-
Články
Top novinky
Reklama- Vzdělávání
- Časopisy
Top články
Nové číslo
- Témata
Top novinky
Reklama- Videa
- Podcasty
Nové podcasty
Reklama- Kariéra
Doporučené pozice
Reklama- Praxe
Top novinky
ReklamaThe Lysine Acetyltransferase Activator Brpf1 Governs Dentate Gyrus Development through Neural Stem Cells and Progenitors
Lysine acetylation refers to addition of the acetyl group to lysine residues after protein synthesis. Little is known about how this modification plays a role in the brain and neural stem cells. It is catalyzed by a group of enzymes known as lysine acetyltransferases. A novel epigenetic regulator called BRPF1 acts as a master activator of three different lysine acetyltransferases and also contains multiple structural domains for histone binding. In this study, we show that forebrain-specific inactivation of the mouse Brpf1 gene causes abnormal development of the dentate gyrus, a key component of the hippocampus. We trace the developmental origin to compromised neural stem cells and progenitors, and demonstrate that Brpf1 loss deregulates neuronal migration and cell cycle progression during development of the dentate gyrus. This is the first report on an epigenetic regulator whose loss has such a profound impact on the hippocampus, especially the dentate gyrus, a brain structure critical for learning, memory and adult neurogenesis.
Published in the journal: . PLoS Genet 11(3): e32767. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1005034
Category: Research Article
doi: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1005034Summary
Lysine acetylation refers to addition of the acetyl group to lysine residues after protein synthesis. Little is known about how this modification plays a role in the brain and neural stem cells. It is catalyzed by a group of enzymes known as lysine acetyltransferases. A novel epigenetic regulator called BRPF1 acts as a master activator of three different lysine acetyltransferases and also contains multiple structural domains for histone binding. In this study, we show that forebrain-specific inactivation of the mouse Brpf1 gene causes abnormal development of the dentate gyrus, a key component of the hippocampus. We trace the developmental origin to compromised neural stem cells and progenitors, and demonstrate that Brpf1 loss deregulates neuronal migration and cell cycle progression during development of the dentate gyrus. This is the first report on an epigenetic regulator whose loss has such a profound impact on the hippocampus, especially the dentate gyrus, a brain structure critical for learning, memory and adult neurogenesis.
Introduction
Lysine acetylation involves covalent addition of an acetyl moiety to the ε-amino group of a lysine residue and is important for modification of both prokaryotic and eukaryotic proteins [1–3]. Proteomic analyses have detected this modification in thousands of mammalian proteins with important roles not only in chromatin-templated nuclear processes but also various cytoplasmic pathways [4–7]. In addition, it is abundant in bacteria [8,9]. Although some of the modification events in bacteria are dependent on acetyl-phosphate [10], this modification is exclusively enzymatic in eukaryotes. In humans, at least 15 known lysine acetyltransferases (KATs) catalyze the forward reaction [2,11–13]. These enzymes are divided into three families, one of which is the MYST family, composed of TIP60 (HIV Tat-interacting protein of 60 kDa), MOZ (monocytic leukemia zinc finger protein), MORF (MOZ-related factor), HBO1 (HAT bound to ORC1) and hMOF (homolog of Drosophila males absent on the first), which are also known as KAT5, KAT6A/MYST3, KAT6B/MYST4, KAT7/MYST2 and KAT8/MYST1, respectively [14–16]. Although mainly referred to as histone acetyltransferases, members of this family also acetylate non-histone substrates, including the tumor suppressor p53 [17–19] and the DNA-damage response regulator DBC1 (deleted in breast cancer 1) [20]. TIP60 and hMOF also carry out autoacetylation essential for their activation [21–25]. Furthermore, four recent studies have revealed that tyrosine phosphorylation of TIP60 links chromatin sensing to ATM signaling and that both TIP60 and hMOF regulate autophagy [26–29]. Thus, this family of acetyltransferases is important in diverse cellular programs.
Molecular and cell-based studies have firmly established that three members of this family, MOZ, MORF and HBO1, form tetrameric complexes with BRPF1 (bromodomain - and PHD finger-containing protein 1), along with two other subunits [30–32]. Within the complexes, BRPF1 functions as a scaffold to bridge subunit interaction, stimulate acetyltransferase activity and restrict substrate specificity [30–32]. Moreover, BRPF1 possesses two PHD fingers for binding to unmodified histone H3 [32], one bromodomain for acetyllysine-recognition [33] and a PWWP domain for specific interaction with methylated histone H3 [34,35]. Thus, BRPF1 is a unique multivalent histone binder able to activate different acetyltransferases.
BRPF1 is highly conserved from Drosophila to humans [reviewed in 16]. In C. elegans, a distantly related protein, Lin-49, regulates neuron asymmetry, hindgut development and fecundity [36–38]. In vertebrates, BRPF1 has two paralogs, BRPF2 and BRPF3 [30,31]. Inactivation of zebrafish Brpf1 alters pharyngeal segmental identity [39], and disruption of medaka fish Brpf1 affects craniofacial and caudal skeletons [40], indicating that fish Brpf1 regulates skeletal development. These studies suggest that mammalian BRPF1 may also play an important role in development. Of relevance, loss of mouse Brpf2 leads to embryonic lethality, with growth retardation, neural tube defects, abnormal eye development and faulty erythropoiesis [41], supporting that BRPF1, BRPF2 and BRPF3 have non-redundant functions in vivo.
As key partners of BRPF1, MOZ and MORF are important in different types of normal and pathological stem cells. Mouse Moz plays a key role in self-renewal and maintenance of hematopoietic stem cells [42,43]. Consistent with this, human MOZ and MORF are rearranged in leukemia and other hematological malignancies [reviewed in 14,16]. One of the resulting fusion proteins is crucial for self-renewal of leukemic stem cells [44,45]. In addition, the MORF gene is frequently altered in castration-resistant prostate cancer [46] and its mutations have been detected in breast cancer [47], although it remains unclear whether related cancer stem cells are affected. The gene is also mutated in four developmental disorders, Noonan syndrome-like disorder [48], Ohdo syndrome [49] and genitopatellar syndrome [50,51] and blepharophimosis-ptosis-epicanthus inversus syndrome [52]. One common characteristic of these disorders is intellectual disability. Related to this, mice with residual MORF expression display neocortical defects [53] and abnormal neural stem cells [54], raising an interesting question whether BRPF1 plays a role in the brain.
The interaction of BRPF1 with MOZ and MORF, as indicated by molecular and cell-based studies [30–32], suggests the exciting possibility that BRPF1 may regulate mammalian development. Related to this, we have recently found that it is essential for mouse embryo survival [55]. Our expression survey has also identified high-level expression of Brpf1 in the brain [55]. Here we examine this further and demonstrate that forebrain-specific inactivation of the mouse Brpf1 gene leads to dentate gyrus hypoplasia, reduces expression of key genes involved and deregulates neural stem cells and progenitors. Upon Brpf1 loss, Sox2+ neural stem cells and Tbr2+ intermediate neuronal progenitors fail to settle at the subgranular zone of the dentate gyrus, one of the two major sites known to harbor adult neural stem cells. This is the first epigenetic regulator to be identified with such an important role in the dentate gyrus.
Results
Dynamic expression of Brpf1 during mouse forebrain development
By using a mouse strain containing a LacZ knockin cassette inserted at the Brpf1 locus (S1A Fig), we have recently detected high β-galactosidase activities in the neocortex and hippocampus [55]. To gain further insights, we examined frozen sections prepared from Brpf1l/+ pre - and post-natal brains more carefully than previously reported [55]. As shown in Fig. 1A (left), strong expression was detected at the marginal zone of the developing neocortex at embryonic day (E) 14.5. At E17.5, very weak expression was present in different regions of the neocortex (Fig. 1B, left). At postnatal day (P) 3, P14 and the adult stage, much stronger expression was found in all six layers of the neocortex, with some enrichment in layers II-III (Fig. 1C-E, left). Similarly, we examined the expression in the hippocampus. At E14.5 and E17.5, no expression was detectable in the hippocampal primordium (Fig. 1A-B, right). Interestingly, at both stages, sparse signals were present in the dentate migration stream (Fig. 1A-B, right). At P3, relatively strong expression appeared in the cornum amonni (CA) regions (Fig. 1C, right), indicating that Brpf1 expression increases dramatically from E17.5 to P3. At P3, only sparse signals were detected in the developing dentate gyrus (Fig. 1C, right). At P14 and the adult stage, strong expression was detected in the dentate gyrus (Fig. 1D-E, right). These results support a potential role of Brpf1 in neocortex and hippocampus development.
Fig. 1. Brpf1 expression during forebrain development. 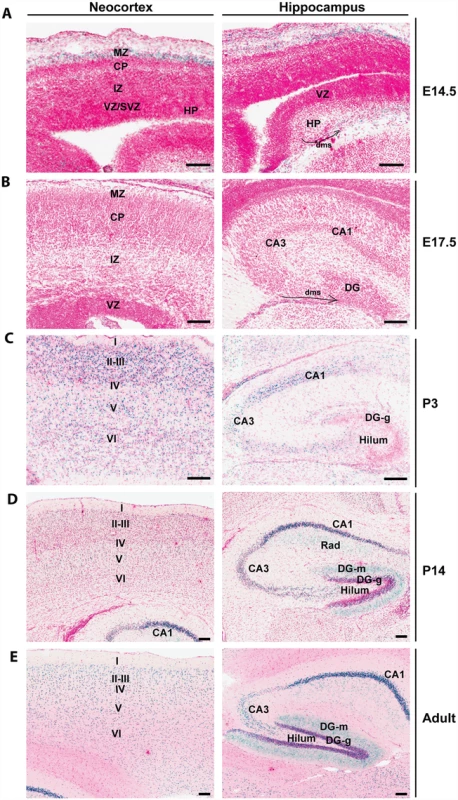
(A) At E14.5, β-galactosidase activity (labeled blue, with nuclei stained red) was detected in the marginal zone (MZ) of the cortical hem, but not in the developing neocortex. In the hippocampus, the signal was detected sparsely in the dentate migration stream (dms, marked by a curved arrow). (B) At E17.5, the expression is very weak in the neocortex and hippocampus. Note the sparse signals detected in the dentate migration stream (dms) marked by a curved arrow. (C-E) After birth, β-galactosidase activity appeared in the neocortex and hippocampus. From P3 onwards, β-galactosidase activity was detected in all the six layers of neocortex and in the cornum amonni (CA) field of the hippocampus. The activity in the dentate gyrus was moderate at P3 but became much stronger at P14 and adult. All images were taken from frozen sections prepared from Brpf1l/+ embryos (A-B) or postnatal brains (C-E); the corresponding wild-type sections showed no β-galactosidase staining [55]. Structures of the developing and adult brains were annotated according to published atlases [87–91]. CA1, cornum amonni 1; CA3, cornum amonni 3; CP, cortical plate; DG, dentate gyrus; DG-g, granular cell layer of dentate gyrus; DG-m, molecular layer of dentate gyrus; HP, hippocampus; I-IV, cortical layers I-VI; IZ, intermediate zone; Rad, radial layer of the hippocampus; SVZ, subventricular zone; VZ, ventricular zone. Scale bars, 100 μm. Generation of forebrain-specific Brpf1 knockouts
To determine the function of Brpf1 in the forebrain, we crossed heterozygous Brpf1f/+ mice (S1A Fig) with the Emx1-Cre strain, which expresses the Cre recombinase from the Emx1 locus and allows LoxP excision in the neocortex and hippocampus [56]. The resulting Brpf1f/+;Emx1-Cre mice appeared normal and intercrosses between them yielded Brpf1f/f;Emx1-Cre (or bKO, short for forebrain conditional knockout) animals. Genomic PCR (S1B Fig) and RT-PCR (S1C Fig) confirmed specific excision in the forebrain but not cerebellum. The specific knockout had minimal effects on the expression of Brpf2, Brpf3, Moz and Morf (S1D Fig). Most of the bKO pups died prior to weaning at P21 [57]. Systematic histological analysis of the mutant brain identified three defective areas: the neocortex, hippocampus and corpus callosum, whereas other brain regions such as the cerebellum were normal [57]. Among these defects, the one in the hippocampus is the most striking and thus investigated here.
