-
Články
Top novinky
Reklama- Vzdělávání
- Časopisy
Top články
Nové číslo
- Témata
Top novinky
Reklama- Videa
- Podcasty
Nové podcasty
Reklama- Kariéra
Doporučené pozice
Reklama- Praxe
Top novinky
ReklamaSuppression of mRNAs Encoding Tegument Tetraspanins from Results in Impaired Tegument Turnover
Schistosomes express a family of integral membrane proteins, called tetraspanins (TSPs), in the outer surface membranes of the tegument. Two of these tetraspanins, Sm-TSP-1 and Sm-TSP-2, confer protection as vaccines in mice, and individuals who are naturally resistant to S. mansoni infection mount a strong IgG response to Sm-TSP-2. To determine their functions in the tegument of S. mansoni we used RNA interference to silence expression of Sm-tsp-1 and Sm-tsp-2 mRNAs. Soaking of parasites in Sm-tsp dsRNAs resulted in 61% (p = 0.009) and 74% (p = 0.009) reductions in Sm-tsp-1 and Sm-tsp-2 transcription levels, respectively, in adult worms, and 67%–75% (p = 0.011) and 69%–89% (p = 0.004) reductions in Sm-tsp-1 and Sm-tsp-2 transcription levels, respectively, in schistosomula compared to worms treated with irrelevant control (luciferase) dsRNA. Ultrastructural morphology of adult worms treated in vitro with Sm-tsp-2 dsRNA displayed a distinctly vacuolated and thinner tegument compared with controls. Schistosomula exposed in vitro to Sm-tsp-2 dsRNA had a significantly thinner and more vacuolated tegument, and morphology consistent with a failure of tegumentary invaginations to close. Injection of mice with schistosomula that had been electroporated with Sm-tsp-1 and Sm-tsp-2 dsRNAs resulted in 61% (p = 0.005) and 83% (p = 0.002) reductions in the numbers of parasites recovered from the mesenteries four weeks later when compared to dsRNA-treated controls. These results imply that tetraspanins play important structural roles impacting tegument development, maturation or stability.
Published in the journal: . PLoS Pathog 6(4): e32767. doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1000840
Category: Research Article
doi: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1000840Summary
Schistosomes express a family of integral membrane proteins, called tetraspanins (TSPs), in the outer surface membranes of the tegument. Two of these tetraspanins, Sm-TSP-1 and Sm-TSP-2, confer protection as vaccines in mice, and individuals who are naturally resistant to S. mansoni infection mount a strong IgG response to Sm-TSP-2. To determine their functions in the tegument of S. mansoni we used RNA interference to silence expression of Sm-tsp-1 and Sm-tsp-2 mRNAs. Soaking of parasites in Sm-tsp dsRNAs resulted in 61% (p = 0.009) and 74% (p = 0.009) reductions in Sm-tsp-1 and Sm-tsp-2 transcription levels, respectively, in adult worms, and 67%–75% (p = 0.011) and 69%–89% (p = 0.004) reductions in Sm-tsp-1 and Sm-tsp-2 transcription levels, respectively, in schistosomula compared to worms treated with irrelevant control (luciferase) dsRNA. Ultrastructural morphology of adult worms treated in vitro with Sm-tsp-2 dsRNA displayed a distinctly vacuolated and thinner tegument compared with controls. Schistosomula exposed in vitro to Sm-tsp-2 dsRNA had a significantly thinner and more vacuolated tegument, and morphology consistent with a failure of tegumentary invaginations to close. Injection of mice with schistosomula that had been electroporated with Sm-tsp-1 and Sm-tsp-2 dsRNAs resulted in 61% (p = 0.005) and 83% (p = 0.002) reductions in the numbers of parasites recovered from the mesenteries four weeks later when compared to dsRNA-treated controls. These results imply that tetraspanins play important structural roles impacting tegument development, maturation or stability.
Introduction
Schistosomes are parasitic trematodes that cause chronic infection in over 207 million people in 76 developing tropical countries. Schistosomiasis is generally associated with poverty, poor water supply and inadequate sanitation [1]. Infection rates and intensities are high in early childhood, peak around 8 to 15 years and decrease in adulthood [2]. Despite effective and inexpensive widespread treatment with the anthelmintic drug praziquantel for over 20 years, this parasitic disease still causes more than 250,000 deaths per year and accounts for 1.7 to 4.5 million disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) lost annually [3].
Humans become infected with schistosomes when they are exposed to free-living cercariae in fresh water. Cercariae penetrate the skin, shed their tails and transform into schistosomula, which reside in the dermis of the skin before entering the blood capillaries to migrate through the vasculature to the portal venous system where they mature into adult worms [4]. The outer surface of schistosomula and adult worms, the tegument, is a multinucleated syncitium that contains tegumental cell bodies situated below the muscular layers. During transformation from cercaria to schistosomula, the outer surface of the tegument (the interface with the host) is remodeled from a single membrane with a prominent glycocalyx into an unusual double membrane (or “heptalaminate”) structure [5]. This double membrane is widely believed to play an essential role in the ability of schistosomes to evade the host immune system, a characteristic that allows them to live for years within their hosts [6]. The outer of the two surface membranes also has the ability to adsorb host blood molecules, masking its non-self status thereby contributing to immune evasion and prolonged survival [7]. We believe that tegumental proteins are ideal targets for immunological and pharmacological intervention [8]. The generation of a large number of S. mansoni expressed sequence tags [9] and the recently completed genome sequence [10], in combination with advances in characterizing the tegument proteome has led to the discovery of many tegument specific proteins [11]. Among them are a group of membrane proteins called tetraspanins, which are highly expressed in the outer tegument membrane of adult schistosomes [12], [13]. To date, five tetraspanin cDNAs have been described from S. mansoni, namely Sm-23 [12], Sm-tsp-1 and Sm-tsp-2 [13], Sm-tetraspanin-B and Sm-tetraspanin-C [14].
