-
Články
Top novinky
Reklama- Vzdělávání
- Časopisy
Top články
Nové číslo
- Témata
Top novinky
Reklama- Videa
- Podcasty
Nové podcasty
Reklama- Kariéra
Doporučené pozice
Reklama- Praxe
Top novinky
ReklamaLamin B1 Polymorphism Influences Morphology of the Nuclear Envelope, Cell Cycle Progression, and Risk of Neural Tube Defects in Mice
Neural tube defects (NTDs), including spina bifida and anencephaly, are common birth defects whose complex multigenic causation has hampered efforts to delineate their molecular basis. The effect of putative modifier genes in determining NTD susceptibility may be investigated in mouse models, particularly those that display partial penetrance such as curly tail, a strain in which NTDs result from a hypomorphic allele of the grainyhead-like-3 gene. Through proteomic analysis, we found that the curly tail genetic background harbours a polymorphic variant of lamin B1, lacking one of a series of nine glutamic acid residues. Lamins are intermediate filament proteins of the nuclear lamina with multiple functions that influence nuclear structure, cell cycle properties, and transcriptional regulation. Fluorescence loss in photobleaching showed that the variant lamin B1 exhibited reduced stability in the nuclear lamina. Genetic analysis demonstrated that the variant also affects neural tube closure: the frequency of spina bifida and anencephaly was reduced three-fold when wild-type lamin B1 was bred into the curly tail strain background. Cultured fibroblasts expressing variant lamin B1 show significantly increased nuclear dysmorphology and diminished proliferative capacity, as well as premature senescence, associated with reduced expression of cyclins and Smc2, and increased expression of p16. The cellular basis of spinal NTDs in curly tail embryos involves a proliferation defect localised to the hindgut epithelium, and S-phase progression was diminished in the hindgut of embryos expressing variant lamin B1. These observations indicate a mechanistic link between altered lamin B1 function, exacerbation of the Grhl3-mediated cell proliferation defect, and enhanced susceptibility to NTDs. We conclude that lamin B1 is a modifier gene of major effect for NTDs resulting from loss of Grhl3 function, a role that is likely mediated via the key function of lamin B1 in maintaining integrity of the nuclear envelope and ensuring normal cell cycle progression.
Published in the journal: . PLoS Genet 8(11): e32767. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1003059
Category: Research Article
doi: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1003059Summary
Neural tube defects (NTDs), including spina bifida and anencephaly, are common birth defects whose complex multigenic causation has hampered efforts to delineate their molecular basis. The effect of putative modifier genes in determining NTD susceptibility may be investigated in mouse models, particularly those that display partial penetrance such as curly tail, a strain in which NTDs result from a hypomorphic allele of the grainyhead-like-3 gene. Through proteomic analysis, we found that the curly tail genetic background harbours a polymorphic variant of lamin B1, lacking one of a series of nine glutamic acid residues. Lamins are intermediate filament proteins of the nuclear lamina with multiple functions that influence nuclear structure, cell cycle properties, and transcriptional regulation. Fluorescence loss in photobleaching showed that the variant lamin B1 exhibited reduced stability in the nuclear lamina. Genetic analysis demonstrated that the variant also affects neural tube closure: the frequency of spina bifida and anencephaly was reduced three-fold when wild-type lamin B1 was bred into the curly tail strain background. Cultured fibroblasts expressing variant lamin B1 show significantly increased nuclear dysmorphology and diminished proliferative capacity, as well as premature senescence, associated with reduced expression of cyclins and Smc2, and increased expression of p16. The cellular basis of spinal NTDs in curly tail embryos involves a proliferation defect localised to the hindgut epithelium, and S-phase progression was diminished in the hindgut of embryos expressing variant lamin B1. These observations indicate a mechanistic link between altered lamin B1 function, exacerbation of the Grhl3-mediated cell proliferation defect, and enhanced susceptibility to NTDs. We conclude that lamin B1 is a modifier gene of major effect for NTDs resulting from loss of Grhl3 function, a role that is likely mediated via the key function of lamin B1 in maintaining integrity of the nuclear envelope and ensuring normal cell cycle progression.
Introduction
Modifier genes have been ascribed significant influence in determining susceptibility to disease in complex traits, as well as partial penetrance and variable expressivity of monogenic conditions [1]. Moreover, modifier genes are considered largely responsible for the phenotypic variation observed when mutations are bred onto different genetic backgrounds in mice. However, identification of modifier genes and determination of their functional effects presents a considerable challenge. Understanding the genetic basis of neural tube defects (NTDs), such as spina bifida and anencephaly, typifies these difficulties.
NTDs are common, severe congenital malformations resulting from failure of closure of the neural tube during embryonic development [2]. In humans, they are among the commonest birth defects, affecting around 1 per 1000 pregnancies worldwide. However, the causes are not well understood owing to their multigenic inheritance and the potential influence of environmental factors, either predisposing or ameliorating [3], [4]. The potential complexity of NTD genetics is illustrated by the fact that more than 200 different genes have been implicated as potential contributors to the overall burden of NTDs, with neural tube closure phenotypes in mouse strains carrying naturally occurring or targeted mutations [5]–[7]. Additionally, in many of these models penetrance is influenced by genetic background, indicating the presence of modifier genes.
The curly tail (ct) mouse mutant is among the most extensively characterised models of NTDs [8]. Approximately 5–10% of homozygous ct/ct embryos develop cranial NTDs (exencephaly), while 15–20% exhibit spinal NTDs (spina bifida), due to failure of closure of neural folds in the prospective brain and low spinal region, respectively. The major ct gene corresponds to a hypomorphic allele of the transcription factor grainyhead-like-3 (Grhl3), null mutants of which display spina bifida with 100% penetrance [9]–[11]. Expression of Grhl3 is diminished in the hindgut of ct mutant embryos, due to an upstream regulatory mutation, resulting in a diminished cellular proliferation rate in the hindgut endoderm [12], [13]. The consequent dorso-ventral growth imbalance leads to excessive ventral curvature of the caudal region of the embryo and, hence, mechanical suppression of neural tube closure at the posterior neuropore [14]. The incidence of curly tail NTDs can be influenced by multiple environmental and genetic factors [8], [15]–[18]. In addition, NTD frequency is also markedly affected by backcross to different strains, indicating the presence of modifier loci in the curly tail genetic background [19]. Thus, it is apparent that the genetic component of predisposition to NTDs is multifactorial in ct, as in humans.
In the current study, we identified lamin B1 as a modifier gene for NTDs in curly tail mice. Lamins are intermediate filament proteins of which the A-type, lamins A and C, are encoded by LMNA while, among the B-type, lamin B1 is encoded by LMNB1 and lamins B2 and B3, are encoded by LMNB2. The nuclear lamina is a protein complex underlying the inner nuclear membrane and composed of a meshwork of lamin polymers and lamin-binding proteins [20]–[22]. In addition to a key structural role in assembly and maintenance of the nuclear envelope, it has become clear that lamins have multiple functions in a diverse range of cellular properties. Thus, lamins influence nuclear shape and size as well as anchoring of protein structures, including nuclear pore complexes, in the nuclear envelope [23], [24]. Additionally, lamins function in DNA synthesis and transcriptional regulation both through interaction with chromatin, to mediate sub-nuclear chromosomal positioning, and by direct interactions with transcription factors [25]–[29].
Highlighting the importance of lamin function, a number of clinically distinct diseases, termed laminopathies, have been found to result from mutation of LMNA [20], [30]. These include muscular dystrophy disorders (e.g. Emery-Dreyfus muscular dystrophy), lipodystrophies, progeria syndromes (e.g. Hutchinson-Gilford progeria syndrome and Atypical Werner syndrome) and peripheral neuropathy (Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 2B1). In contrast to LMNA, coding mutations in LMNB1 have not so far been associated with human disease, although genomic duplication of LMNB1 is thought to cause a progressive demyelinating disorder, adult-onset autosomal dominant leukodystrophy [31], [32]. Mice homozygous for a loss of function allele of Lmnb1 die at birth with reduced growth, impaired lung development and cortical abnormalities in the brain [33], [34], while Lmnb2 knockouts exhibit neuronal migration defects in the cerebral cortex and cerebellum [35]. Lmnb1/lmnb2 double knockouts exhibit a reduced thickness of the brain cortex, with altered cell cycle exit of neuronal progenitors and neuronal migration defects [29], [34]. Forebrain-specific deletion of lmnb1 or lmnb2, allowed study of brain phenotypes at post-natal stages and showed that both genes are individually required for normal development of the cortex [34].
In the current study we identified a polymorphic variant form of lamin B1, present on the genetic background of the curly tail strain. The reduction in length of a series of glutamic acid residues, from nine to eight, was found to cause significant reduction in the stability of the lamin B1 interaction within the nuclear lamina. Genetic analysis, involving generation of curly tail sub-strains carrying combinations of the lamin B1 variant and Grhl3ct mutation demonstrate a dramatic effect of lamin B1 on frequency of NTDs. In parallel, lamin B1 has a profound effect on nuclear morphology and proliferative capacity. Overall, our findings show that Lmnb1 can act as a modifier gene affecting risk of NTDs, an effect that appears to be mediated through impaired cell cycle regulation which summates with the effect of Grhl3 mutation.
Results
In a proteomic analysis of the curly tail mutant, two-dimensional protein gels were generated from samples at embryonic day (E) 10.5: the stage of spinal neural tube closure. Comparison of stage-matched embryos revealed differential migration of a series of three spots, which migrated to a more basic position in gels derived from ct/ct samples than the equivalent spots in congenic wildtype (+ct/+ct) control gels (Figure 1A–1C). This migration change was apparent by the complete absence of the three spots that were detected in the +ct/+ct gels from the ct/ct gels and vice versa. This difference was detected both in analysis of whole embryos and in isolated caudal regions that encompassed the posterior neuropore (PNP), the region of active neural tube closure. In both strains, these spots were identified by liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry as lamin B1 (Table S1). Variation in abundance of some other spots between genotypes was observed, however, no spots other than those corresponding to lamin B1 showed a difference in migration. Neither the abundance of Lmnb1 mRNA nor total lamin B1 protein abundance were found to differ between ct/ct and +ct/+ct embryos, by real time qRT-PCR or western blot respectively (Figure 1D–1F). Moreover, the sites of Lmnb1 expression at neurulation stages were also comparable between genotypes as determined by whole mount in situ hybridisation (Figure 1G–1H). Expression was apparent throughout most of the embryo with the exception of surface ectoderm and the heart (Figure S1), where staining intensity was much lower than in other tissues.