Brpf1 loss leads to partial agenesis of the hippocampus
Nissl staining of brain sections revealed that when compared to the control, the suprapyramidal blade of the dorsal hippocampus in the P10 mutant brain was shorter, with one end remaining attached to the ventricular zone, whereas the infrapyramidal blade was completely missing (Fig. 2A, right). The nuclear layers of CA1 and CA3 appeared more diffusely packed than those in the control (Fig. 2A, right). In the mutant, the junction of CA1 with the subiculum was not as clear-cut as that in the control and the subiculum itself was expanded. Similar changes were found in the mutant brain at P24 (Fig. 2B). More importantly, these defects also appeared in serial sagittal sections and similar abnormalities were found in the ventral hippocampus (Fig. 2C-D), indicating that the entire hippocampal formation is affected. The mouse dentate gyrus develops from the cortical hem around mid-gestation and involves dynamic neuron migration and differentiation, both of which continue in the first two weeks after birth [58,59]. To determine the developmental point when the defects start to occur, we applied Nissl staining to brain sections from E17.5 fetuses and P0 neonates. As shown in Fig. 3A-B, the developing dentate gyrus was underdeveloped at both time points, indicating that the defects originate from prenatal development.
Fig. 2. Forebrain-specific Brpf1 loss causes hypoplasia of the dentate gyrus. 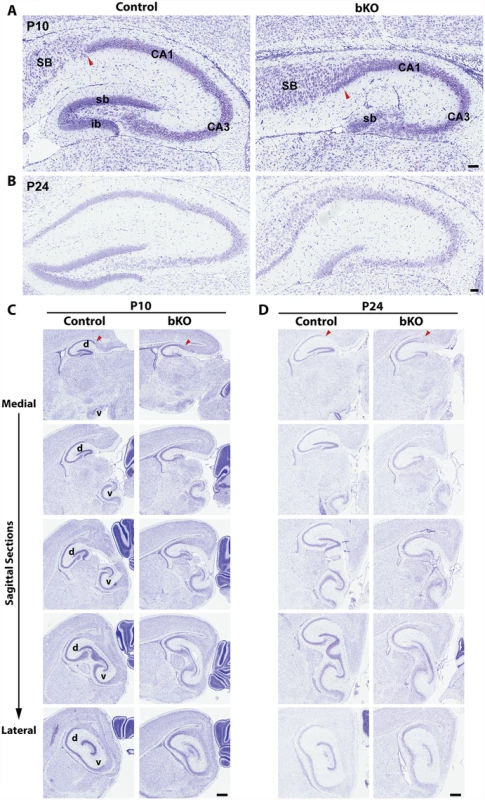
(A-B) Nissl staining was performed on coronal brain sections from P10 and P24 mice. Loss of Brpf1 resulted in underdevelopment of the suprapyramidal blade (sb) and disappearance of the infrapyramidal blade (ib) in the dentate gyrus. The border between cornu ammonis 1 (CA1) and the subiculum (SB) was clearly defined in the wild-type sections but became obscure in the mutant, as indicated by red arrowheads in (A). At P10 and P24, the pyramidal layers of CA1 and CA3 in the mutant sections were not as tightly packed as in the wild-type (A-B). (C-D) Nissl staining of serial brain sections. Five medial-to-lateral sagittal sections were prepared from P10 (C) or P24 (D) wild-type and mutant brains and Nissl-stained to analyze the morphology of the hippocampus at different planes (A). The border between CA1 and the subiculum, marked by red arrowheads, was clearly defined in the wild-type but not mutant sections. v, ventral hippocampus; d, dorsal hippocampus. Scale bars, 100 μm for (A-B) and 0.5 mm for (C-D). Fig. 3. Brpf1 loss impairs dentate gyrus development, dendritic tree formation and neuronal proliferation. 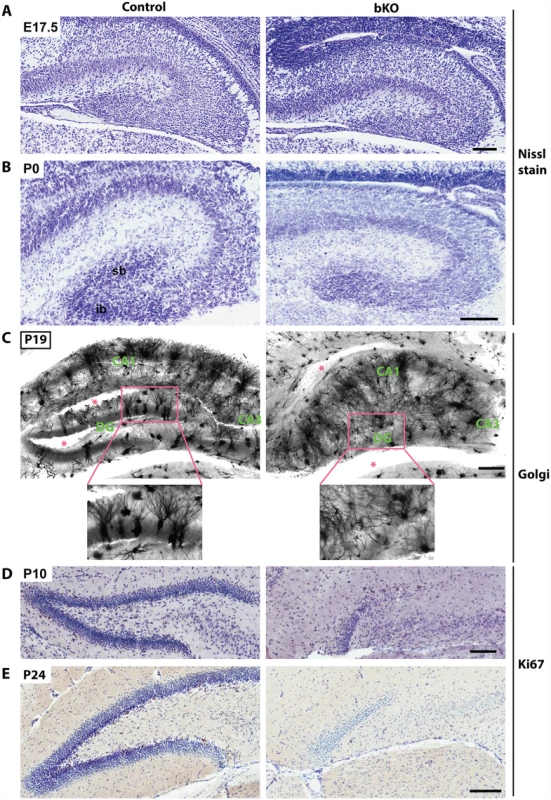
(A-B) Nissl staining of coronal brain sections from E17.5 and P0 mice. At P0, loss of Brpf1 resulted in underdevelopment of the suprapyramidal blade (sb) and disappearance of the infrapyramidal blade (ib) in the developing dentate gyrus. (C) Golgi-Cox staining of coronal brain sections at P19. Representative images of hippocampal regions from the wild-type and bKO brain sections show that the bKO hippocampus possessed disorganized neurons, with less robust dendritic trees. There were also fewer neurons in the mutant dentate gyrus. Red asterisks denote areas accidentally torn during staining. The boxed regions in the top panels are shown in the lower panels at higher magnification. (D-E) Ki67 immunohistochemistry showing that cell proliferation dramatically decreased in the subgranular zone of the bKO dentate gyrus at P10 and P24. The subgranular zones of the control P10 and P24 sections shown here contain 20 and 34 Ki67+ cells, respectively, whereas the corresponding regions of the mutant sections possess either one or no Ki67+ cells. Scale bars, 100 μm for (A-B & D-E) and 200 μm for (C). To characterize the defects further, we performed Golgi-Cox staining to assess formation of axons and dendrites. This staining revealed abnormal axon and dendritic trees in the hippocampus (Fig. 3C). Interestingly, the disorganization was not just limited to the dentate gyrus but also occurred in the CA regions, indicating that Brpf1 is required for proper development of the entire hippocampus. Another method to examine the axons of the dentate granule cells, the so-called mossy fibers, is the Timm’s stain. The first mossy fibers invade CA3 at around P0, and their number gradually increases during postnatal development [60]. We examined mossy fiber development at P8 by Timm’s stain and found that the fiber projection was defective from the very beginning of its development. The suprapyramidal bundles (spb) and the dentate hilum of mossy fibers were virtually missing in the mutant (S2 Fig).
To shed light on the underlying mechanisms for the defects, we examined the sections by immunohistochemical staining with an anti-Ki67 antibody. As shown in Fig. 3D-E, Ki67+ neuronal precursors were enriched in the subgranular zone of the wild-type dentate gyrus at both P10 and P24 (left), but such precursors were missing in the mutant (right), indicating a lack of proliferation in the subgranular zone. These results indicate that Brpf1 is essential for hippocampus development and regulates neuronal proliferation in the dentate gyrus.
Brpf1 loss deregulates neural stem cells and progenitors
To gain mechanistic insights into the observed defects in the hippocampus, we asked whether there are other mutant mice displaying similar phenotypes in the dentate gyrus. Literature search revealed that loss of several transcription factors cause similar hypoplasia in the dentate gyrus, including Sox2 [61], Tlx (tailless) [62], Tbr2 (T-box brain protein 2, also known as eomesodermin) [63], NeuroD1 [64], Emx2 (empty spiracles homeobox 2) [65], neurogenin 2 [66] and FoxG1 (also known as BF1, for brain factor 1) [67]. Among these, Sox2 and Tlx are two well-known neural stem cell markers [68,69], whereas Tbr2 is important for intermediate neuronal progenitors [70]. The unexpected finding that upon loss, Brpf1 shares phenotypes with these three transcription factors in dentate gyrus development suggests a potential link to neural stem cells and progenitors.
The subgranular zone of the dentate gyrus is one of two major sites harboring adult neural stem cells [68]. As noted above, Sox2 is a neural stem cell marker and its loss leads to dentate gyrus hypoplasia [61]. In addition, Ki67+ neuronal precursors disappeared in the subgranular zone of the mutant dentate gyrus (Fig. 3D-E). These observations suggest that Brpf1 loss may deregulate neural stem cells. To investigate this possibility, we performed immunostaining of brain sections with an antibody against Sox2. At P0, Sox2+ neural stem cells were enriched in the wild-type dentate gyrus (Fig. 4A, left two panels). This population was smaller in the mutant dentate gyrus (Fig. 4A, right two panels & Fig. 4D). In support of this, when compared to the wild-type dentate gyrus, the mutant contained a much smaller population of neurons expressing Ctip2 (Fig. 4E-F), a transcription factor important for dentate gyrus development [71]. As development progressed to P10 and P14, wild-type Sox2+ neural stem cells became enriched in the subgranular zone (Fig. 4B-C, left two panels). By contrast, no such enrichment was present in the mutant (Fig. 4B-C, right two panels), suggesting the requirement of Brpf1 for development of Sox2+ neural stem cells in the dentate gyrus.
Fig. 4. Brpf1 loss compromises neural stem cells and neuronal precursors. 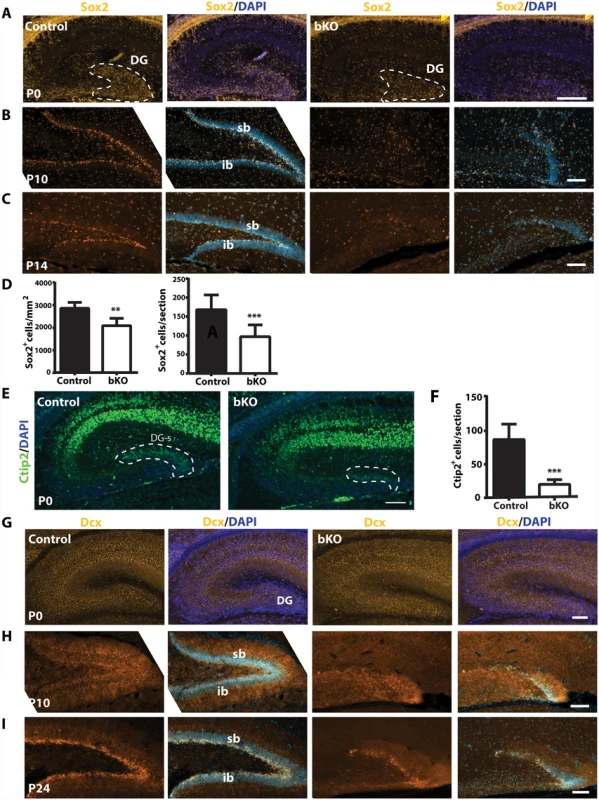
(A-C) Immunofluorescence microscopy to detect Sox2+ neural stem cells (NSCs) on peri- or postnatal brain sections. At P0, Sox2+ NSCs were enriched in the wild-type dentate gyrus (DG) and this population was smaller in the mutant, as quantified in (D). At P10 and P14, Sox2+ NSCs settled in the control subgranular zone (SGZ), while in the mutant, the granule cell layers were hypoplastic and the SGZ harbored few Sox2+ NSCs. (D) Quantification of Sox2+ cells in the control and mutant dentate gyri at P0. There were significantly fewer Sox2+ NSCs within the mutant dentate gyrus per section (right). The number of Sox2+ cells per mm2 within the dentate gyrus also significantly decreased (left). The quantification was based on three pairs of neonates and at least three matched sections per brain. **p<0.01; ***p<0.001. (E) In the hippocampus, Ctip2 expression was restricted to the CA regions and the suprapyramidal blade of the developing dentate gyrus (DG-s) at P0. (F) Quantification of Ctip2+ cells in the wild-type and mutant suprapyramidal blades, outlined in (E), was based on three pairs of neonates and at least three matched sections per brain. ***p<0.001. (G-I) Dcx expression in control and bKO brain sections at three developmental stages. In the mutant dentate gyrus, there were fewer Dcx+ neuronal precursors apparently at P10 (H) and P24 (I). Scale bars: (A-C), 100 μm; (E), 400 μm, (G-I), 100 μm. We also analyzed doublecortin (Dcx)-expressing neuroblasts. At P0, Dcx+ cells were enriched in both wild-type and mutant dentate gyri (Fig. 4G), and the distribution was rather uniform in the developing dentate gyrus. Different from Sox2+ neural stem cells, Dcx+ immature neurons were also present in the pryramidal layers of the CA1 and CA3 regions (Fig. 4G). As the development progressed, Dcx+ immature neurons became enriched in the subgranular zone of the wild-type dentate gyrus at P10 and P24 (Fig. 4H-I, left panels). A similar trend of enrichment was observed in the mutant, but the cell number was greatly reduced (Fig. 4H-I, right panels), supporting that Brpf1 loss comprises Dcx+ neuroblasts.