Tetraspanins are a large superfamily of surface-associated membrane proteins characterized by the conserved structure of four hydrophobic transmembrane domains, a small and large extracellular loop, an interconnecting intracellular loop, and cytoplasmic amino - and carboxyl - termini [15]. Tetraspanins undergo post-translational modification in which palmitate is bound to the membrane proximal cysteine residues and associates with cholesterol-rich domains [16]. This process enables tetraspanins to play key roles in molecular organization of cell membranes, interacting with one another and also specific partner proteins such as integrins, MHC and co-stimulatory molecules to form large signal transducing complexes termed tetraspanin-enriched microdomains (TEMs) [17]. Tetraspanins are widely distributed in many cell types but their physiological roles are mostly unknown. Several lines of evidence have implicated tetraspanins in the regulation of cell adhesion, differentiation, motility, aggregation, cell signaling and sperm-egg fusion [18], [19], [20], [21]. They have been linked to various pathological processes including lymphocyte activation [19], cancer [22], fertilization [23], [24], and interactions between pathogens and host cells such as HIV [25], HCV [26] and Plasmodium [27].
We previously identified two cDNAs, Sm-tsp-1 (Sm01494) and Sm-tsp-2 (Sm12366), in adult S. mansoni using signal sequence trapping [13], and showed that both of these tetraspanins were expressed in the tegument of the adult parasite [28]. Other authors confirmed the surface expression of these tetraspanins using various mass spectrometric approaches to characterize the schistosome surface [11], [29], [30]. We expressed the large extracellular loop of Sm-TSP-1 and Sm-TSP-2 in E. coli and used the soluble recombinant proteins to immunize mice and then challenged them with cercariae. Mice vaccinated with recombinant Sm-TSP-1 and Sm-TSP-2 had significantly reduced adult worm, liver egg and fecal egg burdens [28]. Moreover, strong IgG1 and IgG3 antibody responses against Sm-TSP-2 were detected in sera of individuals deemed putatively resistant (PR) to S. mansoni in comparison to sera from chronically infected individuals [28].
Despite their promise as vaccines against schistosomiasis, the functions of Sm-TSP-1 and Sm-TSP-2 have not yet been elucidated. We therefore employed RNA interference (RNAi) to explore the roles of Sm-tsp-1 and tsp-2 in larval and adult S. mansoni. RNAi has been utilized with S. mansoni to suppress endogenous gene expression in schistosomula [31], adult worms [32], eggs [33] and sporocysts [34]. Here, we show that RNAi results in reductions in expression of Sm-tsp-1 and tsp-2 mRNAs in schistosomula and adult worms, and malformation of the tegument in worms cultured in vitro. Moreover, silencing of tsp-1 and tsp-2 expression in schistosomula results in up to 90% fewer worms maturing to adulthood when introduced into mice compared with parasites exposed to control dsRNAs, highlighting their essential roles in tegument biogenesis and maintenance and further supporting the development of novel therapies targeting these genes and their protein products.
Results
Developmental expression of Sm-tsp-1 and Sm-tsp-2 in S. mansoni
Expression of Sm-tsp-1 and Sm-tsp-2 mRNAs in different stages of the S. mansoni life cycle was determined relative to control Sm-α-tubilin mRNA using qRT-PCR. Sm-tsp-1 and Sm-tsp-2 mRNAs were detected in all stages of the schistosome life cycle with higher levels identified in eggs, miracidia and cercariae than in 5-day old schistosomula, males and female worms for tsp-1; a similar expression profile was observed for tsp-2 but gene expression was notably reduced in cercariae (Figure 1). Interestingly, the highest level of Sm-tsp-1 expression was detected in cercariae whereas Sm-tsp-2 expression was lowest in cercariae.
Fig. 1. Expression of Sm-tsp-1 and Sm-tsp-2 at different stages of the S. mansoni life cycle. 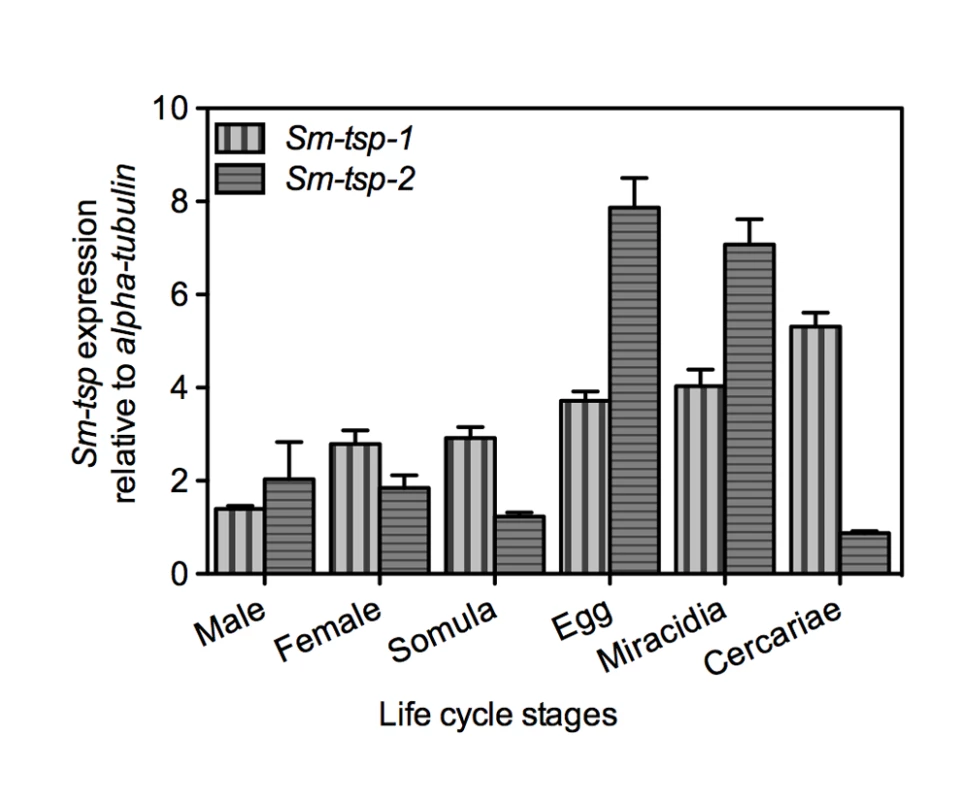
RNA levels of Sm-tsp-1 (vertical bars) and Sm-tsp-2 (horizontal bars) relative to Sm-α-tubulin were analyzed by qRT-PCR. Data are representative of mean±S.E. from three separate experiments. Expression of Sm-TSP-1 and Sm-TSP-2 in the tegument of schistosomula
We previously demonstrated that Sm-TSP-1 and Sm-TSP-2 are expressed on the tegument surface membrane of adult worms [28]. The tegument is fully formed by 3h after cercarial transformation [35], so to determine whether these TSPs are expressed in the tegument at this early stage after host entry and whether they are accessible to antibodies on live parasites, we probed live newly transformed schistosomula with antibodies against both proteins. Both Sm-TSP-1 and Sm-TSP-2 were detected over the entire surface tegument of live schistosomula when probed with mouse anti-TSP-1 or -TSP-2 sera followed by FITC-labelled anti-mouse IgG (Figure 2).