Fig. 1. Lamin B1 shows differential protein migration by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis in curly tail and wild-type embryo samples. 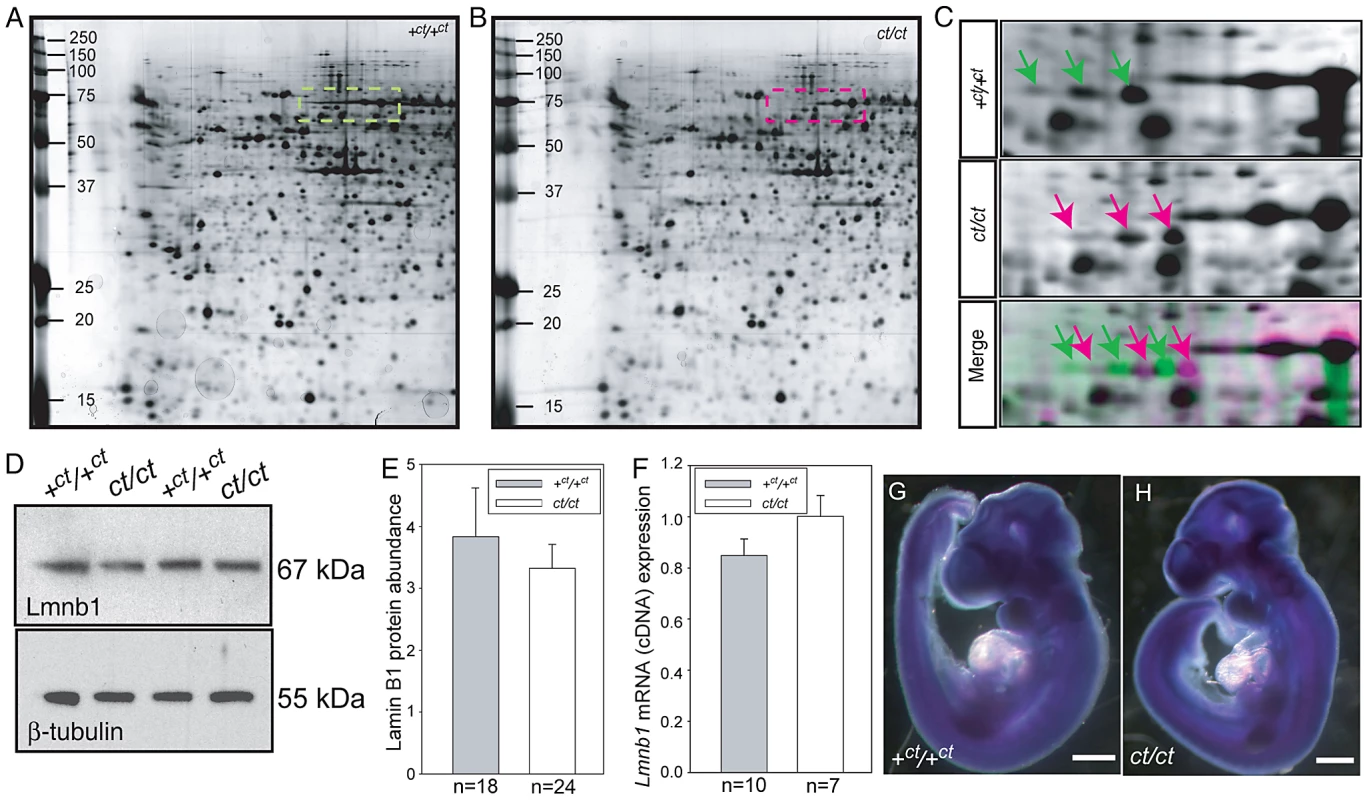
Protein profiles of the caudal region of stage-matched wild-type (A) and curly tail (B) embryos analysed by 2-DE (representative gels shown encompass pH 3.0–5.6 on the x-axis, basic pH to the right). A series of silver-stained protein spots exhibits a different migration pattern (C: enlarged area of gel corresponds to dashed box in A and B). On 2-DE of ct/ct samples, spots (pink arrows and pink spots on merged image) migrate to a more basic position than the corresponding spots on +ct/+ct gels (green arrows and green spots on merged image). Spots whose migration does not differ between samples appear black on the merged image. Western blot (D–E) and qRT-PCR (F) of protein and mRNA samples from the caudal region of +ct/+ct and ct/ct embryos at E10.5 show no significant difference between strains in relative abundance of either lamin B1 protein (normalised to beta-tubulin; arbitrary units) or mRNA (normalised to Gapdh with one wild-type sample chosen as calibrator; value set to 1.0). Number of samples, n, is shown on graphs. (G, H) The distribution of Lmnb1 mRNA at E10.5, as determined by whole mount in situ hybridisation is comparable in wild-type and ct/ct embryos (scale bar represents 1 mm). Altered migration of lamin B1 during the isoelectric focussing step of 2-DE results from a charge difference between the protein in ct/ct and +ct/+ct samples. Such a difference could potentially result from an alteration in primary sequence and the Lmnb1 coding region was therefore sequenced in ct/ct and +ct/+ct genomic DNA and cDNA. A synonymous polymorphism, C612T (annotated as SNP 18 : 56868078), was found in exon 1 of the ct/ct sequence. In addition, a three base-pair GAG deletion (annotated as Deletion 18 : 56909394) was noted in exon 10. This deletion corresponds to one of a sequence of GAG nucleotides at position 1657–1683 of the coding sequence, encoding a stretch of nine glutamic acid (Glu) residues in the tail domain of the wild-type protein (Figure 2A, 2B). Thus, the curly tail Lmnb1 gene encodes eight Glu residues at amino acids 553–560 (here denoted Lmnb18E to indicate number of glutamic acids), as opposed to nine Glu (residues 553–561) encoded by the +ct/+ct sequence (denoted Lmnb19E). Since Glu carries a negative charge, it appeared likely that the difference in number of Glu residues is responsible for the migration difference of lamin B1 spots on 2D gels generated from ct/ct and +ct/+ct samples.
Fig. 2. Lamin B1 shows variation in length of glutamic acid repeat, which significantly affects mobility within the nuclear envelope. 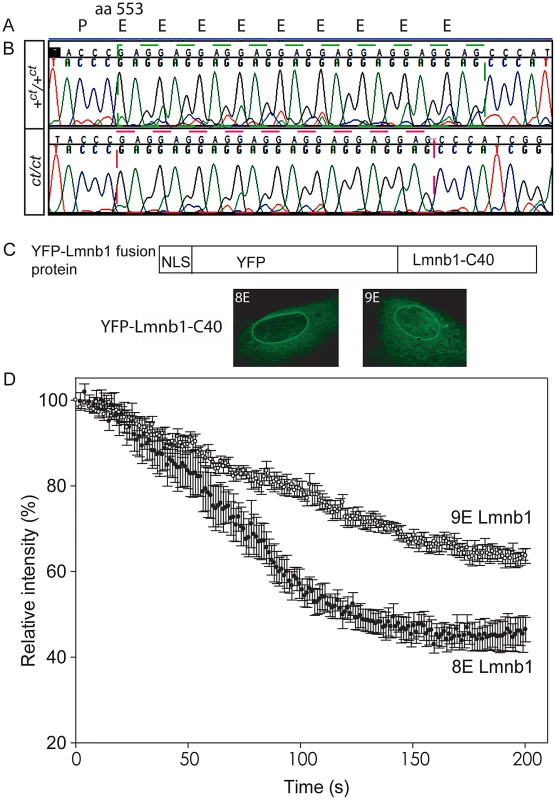
(A) Lamin B1 protein sequence contains a series of Glu (E) residues beginning at amino acid 553, encoded at the genomic level by a GAG repeat. (B) The wild-type (+ct) sequence encodes nine E residues, whereas the curly tail sequence encodes only eight E residues (one fewer GAG). (C–D) Fluorescence loss in photobleaching (FLIP) was performed to examine the mobility of NLS-YFP-Lamin B1 tail domain fusion proteins, containing eight or nine Glu residues. (C) Fusion proteins are shown diagrammatically and localised to the nuclear envelope as expected. (D) The relative intensity of fluorescence in an unbleached region of the nuclear envelope compared with pre-bleaching (time 0) was determined. Mean intensity ± SEM is shown for five nuclei with each construct. There is a more rapid decline in intensity in cells expressing the 8E variant (red circles) compared with the 9E variant (open circles), and differences persist throughout the experiment. Statistical analysis shows a significant difference between the 8E and 9E variants at both the 100 s and 200 s time points (p<0.001, t-test). The Glu repeat in the lamin B1 tail domain is predicted to form an alpha-helix (PSIPRED secondary structure prediction [36]). Loss of a residue would impose a hundred degree rotation on the C-terminal region of the protein. The helix is likely to be capable of interacting with the inner nuclear phospholipid membrane [37]. Given that this region contains another strong membrane interactor, the C-terminal farnesylcysteine, we hypothesised that the interaction of lamin B1 with the nuclear membrane could be affected by variation in the number of Glu residues. We therefore used fluorescence loss in photobleaching (FLIP) to investigate possible functional effects on the stability of the lamin B1 tail domain within the nuclear envelope. Full length laminB1-YFP fusion proteins appeared to be stably integrated into the nuclear lamina without apparent difference between variants. We also tested truncated forms of the protein as these have previously been found to provide greater sensitivity to altered properties in this assay [26]. Fusion proteins comprising a nuclear localisation sequence, YFP and the forty C-terminal residues of lamin B1 were expressed in primary mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) and subjected to FLIP, as previously performed for human lamin B1 [26]. The decline in fluorescence intensity in the unbleached area of membrane was much more rapid in cells expressing Lmnb18E compared with Lmnb19E (Figure 2C). After 100 seconds, there was an approximately 43% decline in intensity in cells expressing Lmnb18E compared with only a 21% decline with Lmnb19E (p<0.001, t-test). This significant difference between variants persisted throughout the analysis, and is indicative of increased mobility, and hence decreased stability of interaction of Lmnb18E within the nuclear envelope.
Sequencing of exon 10 of lamin B1 in a series of mouse strains showed that the wild-type (Lmnb19E) variant of lamin B1 is found in the majority of strains including C57BL/6, C3H/HeJ, SWR, DBA/2J, BALB/c, LPT/Le and CAST/EiJ. However, the Lmnb18E variant occurs in CBA/Ca, a sub-strain of which (CBA/Gr) contributed to the genetic background of the curly tail strain [38]. The variant was also present in the 101 strain and hence in mice harbouring the splotch (Sp2H; Pax3) mutation, which arose in a mutagenesis experiment on a mixed CBA/101 genetic background [39]. The 18 : 56868078 SNP and Deletion 18 : 56909394 were found to be in linkage disequilibrium. Thus, the Lmnb18E variant in ct/ct is characteristic of this particular genetic background.