Intermediate neuronal progenitors are essential for dentate gyrus development [72,73]. Tbr2 is a marker of these progenitors. The similar phenotype of Tbr2 inactivation in the dentate gyrus [63] suggests that these progenitors may also be affected. Intermediate neuronal progenitors are derived from radial glial cells [70], so we first analyzed the expression of Gfap (glial fibrillary acidic protein), a well-known marker of radial glial cells [73]. At E16.5, distribution of Gfap+ glial cells was slightly altered in the mutant dentate gyrus (Fig. 5A). At P0, such cells were enriched at the outer rim of the wild-type dentate gyrus (Fig. 5B, left two panels), but this distribution became disorganized in the mutant (right two panels). At P10, Gfap+ radial glial cells and astrocytes were nicely organized along the granular cell layer of the dentate gyrus and the hippocampal fissure, respectively (Fig. 5C, left two panels), but this pattern became virtually missing in the mutant (right two panels). In particular, there were fewer Gfap+ radial glial cells in the granular cell layer of the mutant dentate gyrus and these cells were disoriented (Fig. 5D).
Fig. 5. Deregulated Gfap expression in the mutant hippocampus. 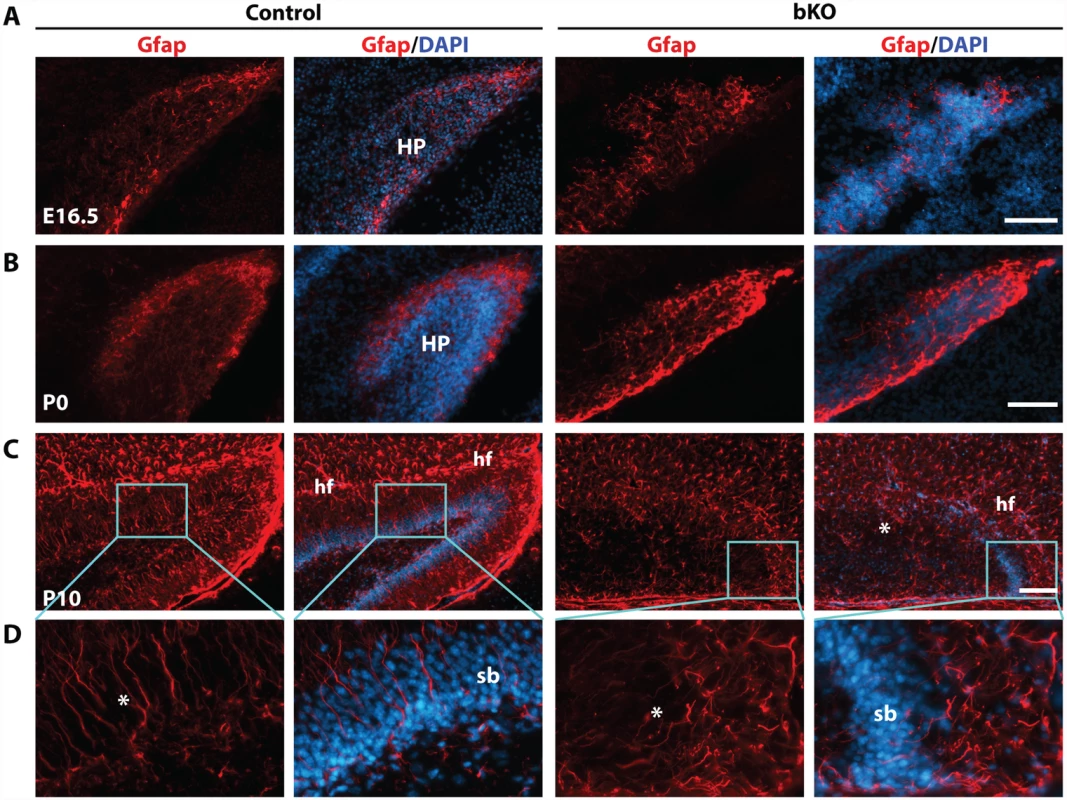
(A-C) Immunofluorescence microscopy to detect Gfap expression on brain sections at E16.5, P0 and P10. Distribution of Gfap+ radial glial cells in the mutant dentate gyri was only slightly disturbed at E16.5 and moderately at P0 (A-B), but it became completely disorganized at P10 (C). (D) High-magnification images of the regions boxed in (C). Compared to the wild-type dentate gyrus, there were few Gfap+ radial glial cells in the mutant (see the areas marked by asterisks). In addition, the hippocampus fissure (hf) was ill-formed in the mutant. HP, hippocampus; sb, suprapyramidal blade; scale bars, 100 μm. We next analyzed intermediate neuronal progenitors with an anti-Tbr2 antibody. At E13.5, Tbr2 expression in the hippocampal primordium was rather similar between the wild-type and mutant (Fig. 6A). By E16.5, Tbr2+ progenitors were present in the wild-type dentate neuroepithelium and migrated along the dentate migratory stream to the forming dentate gyrus (Fig. 6B, left two panels). Such migration was also found in the mutant, but the population was smaller in the forming dentate gyrus (Fig. 6B, right two panels). At P0, a similar difference was found between the wild-type and mutant dentate gyri (Fig. 6C). Quantification confirmed this (Fig. 6E). As the development progressed, Tbr2+ progenitors translocated to the subgranular zone and the hilum of the wild-type dentate gyrus (Fig. 6D, left two panels). In stark contrast, no such translocation was found in the mutant (right two panels), with some of Tbr2+ progenitors stayed at the molecular cell layer (Fig. 6D, right two panels; marked with yellow arrowheads). These results indicate that the abnormalities start at a fetal stage and Brpf1 inactivation impairs the migration of Tbr2+ progenitors.
Fig. 6. Defective Tbr2+ and NeuroD1+ neuronal precursors in the mutant hippocampus. 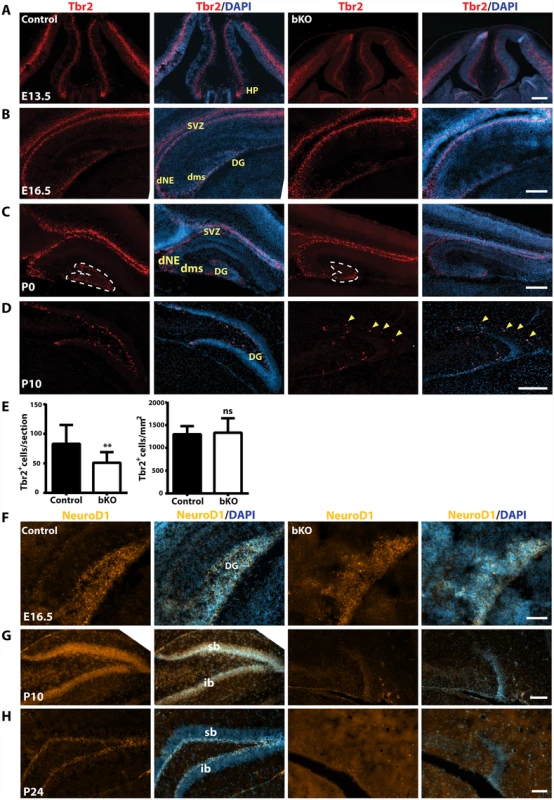
(A-D) Immunostaining to detect Tbr2+ intermediate neuronal progenitors on sections from E13.5, E16.5, P0 and P10 brains. At E13.5 (A), Tbr2 was similarly expressed in the control and mutant neuroepithelium and hippocampus primordium (HP). At E16.5 (B), Tbr2 was similarly expressed in the control and mutant subventricular zones (SVZ) and hippocampi. At P0 and P10, there were fewer Tbr2+ progenitors in the mutant dentate gyrus (C-D). The yellow arrowheads in the right two panels mark four progenitors that failed to settle in the subgranular zone, but stayed at the outer rim of the molecular cell layer. (E) Quantification of Tbr2+ progenitors in the developing dentate gyrus at P0, outlined with clear dash lines in (C). While there was no significant difference in the cell density (right), the Tbr2+ progenitor number per section decreased significantly in the mutant (left). The quantification was based on three pairs of control and mutant brains, with at least three matched sections per brain. **p<0.01; ns, not statistically significant. (F-H) Immunofluorescence microscopy to detect NeuroD1+ neuroblasts on E16.5, P10 and P24 brain sections. At E16.5 (F), NeuroD1 expression was relatively normal in the mutant hippocampus (HP), but it virtually disappeared in the mutant dentate gyrus at P10 (G) and P24 (H). DG, dentate gyrus; dNE, dentate neuroepithelium; dms, dentate migration stream; HP, hippocampus; sb, suprapyramidal blade; ib, infrapyramidal blade; SVZ, subventricular zone; scale bars, 100 μm. We performed additional analyses with antibodies against three neurogenic transcription factors, NeuroD1, neurogenin 2 and FoxG1. At E16.5, NeuroD1+ neuroblasts were enriched in both wild-type and mutant developing dentate gyri, rather uniformly distributed across the granular layer and the hilum (Fig. 6F). As the development progressed to P10, NeuroD1+ neuroblasts became enriched in the granular cell layer in the wild-type dentate gyrus (Fig. 6G, left panels). By contrast, few such cells were present in the mutant dentate gyrus (right panels). At P24, NeuroD1+ neuroblasts were restricted to the wild-type subgranular zone (Fig. 6H, left panels), but almost none was observed in the mutant (right panels). These results indicate that Brpf1 is required for proper development and migration of NeuroD1+ neuroblasts.
Neurogenin 2 is essential for dentate gyrus formation [66]. At P0, distribution of neurogenin 2+ progenitors was ubiquitious in the wild-type and mutant hippocampi (S3A Fig). At P24, all granular neurons in the dentate gyrus and the pyramidal neurons in the CA1 and CA3 regions expressed neurogenin 2 (S3B Fig, left two panels). This expression pattern was also observed in the mutant, but the cells were not as tightly packed in the pyramidal layers of the CA regions and the suprapyramidal blade of the dentate gyrus (right two panels). As expected, the infrapyramidal blade was missing. For immunostaining to detect the brain-specific transcription factor FoxG1, we performed immunostaining with antibodies against FoxG1 and Tuj1, a neuron-specific β-tubulin. This analysis revealed no obvious defects at E13.5 (S4A Fig). At P0, the hippocampal region became slightly disorganized (S4B Fig). At P24, for the wild-type hippocampus, FoxG1 was expressed in pyramidal neurons of the CA1 region and the granular layer of the dentate gyrus, but not in pyramidal neurons of the CA3 region (S4C Fig, left two panels). For the mutant hippocampus, FoxG1 was also expressed in these two regions (S4C Fig, right two panels), but the neurons were much less tightly packed than those in the wild-type hippocampus (S4C Fig). Moreover, unlike the wild-type, FoxG1 expression was also detected in pyramidal neurons of the CA3 region (S4C Fig). As expected, the infrapyramidal blade was absent in the mutant hippocampus (S4C Fig, right two panels). These results support that Brpf1 inactivation alters neurogenesis in the hippocampus.
