-
Články
Top novinky
Reklama- Vzdělávání
- Časopisy
Top články
Nové číslo
- Témata
Top novinky
Reklama- Videa
- Podcasty
Nové podcasty
Reklama- Kariéra
Doporučené pozice
Reklama- Praxe
Top novinky
ReklamaSensing of the Microbial Neighborhood by
article has not abstract
Published in the journal: . PLoS Pathog 9(10): e32767. doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1003661
Category: Pearls
doi: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1003661Summary
article has not abstract
Dual Identities: Candida albicans as Human Commensal and Opportunistic Pathogen
Candida albicans is a polymorphic fungus that inhabits a variety of niches in healthy human bodies. In addition to being a component of the normal microbiota, C. albicans is an opportunistic pathogen that causes superficial mucosal infections as well as disseminated disease. Importantly, C. albicans that is part of the normal microbiota is responsible for seeding these infections [1]. As the fourth most common cause of nosocomial infections, C. albicans is commonly isolated from immunocompromised individuals, including those with HIV, those immunosuppressed due to cancer treatment, and premature babies [2]. The ability of this fungus to present as both as a commensal and as a life-threatening pathogen is due, in large part, to its ability to sense and react to the environment. C. albicans uses quorum sensing to react to other Candida cells, pheromone signaling in the context of mating and sexual biofilm formation, and a variety of mechanisms for interkingdom interactions with the bacterial microbiota. This article highlights the ways in which C. albicans cells signal both to one another and to other microbial species.
Quorum Sensing in C. albicans
C. albicans virulence depends on its ability to switch between distinct morphologic and phenotypic states, and these transitions are directly influenced by its environment. Quorum sensing (QS) is used by C. albicans to communicate with other Candida cells, and is driven by soluble quorum-sensing molecules or autoinducers that are secreted into the environment in a density-dependent manner [3], [4]. QS regulates several pathogenic traits including hyphal (filamentous) growth. This phenomenon is evident by the “inoculum effect,” in which the formation of hyphae is repressed in cells grown at high densities, while cells grown at low densities are able to germinate [5], [6] (Figure 1A). Several key QS molecules have been identified that have antagonistic effects, including farnesol and tyrosol. Farnesol inhibits the yeast-hyphal transition by inhibiting adenylate cyclase (Cyr1), part of a central regulatory pathway that impacts filamentous growth [5]–[8] (Figure 1B). Conversely, tyrosol shortens lag-phase growth in low-density cultures and stimulates germ-tube formation in yeast cells [9]. Other molecules that are potential QS molecules in C. albicans include phenylethyl alcohol, tryptophol, and MARS (morphogenic autoregulatory substance), although the mechanisms of action of these molecules remain unclear [10]–[12]. Thus, multiple QS molecules can impact C. albicans morphology (Figure 1).