Embryos of the CBA/Ca strain do not exhibit developmental abnormalities under normal laboratory conditions, indicating that the Lmnb18E variant alone is insufficient to cause NTDs. Nevertheless, given the possible effect on stability of the lamina, we speculated that this variant could represent one of the modifier genes that are major determinants of penetrance of the curly tail defect. To test this idea, we inter-crossed ct/ct and +ct/+ct mice to generate sub-strains of mice carrying different combinations of the Lmnb1 variant (i.e. Lmnb18E and Lmnb19E; abbreviated hereafter as L8E and L9E) and the Grhl3 mutant allele (Grhl3ct or Grhl3+; abbreviated as Gct and G+). Each sub-strain was maintained in homozygous form for both Lmnb1 and Grhl3 alleles, that is: (i) L8E/8E; Gct/ct (denoted ct8E); (ii) L8E/8E; G+/+ (denoted +ct;8E); (iii) L9E/9E; Gct/ct (denoted ct9E); (iv) L9E/9E; G+/+ (denoted +ct;9E). In the +ct strain the genetic background is approximately 97% curly tail [9] and in each sub-strain it is predicted to be 99.5% curly tail (see Figure S2 for breeding scheme). Embryos were collected at E11.5–15.5 and analysed for the presence or absence of NTDs.
Among embryos of the ct8E sub-strain, the range and frequency of phenotypes was closely similar to that observed in the curly tail (ct) strain which has the same genotype at the Lmnb1 and Grhl3 loci. Defects included spina bifida, tail flexion defects and exencephaly (Figure 3B–3D), while other embryos appeared normal (Figure 3A). Importantly, however, varying the Lmnb1 genotype produced a striking difference in frequency of NTDs (Figure 3E). Thus, spina bifida occurred at significantly lower frequency in the ct9E sub-strain (5.8%) than in curly tail (14.2%) or in the ct8E sub-strain (15.8%). Therefore, homozygosity for the Lmnb18E variant confers approximately three-fold higher risk of spina bifida in Gct/ct embryos, compared with homozygosity for the Lmnb19E variant. Interestingly, although cranial NTDs occur at lower frequency than spina bifida in the curly tail strain, we also observed the rate of exencephaly to be significantly reduced among ct9E embryos (3.0%) compared with curly tail (6.4%) or ct8E embryos (8.2%). As expected, the frequency of exencephaly in the latter two strains did not differ significantly (Figure 3E).
Fig. 3. The frequency of NTDs resulting from mutation of Grhl3 is affected by Lmnb1 genotype. 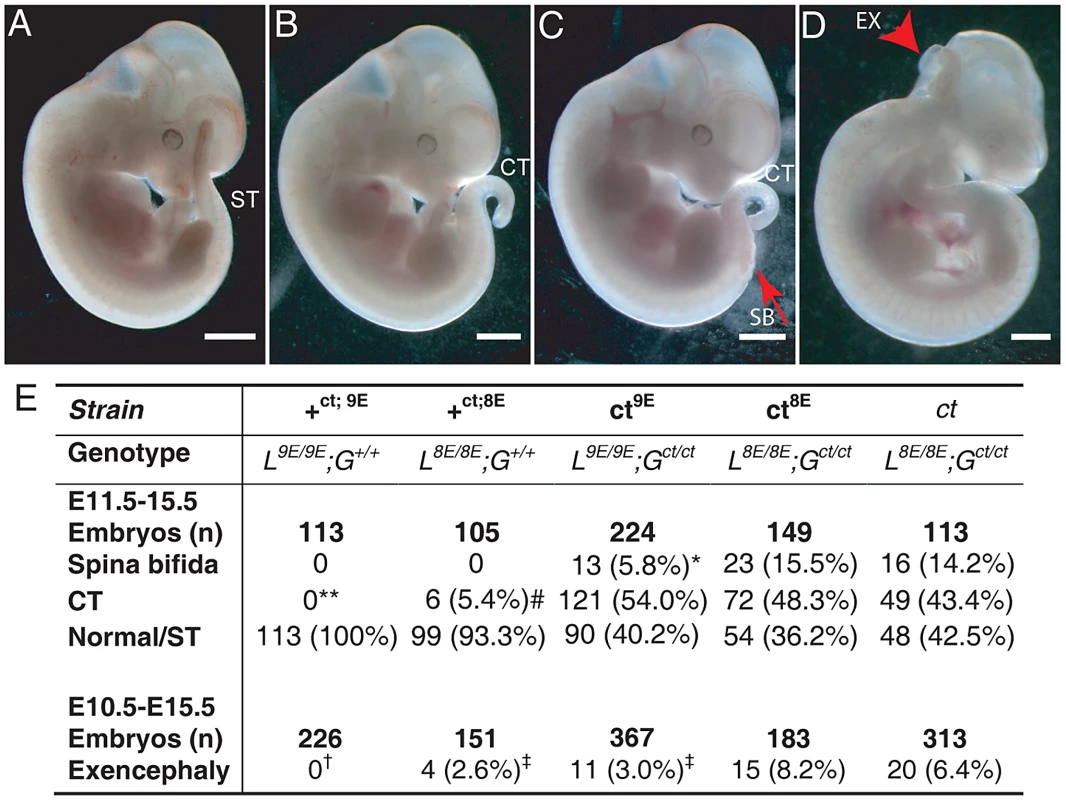
Embryos were scored as (A) apparently normal with a straight tail (ST), or with (B) a tail flexion defect (i.e. curly tail; CT), (C) spina bifida (SB) plus tail flexion defect, and/or (D) exencephaly (arrowhead indicates open hindbrain). Note that exencephaly can occur in association with any of the spinal phenotypes. Embryos shown are from the ct9E sub-strain. The frequency of NTD phenotypes is tabulated (E). The frequency of SB is significantly lower in the ct9E than in the ct8E and ct strains (* p<0.02, χ2 test). Spina bifida and tail flexion defects were never observed among +ct;9E embryos but tail flexion defects did occasionally occur among +ct;8E embryos (** +ct;9E versus +ct;8E; p<0.05; Z-test), although at significantly lower frequency than among ct mutant embryos (# p<0.001; χ2). There is significant variation in the frequency of exencephaly between the sub-strains (p<0.001; χ2) with a significantly lower exencephaly rate among ct9E than ct8E embryos (‡ significantly different from ct8E, p<0.01; Z-test). Exencephaly was not observed in the +ct;9E strain († indicates significant difference from ct and ct8E (p<0.001; Z-test) and ct9E (p<0.02) strains). Exencephaly was observed in the +ct;8E strain, albeit at a significantly lower frequency than in the ct8E strain (‡ p<0.05; Z-test). Although the genetic background of each sub-strain was predicted to be approximately 99.5% curly tail we could not exclude a possible effect of the region of DNA that is tightly linked and inherited with lmnb1. We therefore examined the possibility that a neighbouring gene to lmnb1 could vary in expression between the ct9E and ct8E sub-strains. Using a list of genes that are located within a 41 Mb interval of chromosome 18 centred on lmnb1, we interrogated microarray data generated from RNA of the caudal region of stage-matched ct/ct and +ct/+ct embryos (E10.5; 28–29 somite stage). Among 11 differentially expressed genes (p<0.05; fold-change 1.5-fold or greater), 4 showed a similar trend of differential expression on qRT-PCR analysis of independent ct/ct and +ct/+ct samples. However, none of these genes varied in expression when analysed by qRT-PCR in stage-matched ct9E and ct8E samples (Table S2), suggesting that the phenotypic difference between the sub-strains does not result from differential expression of genes located in proximity to lmnb1. Instead, variation in expression between ct/ct and +ct/+ct samples seem likely to be due to downstream effects of the Grhl3ct mutation in ct/ct embryos.
Embryos of the wild-type congenic curly tail strain (+ct;9E, genotype: L9E/9E; G+/+) do not develop exencephaly, spina bifida or tail flexion defects (Figure 3E) [9]. However, when the Lmnb18E variant was bred onto the Grhl3 wild-type genetic background, to produce mice of L8E/8E; G+/+ genotype (+ct;8E), we observed a low frequency of tail flexion defects, indicative of delayed PNP closure (Figure 3E). Exencephaly was also occasionally observed (Figure 3E). These data demonstrate that the presence of the Lmnb18E variant can predispose to defects of cranial and spinal neural tube closure, even in the absence of the Grhl3 mutation.
Although curly tail NTDs are partially penetrant, affected embryos can be recognised on the basis of an enlarged PNP at E10.5 [40]. In order to examine the effect of Lmnb1 variants on the progress of spinal neural tube closure directly, PNP length was measured in a series of embryos at E10.5 (Figure 4). Among embryos that were wild-type at the Grhl3 locus (+ct and +ct;8E), PNP length diminished rapidly between the 26 and 31 somite stages and, by the 30–31 somite stage, the PNP was very small (12 out of 37 embryos) or closed (25 of 37 embryos). There was no detectable difference between embryos with Lmnb18E/8E and Lmnb19E/9E genotypes. In contrast, mean PNP lengths were significantly larger in the Grhl3ct/ct sub-strains, reflecting an overall delay in closure. Although mean PNP length did not differ between curly tail and the ct8E sub-strain, embryos of the ct9E sub-strain exhibited a more rapid reduction in PNP length from the 28–29 somite stage onwards (Figure 4), indicative of an overall normalisation of spinal neural tube closure. The distribution of PNP lengths in embryos of the ct9E sub-strain was shifted towards smaller values, with a significantly lower mean PNP length. Moreover, only a few ct9E embryos showed very large PNPs, whereas a greater proportion of embryos had completed PNP closure by the 30–31 somite stage (8 of 30 compared with 1 out of 20 among the ct8E sub-strain; p<0.05, z-test; Figure S3). These observations on PNP length correlate with the diminished frequency of spina bifida in the ct9E sub-strain later in development.