It is interesting to note that the impact on Sox2, Tbr2 and NeuroD1 (Figs. 4A-C & 6) is quite different from that on neurogenin 2 and FoxG1 (S3–S4 Figs). With the former three, the positively expressing neural stem cells or neuronal precursors displayed active migration in the dentate gyrus and settled at the subgranular zone (Figs. 4A-C & 6). By contrast, neurogenin 2-expressing progenitors or FoxG1-expressing neurons were rather uniformly distributed in the granular layer (S3–S4 Figs). These two groups of transcription factors appear to regulate different stages of dentate gyrus development. Thus, Brpf1 may regulate different stages of hippocampus development.
Brpf1 loss impairs neuronal migration and cell cycle progression
At the prenatal and postnatal stages, dentate gyrus development involves two waves of neuronal precursors migrating from the neuroepithelium at the ventricular or subventricular zone to the dentate gyrus [58,59,74,75], so we next investigated whether and how Brpf1 loss affects the migration. For this, BrdU was injected into pregnant dams at E12.5, E14.5 and E16.5. The dams were then sacrificed at P0 to isolate the brain for immunohistochemical analysis with an anti-BrdU monoclonal antibody. BrdU+ cells were quantified as three populations, outlined as the primary matrix (1ry), secondary matrix (2ry) and tertiary matrix (3ry) (Fig. 7A, top left) [66]. Representative images of the hippocampal regions are shown in Fig. 7A and the quantification results of the three BrdU+ populations are presented in Fig. 7B. In the first and second matrices, no difference was found between the control and mutant for all three labeling time points. In the tertiary matrix (corresponding to the developing dentate gyrus), there were fewer BrdU+ cells when labeled at E12.5 and E14.5 (Fig. 7A-B), indicating that Brpf1 loss affects migration of neuronal progenitors from the dentate neuroepithelium to the developing dentate gyrus.
Fig. 7. Analysis of neuronal migration in the hippocampus by BrdU labeling. 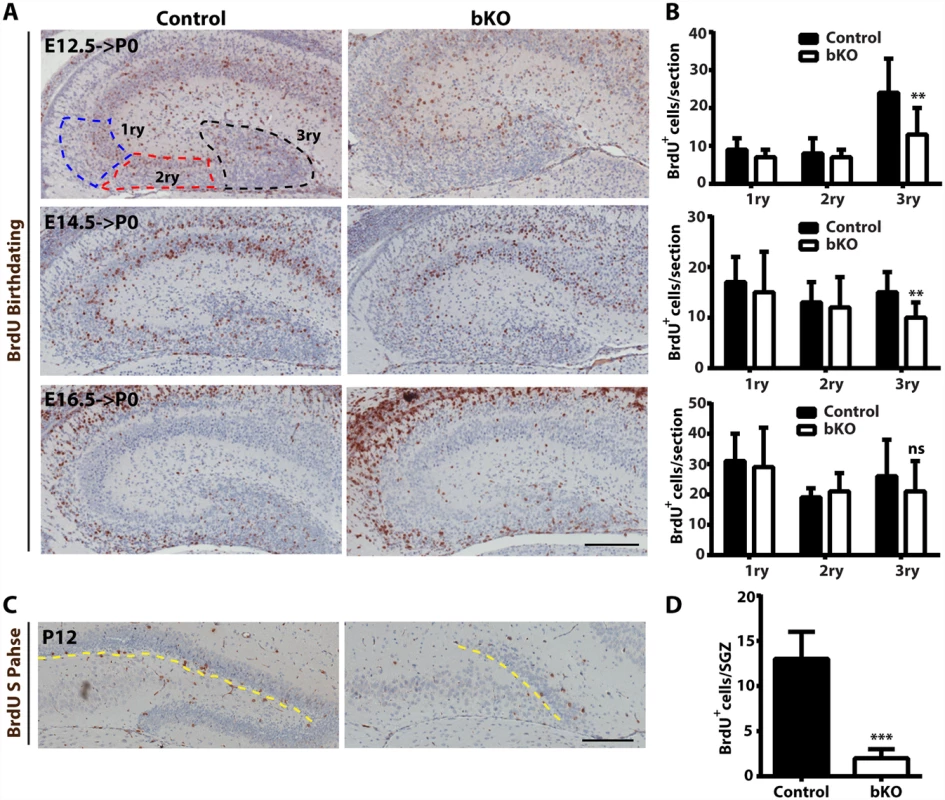
(A-B) After injection with BrdU at E12.5, E14.5 and E16.5, pregnant mice were sacrificed at P0 for immunohistochemical analysis with an anti-BrdU monoclonal antibody. Representative images of the hippocampal regions are shown in (A) and the quantification results of three BrdU+ progenitor populations, outlined as the primary matrix (1ry), secondary matrix (2ry) and tertiary matrix (3ry), are presented in (B). The tertiary matrix corresponds to the developing dentate gyrus. For each time point, the quantification was based on 2 pairs of control and mutant brains, with 4 or 5 matched sections per brain. (C-D) After injection with BrdU at P12, wild-type and mutant pups were sacrificed 1 h later for immunohistochemical analysis with the anti-BrdU antibody. Representative images of the hippocampal regions are shown in (C) and the quantification result of BrdU+ S-phase cells at the subgranular zone (marked with the yellow dashed lines) is presented in (D). The quantification was based on 2 pairs of control and mutant pups, with 4 matched sections per pup. Scale bars, 200 μm; ns, not statistically significant; **p<0.01; ***p<0.001. At both P10 and P24, Ki67+ neuronal precursors virtually disappeared in the subgranular zone of the mutant dentate gyri (Fig. 3D-E). To substantiate this, we performed BrdU labeling and sacrificed the pups 1 h later. Different from the birthdating analysis just described above (Fig. 7A-B), this short labeling protocol was to assess cells with active DNA synthesis. As shown in Fig. 7C-D, this protocol identified dramatic reduction of BrdU+ cells at the mutant subgranular zone at P12. In addition, immunostaining for cleaved caspase 3 failed to evident apoptosis in the wild-type or mutant dentate gyrus. Together, these results indicate that Brpf1 impairs cell cycle progression. To investigate this further, we analyzed cell cycle progression of the progenitors. E15.5 pregnant mice were sacrificed after 1 h pulse of BrdU labeling to retrieve the fetal brain for immunofluorescence microscopy with anti-Ki67 and-BrdU antibodies. Representative images of the hippocampal regions are shown in Fig. 8A and the quantification of the immunostained cells in two regions (outlined with dotted lines) is presented in Fig. 8B. In the dentate neuroepithelium, no difference was detected (Fig. 8B, left). In the dentate migration stream, the number of BrdU+ progenitors was normal but the Ki67+ cycling cell population (at G1, S, G2 and M, but not G0) increased significantly, thereby decreasing the ratio of S-phase (BrdU+) over proliferating (Ki67+) cells (Fig. 7B, right). Moreover, immunostaining analysis of the related sections with an antibody specific to phospho-Ser10 of histone H3 revealed no difference between the wild-type and mutant (Fig. 8C-D), indicating that the M phase of the cell cycle is normal in the mutant. These results indicate that Brpf1 loss impairs cell cycle progression of the dentate migration stream at E15.5, most likely through the G1 phase. Notably, the defects at E15.5 (Fig. 8) were smaller than those at or after P10 (Figs. 3D-E & 7C-D). Consistent with difference, Brpf1 expression in the developing hippocampus was low at E14.5 and E17.5, but increased dramatically after P3 (Fig. 1).
Fig. 8. Cell cycle properties and progenitor number in the mutant dentate gyrus. 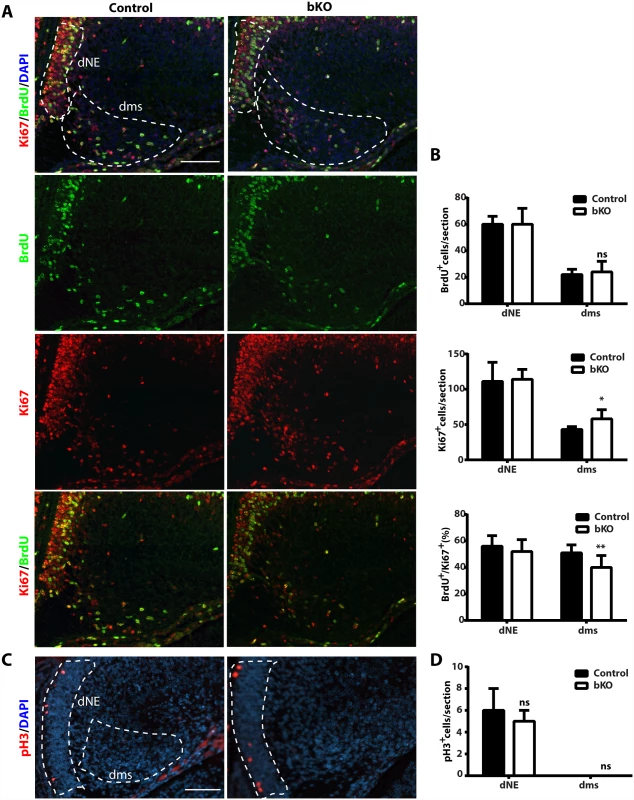
(A-B) After BrdU labeling, E15.5 pregnant mice were sacrificed 1 h later to retrieve fetal brains for subsequent fixing and sectioning. Immunofluorescence microscopy was performed with anti-Ki67 and-BrdU antibodies, with representative images of the hippocampal regions shown in (A) and the quantification of the stained cells in two regions (outlined with dotted lines) presented in (B). The quantification was based on two pairs of control and mutant brains, with 8 matched sections per brain. In the dentate neuroepithelium (dNE), no difference was detected. In the dentate migration stream (dms), the number of BrdU+ progenitors was normal but the Ki67+ cycling cells increased significantly, thereby decreasing the ratio of S-phase (BrdU+) vs proliferating (Ki67+) cells. (C-D) Immunostaining of sections from the same brains as in (A-B) with an antibody specific to phospho-Ser10 of histone H3 (pH3). Representative images of the hippocampal regions are shown in (C) and the quantification of positive cells in two regions (outlined with dashed lines) is presented in (D). No pH3-positive cells were detected in the migration stream. Scale bars: 100 μm; ns, not statistically significant; *p<0.05, **p<0.01. Brpf1 loss deregulates transcription important for dentate gyrus development
Having identified the cellular mechanisms for the observed defects in the dentate gyrus, we then investigated the underlying molecular mechanisms. Brpf1 activates Moz, Morf and Hbo1 [30–32]. These acetyltransferases function as transcriptional coregulators [19,76–79]. Thus, we considered whether Brpf1 inactivation deregulates transcription. For this, we first performed RT-PCR. Brpf1 deletion occurred efficiently (Fig. 9A) [57]. The inactivation did not affect mRNA levels of Brpf2, Brpf3, Moz and Morf (S1D Fig). Similarly, neither Hbo1 nor hMof was altered (Fig. 9B). Importantly, mRNA levels of NeuroD1, Tbr2 and FoxG1 were reduced in the mutant (Fig. 9C). This is consistent with the immunofluorescence microscopic results Figs. (6 & S4). The transcript levels of Emx2 and Tlx were also reduced (Fig. 9C). As these transcription factors are known to be important for dentate gyrus development, these results nicely explain hypoplasia of the bKO dentate gyrus.