Fig. 1. Environmental cues sensed by C. albicans. 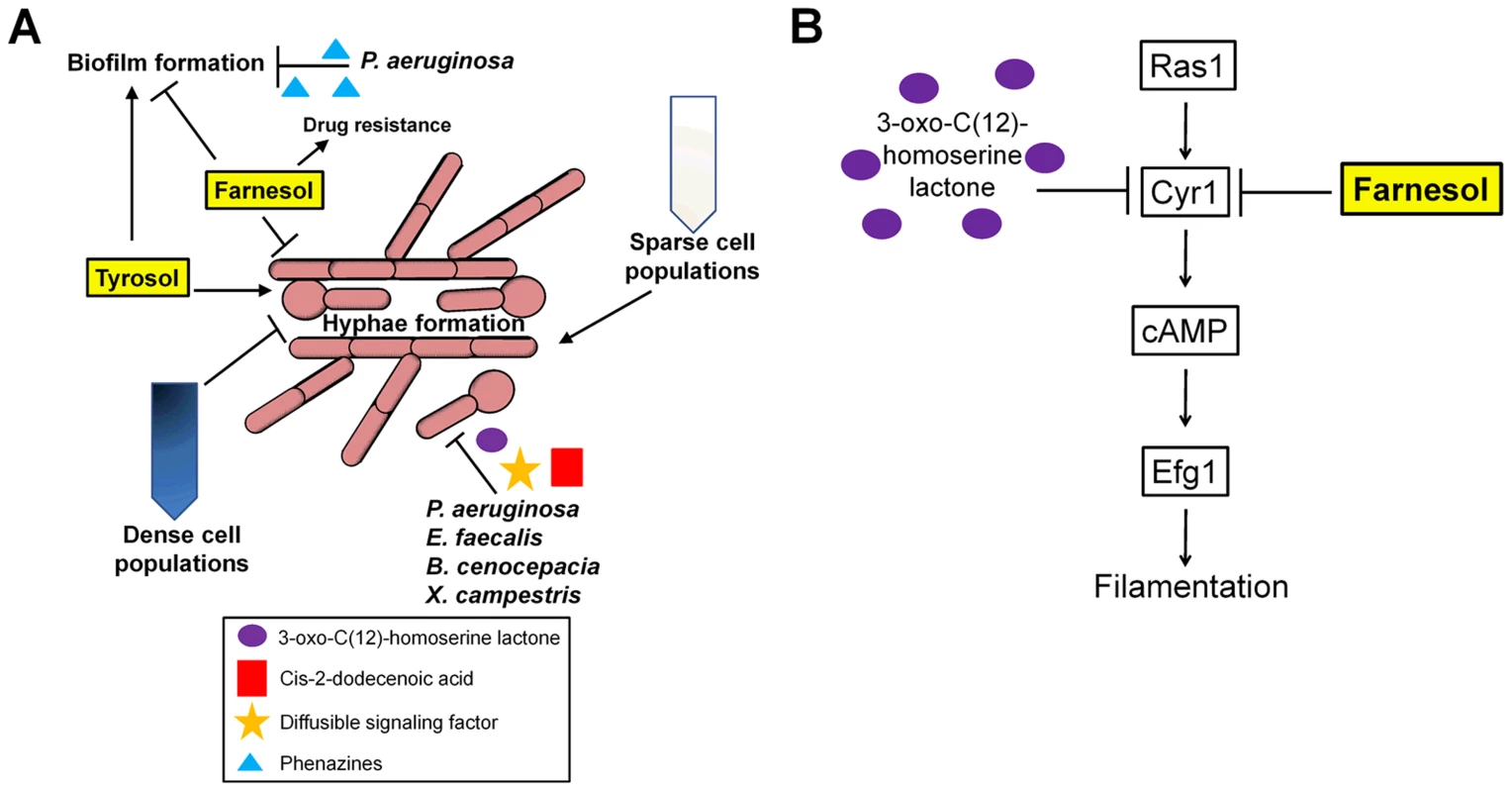
(A) Schematic representation of how C. albicans morphology and biofilm formation is regulated by quorum sensing and signaling with other microbial species. (B) Farnesol and 3-oxo-C(12)-homoserine lactone both act on the Ras1 pathway to inhibit the yeast-to-hyphal transition by inhibiting Cyr1 and cAMP signaling. Quorum sensing also regulates the formation of biofilms, which are structured communities of yeast cells and hyphae that form on host tissues or the surface of implanted medical devices. These structures also accrue an extracellular matrix that is made up of carbohydrates including β-1,3 glucan [13]. As the QS molecule farnesol inhibits filamentation, it also acts to suppress overall biofilm formation [14]. However, farnesol and possibly other filamentation-repressing QS molecules may also promote biofilm-mediated infections by inducing the formation of yeast cells that are then easily dispersed from mature biofilms [15].