Fig. 2. Expression of Sm-TSP-1 or Sm-TSP-2 on the surface of live schistosomula. 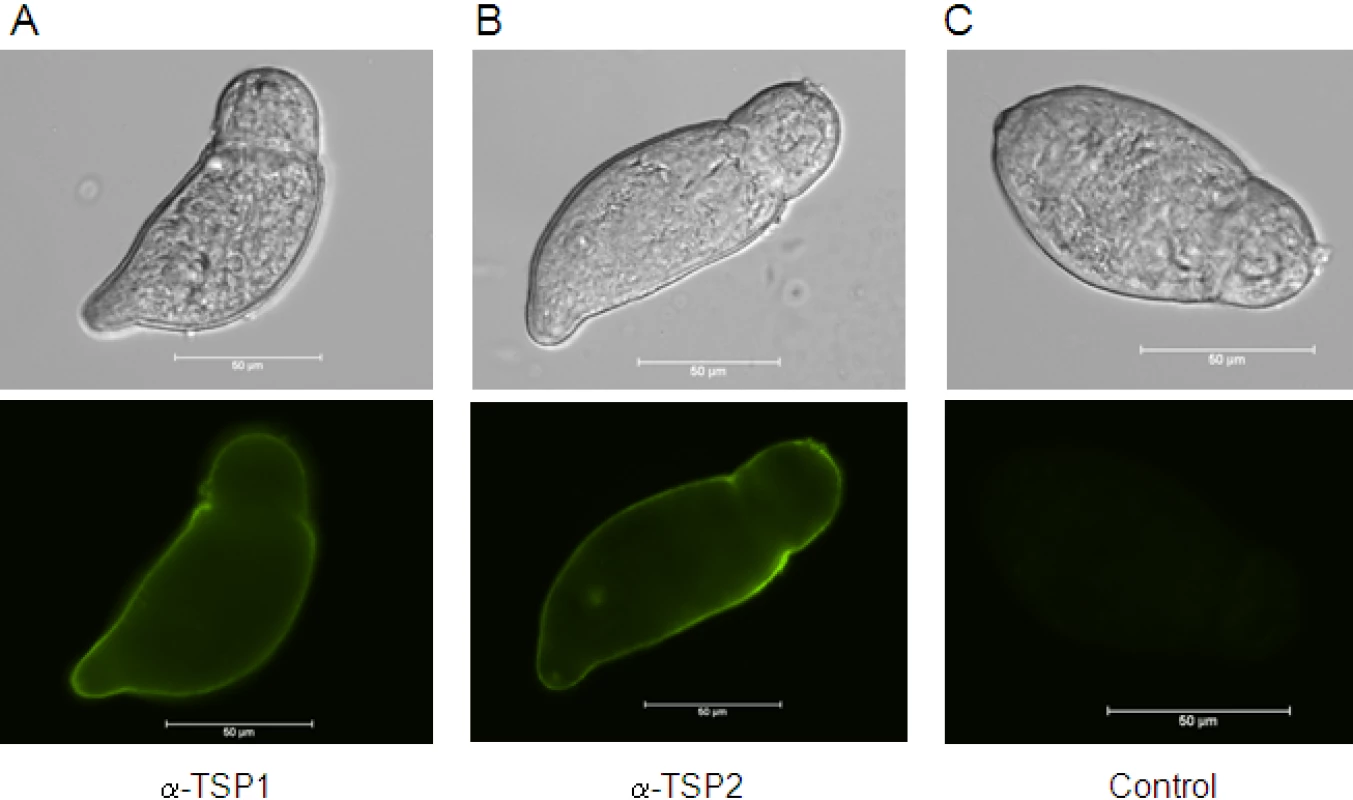
Immunofluorescent labelling of live 3 h schistosomula with antisera raised against Sm-TSP-1 (A) and Sm-TSP-2 (B), and control pre-immune serum (C) followed by anti-mouse Ig-FITC. Schistosomula are shown in bright-field and FITC stained. Scale = 50 µm. dsRNA-mediated knockdown of Sm-tsp expression in adult worms
Adult worms soaked for 7 days in Sm-tsp-1 dsRNA had a 61% (p = 0.009) reduction in Sm-tsp-1 mRNA expression compared to parasites soaked in control dsRNA (Figure 3A). A 74% (p = 0.009) reduction in Sm-tsp-2 mRNA levels was detected in worms that were cultured in media containing Sm-tsp-2 dsRNA compared to parasites soaked in luciferase dsRNA (Figure 3B). Parasites were visually monitored for motility on a daily basis but no differences were detected between groups (not shown).