Fig. 9. Brpf1 loss deregulates gene expression important for hippocampus development. 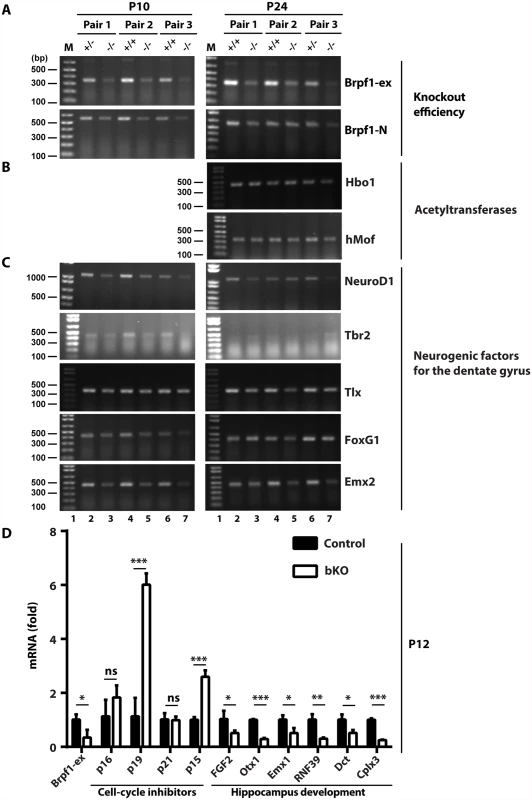
(A-C) RT-PCR analysis of transcripts for Brpf1 (A), the acetyltransfrases Hbo1 and hMof (B), and five transcription factors (C), loss of which is known to cause dentate gyrus hypoplasia (see the text). The primers used are listed in S1 Table. Gapdh was used as the internal control [57]. At P24, Tbr2 expression is known to be limited to the subgranular zone of the dentate gyrus, so the RT-PCR product was not detected. (D) RT-qPCR analysis of transcripts for Brpf1, four cell cycle inhibitors and six genes important for hippocampus development. The p16/19, p15 and six other genes were identified in the microarray analysis of dorsal brain cortices isolated from three pairs of wild-type and mutant pups at P4 [57]. The RT-qPCR analysis was performed on three pairs of dorsal brain cortices at P12 and the average values are shown with standard deviation. Dct, dopachrome tautomerase; Cplx3, presynaptic protein complexin 3. *, p<0.05; **, p<0.01; ***, p<0.001; ns, not statistically significant. As Brpf1 loss affects cell cycle progression (Figs. 3D-E, 7C-D & 8), we analyzed expression of four cell cycle inhibitors, p16, p19, p21 and p15. Among them, p16 and p21 are two known targets of Moz [19,80]. Microarray-based gene expression analysis identified the Cdkn2a (encoding both p16 and p19) and Cdkn2b (encoding p15) genes as two of the top 35 candidates whose transcription was upregulated in the mutant dorsal cortex at P4 [57]. As shown in Fig. 9D, RT-qPCR identified increase in transcripts of p19 and p15, but not p16 or p21. These results indicate that Brpf1 loss promotes p15 and p19 transcription, which may then contribute to deregulated cell cycle progression. The microarray analysis [57] also identified transcriptional reduction in six genes related to hippocampus development (Fig. 9D). RT-qPCR confirmed this (Fig. 9D), supporting that Brpf1 is required for gene expression important for hippocampus development.
Contribution of Moz, Morf and Hbo1 to effects of Brpf1 deletion
As a scaffold, Brpf1 bridges subunit interaction, stimulates enzymatic activity and restricts substrate specificity of Moz, Morf and Hbo1 acetyltransferase complexes [30–32,41], so we asked whether these acetyltransferases contribute to the defects observed in the Brpf1 bKO mice. Related to this, mice with residual Morf expression display defects in the neocortex but not the hippocampus [53], suggesting that either Morf is not the sole mediator or it is not involved at all. Using a knockin LacZ reporter, we have recently detected Moz expression in the hippocampus, with a pattern similar to that of Brpf1 [55]. To investigate the role of Moz in the hippocampus and neocortex, we crossed Mozf/+ mice with the Emx1-Cre strain to obtain Mozf/+;Emx1-Cre mice. Intercrosses yielded Mozf/f;Emx1-Cre mice. They appeared normal and Nissl staining of the brain sections revealed none of the defects observed in the Brpf1-deficient brain, suggesting that like Morf, Moz is either not the sole mediator of Brpf1 or not involved at all.
We then asked whether Hbo1 is involved. For this, we determined its expression in the hippocampus by immunostaining. At P10, Hbo1 was enriched in pyramidal layers of CA1 and CA3, as well as in the granular cell layer of the dentate gyrus (S5A Fig, left two panels). A similar expression pattern was also detected at P4 (S5B Fig, left two panels). When Brpf1 was deleted, the expression of Hbo1 in these three regions became weak at P4 and almost disappeared at P10 (S5A-B Fig, right two panels). The difference was not obvious at E16.5 (S5C Fig). At P12, the total Hbo1 protein level (S5D Fig) at the dorsal cortex was not affected, suggesting that Brpf1 deletion may destabilize Hbo1 specifically at the pyramidal layers of the CA regions and the granular cell layer of the dentate gyrus.
The MYST family of mammalian acetyltransferases is composed of five members: MOZ, MORF, HBO1, TIP60 and hMOF in mammals [16]. MOZ and MORF are almost interchangeable in cell-based assays [31], so we compared the interactions of MOZ, HBO1, TIP60 and hMOF with BRPF1 under the same experimental conditions. As shown in S6 Fig (lanes 1–2 & 5–6), co-expression of BRPF1, ING5 and EAF6, which are known to form a trimeric complex [31], increased the expression levels of MOZ and HBO1, possibly through tetrameric complex formation and subsequent stabilization. This may explain the loss of Hbo1 expression by immunofluorescence microscopy (S5A-B Fig). HBO1 was slightly more efficient than MOZ in co-precipitation of BRPF1 (S6 Fig). Interestingly, HBO1 co-precipitated both ING5 and EAF6 much more efficiently than MOZ, indicating that HBO1 forms a better tetrameric complex than MOZ. By contrast, TIP60 was much less efficient and hMOF displayed no affinity for BRPF1, ING5 and EAF6 (S6 Fig). These cell-based results indicate that although both MOZ and HBO1 interact efficiently and specifically with BRPF1, HBO1 is better than MOZ in forming a tetrameric complex with BRPF1, ING5 and EAF6.
Discussion
Herein we have demonstrated that Brpf1 is dynamically expressed during forebrain development (Fig. 1) and that forebrain-specific inactivation of mouse Brpf1 led to abnormalities in the hippocampus, esp. the dentate gyrus (Fig. 2), highlighting its importance in hippocampal neurogenesis. This is the first report of an epigenetic regulator whose loss exerts such profound effects on hippocampus development. Loss of two other groups of proteins has been reported to yield similar phenotypes. The first group includes eight DNA-binding transcription factors, Sox2 [61], Tlx (tailless) [62], Tbr2 [63], NeuroD1 [64], Emx2 [65], neurogenin 2 [66], Prox1 [81] and FoxG1 (also known as BF1, brain factor 1) [67]. Within the second group, there are three signaling regulators, Cxcr4, smoothened and Kif3a [70,82]. The latter two are important for Hedgehog signaling, while Cxcr4 is a receptor for the chemokine Cxcl12 (also known as stromal cell-derived factor 1). The Cxcl12-Cxcr4 signaling pair is not only important for granular neuron migration during dentate gyrus development [70], but also for the homing and self-renewal of hematopoietic stem cells [83]. Our unexpected finding that Brpf1 plays a similar role in the dentate gyrus suggests a potential link of the DNA-binding transcription factors and the signaling molecules to epigenetic and acetylation regulation by Brpf1. The similar phenotypes suggest that these two groups of regulators and Brpf1 define novel pathways required for patterning the dentate gyrus. The dentate gyrus develops from the cortical hem around mid-gestation, involving subsequent neuron migration and specification until the second week after birth [58,59,74,75]. Brpf1 appeared to regulate developmental processes at the late gestation and postnatal stages (Figs. 4–7). The dentate gyrus is also key to learning and memory, so it will be important to map out how each regulator is involved. The outcome will shed light on neurogenesis in the subgranular zone, a key area with adult neural stem cells [68,73].
The bKO mice are particularly similar to those lacking Tbr2 in terms of dentate gyrus hypoplasia [63]. Specific to intermediate neuronal progenitors, Tbr2 is required for transition from neural stem cells to these progenitors [72]. Since Tbr2+ cells were compromised by Brpf1 inactivation (Fig. 6A-E), Brpf1 may be essential for progression from neural stem cells to the progenitors. Mouse Cxcl12 and its receptor Cxcr4 are important for migration of granular cells to the dentate gyrus [84,85] and Tbr2 controls Cxcr4 expression and regulates Cxcl12 signaling [70], so compromised Cxcl12-Cxcr4 signaling may also contribute to dentate gyrus hypoplasia. In addition, Hedgehog signaling may be involved. First, Smoothened loss causes dentate gyrus hypoplasia [82]. Second, the neural stem cell marker Sox2 is required for Hedgehog signaling and its loss results in similar hypoplasia [61]. Finally, Brpf1 inactivation reduced Sox2 expression (Fig. 4A-D). Thus, Brpf1 is important for production of Sox2+ neural stem cells and Tbr2+ intermediate neuronal progenitors.
As for additional cellular mechanisms, Brpf1 loss led to abnormal migration of neuronal progenitors from the dentate neuroepithelium to the dentate gyrus (Fig. 7A-B). The cell cycle progression was also impaired (Figs. 3D-E, 7C-D & 8). At the molecular level, Brpf1 loss reduced transcription of NeuroD1, Tbr2, Tlx, FoxG1 and Emx2 (Fig. 9C). In addition, transcription of the cell cycle inhibitors p15 and p19 was elevated, whereas the transcript levels of six genes important for hippocampal development were reduced in the mutant (Fig. 9D). Further studies are needed to investigate how Brpf1 loss confers histone acetylation and chromatin changes at these specific loci and across the entire genome.
Brpf1 interacts with Moz, Morf and Hbo1, and stimulates their acetyltransferase activities [30–32], so an interesting question is how these acetyltransferases may mediate the influence of Brpf1, regulate transcription of genes such as Tbr2 and Sox2, and contribute to hippocampus development. Morf is expressed in the hippocampus, but its inactivation does not affect the hippocampus [53]. In the hippocampus, Moz and Hbo1 display expression patterns similar to Brpf1 (Figs. 1 & S5) [55]. All three acetyltransferases interact efficiently with Brpf1 [30–32], although Hbo1 is better than Moz and perhaps also Morf (a Moz paralog) in forming a tetrameric complex with Brpf1, Ing5 and Eaf6 (S6 Fig). Inactivation of either Moz or Morf does not exert the same effects on the hippocampus as Brpf1 deletion [53]. Interestingly, immunofluorescence microscopy identified reduction of Hbo1 expression in the granular cell layer of the dentate gyrus (S5A-B Fig) even though the total protein level in the dorsal cortex was not altered (S5D Fig). The H3K14 acetylation level was not altered in the mutant dorsal cortex (S5D Fig). Related to this, deletion of the Hbo1 gene in mouse embryos or its fibroblasts dramatically reduces the H3K14 acetylation level [41,79]. Thus, even if it has a role, Hbo1 may not be the sole mediator. Instead, Moz, Morf and Hbo1 may have redundant roles in the hippocampus, so Brpf1 may act through all of them. As human HBO1 was slightly better in forming a tetrameric complex with BRPF1, ING5 and EAF6 (S6 Fig), mouse Hbo1 may be a major contributor in mediating Brpf1 functions. Alternatively, Brpf1 may function independently of Moz, Morf and Hbo1. Related to this, in addition to a small region required for interaction with the three acetyltransferases, BRPF1 possesses two PHD fingers for binding to unmodified histone H3 [32], one bromodomain for acetyllysine-recognition [33] and a PWWP domain for interaction with methylated histone H3 [34,35]. It also possesses a motif for interaction with ING5 and EAF6 to form a trimeric complex [31], and ING5 has its own histone binding ability [86]. Global inactivation of Hbo1 is embryonically lethal [79], but specific deletion in different tissues has not been carried out. Further analysis of single and compound brain-specific knockouts of Moz, Morf and Hbo1 will shed light on how Brpf1 may, or may not, act through these acetyltransferases during hippocampus development.