Pheromones Stimulate Both Biofilm Formation and Sexual Reproduction
Long thought to be asexual, mating was discovered in C. albicans over a decade ago [16], [17]. In order to mate, C. albicans cells must be homozygous at the mating-type-like (MTL) locus and undergo a phenotypic switch from the white state to the mating-competent opaque state [18], [19]. The white-opaque switch is regulated by interacting transcriptional feedback loops and these lead to stable expression of Wor1, the master regulator of the opaque state [20] (Figure 2A). Following switching to opaque, a and α cells undergo mating ∼106 times more efficiently than cells in the white state.
Fig. 2. C. albicans white and opaque cells respond differently to pheromone. 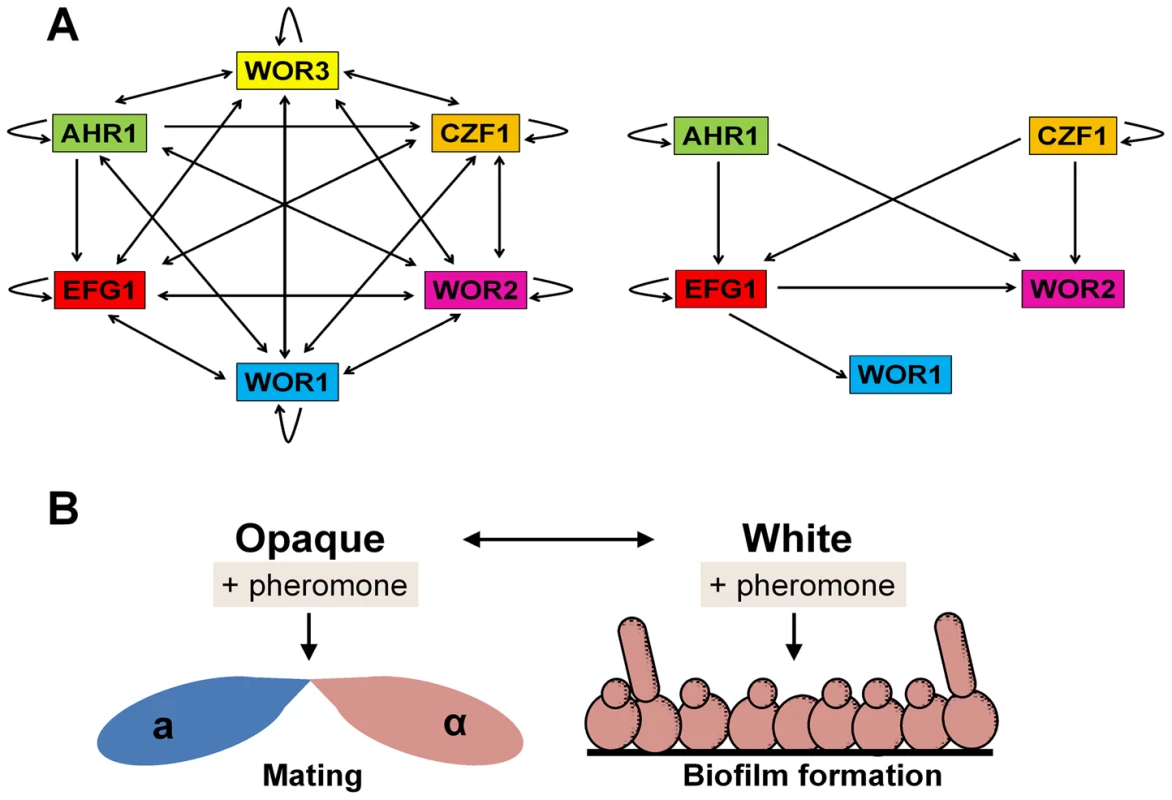
(A) The transcriptional network regulating formation of the opaque cell state (left) and white cell state (right) in C. albicans. Arrows indicate binding of a transcription factor to the promoter of another transcription factor, as determined by Hernday and coworkers [19]. (B) Schematic of the differential response of C. albicans white and opaque cells to pheromone. Pheromones induce mating responses in opaque cells but biofilm formation in white cells. Notably, only opaque cells secrete sexual pheromones, yet both white and opaque a and α cells can respond to pheromones secreted by the opposite mating type. While opaque cells form conjugation tubes and undergo mating, white cells become more adhesive, forming pheromone-induced sexual biofilms [21], [22] (Figure 2B). Sexual biofilms promote the stabilization of pheromone gradients between opaque mating partners, allowing these cells to locate one another more efficiently and to undergo mating [23]. Interspecies pheromone signaling between different Candida species can also drive biofilm formation in white cells and sexual mating in opaque cells, indicating a surprising level of promiscuity in sexual signaling [21]. Mechanistically, pheromone signaling in both white and opaque cells occurs via the same conserved MAPK signaling pathway and Ste12/Cph1 transcription factor [24], [25]. It therefore remains to be seen how distinct phenotypic outputs are generated by the two phenotypic states, as well as the in vivo consequence of sexual biofilm formation.