Fig. 4. Variation in mean PNP length of embryos of the curly tail sub-strains. 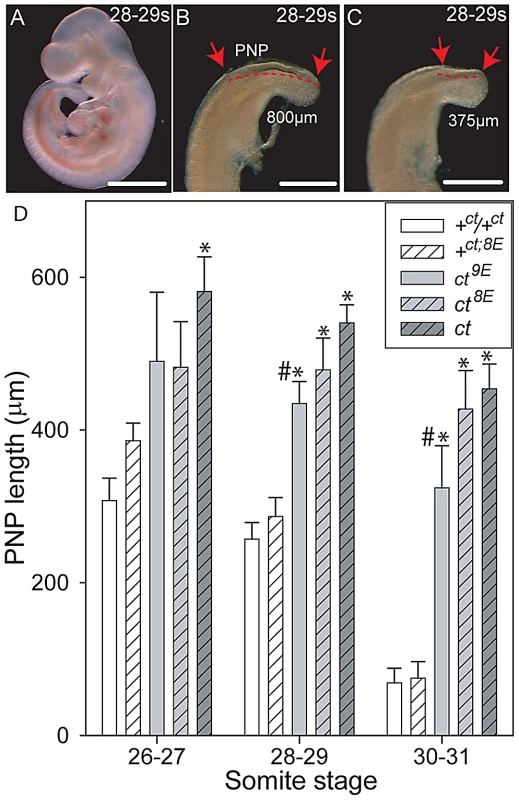
(A–C) Curly tail embryos at the 28–29 somite stage (E10.5), showing whole embryo (A) and enlarged views of two different caudal regions (B, C) to illustrate variable PNP lengths (between the arrows and indicated by dotted lines). An enlarged PNP (e.g. 800 µm length in B) is indicative of delay or failure of closure compared with a smaller PNP (e.g. 375 µm in C). Scale bars represent 1 mm in A and 0.5 mm in B, C. (D) PNP length measurements (mean in µm ± SEM) at somite stages around the time of PNP closure. At 28–29 and 30–31 somites, the mean PNP lengths of embryos of the ct, ct8E and ct9E strains (i.e. Grhl3 mutants; grey bars) are significantly larger than those of stage-matched embryos wild-type at the Grhl3 locus (i.e. +ct and +ct;8E; white bars), regardless of Lmnb1 genotype (* significantly different from Grhl3 wild-type strains, p<0.001; ANOVA and Holm-Sidak pairwise comparisons). This difference is also observed for the ct strain at the 26–27 somite stage. At each stage, the mean PNP length of +ct8E embryos is larger than for +ct embryos, but this difference does not reach statistical significance. Among ct sub-strains, embryos carrying the Lmnb19E allele had the smallest PNP lengths at each stage analysed (# significantly different from ct strain; p<0.001). Number of embryos corresponding to each bar: n = 5–16 at the 26–27 somite stage; n = 14–66 at the 28–29 and 30–31 somite stages. Generation of the curly tail sub-strains provided an opportunity to test directly whether the variation in number of Glu residues is responsible for the 2-DE migration difference of lamin B1 in curly tail and wild-type samples. 2D gels were generated from mouse strains expressing the Lmnb18E (ct, ct8E, +8E) or Lmnb19E (+ct, ct9E) variants. In each case the migration pattern corresponded with the number of Glu residues (Figure S4), confirming that the characteristic strain-dependent 2-DE pattern reflects the Lmnb1 polymorphism.
We hypothesised that the mechanism by which variation in lamin B1 sequence affects risk of NTDs could relate to the apparent effect on stability of the nuclear lamina, as shown by FLIP. In order to further examine the effects of the lamin B1 variants, we examined nuclear morphology in MEFs derived from embryos of differing strains. We previously showed that Grhl3 is expressed in MEFs and that the expression deficit is observed in cells derived from curly tail embryos, as in the embryos themselves [41]. Immunostaining for lamin A and lamin B1 allowed visualisation of nuclear shape and, among curly tail MEFs, many nuclei showed a high degree of irregularity in shape, including herniations and/or lobulations (Figure 5A). Moreover, in a proportion of curly tail cells, lamin B1 staining was discontinuous. Lamin A showed a similar distribution to lamin B1, suggesting that the variant lamin B1 imposes a dysmorphic phenotype on the nuclear lamina as a whole. Abnormalities were much less frequent in nuclei of the +ct;9E and C57BL/6 strains, carrying wild-type alleles of Lmnb1 and Grhl3. To provide a quantitative measure of nuclear morphology, the contour ratio (4???×area/perimeter) of DAPI-stained nuclei was analysed (Figure 5B, 5C). The mean contour ratio was significantly lower for ct nuclei than for any of the other strains (Figure 5B). Consistent with these findings, compared with other strains examined, a significantly greater proportion of ct nuclei showed a contour ratio of less than 0.7 (Figure 5C), which is considered abnormal [42].
Fig. 5. Nuclear morphology is influenced by Lamin B1 variation. 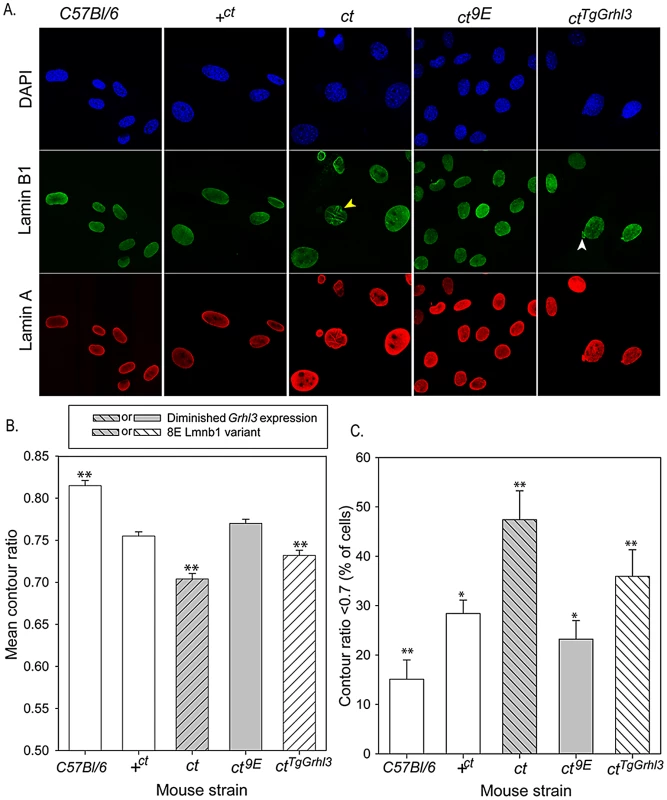
(A) MEFs derived from embryos of various genotypes were stained with DAPI (blue) and antibodies to lamin B1 (green) and lamin A (red) to highlight the nuclear lamina. Abnormalities observed include lobulations (yellow arrowhead) and herniations (white arrowhead). (B, C) Analysis of MEF nuclei reveals significant differences between sub-strains in (B) mean contour ratio and (C) percentage of nuclei with contour ratio lower than 0.7, which is considered dysmorphic (p<0.001; ANOVA). (B) Mean contour ratio (expressed as mean ± SEM) is significantly higher in C57BL/6 and significantly lower in ct than all other strains. (C) Compared with all other strains, ct has a significantly higher frequency of dysmorphic nuclei (47.4±5.8%) and C57BL/6 (15.1±3.9%) has significantly fewer dysmorphic nuclei (** significant difference from all other strains, p<0.01). The proportion of dysmorphic nuclei is lower in strains with the wild-type Lmnb19E allele, but higher than in C57BL/6; * indicates significantly different from all other strains (p<0.01 for comparison with C57Bl/6, ct and ctTgGrhl3 and p<0.05 for comparison with +ct or ct9E). Over-expression of Grhl3 partially normalises nuclear phenotype in the ctTgGrhl3 strain (despite presence of Lmnb18E variant as in ct). The mean contour ratio is significantly higher than in the ct strain but lower than in ct9E or +ct strains (** indicates significant difference compared with all other strains tested, p<0.01). Values are an average of 9–15 experiments, using 2–3 independent cell lines for each strain. Total number of cells analysed: 579 C57BL/6; 895 +ct; 757 ct; 882 ct9E; 837 ctTgGrhl3. The curly tail nuclear dysmorphology phenotype was rescued by the presence of the Lmnb19E variant in the ct9E sub-strain (Figure 5), correlating with the apparent increased stability of the lamina when this variant is present, as observed by FLIP (Figure 2C). Interestingly, in MEFs from a transgenic ct strain, ctTgGrhl3 in which Grhl3 expression is reinstated by over-expression from a Grhl3-containing BAC [9], the nuclear morphology was intermediate between that of ct and ct9E MEFs (Figure 5). Thus, although ctTgGrhl3 mice are on an identical genetic background to ct, including the Lmnb18E variant, it appears that over-expression of Grhl3 is sufficient to partially ameliorate the nuclear dysmorphology phenotype. The mean contour ratio of nuclei was higher, and the proportion of abnormal nuclei was lower, for C57BL/6 than any of the other strains, including +ct;9E (Figure 5). Thus, in addition to lamin B1 sequence and Grhl3 expression, other factors associated with the curly tail genetic background may influence nuclear morphology. Overall, among strains with the curly tail genetic background, those that express the Lmnb19E variant (+ct;9E and ct9E) have a significantly higher mean contour ratio (Figure 5B) and fewer dysmorphic nuclei (Figure 5C) than those that express the Lmnb18E variant (ct and ctTgGrhl3).
The effect of the Lmnb18E variant on nuclear morphology and the known function of lamins in nuclear function, including DNA replication [24], prompted us to investigate the effect of the Glu variant on proliferative capacity in ct cells. MEFs were plated and counted after 4 hours (t = 0) and after successive 24 hour periods up to 5 days. Growth curves showed that ct8E MEFs proliferate significantly more slowly than their ct9E counterparts over the first four days in culture (p<0.05; Multiple linear regression, R2 = 0.948) and then undergo a ‘proliferative crisis’ where cell numbers cease to increase (Figure 6A). The experiment was performed on three separate occasions using independent cell lines, with the same result each time. Therefore, in addition to nuclear dysmorphology, the Lmnb18E variant is associated with an apparent reduction in proliferative capacity in ct cells. In contrast, ct9E cells continued to proliferate at a similar rate to wild-type +8E cells at day 5 (Figure 6A). In accordance with the growth curve data, we also noted that when MEFs were repeatedly passaged, ct8E fibroblasts show a dramatic loss of proliferative capacity from passage 5 onwards, whereas ct9E continue to exhibit similar doubling times up to at least passage 8.