In summary, we have taken a mouse genetic approach and demonstrated that Brpf1 is important for development of the hippocampus, especially the dentate gyrus, one of the two major areas with active adult neurogenesis. Mechanistically, Brpf1 is important for proper development of related neural stem cells and intermediate progenitors by regulating neuronal migration, cell cycle progression and transcription of related genes. Further studies are needed to investigate its molecular and genetic interaction with related transcription factors, histone acetyltransferases and other chromatin regulators, and to determine the genome-wide action during hippocampus development.
Methods
Maintenance of mouse colonies and use of mice
Mouse strains were maintained in a newly established animal facility at McGill University and all procedures involving the use of mice were performed according to guidelines and protocols approved by the McGill Animal Use Committee.
Generation of knockout mice
Heterozygous Brpf1l mice have been described [55]. A promoterless LacZ cassette is between two FRT sites, while two loxP sites flank exons 4–6 of Brpf1 (S1A Fig). For genotyping, genomic PCR with primers Brpf1-F1 and-R1 generated a 227-bp band for wild-type, whereas genomic PCR with primers Brpf1-F1 and-mR1 produced a 162-bp fragment for the knock-in allele (S1A Fig). The LacZ cassette was deleted by breeding with PGK1-FLPo mice (Jackson Laboratory) to obtain the conditional allele Brpf1f (S1A Fig). Cross of Brpf1f/+ mice with Emx1-Cre mice (Jackson Laboratory) resulted in the heterozygote Brpf1f/+;Emx1-Cre (or Brpf1+/-, S1A Fig), and subsequent intercrosses yielded the homozygote Brpf1f/f;Emx1-Cre (or Brpf1-/-, referred to as bKO). The lines were maintained on the C57BL/6J background. Heterozygous Mozl/+ mice have been described [55] and Mozf/+ mice were generated as described above. Cross of Mozf/+ mice with Emx1-Cre mice (Jackson Laboratory) resulted in Mozf/+;Emx1-Cre, and subsequent intercrosses yielded Mozf/f;Emx1-Cre. Moz lines were maintained on a mixed C57BL/6J-CD1 genetic background. Other experimental procedures are presented in S1 Text.
Supporting Information
Zdroje
1. Kouzarides T (2000) Acetylation: a regulatory modification to rival phosphorylation? EMBO J 19 : 1176–1179. 10716917
2. Sterner DE, Berger SL (2000) Acetylation of histones and transcription-related factors. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 64 : 435–459. 10839822
3. Yang XJ, Seto E (2008) Lysine acetylation: codified crosstalk with other posttranslational modifications. Mol Cell 31 : 449–461. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2008.07.002 18722172
4. Kim SC, Sprung R, Chen Y, Xu Y, Ball H, et al. (2006) Substrate and functional diversity of lysine acetylation revealed by a proteomics survey. Mol Cell 23 : 607–618. 16916647
5. Choudhary C, Kumar C, Gnad F, Nielsen ML, Rehman M, et al. (2009) Lysine acetylation targets protein complexes and co-regulates major cellular functions. Science 325 : 834–840. doi: 10.1126/science.1175371 19608861
6. Zhao S, Xu W, Jiang W, Yu W, Lin Y, et al. (2010) Regulation of cellular metabolism by protein lysine acetylation. Science 327 : 1000–1004. doi: 10.1126/science.1179689 20167786
7. Kaluarachchi Duffy S, Friesen H, Baryshnikova A, Lambert JP, Chong YT, et al. (2012) Exploring the yeast acetylome using functional genomics. Cell 149 : 936–948. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.02.064 22579291
8. Zhang J, Sprung R, Pei J, Tan X, Kim S, et al. (2009) Lysine acetylation is a highly abundant and evolutionarily conserved modification in Escherichia coli. Mol Cell Proteomics 8 : 215–225. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M800187-MCP200 18723842
9. Wang Q, Zhang Y, Yang C, Xiong H, Lin Y, et al. (2010) Acetylation of metabolic enzymes coordinates carbon source utilization and metabolic flux. Science 327 : 1004–1007. doi: 10.1126/science.1179687 20167787
10. Weinert BT, Iesmantavicius V, Wagner SA, Scholz C, Gummesson B, et al. (2013) Acetyl-phosphate is a critical determinant of lysine acetylation in E. coli. Mol Cell 51 : 265–272. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2013.06.003 23830618
11. Roth SY, Denu JM, Allis CD (2001) Histone acetyltransferases. Annu Rev Biochem 70 : 81–120. 11395403
12. Carrozza MJ, Utley RT, Workman JL, Cote J (2003) The diverse functions of histone acetyltransferase complexes. Trends Genet 19 : 321–329. 12801725
13. Allis CD, Berger SL, Cote J, Dent S, Jenuwien T, et al. (2007) New nomenclature for chromatin-modifying enzymes. Cell 131 : 633–636. 18022353
14. Lafon A, Chang CS, Scott EM, Jacobson SJ, Pillus L (2007) MYST opportunities for growth control: yeast genes illuminate human cancer gene functions. Oncogene 26 : 5373–5384. 17694079
15. Rea S, Xouri G, Akhtar A (2007) Male absent on the first: from Drosophila to humans. Oncogene 26 : 5385–5394. 17694080
16. Yang XJ, Ullah M (2007) MOZ and MORF, two large MYSTic HATs in normal and cancer stem cells. Oncogene 26 : 5408–5419. 17694082
17. Sykes SM, Mellert HS, Holbert MA, Li K, Marmorstein R, et al. (2006) Acetylation of the p53 DNA-binding domain regulates apoptosis induction. Mol Cell 24 : 841–851. 17189187
18. Tang Y, Luo J, Zhang W, Gu W (2006) Tip60-dependent acetylation of p53 modulates the decision between cell-cycle arrest and apoptosis. Mol Cell 24 : 827–839. 17189186
19. Rokudai S, Laptenko O, Arnal SM, Taya Y, Kitabayashi I, et al. (2013) MOZ increases p53 acetylation and premature senescence through its complex formation with PML. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 110 : 3895–3900. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1300490110 23431171
20. Zheng H, Yang L, Peng L, Izumi V, Koomen J, et al. (2013) hMOF Acetylation of DBC1/CCAR2 Prevents Binding and Inhibition of SirT1. Mol Cell Biol epub.
21. Wang J, Chen J (2010) SIRT1 regulates autoacetylation and histone acetyltransferase activity of TIP60. J Biol Chem 285 : 11458–11464. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.087585 20100829
22. Lu L, Li L, Lv X, Wu XS, Liu DP, et al. (2011) Modulations of hMOF autoacetylation by SIRT1 regulate hMOF recruitment and activities on the chromatin. Cell Res 21 : 1182–1195. doi: 10.1038/cr.2011.71 21502975
23. Sun B, Guo S, Tang Q, Li C, Zeng R, et al. (2011) Regulation of the histone acetyltransferase activity of hMOF via autoacetylation of Lys274. Cell Res 21 : 1262–1266. doi: 10.1038/cr.2011.105 21691301
24. Peng L, Ling H, Yuan Z, Fang B, Bloom G, et al. (2012) SIRT1 negatively regulates the activities, functions, and protein levels of hMOF and TIP60. Mol Cell Biol 32 : 2823–2836. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00496-12 22586264
25. Yuan H, Rossetto D, Mellert H, Dang W, Srinivasan M, et al. (2012) MYST protein acetyltransferase activity requires active site lysine autoacetylation. EMBO J 31 : 58–70. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2011.382 22020126
26. Kaidi A, Jackson SP (2013) KAT5 tyrosine phosphorylation couples chromatin sensing to ATM signalling. Nature 498 : 70–74. doi: 10.1038/nature12201 23708966
27. Fullgrabe J, Lynch-Day MA, Heldring N, Li W, Struijk RB, et al. (2013) The histone H4 lysine 16 acetyltransferase hMOF regulates the outcome of autophagy. Nature 500 : 468–471. doi: 10.1038/nature12313 23863932
28. Yi C, Ma M, Ran L, Zheng J, Tong J, et al. (2012) Function and molecular mechanism of acetylation in autophagy regulation. Science 336 : 474–477. doi: 10.1126/science.1216990 22539722
29. Lin SY, Li TY, Liu Q, Zhang C, Li X, et al. (2012) GSK3-TIP60-ULK1 signaling pathway links growth factor deprivation to autophagy. Science 336 : 477–481. doi: 10.1126/science.1217032 22539723
30. Doyon Y, Cayrou C, Ullah M, Landry AJ, Cote V, et al. (2006) ING tumor suppressors are critical regulators of chromatin acetylation required for genome expression and perpetuation. Mol Cell 21 : 51–64. 16387653
31. Ullah M, Pelletier N, Xiao L, Zhao SP, Wang K, et al. (2008) Molecular architecture of quartet MOZ/MORF histone acetyltransferase complexes. Mol Cell Biol 28 : 6828–6843. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01297-08 18794358
32. Lalonde M, Glass KC, Avakumov N, Joncas F, Saksouk N, et al. (2013) Exchange of associated factors directs a switch in HBO1 acetyltransferase histone tail specificity. Genes Dev 27 : 2009–2024. doi: 10.1101/gad.223396.113 24065767
33. Lubula MY, Eckenroth BE, Carlson S, Poplawski A, Chruszcz M, et al. (2014) Structural insights into recognition of acetylated histone ligands by the BRPF1 bromodomain. FEBS Lett 588 : 3844–3854. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2014.09.028 25281266
34. Vezzoli A, Bonadies N, Allen MD, Freund SM, Santiveri CM, et al. (2010) Molecular basis of histone H3K36me3 recognition by the PWWP domain of Brpf1. Nat Struct Mol Biol 17 : 617–619. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.1797 20400950
35. Wu H, Zeng H, Lam R, Tempel W, Amaya MF, et al. (2011) Structural and histone binding ability characterizations of human PWWP domains. PLoS One 6: e18919. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0018919 21720545
36. Chamberlin HM, Thomas JH (2000) The bromodomain protein LIN-49 and trithorax-related protein LIN-59 affect development and gene expression in Caenorhabditis elegans. Development 127 : 713–723. 10648230
37. Chang S, Johnston RJ Jr., Hobert O A transcriptional regulatory cascade that controls left/right asymmetry in chemosensory neurns of C. elegans. Genes Dev 17 : 2123–2137. 12952888
38. O’Meara MM, Zhang F, Hobert O (2010) Maintenance of neuronal laterality in Caenorhabditis elegans through MYST histone acetyltransferase complex components LSY-12, LSY-13 and LIN-49. Genetics 186 : 1497–1502. doi: 10.1534/genetics.110.123661 20923973
39. Laue K, Daujat S, Crump JG, Plaster N, Roehl HH, et al. (2008) The multidomain protein Brpf1 binds histones and is required for Hox gene expression and segmental identity. Development 135 : 1935–1946. doi: 10.1242/dev.017160 18469222
40. Hibiya K, Katsumoto T, Kondo T, Kitabayashi I, Kudo A (2009) Brpf1, a subunit of the MOZ histone acetyl transferase complex, maintains expression of anterior and posterior Hox genes for proper patterning of craniofacial and caudal skeletons. Dev Biol 329 : 176–190. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2009.02.021 19254709
41. Mishima Y, Miyagi S, Saraya A, Negishi M, Endoh M, et al. (2011) The Hbo1-Brd1/Brpf2 complex is responsible for global acetylation of H3K14 and required for fetal liver erythropoiesis. Blood 118 : 2443–2453. doi: 10.1182/blood-2011-01-331892 21753189
42. Katsumoto T, Aikawa Y, Iwama A, Ueda S, Ichikawa H, et al. (2006) MOZ is essential for maintenance of hematopoietic stem cells. Genes Dev 20 : 1321–1330. 16702405
43. Thomas T, Corcoran LM, Gugasyan R, Dixon MP, Brodnicki T, et al. (2006) Monocytic leukemia zinc finger protein is essential for the development of long-term reconstituting hematopoietic stem cells. Genes Dev 20 : 1175–1186. 16651658
44. Deguchi K, Ayton PM, Carapeti M, Kutok JL, Snyder CS, et al. (2003) MOZ-TIF2-induced acute myeloid leukemia requires the MOZ nucleosome binding motif and TIF2-mediated recruitment of CBP. Cancer Cell 3 : 259–271. 12676584
45. Huntly BJ, Shigematsu H, Deguchi K, Lee BH, Mizuno S, et al. (2004) MOZ-TIF2, but not BCR-ABL, confers properties of leukemic stem cells to committed murine hematopoietic progenitors. Cancer Cell 6 : 587–596. 15607963
46. Grasso CS, Wu YM, Robinson DR, Cao X, Dhanasekaran SM, et al. (2012) The mutational landscape of lethal castration-resistant prostate cancer. Nature 487 : 239–243. doi: 10.1038/nature11125 22722839
47. Lynch H, Wen H, Kim YC, Snyder C, Kinarsky Y, et al. (2013) Can Unknown Predisposition in Familial Breast Cancer be Family-Specific? Breast J 19 : 520–528. doi: 10.1111/tbj.12145 23800003
48. Kraft M, Cirstea IC, Voss AK, Thomas T, Goehring I, et al. (2011) Disruption of the histone acetyltransferase MYST4 leads to a Noonan syndrome-like phenotype and hyperactivated MAPK signaling in humans and mice. J Clin Invest 121 : 3479–3491. doi: 10.1172/JCI43428 21804188
49. Clayton-Smith J, O’Sullivan J, Daly S, Bhaskar S, Day R, et al. (2011) Whole-Exome-Sequencing Identifies Mutations in Histone Acetyltransferase Gene KAT6B in Individuals with the Say-Barber-Biesecker Variant of Ohdo Syndrome. Am J Hum Genet 89 : 675–681. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2011.10.008 22077973
50. Simpson MA, Deshpande C, Dafou D, Vissers LE, Woollard WJ, et al. (2012) De Novo Mutations of the Gene Encoding the Histone Acetyltransferase KAT6B Cause Genitopatellar Syndrome. Am J Hum Genet 90 : 290–294. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2011.11.024 22265017
51. Campeau PM, Kim JC, Lu JT, Schwartzentruber JA, Abdul-Rahman OA, et al. (2012) Mutations in KAT6B, Encoding a Histone Acetyltransferase, Cause Genitopatellar Syndrome. Am J Hum Genet 90 : 282–289. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2011.11.023 22265014
52. Yu HC, Geiger EA, Medne L, Zackai EH, Shaikh TH (2014) An individual with blepharophimosis-ptosis-epicanthus inversus syndrome (BPES) and additional features expands the phenotype associated with mutations in KAT6B. Am J Med Genet A 164 : 950–957.