Fig. 3. Suppression of Sm-tsp mRNAs in adult parasites by RNAi. 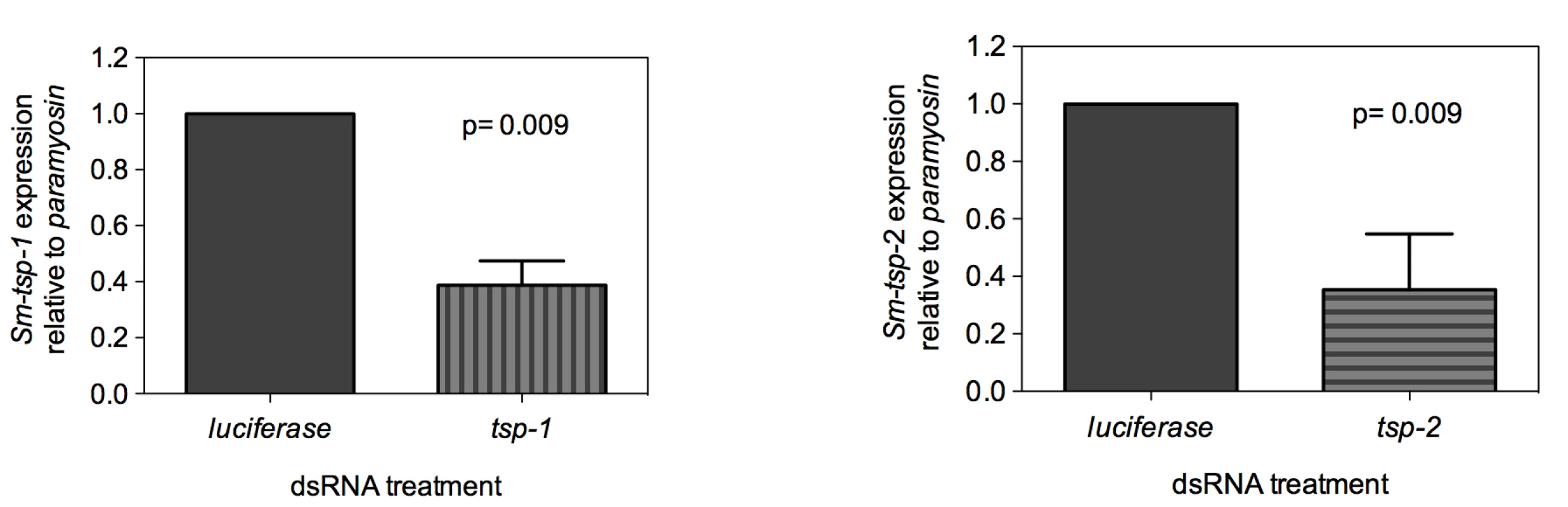
Sm-tsp-1 (A) and Sm-tsp-2 (B) transcript levels relative to Sm-paramyosin (mean±S.E.) in adult parasites soaked for 7 days with 1 µg/ml of Sm-tsp or luciferase control dsRNAs. dsRNA-mediated knockdown of Sm-tsp expression in schistosomula
Soaking of 3 h old schistosomula in Sm-tsp-1 dsRNA for 7, 14 and 21 days caused 75% (p<0.001), 67% (p = 0.019) and 69% (p = 0.021) decreases in Sm-tsp-1 mRNA expression in comparison to the control group (Figure 4A). Larval parasites incubated with Sm-tsp-2 dsRNA for 7 days exhibited an 88% (p<0.001) decrease in Sm-tsp-2 transcript levels compared to luciferase dsRNA treated schistosomula (Figure 4B). RNAi knockdown was maintained with reductions of 82% (p = 0.004) and 69% (p = 0.021) at days 14 and 21, respectively, compared to the control group. As observed in adult worms, suppression of Sm-tsp RNAs resulted in no obvious phenotypic differences compared to the luciferase dsRNA-treated control group when examined by light microscopy. Cultures were visually inspected using a light microscope on a daily basis and no differences in early growth and development of schistosomula (development of intestinal ceca or size of schistosomula) [36] were apparent between test and control dsRNA treated groups.
Fig. 4. Suppression of Sm-tsp mRNAs in schistosomula by RNAi. 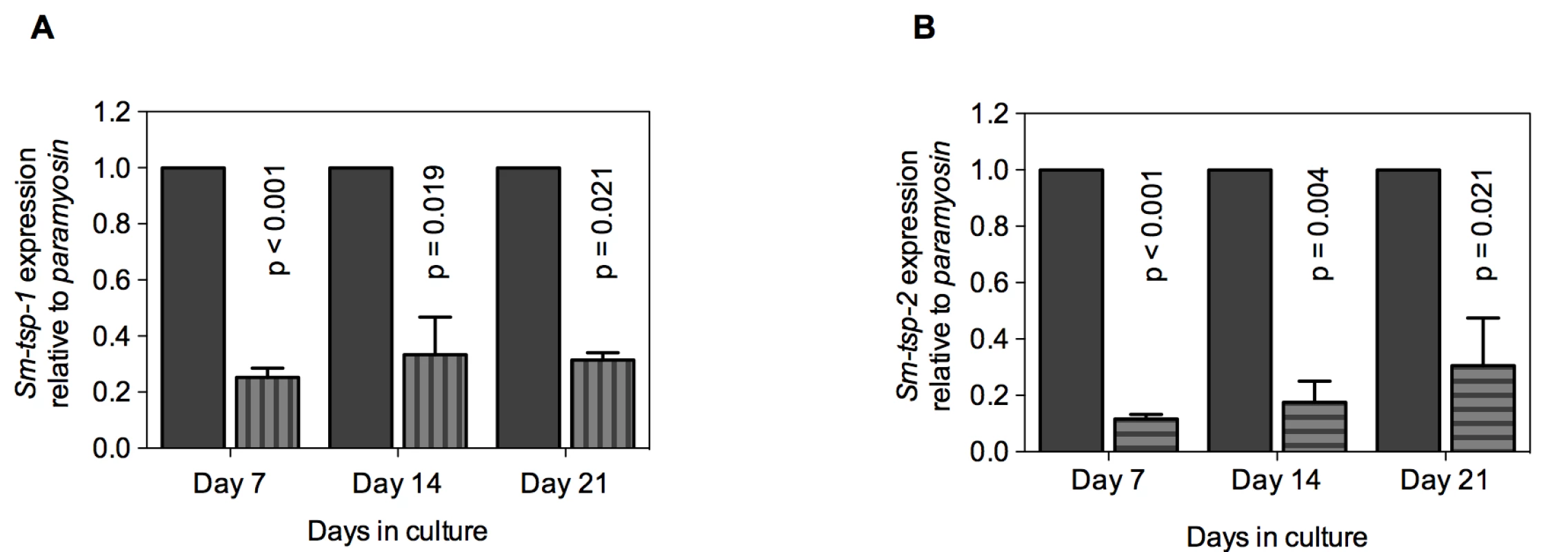
Sm-tsp-1 (A) and Sm-tsp-2 (B) transcript levels relative to Sm-paramyosin (mean±S.E.) in schistosomula soaked for 7, 14 and 21 days with 1 µg/ml of Sm-tsp or luciferase control dsRNAs. Reduction in Sm-TSP2 protein expression in parasites treated with Sm-tsp-2 dsRNA
To determine whether knockdown of Sm-tsp-2 RNA was evident at the protein level, we performed Western blot analysis on dsRNA treated adult (Figure 5A) and larval (Figure 5B) parasites. Parasites were treated with Sm-tsp-2 or luciferase dsRNAs, lysed in 1% Triton X-100 and immunoblotted with anti-Sm-TSP-2 or anti-Sm-Pmy antibodies which target a sub-tegumental muscle protein, paramyosin [37]. Sm-TSP-2 protein expression was decreased in adult worms treated with Sm-tsp-2 dsRNA compared to worms treated with luciferase dsRNA for the four concentrations (2.0, 1.0, 0.5 and 0.25 µg) tested. In contrast, the Sm-Pmy protein expression levels did not change in both test and control groups. The experiment was repeated three times with similar results and a representative image is shown (Figure 5A). Densitometry analysis was performed on each band and the ratio of Sm-TSP-2 to Sm-Pmy at each concentration was calculated. Analysis of whole worm lysates (0.25 µg) by densitometry (not shown) revealed an average of 61% (p = 0.027) reduction in Sm-TSP-2 expression in adult worms treated with Sm-tsp-2 dsRNA