QS also influences mating of C. albicans. Farnesol is produced by white cells growing aerobically but not by opaque cells, regardless of whether they are grown in aerobic or anaerobic environments [26]. Farnesol has been shown to kill opaque cells and decrease the mating efficiency under aerobic conditions, while not affecting white cells [26]. Aerobic production of farnesol may therefore restrict opaque cell formation and C. albicans mating to anaerobic sites in the body.
Interkingdom Interactions between C. albicans and Bacteria
C. albicans exists in many niches in the human body including the skin, oral cavity, gastrointestinal (GI), and reproductive tracts. Therefore, it inevitably encounters and interacts with many other microbial species, and these interactions affect the survival, colonization, and pathogenesis of the organisms involved.
The gram-negative bacterium Pseudomonas aeruginosa is often co-isolated with C. albicans from patients with hospital-acquired infections, particularly those linked with colonization of medical devices such as catheters, patients with cystic fibrosis, and burn victims [27]. These two microbial species exhibit extensive crosstalk through secreted signaling molecules. P. aeruginosa harbors two QS systems and is able to establish an infection by attaching to and forming biofilms on C. albicans filaments, which, in turn, restricts their growth and causes death of the fungal cell [28]. Pyocyanin, haemolytic phospholipase C, phenazines, as well as other virulence factors, including GacA, LasR, RhlR, and RpoN, have been shown to limit the growth of C. albicans. Moreover, phenazines impair C. albicans biofilm formation and alter its metabolism thereby further decreasing virulence [29], [30] (Figure 1A). P. aeruginosa is also able to suppress the yeast-hyphal transition by producing the QS signaling molecule 3-oxo-C12 homoserine lactone (HSL) [28] (Figure 1B). Other bacteria also secrete substances that repress hyphal growth including two proteases regulated by the Fsr QS system in Enterococcus faecalis, cis-2-dodecenoic acid (BDSF) in Burkholderia cenocepacia, and diffusible signal factor (DSF) in Xanthomonas campestris [31]–[33] (Figure 1A). Increased C. albicans virulence is observed in the presence of P. aeruginosa, especially in the context of burn wounds. This is thought to be due to LasB (pseudolysin), a proteolytic enzyme produced by P. aeruginosa [34]. LasB has been implicated in playing a role in swarming motility and biofilm formation, and it is possible that through its proteolytic activity LasB is generating an amino acid signal that allows for increased biofilm formation and virulence.