53. Thomas T, Voss AK, Chowdhury K, Gruss P (2000) Querkopf, a MYST family histone acetyltransferase, is required for normal cerebral cortex development. Development 127 : 2537–2548. 10821753
54. Sheikh BN, Dixon MP, Thomas T, Voss AK (2012) Querkopf is a key marker of self-renewal and multipotency of adult neural stem cells. J Cell Sci 125 : 295–309. doi: 10.1242/jcs.077271 22331353
55. You L, Chen L, Panney J, Miao D, Yang XJ (2014) Expression atlas of the epigenetic regulator Brpf1 and its requirement for survival of mouse embryos. Epigenetics 9 : 860–872. doi: 10.4161/epi.28530 24646517
56. Gorski JA, Talley T, Qiu M, Puelles L, Rubenstein JL, et al. (2002) Cortical excitatory neurons and glia, but not GABAergic neurons, are produced in the Emx1-expressing lineage. J Neurosci 22 : 6309–6314. 12151506
57. You L, Zou J, Zhao H, Bertos NR, Park M, et al. (2015) Deficiency of the chromatin regulator Brpf1 causes abnormal brain development. J Biol Chem: e-pub.
58. Forster E, Zhao S, Frotscher M (2006) Laminating the hippocampus. Nat Rev Neurosci 7 : 259–267. 16543914
59. Li G, Pleasure SJ (2007) Genetic regulation of dentate gyrus morphogenesis. Prog Brain Res 163 : 143–152. 17765716
60. Suto F, Tsuboi M, Kamiya H, Mizuno H, Kiyama Y, et al. (2007) Interactions between plexin-A2, plexin-A4, and semaphorin 6A control lamina-restricted projection of hippocampal mossy fibers. Neuron 53 : 535–547. 17296555
61. Favaro R, Valotta M, Ferri AL, Latorre E, Mariani J, et al. (2009) Hippocampal development and neural stem cell maintenance require Sox2-dependent regulation of Shh. Nat Neurosci 12 : 1248–1256. doi: 10.1038/nn.2397 19734891
62. Monaghan AP, Bock D, Gass P, Schwager A, Wolfer DP, et al. (1997) Defective limbic system in mice lacking the tailless gene. Nature 390 : 515–517. 9394001
63. Arnold SJ, Huang GJ, Cheung AF, Era T, Nishikawa S, et al. (2008) The T-box transcription factor Eomes/Tbr2 regulates neurogenesis in the cortical subventricular zone. Genes Dev 22 : 2479–2484. doi: 10.1101/gad.475408 18794345
64. Liu M, Pleasure SJ, Collins AE, Noebels JL, Naya FJ, et al. (2000) Loss of BETA2/NeuroD leads to malformation of the dentate gyrus and epilepsy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 97 : 865–870. 10639171
65. Pellegrini M, Mansouri A, Simeone A, Boncinelli E, Gruss P (1996) Dentate gyrus formation requires Emx2. Development 122 : 3893–3898. 9012509
66. Galichet C, Guillemot F, Parras CM (2008) Neurogenin 2 has an essential role in development of the dentate gyrus. Development 135 : 2031–2041. doi: 10.1242/dev.015115 18448566
67. Tian C, Gong Y, Yang Y, Shen W, Wang K, et al. (2012) Foxg1 has an essential role in postnatal development of the dentate gyrus. J Neurosci 32 : 2931–2949. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5240-11.2012 22378868
68. Zhao C, Deng W, Gage FH (2008) Mechanisms and functional implications of adult neurogenesis. Cell 132 : 645–660. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2008.01.033 18295581
69. Zhang CL, Zou Y, He W, Gage FH, Evans RM (2008) A role for adult TLX-positive neural stem cells in learning and behaviour. Nature 451 : 1004–1007. doi: 10.1038/nature06562 18235445
70. Hodge RD, Garcia AJ 3rd, Elsen GE, Nelson BR, Mussar KE, et al. (2013) Tbr2 expression in Cajal-Retzius cells and intermediate neuronal progenitors is required for morphogenesis of the dentate gyrus. J Neurosci 33 : 4165–4180. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4185-12.2013 23447624
71. Simon R, Brylka H, Schwegler H, Venkataramanappa S, Andratschke J, et al. (2012) A dual function of Bcl11b/Ctip2 in hippocampal neurogenesis. EMBO J 31 : 2922–2936. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2012.142 22588081
72. Hodge RD, Nelson BR, Kahoud RJ, Yang R, Mussar KE, et al. (2012) Tbr2 is essential for hippocampal lineage progression from neural stem cells to intermediate progenitors and neurons. J Neurosci 32 : 6275–6287. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0532-12.2012 22553033
73. Kriegstein A, Alvarez-Buylla A (2009) The glial nature of embryonic and adult neural stem cells. Annu Rev Neurosci 32 : 149–184. doi: 10.1146/annurev.neuro.051508.135600 19555289
74. Altman J, Bayer SA (1990) Migration and distribution of two populations of hippocampal granule cell precursors during the perinatal and postnatal periods. J Comp Neurol 301 : 365–381. 2262596
75. Yu DX, Marchetto MC, Gage FH (2014) How to make a hippocampal dentate gyrus granule neuron. Development 141 : 2366–2375. doi: 10.1242/dev.096776 24917496
76. Champagne N, Bertos NR, Pelletier N, Wang AH, Vezmar M, et al. (1999) Identification of a human histone acetyltransferase related to monocytic leukemia zinc finger protein. J Biol Chem 274 : 28528–28536. 10497217
77. Champagne N, Pelletier N, Yang XJ (2001) The monocytic leukemia zinc finger protein MOZ is a histone acetyltransferase. Oncogene 20 : 404–409. 11313971
78. Kitabayashi I, Aikawa Y, Nguyen LA, Yokoyama A, Ohki M (2001) Activation of AML1-mediated transcription by MOZ and inhibition by the MOZ-CBP fusion protein. EMBO J 20 : 7184–7196. 11742995
79. Kueh AJ, Dixon MP, Voss AK, Thomas T (2011) HBO1 is required for H3K14 acetylation and normal transcriptional activity during embryonic development. Mol Cell Biol 31 : 845–860. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00159-10 21149574
80. Perez-Campo FM, Costa G, Lie ALM, Stifani S, Kouskoff V, et al. (2014) MOZ-mediated repression of p16(INK) (4) (a) is critical for the self-renewal of neural and hematopoietic stem cells. Stem Cells 32 : 1591–1601. doi: 10.1002/stem.1606 24307508
81. Lavado A, Lagutin OV, Chow LM, Baker SJ, Oliver G (2010) Prox1 is required for granule cell maturation and intermediate progenitor maintenance during brain neurogenesis. PLoS Biol 8: e1000565. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1000565 21203589
82. Han YG, Spassky N, Romaguera-Ros M, Garcia-Verdugo JM, Aguilar A, et al. (2008) Hedgehog signaling and primary cilia are required for the formation of adult neural stem cells. Nat Neurosci 11 : 277–284. doi: 10.1038/nn2059 18297065
83. Greenbaum A, Hsu YM, Day RB, Schuettpelz LG, Christopher MJ, et al. (2013) CXCL12 in early mesenchymal progenitors is required for haematopoietic stem-cell maintenance. Nature 495 : 227–230. doi: 10.1038/nature11926 23434756
84. Lu M, Grove EA, Miller RJ (2002) Abnormal development of the hippocampal dentate gyrus in mice lacking the CXCR4 chemokine receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 99 : 7090–7095. 11983855
85. Bagri A, Gurney T, He X, Zou YR, Littman DR, et al. (2002) The chemokine SDF1 regulates migration of dentate granule cells. Development 129 : 4249–4260. 12183377
86. Klein BJ, Lalonde ME, Cote J, Yang XJ, Kutateladze TG (2014) Crosstalk between epigenetic readers regulates the MOZ/MORF HAT complexes. Epigenetics 9 : 186–193. doi: 10.4161/epi.26792 24169304
87. Dong HW (2008) Allen Reference Altas, a digital brain atlas of the C57BL/6J male mouse. Hoboken, New Jersey: John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
88. Paxinos G, Franklin KBJ (2008) The Mouse Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates: Academic Press.
89. Paxinos G, Halliday GM, Watson C, Koutcherov Y, Wang H (2006) Atlas of the Developing Mouse Brain at E17.5, P0 and P6, 1st Edition. Amsteram, Boston, Heidelberg, London, New York: Elsevier, Academic Press.