compared to the control luciferase group. For RNAi treated schistosomula, the amount of Sm-TSP-2 protein expressed by schistosomula after 7 days in culture with Sm-tsp-2 dsRNA was reduced compared to parasites soaked in luciferase dsRNA (Figure 5B). Densitometry analysis of lysates (2 µg, 1 µg and 0.5 µg) showed an average decline of 36% (data not shown). This decrease was lower than expected since suppression of Sm-tsp-2 mRNA was more pronounced in schistosomula than in adult parasites. Adult and larval parasites soaked in Sm-tsp-1 dsRNA demonstrated no obvious differences in protein expression to luciferase dsRNA control worms by Western blotting analysis (data not shown).
Fig. 5. Protein expression levels of parasites treated with Sm-tsp-2 dsRNA. 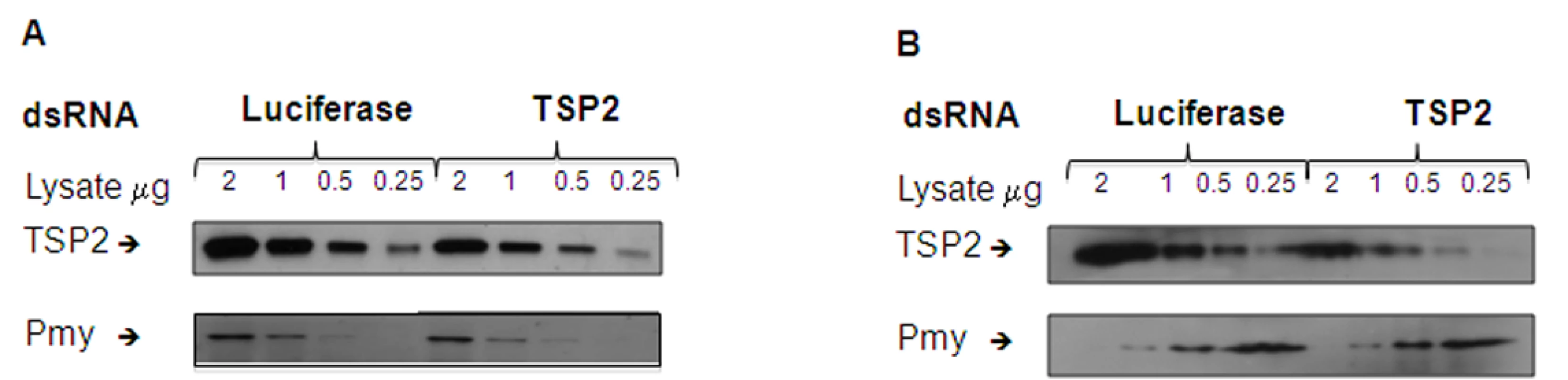
Protein extracts from adult parasites (A) and schistosomula (B) treated with Sm-tsp-2 or luciferase dsRNAs for 7 days were loaded onto a 12% SDS-PAGE gel at 2, 1, 0.5 and 0.25 µg. Proteins were transferred onto nitrocellulose and immunoblotted with anti-Sm-TSP2 or anti-Sm-Pmy monoclonal antibodies. The intensity of paramyosin expression was evaluated to determine equal protein loading. Suppression of Sm-tsp-2 mRNA results in malformation of the tegument when observed using transmission electron microscopy
Adult parasites and schistosomula treated with Sm-tsp-2 dsRNA in vitro displayed modified tegument structure when visualized with transmission electron microscopy (TEM) compared with luciferase dsRNA treated controls (Figure 6). The tegument of adult worms incubated in vitro in Sm-tsp-2 dsRNA (Figure 6C,E) was more highly vacuolated than luciferase dsRNA controls (Figure 6A), with extensive and enlarged vacuoles throughout the surface layer. The tegument of these parasites had less apparent cytoplasm and hence fewer cytoplasmic inclusions and was frequently much thinner than that of controls (Figure 6C,E). Schistosomula transformed and cultured in vitro presented a tegument that resembled that of larvae from natural or experimental infection (Figure 6B) [38]. The tegument in Sm-tsp-2 dsRNA treated schistosomula (Figure 6D,F) was consistently thinner than those of luciferase controls (P<0.001), measuring on average 0.3784±0.016 µm compared with 0.5842±0.323 µm for luciferase controls (Figure 6G). Volume density measures for invaginations and clear vesicular compartments of the tegument showed higher volumes for these compartments in Sm-tsp-2 treated schistosomula (p = 0.014; Figure 6F). The morphology of the schistosomula tegument was consistent with a failure to close invaginations of the surface (Figure 6D,F). Adult worms and schistosomula soaked in Sm-tsp-1 dsRNA showed no obvious differences to luciferase dsRNA control worms when examined by transmission electron microscopy (data not shown).
