origin and Increases with Disease Severity
- Multiple Opposing Constraints Govern Chromosome Interactions during Meiosis
- Transcriptional Dynamics Elicited by a Short Pulse of Notch Activation Involves Feed-Forward Regulation by Genes
- Dynamic Large-Scale Chromosomal Rearrangements Fuel Rapid Adaptation in Yeast Populations
- Heterologous Gln/Asn-Rich Proteins Impede the Propagation of Yeast Prions by Altering Chaperone Availability
- Gene Copy-Number Polymorphism Caused by Retrotransposition in Humans
- An Incompatibility between a Mitochondrial tRNA and Its Nuclear-Encoded tRNA Synthetase Compromises Development and Fitness in
- Secondary Metabolism and Development Is Mediated by LlmF Control of VeA Subcellular Localization in
- Single-Stranded Annealing Induced by Re-Initiation of Replication Origins Provides a Novel and Efficient Mechanism for Generating Copy Number Expansion via Non-Allelic Homologous Recombination
- Tbx2 Controls Lung Growth by Direct Repression of the Cell Cycle Inhibitor Genes and
- Suv4-20h Histone Methyltransferases Promote Neuroectodermal Differentiation by Silencing the Pluripotency-Associated Oct-25 Gene
- A Conserved Helicase Processivity Factor Is Needed for Conjugation and Replication of an Integrative and Conjugative Element
- Telomerase-Null Survivor Screening Identifies Novel Telomere Recombination Regulators
- Genome-Wide Analysis Reveals Selection for Important Traits in Domestic Horse Breeds
- Coordinated Degradation of Replisome Components Ensures Genome Stability upon Replication Stress in the Absence of the Replication Fork Protection Complex
- Nkx6.1 Controls a Gene Regulatory Network Required for Establishing and Maintaining Pancreatic Beta Cell Identity
- HIF- and Non-HIF-Regulated Hypoxic Responses Require the Estrogen-Related Receptor in
- Delineating a Conserved Genetic Cassette Promoting Outgrowth of Body Appendages
- The Telomere Capping Complex CST Has an Unusual Stoichiometry, Makes Multipartite Interaction with G-Tails, and Unfolds Higher-Order G-Tail Structures
- Comprehensive Methylome Characterization of and at Single-Base Resolution
- Loci Associated with -Glycosylation of Human Immunoglobulin G Show Pleiotropy with Autoimmune Diseases and Haematological Cancers
- Switchgrass Genomic Diversity, Ploidy, and Evolution: Novel Insights from a Network-Based SNP Discovery Protocol
- Centromere-Like Regions in the Budding Yeast Genome
- Sequencing of Loci from the Elephant Shark Reveals a Family of Genes in Vertebrate Genomes, Forged by Ancient Duplications and Divergences
- Mendelian and Non-Mendelian Regulation of Gene Expression in Maize
- Mutational Spectrum Drives the Rise of Mutator Bacteria
- Human Disease-Associated Genetic Variation Impacts Large Intergenic Non-Coding RNA Expression
- The Roles of Whole-Genome and Small-Scale Duplications in the Functional Specialization of Genes
- Sex-Specific Signaling in the Blood–Brain Barrier Is Required for Male Courtship in
- A Newly Uncovered Group of Distantly Related Lysine Methyltransferases Preferentially Interact with Molecular Chaperones to Regulate Their Activity
- Is Required for Leptin-Mediated Depolarization of POMC Neurons in the Hypothalamic Arcuate Nucleus in Mice
- Unlocking the Bottleneck in Forward Genetics Using Whole-Genome Sequencing and Identity by Descent to Isolate Causative Mutations
- The Role of Autophagy in Genome Stability through Suppression of Abnormal Mitosis under Starvation
- MTERF3 Regulates Mitochondrial Ribosome Biogenesis in Invertebrates and Mammals