Fig. 6. Cell cycle progression is impaired in curly tail cells and embryos expressing the Lmnb18E variant. 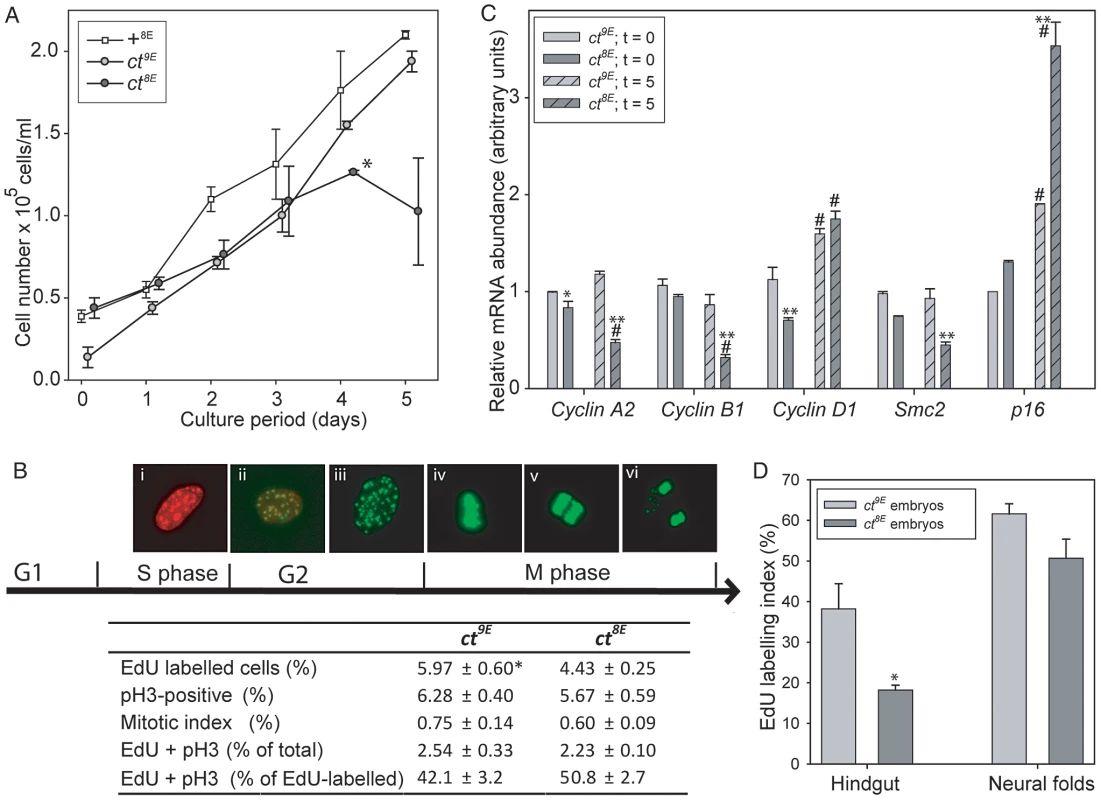
In cultured embryonic fibroblasts (A–C), analysis of growth curves (A) shows that ct8E cells proliferate significantly slower than ct9E cells (*p<0.05; multiple linear regression for days 0–4) and then undergo a ‘growth crisis’ after 4 days culture. (B) Cell cycle analysis was performed at day 0 (5 hours of culture) using EdU to label cells as they progress through S phase (Bi) and anti-phospho Histone H3 (pH 3) to label cells in G2/M (Bii–vi). Mitotis was scored visually as cells that were in prophase, metaphase (Biv), anaphase (Bv) or telophase (Bvi). Data represents the mean of three experiments, each using an independent cell line, plated in triplicate. ct8E cells show significantly reduced EdU labelling (* p<0.05; t-test). There is a trend towards reduced pH 3 labelling and mitotic index in ct8E cells, but this difference is not statistically significant. The proportion of cells double-labelled with EdU and pH 3 (Bii) does not differ between ct8E and ct9E cells. (C) Expression of cell cycle regulators determined by qRT-PCR. For each gene, significant differences in the comparison of ct8E and ct9E cells cultured for the same period are indicated (* p<0.05, ** p<0.01; ANOVA with Holm-Sidak Pairwise Comparison). Expression differences between 0 and 5 days in culture for cells of the same genotype are indicated (# p<0.05). (D) Analysis of proliferation in embryos at E10.5 showed that EdU labeling index was significantly diminished in the hindgut of ct8E compared with ct9E embryos (* p<0.02; t-test). To further investigate cell cycle properties of ct8E and ct9E cells, labelling with 5-ethynyl-2′-deoxyuridine (EdU; to monitor S-phase progression) and immunostaining for phospho-histone H3 (pH 3; a marker of mitosis) were performed on day 0. This is well before the profound loss of proliferative capacity that occurs in ct8E cells after extended culture and it was therefore predicted that differences, if present, may be subtle. However, corresponding with growth curve data, we observed significantly fewer EdU-labelled ct8E cells than ct9E cells (Figure 6B), together with a non-significant reduction in pH 3 labelling (cells in G2/M phase) and mitotic index. Consistent with the reduced EdU labelling in ct8E cells, indicating that fewer cells had passed through S-phase, we observed a slightly lower proportion of EdU/pH 3 double-labelled nuclei. However, there was no difference between strains in the number of double-labelled cells as a proportion of the total number of EdU-labelled cells (Figure 6B), suggesting that progression from S-phase to G2 is not defective in ct8E cells.
We next examined the expression of key regulators of cell cycle expression by qRT-PCR, 4 hours after plating (t = 0, as for cell cycle analysis) and after 5 days of culture (t = 5). The reduced proliferative capacity of ct8E cells during the initial growth period was associated with significantly lower expression of Ccnd1, encoding cyclin D1 (Figure 6C). After 5 days, the expression of Ccna2 and Ccnb1 (encoding cyclin A2 and cyclin B1, respectively) was also significantly reduced in ct8E compared with ct9E cells, consistent with diminished cell cycle progression [43], [44]. Conversely, there was a dramatic increase in expression of p16Ink4a (Figure 6C), which suppresses cell cycle progression through inhibition of cyclin D-dependent kinases [45] and is a hallmark of cells entering senescence. The expression of p16Ink4a was also increased in ct9E cells at t = 5 compared with t = 0, but to a much lesser extent. In addition, at both stages ct8E cells also exhibited a significant reduction in expression of Smc2, which encodes a core component of the condensin I and II complexes that play key roles in chromosome condensation during mitosis [46], [47]. We conclude that changes in expression of cell cycle-associated proteins are consistent with reduced cell cycle progression in cells expressing the Lmnb18E variant, compared with those expressing the wild-type Lmnb19E variant.
Finally, we tested whether the Lmnb1 variants were also associated with differences in cellular proliferation rate in the developing embryo. Analysis was performed on the neural folds and hindgut at the axial level of the closing PNP, at the stage at which the underlying defect in proliferation in the hindgut of affected curly tail embryos was reported [12], [13]. Consistent with the findings in cultured cells, the EdU labelling index was lower in ct8E than in ct9E embryos, particularly in the hindgut (Figure 6D, Table S3). Mitotic index was similar in the sub-strains (Table S3). The diminished S-phase progression of cells in the hindgut of ct8E embryos corresponds with the proliferation defect that is known to underlie spinal NTDs in curly tail embryos.
Discussion
The multifactorial, partially penetrant genetics of the curly tail mouse provided an opportunity to investigate the Lmnb1 polymorphism as a potential modifier of susceptibility to NTDs. In the context of the genetic background of the curly tail mouse, we observed a major effect of lamin B1 on development of the neural tube, the embryonic precursor of the brain and spinal cord. Curly tail sub-strains expressing the Lmnb18E variant demonstrate failure of neural tube closure with significantly higher frequency than those that express wild-type protein. Thus, although both the curly tail sub-strains (ct9E and ct8E) are homozygous for the Grhl3ct mutation, which results in diminished Grhl3 expression [9], there is a three-fold difference in the frequency of NTDs depending on the co-existing Lmnb1 genotype. Strikingly, although exencephaly occurs at much lower frequency than spina bifida, Lmnb1 also affected the penetrance of these defects to a similar extent as spinal NTDs, with approximately 65% reduction in frequency among ct9E compared with ct8E embryos. Interestingly, it appears that the Lmnb18E variant may confer susceptibility to NTDs even in the absence of a Grhl3 mutation, at least in the context of the ct genetic background. Thus, +ct;8E embryos that are wild-type for Grhl3 but which carry the Lmnb18E variant developed occasional tail flexion defects and/or exencephaly. In contrast, spinal NTDs can be prevented by transgenic over-expression of Grhl3 expression (ctTgGrhl3) [9], despite the presence of the Lmnb18E variant.
The possible functional effect of polymorphic variants has been explored in very few proteins, to date. We found that the loss of a single Glu, in Lmnb18E, compromises the stability of lamin B1's interaction within the nuclear lamina. This effect is predicted to result from disturbance of the conformation of the C-terminal region of the protein, owing to the location of the variant Glu residue in a predicted alpha-helix.
The effect of the Glu repeat polymorphism on lamina stability in FLIP analysis correlates with the observation of a higher proportion of dysmorphic nuclei in ct MEFs that express the Lmnb18E variant compared with Lmnb19E. Abnormalities in lamin immunostaining and nuclear shape are reminiscent of cells with nuclear envelope abnormalities, such as from progeria models [42], lamin B1 mutant mice [33], [34] and following shRNA-mediated silencing of lamin B1 [48]. Using contour ratio analysis, abnormal nuclei were observed in around 47% of primary embryonic curly tail fibroblasts (current study), compared with 68% of primary dermal fibroblasts derived from a patient with Hutchison-Gilford progeria syndrome [42]. Only 7–15% of nuclei among control fibroblasts exhibited such abnormalities. In these previously reported examples, abnormalities of cell proliferation, chromosome position, transcription factor localisation and gene expression have all been noted [22], [26], [33].
We found a strong correlation between frequency of dysmorphic nuclei in MEFs derived from embryos of the ct strain, and frequency of NTDs. For example, among mice homozygous for the Grhl3ct hypomorphic allele, presence of the wild-type Lmnb19E led to a reduced NTD frequency and an increased proportion of ‘normalised’ nuclei in MEFs. These findings suggest that nuclear lamina function plays a contributory role to the efficiency of neural tube closure during embryogenesis. Whether altered nuclear structure directly affects NTD risk or is a secondary marker of altered lamin B1 function is not known. To investigate the cellular mechanism by which lamin B1 affects embryonic development we focussed on a possible effect on cell cycle progression, in view of the known tissue-specific cell cycle defect that underlies spinal NTDs in curly tail mice [8].
Lamin B1 functions in nuclear envelope breakdown/assembly and mitotic spindle formation [23], [25], [49]. In addition, lamin B types are spatially associated with and required for DNA synthesis during S-phase [50]. Effects of lamin B1 dysfunction on cell cycle regulation could also be mediated through altered regulation of gene expression. For example, sequestration of the transcription factor Oct-1 at the nuclear periphery is lost in cells expressing a truncated form of lamin B1, resulting in mis-expression of target genes, including cell cycle mediators [27], [51]. In ct fibroblasts expressing the Lmnb18E variant, analysis of growth curves and cell cycle markers revealed diminished proliferative capacity and premature senescence, accompanied by characteristic changes in expression of cell cycle mediators. Cell labelling experiments suggest that the reduced proliferation rate of ct8E cells does not result from a defect at the S-phase/G2 transition but more likely from impairment of G1 or G1/S transition. Such an idea is consistent with the reduced expression of cyclin D1, which promotes progression through G1/S. The proliferative crisis that occurs in ct8E following extended culture is accompanied by reduced expression of cyclins A2 and B1, which function at G2/M [52], and increased expression of p16Ink4a. Although our study addresses an amino acid change rather than reduced expression, these observations are consistent with recent studies showing that silencing of Lmnb1 expression reduces proliferation rate and induces premature senescence in fibroblast cell lines [53]. Altered cell cycle exit is also thought to be responsible for reduced thickness of the cortex in lmnb1/lmnb2 knockout embryos [29], [34].