Fig. 6. Ultrastructure of the tegument of parasites treated with Sm-tsp-2 dsRNA RNA observed using transmission electron microscopy. 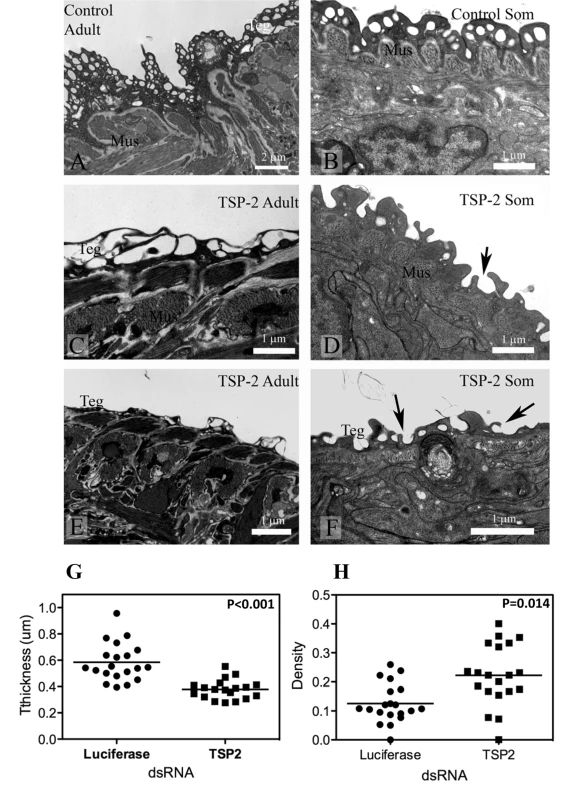
A. Tegument of adult female treated with luciferase dsRNA. B. Tegument of schistosomulum incubated for 7 days with luciferase dsRNA. C and E. Tegument of adult female incubated with Sm-tsp-2 dsRNA. The tegument is more highly vacuolated (C) and thinner (E) compared with controls. D and F. Tegument of schistosomula incubated for 7 days with Sm-tsp-2 dsRNA. Digitate extensions (arrows) are more abundant on the surface of the tegument. Abbreviations: Mus-muscles; teg-surface layer of tegument. The tegument of schistosomula were thinner, p<0.001 (G) and more dense, p = 0.014 (H) in Sm-tsp-2 dsRNA treated schistosomula. Suppression of Sm-tsp mRNAs in schistosomula affects parasite survival in vivo
In the mammalian host, larval schistosomes migrate from the skin through the lungs to the liver and then mature in the mesenteric veins [4]. In an effort to mimic in vivo conditions, 3 h schistosomula were electroporated with 100 µg/ml of Sm-tsp-1, Sm-tsp-2 or luciferase dsRNA and then injected intramuscularly into female C57BL/6 mice. Four weeks later mice were perfused to determine the number of parasites that reached maturity in the mesenteries. Significantly fewer parasites were recovered from the mesenteric veins compared to the luciferase control group (see Figure 7A for results of three experiments). Mice injected with schistosomula that were electroporated with Sm-tsp-1 dsRNA yielded 48% (p = 0.045), 60% (p = 0.009) and 67% (p = 0.019) reduction in the number of parasites recovered for Experiments 1, 2 and 3, respectively in comparison to the luciferase control group. Schistosomula pretreated with Sm-tsp-2 dsRNA and then injected into mice resulted in 70% (p = 0.039), 91% (p = 0.009) and 78% (p = 0.018) decreases in parasite survival for Experiments 1, 2 and 3, respectively when compared to the luciferase dsRNA group. The numbers of mature worms harvested from the luciferase control group were very low, with recovery ranging from 0.5-1.5%, however the data was consistent between three experiments, with a reproducible and significant reduction in worm recovery rates between tsp and luciferase dsRNA treated parasites.