Bacterial species that comprise the normal microbiota can also inhibit C. albicans from colonizing in vivo niches. For example, Lactobacillus sp., Enterococcus faecalis, and other bacterial flora restrict C. albicans colonization through the production of signaling molecules such as indole and metabolic by-products of lactic acid bacteria, which regulate factors responsible for the formation of filaments and biofilms [35]–[37]. Other proposed mechanisms by which commensal bacteria prevent C. albicans colonization include the production of hydrogen peroxide or organic acids, alteration of the host immune response, or by physically blocking bodily niches thereby preventing fungal adherence and invasion [37], [38]. Hence, it is not surprising that broad-spectrum antibiotic use is associated with C. albicans infections, and a treatment option for these infections includes the use of probiotics to repopulate the normal flora [37].
Bacteria also provide fungi with compounds that can enhance fungal virulence and, conversely, fungi can enhance bacterial virulence. For example, endotoxin (LPS) from Escherichia coli is considered an important contributor to virulence in co-infection experiments, and it has recently been shown that C. albicans responds directly to LPS [39], [40]. In addition, bacterial peptidoglycan molecules present in human serum induce hyphae formation in C. albicans, promoting tissue invasion and pathogenesis by this species [41]. C. albicans can also increase the virulence of bacterial pathogens such as E. faecalis, Staphylococcus aureus, and Serratia marcescens, as co-infection results in more severe disease than infection with the bacterial species alone [42]. Presumably, unidentified QS molecules and other virulence determinants are responsible for signaling between the different species thereby resulting in increased virulence.
Bacterial and fungal species are able to form mixed-species biofilms in oral environments, burn wounds, catheters, and other niches. These biofilms protect the microbial community from environmental pressures such as antibiotics and the host immune system. In the oral cavity, commensal Streptococcus species adhere to C. albicans cell wall proteins and adhesins including SspA, SspB, and Als3, thereby enhancing biofilm formation [43], [44]. Streptococcus species can also absorb protein components from saliva resulting in increased adherence and hyphal development in C. albicans, strengthening the biofilm and providing additional places for Streptococcus cells to bind [44]. Extracellular matrix production by S. epidermidis can inhibit penetration of antifungal drugs such as fluconazole in mixed-species biofilms [13].
Together, these findings reveal the complexities of mixed-species biofilms and the role that these structures play in responses to antimicrobial therapy. It is likely that these interactions represent the proverbial tip of the iceberg, and that further studies will be necessary to define how microbial species affect colonization and infection by Candida species, and for developing medical interventions that target these human pathogens.
Zdroje
1. FridkinSK, JarvisWR (1996) Epidemiology of nosocomial fungal infections. Clin Microbiol Rev 9 : 499–511.
2. WisplinghoffH, BischoffT, TallentSM, SeifertH, WenzelRP, et al. (2004) Nosocomial bloodstream infections in US hospitals: analysis of 24,179 cases from a prospective nationwide surveillance study. Clin Infect Dis 39 : 309–317.
3. AlbuquerqueP, CasadevallA (2012) Quorum sensing in fungi–a review. Med Mycol 50 : 337–345.
4. HoganDA (2006) Talking to themselves: autoregulation and quorum sensing in fungi. Eukaryot Cell 5 : 613–619.
5. HornbyJM, JensenEC, LisecAD, TastoJJ, JahnkeB, et al. (2001) Quorum sensing in the dimorphic fungus Candida albicans is mediated by farnesol. Appl Environ Microbiol 67 : 2982–2992.
6. OhKB, MiyazawaH, NaitoT, MatsuokaH (2001) Purification and characterization of an autoregulatory substance capable of regulating the morphological transition in Candida albicans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 98 : 4664–4668.
7. LindsayAK, DeveauA, PiispanenAE, HoganDA (2012) Farnesol and cyclic AMP signaling effects on the hypha-to-yeast transition in Candida albicans. Eukaryot Cell 11 : 1219–1225.
8. PiispanenAE, GrahlN, HollomonJM, HoganDA (2013) Regulated proteolysis of Candida albicans Ras1 is involved in morphogenesis and quorum sensing regulation. Mol Microbiol 89 : 166–178.