90. Schambra U (2008) Prenatal mouse brain atlas. New York: Springer.
91. Altman J, Bayer SA (1995) Atlas of prenatal rat brain development. Roca Raton: CRC Press.
Štítky
Genetika Reprodukční medicína
Článek NLRC5 Exclusively Transactivates MHC Class I and Related Genes through a Distinctive SXY ModuleČlánek Inhibition of Telomere Recombination by Inactivation of KEOPS Subunit Cgi121 Promotes Cell LongevityČlánek HOMER2, a Stereociliary Scaffolding Protein, Is Essential for Normal Hearing in Humans and MiceČlánek LRGUK-1 Is Required for Basal Body and Manchette Function during Spermatogenesis and Male FertilityČlánek The GATA Factor Regulates . Developmental Timing by Promoting Expression of the Family MicroRNAsČlánek Systems Biology of Tissue-Specific Response to Reveals Differentiated Apoptosis in the Tick VectorČlánek Phenotype Specific Analyses Reveal Distinct Regulatory Mechanism for Chronically Activated p53Článek The Nuclear Receptor DAF-12 Regulates Nutrient Metabolism and Reproductive Growth in NematodesČlánek The ATM Signaling Cascade Promotes Recombination-Dependent Pachytene Arrest in Mouse SpermatocytesČlánek The Small Protein MntS and Exporter MntP Optimize the Intracellular Concentration of Manganese
Článek vyšel v časopisePLOS Genetics
Nejčtenější tento týden
2015 Číslo 3
-
Všechny články tohoto čísla
- NLRC5 Exclusively Transactivates MHC Class I and Related Genes through a Distinctive SXY Module
- Licensing of Primordial Germ Cells for Gametogenesis Depends on Genital Ridge Signaling
- A Genomic Duplication is Associated with Ectopic Eomesodermin Expression in the Embryonic Chicken Comb and Two Duplex-comb Phenotypes
- Genome-wide Association Study and Meta-Analysis Identify as Genome-wide Significant Susceptibility Gene for Bladder Exstrophy
- Mutations of Human , Encoding the Mitochondrial Asparaginyl-tRNA Synthetase, Cause Nonsyndromic Deafness and Leigh Syndrome
- Exome Sequencing in an Admixed Isolated Population Indicates Variants Confer a Risk for Specific Language Impairment
- Genome-Wide Association Studies in Dogs and Humans Identify as a Risk Variant for Cleft Lip and Palate
- Rapid Evolution of Recombinant for Xylose Fermentation through Formation of Extra-chromosomal Circular DNA
- The Ribosome Biogenesis Factor Nol11 Is Required for Optimal rDNA Transcription and Craniofacial Development in
- Methyl Farnesoate Plays a Dual Role in Regulating Metamorphosis
- Maternal Co-ordinate Gene Regulation and Axis Polarity in the Scuttle Fly
- Maternal Filaggrin Mutations Increase the Risk of Atopic Dermatitis in Children: An Effect Independent of Mutation Inheritance
- Inhibition of Telomere Recombination by Inactivation of KEOPS Subunit Cgi121 Promotes Cell Longevity
- Clonality and Evolutionary History of Rhabdomyosarcoma
- HOMER2, a Stereociliary Scaffolding Protein, Is Essential for Normal Hearing in Humans and Mice
- Methylation-Sensitive Expression of a DNA Demethylase Gene Serves As an Epigenetic Rheostat
- BREVIPEDICELLUS Interacts with the SWI2/SNF2 Chromatin Remodeling ATPase BRAHMA to Regulate and Expression in Control of Inflorescence Architecture
- Seizures Are Regulated by Ubiquitin-specific Peptidase 9 X-linked (USP9X), a De-Ubiquitinase
- The Fun30 Chromatin Remodeler Fft3 Controls Nuclear Organization and Chromatin Structure of Insulators and Subtelomeres in Fission Yeast
- A Cascade of Iron-Containing Proteins Governs the Genetic Iron Starvation Response to Promote Iron Uptake and Inhibit Iron Storage in Fission Yeast
- Mutation in MRPS34 Compromises Protein Synthesis and Causes Mitochondrial Dysfunction
- LRGUK-1 Is Required for Basal Body and Manchette Function during Spermatogenesis and Male Fertility
- Cis-Regulatory Mechanisms for Robust Olfactory Sensory Neuron Class-restricted Odorant Receptor Gene Expression in
- Effects on Murine Behavior and Lifespan of Selectively Decreasing Expression of Mutant Huntingtin Allele by Supt4h Knockdown
- HDAC4-Myogenin Axis As an Important Marker of HD-Related Skeletal Muscle Atrophy
- A Conserved Domain in the Scc3 Subunit of Cohesin Mediates the Interaction with Both Mcd1 and the Cohesin Loader Complex
- Selective and Genetic Constraints on Pneumococcal Serotype Switching
- Bacterial Infection Drives the Expression Dynamics of microRNAs and Their isomiRs
- The GATA Factor Regulates . Developmental Timing by Promoting Expression of the Family MicroRNAs
- Accumulation of Glucosylceramide in the Absence of the Beta-Glucosidase GBA2 Alters Cytoskeletal Dynamics
- Reproductive Isolation of Hybrid Populations Driven by Genetic Incompatibilities
- The Contribution of Alu Elements to Mutagenic DNA Double-Strand Break Repair
- Systems Biology of Tissue-Specific Response to Reveals Differentiated Apoptosis in the Tick Vector
- Tfap2a Promotes Specification and Maturation of Neurons in the Inner Ear through Modulation of Bmp, Fgf and Notch Signaling
- The Lysine Acetyltransferase Activator Brpf1 Governs Dentate Gyrus Development through Neural Stem Cells and Progenitors
- PHABULOSA Controls the Quiescent Center-Independent Root Meristem Activities in
- DNA Polymerase ζ-Dependent Lesion Bypass in Is Accompanied by Error-Prone Copying of Long Stretches of Adjacent DNA
- Examining the Evolution of the Regulatory Circuit Controlling Secondary Metabolism and Development in the Fungal Genus
- Zinc Finger Independent Genome-Wide Binding of Sp2 Potentiates Recruitment of Histone-Fold Protein Nf-y Distinguishing It from Sp1 and Sp3
- GAGA Factor Maintains Nucleosome-Free Regions and Has a Role in RNA Polymerase II Recruitment to Promoters
- Neurospora Importin α Is Required for Normal Heterochromatic Formation and DNA Methylation
- Ccr4-Not Regulates RNA Polymerase I Transcription and Couples Nutrient Signaling to the Control of Ribosomal RNA Biogenesis
- Phenotype Specific Analyses Reveal Distinct Regulatory Mechanism for Chronically Activated p53
- A Systems-Level Interrogation Identifies Regulators of Blood Cell Number and Survival
- Morphological Mutations: Lessons from the Cockscomb
- Genetic Interaction Mapping Reveals a Role for the SWI/SNF Nucleosome Remodeler in Spliceosome Activation in Fission Yeast
- The Role of China in the Global Spread of the Current Cholera Pandemic
- The Nuclear Receptor DAF-12 Regulates Nutrient Metabolism and Reproductive Growth in Nematodes
- A Zinc Finger Motif-Containing Protein Is Essential for Chloroplast RNA Editing
- Resistance to Gray Leaf Spot of Maize: Genetic Architecture and Mechanisms Elucidated through Nested Association Mapping and Near-Isogenic Line Analysis
- Small Regulatory RNA-Induced Growth Rate Heterogeneity of
- Mitochondrial Dysfunction Reveals the Role of mRNA Poly(A) Tail Regulation in Oculopharyngeal Muscular Dystrophy Pathogenesis
- Complex Genomic Rearrangements at the Locus Include Triplication and Quadruplication
- Male-Biased Aganglionic Megacolon in the TashT Mouse Line Due to Perturbation of Silencer Elements in a Large Gene Desert of Chromosome 10
- Sex Ratio Meiotic Drive as a Plausible Evolutionary Mechanism for Hybrid Male Sterility
- Tertiary siRNAs Mediate Paramutation in .
- RECG Maintains Plastid and Mitochondrial Genome Stability by Suppressing Extensive Recombination between Short Dispersed Repeats
- Escape from X Inactivation Varies in Mouse Tissues
- Opposite Phenotypes of Muscle Strength and Locomotor Function in Mouse Models of Partial Trisomy and Monosomy 21 for the Proximal Region
- Glycosyl Phosphatidylinositol Anchor Biosynthesis Is Essential for Maintaining Epithelial Integrity during Embryogenesis
- Hyperdiverse Gene Cluster in Snail Host Conveys Resistance to Human Schistosome Parasites
- The Class Homeodomain Factors and Cooperate in . Embryonic Progenitor Cells to Regulate Robust Development
- Recombination between Homologous Chromosomes Induced by Unrepaired UV-Generated DNA Damage Requires Mus81p and Is Suppressed by Mms2p
- Synergistic Interactions between Orthologues of Genes Spanned by Human CNVs Support Multiple-Hit Models of Autism
- Gene Networks Underlying Convergent and Pleiotropic Phenotypes in a Large and Systematically-Phenotyped Cohort with Heterogeneous Developmental Disorders
- The ATM Signaling Cascade Promotes Recombination-Dependent Pachytene Arrest in Mouse Spermatocytes
- Combinatorial Control of Light Induced Chromatin Remodeling and Gene Activation in
- Linking Aβ42-Induced Hyperexcitability to Neurodegeneration, Learning and Motor Deficits, and a Shorter Lifespan in an Alzheimer’s Model
- The Complex Contributions of Genetics and Nutrition to Immunity in
- NatB Domain-Containing CRA-1 Antagonizes Hydrolase ACER-1 Linking Acetyl-CoA Metabolism to the Initiation of Recombination during . Meiosis
- Transcriptomic Profiling of Reveals Reprogramming of the Crp Regulon by Temperature and Uncovers Crp as a Master Regulator of Small RNAs
- Osteopetrorickets due to Snx10 Deficiency in Mice Results from Both Failed Osteoclast Activity and Loss of Gastric Acid-Dependent Calcium Absorption
- A Genomic Portrait of Haplotype Diversity and Signatures of Selection in Indigenous Southern African Populations
- Sequence Features and Transcriptional Stalling within Centromere DNA Promote Establishment of CENP-A Chromatin
- Inhibits Neuromuscular Junction Growth by Downregulating the BMP Receptor Thickveins
- Replicative DNA Polymerase δ but Not ε Proofreads Errors in and in
- Unsaturation of Very-Long-Chain Ceramides Protects Plant from Hypoxia-Induced Damages by Modulating Ethylene Signaling in
- The Small Protein MntS and Exporter MntP Optimize the Intracellular Concentration of Manganese
- A Meta-analysis of Gene Expression Signatures of Blood Pressure and Hypertension
- Pervasive Variation of Transcription Factor Orthologs Contributes to Regulatory Network Evolution
- Network Analyses Reveal Novel Aspects of ALS Pathogenesis
- A Role for the Budding Yeast Separase, Esp1, in Ty1 Element Retrotransposition
- Nab3 Facilitates the Function of the TRAMP Complex in RNA Processing via Recruitment of Rrp6 Independent of Nrd1
- A RecA Protein Surface Required for Activation of DNA Polymerase V
- PLOS Genetics
- Archiv čísel
- Aktuální číslo
- Informace o časopisu
Nejčtenější v tomto čísle- Clonality and Evolutionary History of Rhabdomyosarcoma
- Morphological Mutations: Lessons from the Cockscomb
- Maternal Filaggrin Mutations Increase the Risk of Atopic Dermatitis in Children: An Effect Independent of Mutation Inheritance
- Transcriptomic Profiling of Reveals Reprogramming of the Crp Regulon by Temperature and Uncovers Crp as a Master Regulator of Small RNAs
Kurzy
Zvyšte si kvalifikaci online z pohodlí domova
Současné možnosti léčby obezity
nový kurzAutoři: MUDr. Martin Hrubý
Všechny kurzyPřihlášení#ADS_BOTTOM_SCRIPTS#Zapomenuté hesloZadejte e-mailovou adresu, se kterou jste vytvářel(a) účet, budou Vám na ni zaslány informace k nastavení nového hesla.
- Vzdělávání