Rather than a generalised growth retarding effect of the lamin B1 variant, it appears that there is an additive effect with the Grhl3ct mutation. Cell cycle differences between ct8E and ct9E cells therefore suggest a mechanism by which Lmnb1 genotype affects the morphogenetic movements of neural tube closure in curly tail mutant embryos. It was previously found that: (i) the cellular basis of spinal NTDs in curly tail mutant embryos involves a proliferation defect in cells of the hindgut which causes excessive axial curvature [12]; and (ii) inhibition of proliferation by anti-mitotics or experimental growth retardation increases frequency of cranial NTDs [18], [54]. Therefore, the reduction in cellular proliferation rate resulting from the combination of diminished Grhl3 expression together with perturbation of lamin B1 function, would be predicted to exacerbate both spinal and cranial neurulation, as we observe. In support of this model, and correlated with prevention of NTDs in embryos, reinstatement of Grhl3 expression in cultured cells that express the Lmnb18E variant partially normalises nuclear morphology (e.g. in ctTgGrhl3) and proliferative capacity (e.g. growth curves of +ct;8E and ct9E cells do not differ). Moreover, in vivo analysis confirmed that proliferation is diminished in the hindgut of ct8E compared with ct9E embryos, which suggests an explanation for their greater susceptibility to spinal NTDs.
Overall, our findings show that Lmnb1 is a modifier gene that has a significant influence on the risk of NTDs in curly tail (Grhl3ct) embryos. We propose that the Lmnb18E polymorphism and Grhl3ct mutation interact genetically to influence nuclear morphology and proliferation, and hence susceptibility to NTDs. The influence of gene-gene interactions on susceptibility to NTDs in the curly tail model parallels the apparent multigenic etiology of the corresponding human conditions. Thus, it appears possible that some individuals carry ‘risk’ alleles that are insufficient to cause NTDs when present in isolation, but confer susceptibility to NTDs when co-inherited with other predisposing alleles. We speculate that variation in human lamin B1, either in the Glu repeat or elsewhere in the protein, would be worthy of investigation in the context of human NTDs.
Methods
Maintenance of mice and genotyping
Curly tail (ct/ct), genetically-matched (partially congenic) wild-type (+ct/+ct) and transgenic curly tail mice carrying a Grhl3-expressing BAC (Grhl3ct/Grhl3;Tg(Grhl3)1NDEG, here referred to as ctTgGrhl3) were as described previously [8], [9]. A two-step breeding programme (Figure S2) was used to generate mice carrying different combinations of the Grhl3 alleles (referred to as Grhl3+ or Grhl3ct) and Lmnb1 variants (referred to as Lmnb19E and Lmnb18E). Mice of genotype Grhl3ct/ct; Lmnb18E/8E, Grhl3ct/ct; Lmnb19E/9E and Grhl3+/+; Lmnb18E/8E were selected and inter-crossed to establish independent colonies.
The Grhl3ct allele was genotyped on the basis of the putative mutation, C-21350T, upstream of Grhl3 by PCR amplification of genomic DNA with restriction digest of PCR products [9]. Genotyping was confirmed by PCR amplification of polymorphic microsatellite markers, D4Bwg1551e and D4Mit204, downstream of Grhl3. The Lmnb1 GAG repeat variant (Deletion, 18 : 56909394) was genotyped by PCR amplification of genomic DNA using primers that encompass the repeat (5′-GACCACCATACCCGAGGAG and 5′ - TCCACAGCCACTCCGATG), with separation of products on 5% agarose gels. The C612T SNP (18 : 56868078) creates a HindIII restriction site, allowing genotyping by PCR amplification of exon 1 (using primer pair 5′-GGCCTGTGGTTTGTACCTTC-3′ and 5′-GGCACCCCTGTTCAGTTCTA-3′), followed by restriction digest of the PCR product.
Collection of embryos
Experimental litters were generated by timed matings. Pregnant females were killed at embryonic day by cervical dislocation and embryos were dissected from the uterus in Dulbecco's Modified Eagle's Medium (Invitrogen) containing 10% fetal calf serum (Sigma). At E10.5, the caudal regions of individual embryos at the 30–31 somite stage were excised at the level of somite 15, rinsed in phosphate buffered saline (PBS) and stored at −80°C prior to analysis by 2-DE or Western blot. For in situ hybridisation embryos were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde (PFA) in PBS at 4°C overnight. Animal studies were carried out under regulations of the Animals (Scientific Procedures) Act 1986 of the UK Government, and in according with guidance issued by the Medical Research Council, UK in Responsibility in the Use of Animals for Medical Research (July 1993).
Two-dimensional gel electrophoresis (2-DE)
Samples, comprising whole embryos (n = 10 of each genotype) or individual caudal regions (n = 10 of each genotype), were prepared by sonication in lysis buffer as described previously [55]. Proteins were separated by isoelectric focussing on pH gradients of pH 4–7 or 3–5.6, followed by SDS-PAGE on 12% polyacrylamide gels, as described [56]. Gels were fixed and stained using PlusOne silver stain (GE Healthcare) and scanned using a GS-800 calibrated densitometer (BioRad). Gel images were analysed using Progenesis SameSpots (Non-linear Dynamics) with separate between-genotype comparisons for whole embryos (n = 5 pH 4–7 and 5 pH 3–5.6 gels for each genotype) and caudal regions (n = 5 pH 4–7 and 5 pH 3–5.6 gels for each genotype).
Liquid chromatography electrospray tandem mass spectrometry (LC-ESI-MS/MS)
Protein spots were excised manually from a minimum of four different gels, so that each spot was analyzed at least in quadruplicate, subjected to in-gel digestion with trypsin and analyzed by LC-ESI-MS/MS (QToF-micro; Waters Corp.) as described previously [55]. Mass spectrometry data were searched against the SwissProt database using the MASCOT search algorithm (Matrix Science, London, UK). One missed cleavage per peptide was allowed.
Sequence analysis
Genomic DNA fragments spanning exons of Lmnb1 were amplified by PCR (see Table S4 for primer sequences). Purified PCR products were sequenced using big dye terminator chemistry (Applied Biosystems) and analysed on a MegaBACE 1000 (Amersham). Sequence reads derived from both strands were assembled, aligned and analysed for nucleotide differences using Sequencher (GeneCodes).
Western blot
Protein lysates (1 µg per lane) in RIPA buffer were run on 10% Bis-Tris gels (NuPage, Invitrogen) and transferred to PVDF membrane (XCell II Blot Module, Invitrogen). Immunodetection was performed by standard methodology using antibodies to lamin B1 (S-20) and β-tubulin for normalisation (primary antibodies from Santa Cruz Biotechnology and used at 1∶1000). Proteins were detected using horseradish peroxidise-conjugated secondary antibodies (DAKO), followed by development with ECL plus Western blotting detection system (GE Healthcare). Films were scanned on a GS-800 Densitometer (Bio-Rad) for quantification.
Quantitative real–time RT–PCR
RNA was purified (TRIzol Reagent, Invitrogen) from isolated caudal regions of E10.5 embryos or from MEFs, genomic DNA removed by DNase I digestion (DNA-free, Ambion) and first strand cDNA synthesis carried out (SuperScript II, Invitrogen). qRT-PCR was performed (MESA Blue Mastermix for SYBR Assay, Eurogentec) on a 7500 Fast Real Time PCR system (Applied Biosystems), with each sample analysed in triplicate. Primers for Lmnb1 were designed to amplify a 221 bp product (nucleotides 1267–1487 of coding sequence (Ensembl NM 010721.1; ENSMUSG00000024590). Additional primer pairs were: cyclin A2 (Ccna2) 5′-CATGTCACTGCTGGTCCTTC and 5′ - TGATTCAAAACTGCCATCCA); cyclin B1 (Ccnb1) 5′-GGAAATTCTTGACAACGGTG and 5′-TGCCTTTGTCACGGCCTTAG; Cyclin D1 (Ccnd1) 5′-GCGTACCCTGACACCAATCT and 5′-CTCTTCGCACTTCTGCTCCT; Smc2 5′-AAATAGCCGCCCAGAAAACT and 5′-GAGCGTTCCTTGGTGTCTTC. Primers for p16Ink4a were described previously [27]. Results were normalized to Gapdh as described previously [9].
For microarray, RNA was further purified using the RNeasy Micro Kit (Qiagen), followed by cDNA synthesis, linear amplification and labelling of cRNA using GeneChip 3′IVT Express Kit (Affymetrix). RNA and cRNA quantity and quality were determined by Nanodrop spectrophotometer and Bioanalyser 2100 (Agilent). Affymetrix Mouse 430_2 arrays were hybridised as standard (www.affymetrix.co.uk). Files were processed in GeneSpring GX (Agilent Technologies), with application of GC-RMA normalisation and Benjamimi-Hochberg multiple testing correction.
Whole-mount in situ hybridisation
Whole-mount in situ hybridisation, was performed as described previously [9], using a digoxygenin-labelled 561 bp cRNA probe which was complementary to nucleotides 726–1286 of the Lmnb1 transcript/coding sequence. Embryos were embedded in gelatine-albumin and sectioned at 50 µm thickness on a vibratome.
Photobleaching experiments
Constructs were generated in pcDNA3.1 vector by standard cloning methods, to express fusion proteins composed of a nuclear localisation signal, yellow fluorescent protein and full-length lamin B1 or C-terminal region. Plasmids were transfected into MEFs and FLIP was performed as described previously [51]. In brief, a region of interest (ROI) was photobleached at full laser power while scanning at 4% laser power elsewhere. For quantitative analysis, background intensity was subtracted, and intensities of a specific ROI outside the photobleached area were measured over time and normalized using intensities of an ROI in a transfected but non-bleached cell.
Immunofluorescent labelling and laser-scanning confocal microscopy
MEFs, derived from pools of 3–6 embryos at E13.5, were fixed in 4% PFA in PBS for 10 min, permeabilized with 0.4% Triton X-100 in PBS for 5 min, and blocked with 0.4% fish skin gelatine in PBS for 30 min at room temperature. Incubations with primary and secondary antibodies were for 1 h each at room temperature. Primary antibodies were mouse anti-lamin B1 (8D1; [57] and rabbit anti-lamin A (ab26300: Abcam). Secondary antibodies were donkey anti–mouse and anti–rabbit (Jackson ImmunoResearch Laboratories) conjugated to Alexa Fluor 488 and Cy5 respectively. Imaging was performed using a confocal microscope (LSM 510 META; Carl Zeiss, Inc.) on an Axio Imager.Z1 (Carl Zeiss, Inc.) with a 63× NA 1.4 oil immersion objective lens. Laser lines used were 405 nm, 488 nm and 633 nm to excite DAPI, Alexa Fluor 488 and Cy5, respectively. Fluorescence was detected using the following filters: base pairs 420–480, base pairs 505–530 and long pass 650. Images were analyzed using MetaMorph (MDS Analytical Technologies) or Image Browser (Carl Zeiss, Inc.) software.