9. ChenH, FujitaM, FengQ, ClardyJ, FinkGR (2004) Tyrosol is a quorum-sensing molecule in Candida albicans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101 : 5048–5052.
10. HazenKC, CutlerJE (1983) Isolation and purification of morphogenic autoregulatory substance produced by Candida albicans. J Biochem 94 : 777–783.
11. GhoshS, KebaaraBW, AtkinAL, NickersonKW (2008) Regulation of aromatic alcohol production in Candida albicans. Appl Environ Microbiol 74 : 7211–7218.
12. ChauhanNM, RautJS, KaruppayilSM (2011) A morphogenetic regulatory role for ethyl alcohol in Candida albicans. Mycoses 54: e697–703.
13. Al-FattaniMA, DouglasLJ (2006) Biofilm matrix of Candida albicans and Candida tropicalis: chemical composition and role in drug resistance. J Med Microbiol 55 : 999–1008.
14. RamageG, SavilleSP, WickesBL, Lopez-RibotJL (2002) Inhibition of Candida albicans biofilm formation by farnesol, a quorum-sensing molecule. Appl Environ Microbiol 68 : 5459–5463.
15. BlankenshipJR, MitchellAP (2006) How to build a biofilm: a fungal perspective. Curr Opin Microbiol 9 : 588–594.
16. HullCM, RaisnerRM, JohnsonAD (2000) Evidence for mating of the “asexual” yeast Candida albicans in a mammalian host. Science 289 : 307–310.
17. MageeBB, MageePT (2000) Induction of mating in Candida albicans by construction of MTLa and MTLalpha strains. Science 289 : 310–313.
18. MillerMG, JohnsonAD (2002) White-opaque switching in Candida albicans is controlled by mating-type locus homeodomain proteins and allows efficient mating. Cell 110 : 293–302.
19. HerndayAD, LohseMB, FordycePM, NobileCJ, DerisiJL, et al. (2013) Structure of the transcriptional network controlling white-opaque switching in Candida albicans. Mol Microbiol 90 : 22–35.
20. ZordanRE, MillerMG, GalgoczyDJ, TuchBB, JohnsonAD (2007) Interlocking transcriptional feedback loops control white-opaque switching in Candida albicans. PLoS Biol 5: e256 doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.0050256
21. AlbyK, BennettRJ (2011) Interspecies pheromone signaling promotes biofilm formation and same-sex mating in Candida albicans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108 : 2510–2515.
22. DanielsKJ, SrikanthaT, LockhartSR, PujolC, SollDR (2006) Opaque cells signal white cells to form biofilms in Candida albicans. EMBO J 25 : 2240–2252.
23. ParkYN, DanielsKJ, PujolC, SrikanthaT, SollDR (2013) Candida albicans forms a specialized “sexual” as well as “pathogenic” biofilm. Eukaryot Cell 12 : 1120–1131.
24. LinC-H, KabrawalaS, FoxEP, NobileCJ, JohnsonAD, et al. (2013) Genetic control of conventional and pheromone-stimulated biofilm formation in Candida albicans. PLoS Pathog 9: e1003305 doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1003305
25. YiS, SahniN, DanielsKJ, PujolC, SrikanthaT, et al. (2008) The same receptor, G protein, and mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway activate different downstream regulators in the alternative white and opaque pheromone responses of Candida albicans. Mol Biol Cell 19 : 957–970.
26. DumitruR, NavarathnaDH, SemighiniCP, ElowskyCG, DumitruRV, et al. (2007) In vivo and in vitro anaerobic mating in Candida albicans. Eukaryot Cell 6 : 465–472.
27. PierceGE (2005) Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Candida albicans, and device-related nosocomial infections: implications, trends, and potential approaches for control. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 32 : 309–318.
28. HoganDA, KolterR (2002) Pseudomonas-Candida interactions: an ecological role for virulence factors. Science 296 : 2229–2232.