- Downregulation and Altered Splicing by in a Mouse Model of Facioscapulohumeral Muscular Dystrophy (FSHD)
- NBR1-Mediated Selective Autophagy Targets Insoluble Ubiquitinated Protein Aggregates in Plant Stress Responses
- Retroactive Maintains Cuticle Integrity by Promoting the Trafficking of Knickkopf into the Procuticle of
- Phenome-Wide Association Study (PheWAS) for Detection of Pleiotropy within the Population Architecture using Genomics and Epidemiology (PAGE) Network
- Genetic and Functional Modularity of Activities in the Specification of Limb-Innervating Motor Neurons
- A Population Genetic Model for the Maintenance of R2 Retrotransposons in rRNA Gene Loci
- A Quartet of PIF bHLH Factors Provides a Transcriptionally Centered Signaling Hub That Regulates Seedling Morphogenesis through Differential Expression-Patterning of Shared Target Genes in
- A Genome-Wide Integrative Genomic Study Localizes Genetic Factors Influencing Antibodies against Epstein-Barr Virus Nuclear Antigen 1 (EBNA-1)
- Mutation of the Diamond-Blackfan Anemia Gene in Mouse Results in Morphological and Neuroanatomical Phenotypes
- Life, the Universe, and Everything: An Interview with David Haussler
- Alternative Oxidase Expression in the Mouse Enables Bypassing Cytochrome Oxidase Blockade and Limits Mitochondrial ROS Overproduction
- An Evolutionarily Conserved Synthetic Lethal Interaction Network Identifies FEN1 as a Broad-Spectrum Target for Anticancer Therapeutic Development
- The Flowering Repressor Underlies a Novel QTL Interacting with the Genetic Background
- Telomerase Is Required for Zebrafish Lifespan
- and Diversified Expression of the Gene Family Bolster the Floral Stem Cell Network
- Susceptibility Loci Associated with Specific and Shared Subtypes of Lymphoid Malignancies
- An Insertion in 5′ Flanking Region of Causes Blue Eggshell in the Chicken
- Increased Maternal Genome Dosage Bypasses the Requirement of the FIS Polycomb Repressive Complex 2 in Arabidopsis Seed Development
- WNK1/HSN2 Mutation in Human Peripheral Neuropathy Deregulates Expression and Posterior Lateral Line Development in Zebrafish ()
- Synergistic Interaction of Rnf8 and p53 in the Protection against Genomic Instability and Tumorigenesis
- Dot1-Dependent Histone H3K79 Methylation Promotes Activation of the Mek1 Meiotic Checkpoint Effector Kinase by Regulating the Hop1 Adaptor
- A Heterogeneous Mixture of F-Series Prostaglandins Promotes Sperm Guidance in the Reproductive Tract
- Starvation, Together with the SOS Response, Mediates High Biofilm-Specific Tolerance to the Fluoroquinolone Ofloxacin
- Directed Evolution of a Model Primordial Enzyme Provides Insights into the Development of the Genetic Code
- Genome-Wide Screens for Tinman Binding Sites Identify Cardiac Enhancers with Diverse Functional Architectures
- PLOS Genetics
- Archiv čísel
- Aktuální číslo
- Informace o časopisu
Nejčtenější v tomto čísle- Function and Regulation of , a Gene Implicated in Autism and Human Evolution
- An Insertion in 5′ Flanking Region of Causes Blue Eggshell in the Chicken
- Comprehensive Methylome Characterization of and at Single-Base Resolution
- Susceptibility Loci Associated with Specific and Shared Subtypes of Lymphoid Malignancies
Kurzy
Zvyšte si kvalifikaci online z pohodlí domova
Současné možnosti léčby obezity
nový kurzAutoři: MUDr. Martin Hrubý
Všechny kurzyPřihlášení#ADS_BOTTOM_SCRIPTS#Zapomenuté hesloZadejte e-mailovou adresu, se kterou jste vytvářel(a) účet, budou Vám na ni zaslány informace k nastavení nového hesla.
- Vzdělávání