Cell cycle analysis
MEFs were plated onto 13 mm cover slips (passage 3; 1.0×105 cells per well in triplicate), cultured for 5 hours prior to addition of 10 µM EdU (Invitrogen). After 1 hour cells were fixed and processed for detection of EdU (Click-It EdU Imaging Kit). Cells were then washed in 0.1% Triton-X100 in PBS and blocked for 30 min (5% heat-inactivated goat serum, PBS-0.1% Triton, 0.15% glycine, 2 mg/ml BSA) prior to immunohistochemistry for phospho-histone H3. Primary and secondary antibodies were anti-phospho histone H3 (1∶250, Millipore) and Alexa Fluor 488-conjugated anti-rabbit (1∶500, Invitrogen). For nuclear staining, cells were incubated with Hoechst (1∶2,000 in PBS). Ten random fields were analysed per cover slip using Image J software (U.S. National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, Maryland, USA). Cells in mitosis were scored by visual inspection of pH 3-positive cells. The experiment was repeated three times, each using an independent cell line.
For in vivo proliferation analysis, mice were injected with 150 µg EdU at E10.5. Embryos were collected after 90 minutes, fixed in 4% PFA and processed for embedding in paraffin wax. Transverse 7 µm sections at the axial level of the closing neural folds were used for proliferation analysis (5–7 sections per embryo), as described previously [12]. Detection of EdU (Click-It EdU Imaging Kit) was followed by immunohistochemistry for phospho-histone H3 (as above) as described [13]. Fluorescent images were collected on an Axiophot microscope (Zeiss) with a DC500 camera (Leica), using FireCam software (Leica). Images were analysed using the Cell Counter plugin in Image J.
Statistical analysis
All statistical analysis was carried out using SigmaStat (version 3.5; Systat Software Inc).
Supporting Information
Zdroje
1. NadeauJH (2003) Modifier genes and protective alleles in humans and mice. Curr Opin Genet Dev 13 : 290–295.
2. CoppAJ, GreeneNDE (2010) Genetics and development of neural tube defects. J Pathol 220 : 217–230.
3. BassukAG, KibarZ (2009) Genetic basis of neural tube defects. Semin Pediatr Neurol 16 : 101–110.
4. GreeneNDE, StanierP, CoppAJ (2009) Genetics of human neural tube defects. Hum Mol Genet 18: R113–R129.
5. CoppAJ, GreeneNDE, MurdochJN (2003) The genetic basis of mammalian neurulation. Nat Rev Genet 4 : 784–793.
6. HarrisMJ, JuriloffDM (2010) An update to the list of mouse mutants with neural tube closure defects and advances toward a complete genetic perspective of neural tube closure. Birth Defects Res A Clin Mol Teratol 88 : 653–669.
7. HarrisMJ, JuriloffDM (2007) Mouse mutants with neural tube closure defects and their role in understanding human neural tube defects. Birth Defects Res A Clin Mol Teratol 79 : 187–210.
8. Van StraatenHWM, CoppAJ (2001) Curly tail: a 50-year history of the mouse spina bifida model. Anat Embryol 203 : 225–237.
9. GustavssonP, GreeneND, LadD, PauwsE, de CastroSC, et al. (2007) Increased expression of Grainyhead-like-3 rescues spina bifida in a folate-resistant mouse model. Hum Mol Genet 16 : 2640–2646.
10. TingSB, WilanowskiT, AudenA, HallM, VossAK, et al. (2003) Inositol - and folate-resistant neural tube defects in mice lacking the epithelial-specific factor Grhl-3. Nature Med 9 : 1513–1519.
11. YuZ, LinKK, BhandariA, SpencerJA, XuX, et al. (2006) The Grainyhead-like epithelial transactivator Get-1/Grhl3 regulates epidermal terminal differentiation and interacts functionally with LMO4. Dev Biol 299 : 122–136.
12. CoppAJ, BrookFA, RobertsHJ (1988) A cell-type-specific abnormality of cell proliferation in mutant (curly tail) mouse embryos developing spinal neural tube defects. Development 104 : 285–295.
13. GustavssonP, CoppAJ, GreeneND (2008) Grainyhead genes and mammalian neural tube closure. Birth Defects Res A Clin Mol Teratol 82 : 728–735.
14. BrookFA, ShumASW, Van StraatenHWM, CoppAJ (1991) Curvature of the caudal region is responsible for failure of neural tube closure in the curly tail (ct) mouse embryo. Development 113 : 671–678.
15. ChenW-H, Morriss-KayGM, CoppAJ (1995) Genesis and prevention of spinal neural tube defects in the curly tail mutant mouse: involvement of retinoic acid and its nuclear receptors RAR-beta and RAR-gamma. Development 121 : 681–691.
16. CoppAJ, CrollaJA, BrookFA (1988) Prevention of spinal neural tube defects in the mouse embryo by growth retardation during neurulation. Development 104 : 297–303.
17. GreeneNDE, CoppAJ (1997) Inositol prevents folate-resistant neural tube defects in the mouse. Nature Med 3 : 60–66.
18. BurrenKA, ScottJM, CoppAJ, GreeneND (2010) The genetic background of the curly tail strain confers susceptibility to folate-deficiency-induced exencephaly. Birth Defects Res A Clin Mol Teratol 88 : 76–83.
19. NeumannPE, FrankelWN, LettsVA, CoffinJM, CoppAJ, et al. (1994) Multifactorial inheritance of neural tube defects: Localization of the major gene and recognition of modifiers in ct mutant mice. Nature Genet 6 : 357–362.
20. CapellBC, CollinsFS (2006) Human laminopathies: nuclei gone genetically awry. Nat Rev Genet 7 : 940–952.
21. GruenbaumY, MargalitA, GoldmanRD, ShumakerDK, WilsonKL (2005) The nuclear lamina comes of age. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 6 : 21–31.
22. WormanHJ, FongLG, MuchirA, YoungSG (2009) Laminopathies and the long strange trip from basic cell biology to therapy. J Clin Invest 119 : 1825–1836.
23. HutchisonCJ (2002) Lamins: building blocks or regulators of gene expression? Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 3 : 848–858.
24. DechatT, PfleghaarK, SenguptaK, ShimiT, ShumakerDK, et al. (2008) Nuclear lamins: major factors in the structural organization and function of the nucleus and chromatin. Genes Dev 22 : 832–853.
25. GoldmanRD, GruenbaumY, MoirRD, ShumakerDK, SpannTP (2002) Nuclear lamins: building blocks of nuclear architecture. Genes Dev 16 : 533–547.
26. MalhasA, LeeCF, SandersR, SaundersNJ, VauxDJ (2007) Defects in lamin B1 expression or processing affect interphase chromosome position and gene expression. J Cell Biol 176 : 593–603.
27. MalhasA, SaundersNJ, VauxDJ (2010) The nuclear envelope can control gene expression and cell cycle progression via miRNA regulation. Cell Cycle 9 : 531–539.
28. MekhailK, MoazedD (2010) The nuclear envelope in genome organization, expression and stability. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 11 : 317–328.
29. KimY, SharovAA, McDoleK, ChengM, HaoH, et al. (2011) Mouse B-type lamins are required for proper organogenesis but not by embryonic stem cells. Science 334 : 1706–1710.
30. WormanHJ, OstlundC, WangY (2010) Diseases of the nuclear envelope. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 2: a000760.
31. PadiathQS, SaigohK, SchiffmannR, AsaharaH, YamadaT, et al. (2006) Lamin B1 duplications cause autosomal dominant leukodystrophy. Nat Genet 38 : 1114–1123.
32. SchusterJ, SundblomJ, ThuressonAC, Hassin-BaerS, KlopstockT, et al. (2011) Genomic duplications mediate overexpression of lamin B1 in adult-onset autosomal dominant leukodystrophy (ADLD) with autonomic symptoms. Neurogenetics 12 : 65–72.
33. VergnesL, PeterfyM, BergoMO, YoungSG, ReueK (2004) Lamin B1 is required for mouse development and nuclear integrity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101 : 10428–10433.
34. CoffinierC, JungHJ, NobumoriC, ChangS, TuY, et al. (2011) Deficiencies in lamin B1 and lamin B2 cause neurodevelopmental defects and distinct nuclear shape abnormalities in neurons. Mol Biol Cell 22 : 4683–4693.
35. CoffinierC, ChangSY, NobumoriC, TuY, FarberEA, et al. (2010) Abnormal development of the cerebral cortex and cerebellum in the setting of lamin B2 deficiency. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107 : 5076–5081.
36. JonesDT (1999) Protein secondary structure prediction based on position-specific scoring matrices. J Mol Biol 292 : 195–202.
37. SubramanianG, HjelmRP, DemingTJ, SmithGS, LiY, SafinyaCR (2000) Structure of complexes of cationic lipids and poly(glutamic acid) polypeptides: a pinched lamellar phase. J Am Chem Soc 122 : 26–34.
38. GrunebergH (1954) Genetical studies on the skeleton of the mouse. VIII. Curly tail. J Genet 52 : 52–67.
39. BeecheyCV, SearleAG (1986) Mutations at the Sp locus. Mouse News Letter 75 : 28.
40. CoppAJ (1985) Relationship between timing of posterior neuropore closure and development of spinal neural tube defects in mutant (curly tail) and normal mouse embryos in culture. J Embryol Exp Morphol 88 : 39–54.
41. De CastroSC, LeungKY, SaveryD, BurrenK, RozenR, et al. (2010) Neural tube defects induced by folate deficiency in mutant curly tail (Grhl3) embryos are associated with alteration in folate one-carbon metabolism but are unlikely to result from diminished methylation. Birth Defects Res A Clin Mol Teratol 88 : 612–618.
42. ScaffidiP, MisteliT (2005) Reversal of the cellular phenotype in the premature aging disease Hutchinson-Gilford progeria syndrome. Nature Med 11 : 440–445.
43. BudirahardjaY, GonczyP (2009) Coupling the cell cycle to development. Development 136 : 2861–2872.
44. HocheggerH, TakedaS, HuntT (2008) Cyclin-dependent kinases and cell-cycle transitions: does one fit all? Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 9 : 910–916.
45. LiJ, PoiMJ, TsaiMD (2011) Regulatory mechanisms of tumor suppressor P16(INK4A) and their relevance to cancer. Biochemistry 50 : 5566–5582.
46. LegagneuxV, CubizollesF, WatrinE (2004) Multiple roles of Condensins: a complex story. Biol Cell 96 : 201–213.
47. FazzioTG, PanningB (2010) Condensin complexes regulate mitotic progression and interphase chromatin structure in embryonic stem cells. J Cell Biol 188 : 491–503.
48. ShimiT, PfleghaarK, KojimaS, PackCG, SoloveiI, et al. (2008) The A - and B-type nuclear lamin networks: microdomains involved in chromatin organization and transcription. Genes Dev 22 : 3409–3421.
49. TsaiMY, WangS, HeidingerJM, ShumakerDK, AdamSA, et al. (2006) A mitotic lamin B matrix induced by RanGTP required for spindle assembly. Science 311 : 1887–1893.