29. HolcombeLJ, McAlesterG, MunroCA, EnjalbertB, BrownAJ, et al. (2010) Pseudomonas aeruginosa secreted factors impair biofilm development in Candida albicans. Microbiology 156 : 1476–1486.
30. MoralesDK, GrahlN, OkegbeC, DietrichLE, JacobsNJ, et al. (2013) Control of Candida albicans metabolism and biofilm formation by Pseudomonas aeruginosa phenazines. mBio 4: e00526–00512.
31. CruzMR, GrahamCE, GaglianoBC, LorenzMC, GarsinDA (2013) Enterococcus faecalis inhibits hyphal morphogenesis and virulence of Candida albicans. Infect Immun 81 : 189–200.
32. BoonC, DengY, WangLH, HeY, XuJL, et al. (2008) A novel DSF-like signal from Burkholderia cenocepacia interferes with Candida albicans morphological transition. ISME J 2 : 27–36.
33. WangLH, HeY, GaoY, WuJE, DongYH, et al. (2004) A bacterial cell-cell communication signal with cross-kingdom structural analogues. Mol Microbiol 51 : 903–912.
34. RouxD, GaudryS, DreyfussD, El-BennaJ, de ProstN, et al. (2009) Candida albicans impairs macrophage function and facilitates Pseudomonas aeruginosa pneumonia in rat. Crit Care Med 37 : 1062–1067.
35. OhS, GoGW, MylonakisE, KimY (2012) The bacterial signalling molecule indole attenuates the virulence of the fungal pathogen Candida albicans. J Appli Microbiol 113 : 622–628.
36. KennedyMJ, VolzPA (1985) Ecology of Candida albicans gut colonization: inhibition of Candida adhesion, colonization, and dissemination from the gastrointestinal tract by bacterial antagonism. Infect Immun 49 : 654–663.
37. WargoMJ, HoganDA (2006) Fungal–bacterial interactions: a mixed bag of mingling microbes. Curr Opin Microbiol 9 : 359–364.
38. MoralesDK, HoganDA (2010) Candida albicans interactions with bacteria in the context of human health and disease. PLoS Pathog 6: e1000886 doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1000886
39. BandaraHM, BPKC, WattRM, JinLJ, SamaranayakeLP (2013) Pseudomonas aeruginosa lipopolysaccharide inhibits Candida albicans hyphae formation and alters gene expression during biofilm development. Mol Oral Microbiol 28 : 54–69.
40. RogersH, WilliamsDW, FengGJ, LewisMA, WeiXQ (2013) Role of bacterial lipopolysaccharide in enhancing host immune response to Candida albicans. Clin Dev Immunol 2013 : 320168.
41. XuXL, LeeRT, FangHM, WangYM, LiR, et al. (2008) Bacterial peptidoglycan triggers Candida albicans hyphal growth by directly activating the adenylyl cyclase Cyr1p. Cell Host Microbe 4 : 28–39.
42. CarlsonE (1983) Enhancement by Candida albicans of Staphylococcus aureus, Serratia marcescens, and Streptococcus faecalis in the establishment of infection in mice. Infect Immun 39 : 193–197.
43. PelegAY, HoganDA, MylonakisE (2010) Medically important bacterial-fungal interactions. Nat Rev Microbiol 8 : 340–349.
44. HarriottMM, NoverrMC (2011) Importance of Candida-bacterial polymicrobial biofilms in disease. Trends Microbiol 19 : 557–563.
Štítky
Hygiena a epidemiologie Infekční lékařství Laboratoř
Článek vyšel v časopisePLOS Pathogens
Nejčtenější tento týden
2013 Číslo 10- Jak souvisí postcovidový syndrom s poškozením mozku?
- Měli bychom postcovidový syndrom léčit antidepresivy?