Fig. 7. Infection of mice with Sm-tsp dsRNA treated schistosomula. 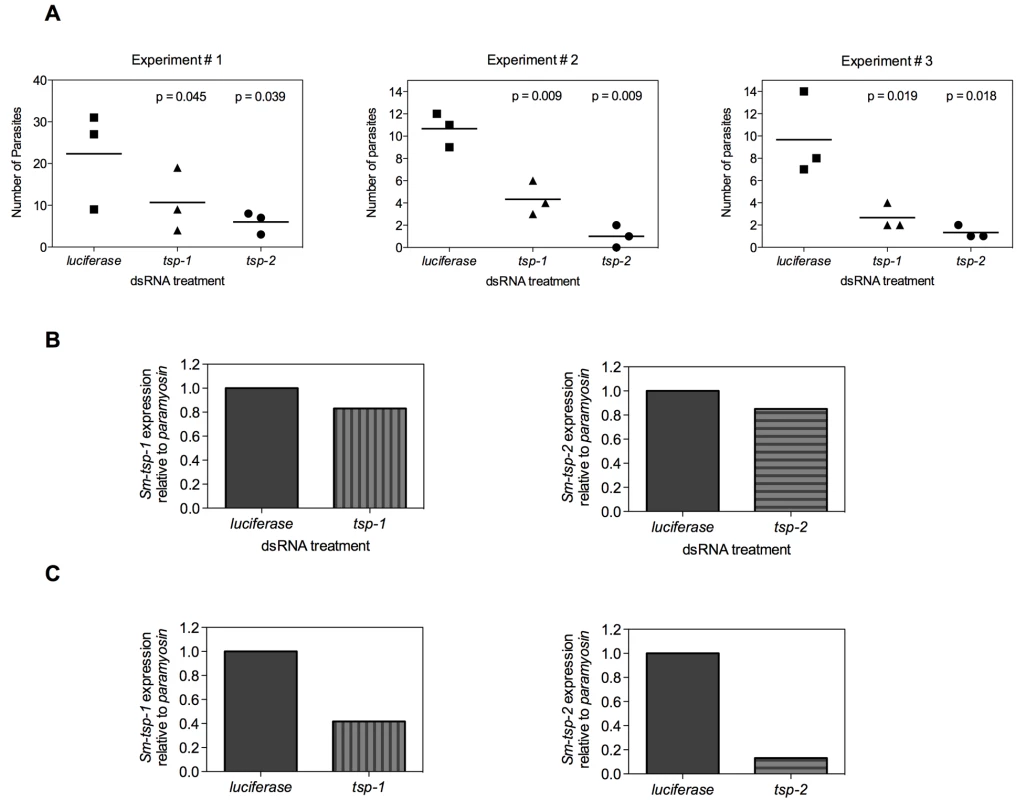
Schistosomula were electroporated with 100 µg/ml of Sm-tsp-1, Sm-tsp-2 or luciferase dsRNAs, washed and counted. C57BL/6 female mice were immunized intramuscularly with 2,000 dsRNA treated schistosomula and were perfused 4 weeks later to determine parasite numbers (A). Expression of Sm-tsp-1 and Sm-tsp-2 mRNA transcript levels of parasites harvested from Experiment 1 (B). The Sm-tsp-1 and Sm-tsp-2 transcript levels of schistosomula that were electroporated and concurrently cultured in vitro for 4 weeks were also determined (C). RNA was extracted from surviving worms that were perfused from mice and transcript levels were analyzed by qRT-PCR. Sm-tsp-1 expression was only slightly lower (17%) in worms recovered from mice that were infected with Sm-tsp-1 dsRNA-treated schistosomula compared to the control group. Likewise, Sm-tsp-2 expression was slightly reduced (15%) in worms recovered from mice that were infected with Sm-tsp-2 dsRNA treated worms compared to the luciferase control group (Figure 7B). However, when the same batch of dsRNA electroporated schistosomula were cultured in vitro for the same period of time (4 weeks), as opposed to being injected into mice, significant knockdown of Sm-tsp-1 and Sm-tsp-2 transcripts by 58% and 87%, respectively (Figure 7C), was observed. These results illustrate that silencing of Sm-tsp-1 and Sm-tsp-2 by either soaking or electroporation leads to suppression of tetraspanin genes in schistosomes, and suppression is maintained for at least 4 weeks in culture. The data also implies one of three possible outcomes for Sm-tsp dsRNA treated schistosomula that survived to adulthood after being transferred into mice; (1) RNAi was not as effective in those individual schistosomula that survived in mice as opposed to those that perished; (2) some of the RNAi treated parasites received (or took up) less dsRNA, and therefore the efficacy of gene suppression was variable between individuals in a single electroporated batch; (3) it is also possible that host developmental cues stimulate transcription.
Discussion
Schistosomes express a family of tetraspanins in their tegument. Sm23 was the first tetraspanin identified in S. mansoni [12], and is of interest as a DNA vaccine antigen against schistosomiasis [39]. Its orthologue from S. japonicum, Sj23, protects water buffaloes against challenge infection when administered as a DNA vaccine [39]. We identified two additional tetraspanins, Sm-tsp-1 and Sm-tsp-2, which showed high levels of protection when administered to mice as recombinant protein vaccines against S. mansoni [13], [28]. However, despite the protective efficacy that these tetraspanins afford, their functions in the parasite are unknown. To understand the roles that these proteins play in the schistosome tegument, we herein explored the effects of silencing the expression of Sm-tsp-1 and Sm-tsp-2 mRNAs in adult and larval S. mansoni.
RNAi has been used to suppress a number of schistosome genes in an effort to determine their functions [40], [41]. Soaking of S. mansoni with dsRNA encoding the intestinal protease cathepsin B (SmCB1), resulted in greater than 10-fold decrease in SmCB1 mRNA levels and significant growth inhibition compared to parasites treated with control dsRNA [42]. Suppression of the mRNA encoding another intestinal protease, S. mansoni cathepsin D (SmCD), in schistosomula by electroporation with dsRNA led to reduction in RNA transcript levels, growth retardation in vitro and in vivo, and decreased cathepsin D enzymatic activity [43]. Silencing of the SmAQP gene encoding a water channel protein by electroporating schistosomula with short interfering RNAs suppressed mRNA and protein expression in the tegument, and treated parasites cultured in vitro exhibited stunted growth and lower viability [44]. RNAi has been used to determine the functional importance of tetraspanins in other organisms [45]. Suppression of tetraspanin-15 mRNA by feeding C. elegans with dsRNA resulted in dissociation of the cuticle and degeneration of the hypodermis, compromising epidermal integrity [46]. RNAi has also been used to determine the function of human tetraspanins in various cell types [45]. For example, the CD151 tetraspanin interacts with membrane proteins including the laminin-binding integrin α3β1; when lung adenocarcinoma cells were cultured on laminin-511 and then treated with CD151 siRNA, abnormal membrane protrusions on laminin-511 were apparent and tyrosine phosphorylation dependent signalling was reduced [47]. These findings indicate a role for tetraspanins in the maintenance of cell membrane biogenesis and structural integrity, and support our observations on the compromised tegument membrane formation in S. mansoni when tsp mRNA expression is suppressed.