50. MoirRD, SpannTP, HerrmannH, GoldmanRD (2000) Disruption of nuclear lamin organization blocks the elongation phase of DNA replication. J Cell Biol 149 : 1179–1192.
51. MalhasAN, LeeCF, VauxDJ (2009) Lamin B1 controls oxidative stress responses via Oct-1. J Cell Biol 184 : 45–55.
52. GongD, PomereningJR, MyersJW, GustavssonC, JonesJT, et al. (2007) Cyclin A2 regulates nuclear-envelope breakdown and the nuclear accumulation of cyclin B1. Curr Biol 17 : 85–91.
53. ShimiT, Butin-IsraeliV, AdamSA, HamanakaRB, GoldmanAE, et al. (2011) The role of nuclear lamin B1 in cell proliferation and senescence. Genes Dev 25 : 2579–2593.
54. SellerMJ, PerkinsKJ (1986) Effect of mitomycin C on the neural tube defects of the curly-tail mouse. Teratology 33 : 305–309.
55. GreeneND, BamideleA, ChoyM, de CastroSC, WaitR, et al. (2007) Proteome changes associated with hippocampal MRI abnormalities in the lithium pilocarpine-induced model of convulsive status epilepticus. Proteomics 7 : 1336–1344.
56. GreeneNDE, LeungKY, WaitR, BegumS, DunnMJ, et al. (2002) Differential protein expression at the stage of neural tube closure in the mouse embryo. J Biol Chem 277 : 41645–41651.
57. MaskeCP, HollinsheadMS, HigbeeNC, BergoMO, YoungSG, et al. (2003) A carboxyl-terminal interaction of lamin B1 is dependent on the CAAX endoprotease Rce1 and carboxymethylation. J Cell Biol 162 : 1223–1232.
Štítky
Genetika Reprodukční medicína
Článek The Covariate's DilemmaČlánek Plant Vascular Cell Division Is Maintained by an Interaction between PXY and Ethylene SignallingČlánek Lessons from Model Organisms: Phenotypic Robustness and Missing Heritability in Complex Disease
Článek vyšel v časopisePLOS Genetics
Nejčtenější tento týden
2012 Číslo 11
-
Všechny články tohoto čísla
- Inference of Population Splits and Mixtures from Genome-Wide Allele Frequency Data
- The Covariate's Dilemma
- Plant Vascular Cell Division Is Maintained by an Interaction between PXY and Ethylene Signalling
- Plan B for Stimulating Stem Cell Division
- Discovering Thiamine Transporters as Targets of Chloroquine Using a Novel Functional Genomics Strategy
- Is a Modifier of Mutations in Retinitis Pigmentosa with Incomplete Penetrance
- Evolutionarily Ancient Association of the FoxJ1 Transcription Factor with the Motile Ciliogenic Program
- Genome Instability Caused by a Germline Mutation in the Human DNA Repair Gene
- Transcription Factor Oct1 Is a Somatic and Cancer Stem Cell Determinant
- Controls of Nucleosome Positioning in the Human Genome
- Disruption of Causes Defective Meiotic Recombination in Male Mice
- A Novel Human-Infection-Derived Bacterium Provides Insights into the Evolutionary Origins of Mutualistic Insect–Bacterial Symbioses
- Trps1 and Its Target Gene Regulate Epithelial Proliferation in the Developing Hair Follicle and Are Associated with Hypertrichosis
- Zcchc11 Uridylates Mature miRNAs to Enhance Neonatal IGF-1 Expression, Growth, and Survival
- Population-Based Resequencing of in 10,330 Individuals: Spectrum of Genetic Variation, Phenotype, and Comparison with Extreme Phenotype Approach
- HP1a Recruitment to Promoters Is Independent of H3K9 Methylation in
- Transcription Elongation and Tissue-Specific Somatic CAG Instability
- A Germline Polymorphism of DNA Polymerase Beta Induces Genomic Instability and Cellular Transformation
- Interallelic and Intergenic Incompatibilities of the () Gene in Mouse Hybrid Sterility
- Comparison of Mitochondrial Mutation Spectra in Ageing Human Colonic Epithelium and Disease: Absence of Evidence for Purifying Selection in Somatic Mitochondrial DNA Point Mutations
- Mutations in the Transcription Elongation Factor SPT5 Disrupt a Reporter for Dosage Compensation in Drosophila
- Evolution of Minimal Specificity and Promiscuity in Steroid Hormone Receptors
- Blockade of Pachytene piRNA Biogenesis Reveals a Novel Requirement for Maintaining Post-Meiotic Germline Genome Integrity
- RHOA Is a Modulator of the Cholesterol-Lowering Effects of Statin
- MIG-10 Functions with ABI-1 to Mediate the UNC-6 and SLT-1 Axon Guidance Signaling Pathways
- Loss of the DNA Methyltransferase MET1 Induces H3K9 Hypermethylation at PcG Target Genes and Redistribution of H3K27 Trimethylation to Transposons in
- Genome-Wide Association Studies Reveal a Simple Genetic Basis of Resistance to Naturally Coevolving Viruses in
- The Principal Genetic Determinants for Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma in China Involve the Class I Antigen Recognition Groove
- Molecular, Physiological, and Motor Performance Defects in DMSXL Mice Carrying >1,000 CTG Repeats from the Human DM1 Locus
- Genomic Study of RNA Polymerase II and III SNAP-Bound Promoters Reveals a Gene Transcribed by Both Enzymes and a Broad Use of Common Activators
- Long Telomeres Produced by Telomerase-Resistant Recombination Are Established from a Single Source and Are Subject to Extreme Sequence Scrambling
- The Yeast SR-Like Protein Npl3 Links Chromatin Modification to mRNA Processing
- Deubiquitylation Machinery Is Required for Embryonic Polarity in
- dJun and Vri/dNFIL3 Are Major Regulators of Cardiac Aging in Drosophila
- CtIP Is Required to Initiate Replication-Dependent Interstrand Crosslink Repair
- Notch-Mediated Suppression of TSC2 Expression Regulates Cell Differentiation in the Intestinal Stem Cell Lineage
- A Combination of H2A.Z and H4 Acetylation Recruits Brd2 to Chromatin during Transcriptional Activation
- Network Analysis of a -Mouse Model of Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease Identifies HNF4α as a Disease Modifier
- Mitosis in Neurons: Roughex and APC/C Maintain Cell Cycle Exit to Prevent Cytokinetic and Axonal Defects in Photoreceptor Neurons
- CELF4 Regulates Translation and Local Abundance of a Vast Set of mRNAs, Including Genes Associated with Regulation of Synaptic Function
- Mechanisms Employed by to Prevent Ribonucleotide Incorporation into Genomic DNA by Pol V
- The Genomes of the Fungal Plant Pathogens and Reveal Adaptation to Different Hosts and Lifestyles But Also Signatures of Common Ancestry
- A Genome-Scale RNA–Interference Screen Identifies RRAS Signaling as a Pathologic Feature of Huntington's Disease
- Lessons from Model Organisms: Phenotypic Robustness and Missing Heritability in Complex Disease
- Population Genomic Scan for Candidate Signatures of Balancing Selection to Guide Antigen Characterization in Malaria Parasites
- Tissue-Specific Regulation of Chromatin Insulator Function
- Disruption of Mouse Cenpj, a Regulator of Centriole Biogenesis, Phenocopies Seckel Syndrome
- Genome, Functional Gene Annotation, and Nuclear Transformation of the Heterokont Oleaginous Alga CCMP1779
- Antagonistic Gene Activities Determine the Formation of Pattern Elements along the Mediolateral Axis of the Fruit
- Lung eQTLs to Help Reveal the Molecular Underpinnings of Asthma
- Identification of the First ATRIP–Deficient Patient and Novel Mutations in ATR Define a Clinical Spectrum for ATR–ATRIP Seckel Syndrome
- Cooperativity of , , and in Malignant Breast Cancer Evolution
- Loss of Prohibitin Membrane Scaffolds Impairs Mitochondrial Architecture and Leads to Tau Hyperphosphorylation and Neurodegeneration
- Microhomology Directs Diverse DNA Break Repair Pathways and Chromosomal Translocations
- MicroRNA–Mediated Repression of the Seed Maturation Program during Vegetative Development in
- Selective Pressure Causes an RNA Virus to Trade Reproductive Fitness for Increased Structural and Thermal Stability of a Viral Enzyme
- The Tumor Suppressor Gene Retinoblastoma-1 Is Required for Retinotectal Development and Visual Function in Zebrafish
- Regions of Homozygosity in the Porcine Genome: Consequence of Demography and the Recombination Landscape
- Histone Methyltransferases MES-4 and MET-1 Promote Meiotic Checkpoint Activation in
- Polyadenylation-Dependent Control of Long Noncoding RNA Expression by the Poly(A)-Binding Protein Nuclear 1
- A Unified Method for Detecting Secondary Trait Associations with Rare Variants: Application to Sequence Data
- Genetic and Biochemical Dissection of a HisKA Domain Identifies Residues Required Exclusively for Kinase and Phosphatase Activities
- Informed Conditioning on Clinical Covariates Increases Power in Case-Control Association Studies
- Biochemical Diversification through Foreign Gene Expression in Bdelloid Rotifers
- Genomic Variation and Its Impact on Gene Expression in
- Spastic Paraplegia Mutation N256S in the Neuronal Microtubule Motor KIF5A Disrupts Axonal Transport in a HSP Model
- Lamin B1 Polymorphism Influences Morphology of the Nuclear Envelope, Cell Cycle Progression, and Risk of Neural Tube Defects in Mice
- A Targeted Glycan-Related Gene Screen Reveals Heparan Sulfate Proteoglycan Sulfation Regulates WNT and BMP Trans-Synaptic Signaling
- Dopaminergic D2-Like Receptors Delimit Recurrent Cholinergic-Mediated Motor Programs during a Goal-Oriented Behavior
- PLOS Genetics
- Archiv čísel
- Aktuální číslo
- Informace o časopisu
Nejčtenější v tomto čísle- Mechanisms Employed by to Prevent Ribonucleotide Incorporation into Genomic DNA by Pol V
- Inference of Population Splits and Mixtures from Genome-Wide Allele Frequency Data
- Zcchc11 Uridylates Mature miRNAs to Enhance Neonatal IGF-1 Expression, Growth, and Survival
- Histone Methyltransferases MES-4 and MET-1 Promote Meiotic Checkpoint Activation in
Kurzy
Zvyšte si kvalifikaci online z pohodlí domova
Současné možnosti léčby obezity
nový kurzAutoři: MUDr. Martin Hrubý
Všechny kurzyPřihlášení#ADS_BOTTOM_SCRIPTS#Zapomenuté hesloZadejte e-mailovou adresu, se kterou jste vytvářel(a) účet, budou Vám na ni zaslány informace k nastavení nového hesla.
- Vzdělávání