- Farmakovigilanční studie perorálních antivirotik indikovaných v léčbě COVID-19
- 10 bodů k očkování proti COVID-19: stanovisko České společnosti alergologie a klinické imunologie ČLS JEP
-
Všechny články tohoto čísla
- Are We There Yet? Recent Progress in the Molecular Diagnosis and Novel Antifungal Targeting of and Invasive Aspergillosis
- Fungal Iron Availability during Deep Seated Candidiasis Is Defined by a Complex Interplay Involving Systemic and Local Events
- Emergence of Azole-Resistant Strains due to Agricultural Azole Use Creates an Increasing Threat to Human Health
- Fungal Adenylyl Cyclase Acts As a Signal Sensor and Integrator and Plays a Central Role in Interaction with Bacteria
- Sensing of the Microbial Neighborhood by
- Antivirulence Therapy for Animal Production: Filling an Arsenal with Novel Weapons for Sustainable Disease Control
- The Cell Biology of : How to Teach Using Animations
- A Structure-Guided Mutation in the Major Capsid Protein Retargets BK Polyomavirus
- RNA Biology in Fungal Phytopathogens
- , , and the Human Mouth: A Sticky Situation
- The Gene Is Essential for Resistance to Human Serum in
- Unisexual Reproduction Drives Evolution of Eukaryotic Microbial Pathogens
- Bacterial Pathogens Activate a Common Inflammatory Pathway through IFNλ Regulation of PDCD4
- Bats and Viruses: Friend or Foe?
- Protein Trafficking through the Endosomal System Prepares Intracellular Parasites for a Home Invasion
- IL-22 Mediates Goblet Cell Hyperplasia and Worm Expulsion in Intestinal Helminth Infection
- B Cells Enhance Antigen-Specific CD4 T Cell Priming and Prevent Bacteria Dissemination following Genital Tract Infection
- Alternative Roles for CRISPR/Cas Systems in Bacterial Pathogenesis
- Chemicals, Climate, and Control: Increasing the Effectiveness of Malaria Vector Control Tools by Considering Relevant Temperatures
- Dengue Vaccines: Strongly Sought but Not a Reality Just Yet
- Feeding Uninvited Guests: mTOR and AMPK Set the Table for Intracellular Pathogens
- Driven Enforced Viral Replication in Dendritic Cells Contributes to Break of Immunological Tolerance in Autoimmune Diabetes
- IL-4Rα-Associated Antigen Processing by B Cells Promotes Immunity in Infection
- A Gammaherpesvirus Uses Alternative Splicing to Regulate Its Tropism and Its Sensitivity to Neutralization
- MicroRNA-155 Promotes Autophagy to Eliminate Intracellular Mycobacteria by Targeting Rheb
- Epigenetic Dominance of Prion Conformers
- MAIT Cells Detect and Efficiently Lyse Bacterially-Infected Epithelial Cells
- The Role of TcdB and TccC Subunits in Secretion of the Tcd Toxin Complex
- A Mechanism for the Inhibition of DNA-PK-Mediated DNA Sensing by a Virus
- PLOS Pathogens
- Archiv čísel
- Aktuální číslo
- Informace o časopisu
Nejčtenější v tomto čísle- Dengue Vaccines: Strongly Sought but Not a Reality Just Yet
- MicroRNA-155 Promotes Autophagy to Eliminate Intracellular Mycobacteria by Targeting Rheb
- Alternative Roles for CRISPR/Cas Systems in Bacterial Pathogenesis
- Feeding Uninvited Guests: mTOR and AMPK Set the Table for Intracellular Pathogens
Kurzy
Zvyšte si kvalifikaci online z pohodlí domova
Současné možnosti léčby obezity
nový kurzAutoři: MUDr. Martin Hrubý
Všechny kurzyPřihlášení#ADS_BOTTOM_SCRIPTS#Zapomenuté hesloZadejte e-mailovou adresu, se kterou jste vytvářel(a) účet, budou Vám na ni zaslány informace k nastavení nového hesla.
- Vzdělávání