Numerous reports have documented molecular interactions between tetraspanins and MHC, and involvement of human tetraspanins in regulating T cell co-stimulation and peptide/MHC presentation [48], [49], [50], indicating additional, non-structural roles. Schistosomes acquire host MHC onto their surfaces [51], presenting the intriguing possibility that they function as a receptor for host MHC. However, the majority of mammalian tetraspanin binding partners identified to date are membrane proteins rather than extracellular ligands [45]; moreover, our data presented here implies that schistosome tetraspanins are pivotal for proper tegument formation, even during in vitro culture in the absence of immune cells, supporting a structural role in the establishment and maintenance of the tegument. Indeed, the tetraspanin CD9 complexes with numerous proteins including Ig-containing proteins [52], a family of proteins which are also present in the S. mansoni tegument membrane [30]. Various authors have described the contribution of tetraspanins, such as CD9 and CD151, with members of the integrin family in promoting cell-cell interactions and migration [53], [54], [55]. Mass spectrometric analysis of the S. mansoni tegument revealed a β-integrin subunit in the sub-tegumental layer [29]. Suppression of tetraspanin mRNA expression in schistosomes may affect lateral interactions with integrins in the tegument, and the parasite's ability to migrate through the lungs to the liver and mesenteries where they would mature. The binding partner(s) associated with Sm-TSP-1 or Sm-TSP-2, or any of the other three S. mansoni tegument tetraspanins, have yet to be identified. We have produced monoclonal antibodies to Sm-TSP-2 and these antibodies are being used to immunoprecipitate Sm-TSP-2 and its binding partners in an effort to unravel the tegumental tetraspanin web.
To assess the viability of dsRNA treated parasites in vivo, we injected tsp or luciferase dsRNA treated parasites into mice via the intramuscular route [56]. Recovery of adult worms from the mesenteries 4 weeks later was very low but was in agreement with other reports where newly transformed schistosomula were electroporated with dsRNAs prior to intramuscular injection into mice and subsequent recovery of adult worms from the mesenteries [41]. The natural route of S. mansoni infection is through percutaneous penetration of cercariae; exposure of laboratory mice to cercariae is generally performed via the abdomen or tail. Intramuscular injection of mice with schistosomula is not the natural infection route and consequently may have contributed to the low recovery rates. Despite the low recovery of adult parasites, we consistently over three experiments recovered significantly fewer worms from the mice injected with tsp dsRNA treated parasites. Moreover, tsp mRNA levels in those parasites that were recovered from mice were higher than levels in parasites cultured in vitro for the same time period after electroporation with dsRNAs, indicating that the parasites that survived in vivo had not succumbed to the effects of RNAi.
We envisage that interruption of Sm-TSP-1 and TSP-2 protein expression in the tegument of maturing schistosomula results in impaired turnover of the tegument apical membrane complex. Our observations from adults and schistosomula treated with Sm-tsp-2 dsRNA would indicate that a likely role for Sm-tsp-2 is in invagination and internalization of the surface membrane, and perhaps the closure and internalization of surface invaginations. This postulate is consistent with the suggestion that TSP-2 binds other parasite sub-surface and surface molecules in the tegument. The vaccine efficacy of TSP-2 may thus result from impairment of the surface recycling mechanisms in developing and adult schistosomes. While this impaired surface turnover was not deleterious to in vitro cultivated adult worms and schistosomula, the effect was particularly marked in treated schistosomula transferred into the host. In addition, schistosomes have the capacity to adsorb host blood molecules that mask antigenic epitopes from the host's immune system [7]. By affecting surface tegument development and turnover, suppression of tsp expression (and potential disruption of TEMs) may render the organism susceptible to immune recognition and clearance.
Materials and Methods
Ethics statement
All animals were maintained in accordance with the guidelines of the Animal Ethics Committee (AEC) of Queensland Institute of Medical Research and the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC) of The University of Pennsylvania. All studies and procedures were reviewed and approved by the AEC and IACUC of Queensland Institute of Medical Research and The University of Pennsylvania respectively.
Parasites
The Puerto Rican strain of S. mansoni and Biomphalaria glabrata snails were provided by the National Institutes of Allergy and Infectious Diseases Schistosomiasis Resource Centre at the Biomedical Research Institute (Rockville, Maryland, USA). B. glabrata infected with miracidia were exposed to incandescent light for 1h to obtain cercariae which were used to percutaneously infect 6–8 week old C57BL/6 female mice (www.jax.org). After 8 weeks, adult parasites were recovered by hepatic-portal perfusion and then washed three times with wash medium containing RPMI 1640, 1% antibiotic/antimycotic and 10 mM Hepes (www.invitrogen.com) before experimentation.
To obtain schistosomula, cercariae were passed through a 22-gauge emulsifying needle 25 times to mechanically shear the cercarial tails from the bodies [57]. The resulting schistosomula were isolated from free tails by centrifugation through a 60% percoll gradient [58], washed three times with washing medium and incubated at 37°C under 5% CO2 atmosphere before experimentation.
Immunofluorescent labelling of live schistosomula
Three hour schistosomula (n = 500) were blocked in blocking buffer containing 1% goat serum in Dulbecco's Phosphate Buffered Saline (DPBS) containing MgCl2 and CaCl2 (www.invitrogen.com). Schistosomula were labelled with sera against recombinant Sm-TSP-1, Sm-TSP-2 or control pre-vaccination sera [28] diluted to 1∶50 in blocking buffer for 1 h. Secondary goat anti-mouse Ig-FITC (www.chemicon.com) was then introduced at 1∶100 dilution in blocking buffer for 1 h followed by 4% paraformaldehyde to fix the parasites. Incubations were carried out at 4°C and parasites were washed in DPBS between incubations. Approximately 200 schistosomula were examined using a Leica MRIRB microscope and DC500 camera (www.leica.com).
Synthesis of dsRNAs
dsRNAs were prepared from DNA templates that were amplified by PCR from S. mansoni paired adult worm cDNA using primers flanked with T7 RNA polymerase promoter sequence (underlined) at the 5′ ends. A 523 bp fragment of the Sm-tsp-1 coding DNA was generated using primers (forward: 5′-TAATACGACTCACTATAGGGACTTGCTTCGGGACAACAAC-3′, reverse: 5′-TAATACGACTCACTATAGGGTTCGAAAGCTGCAATAGAAACA-3′) and a 565 bp fragment of the Sm-tsp-2 coding DNA was produced using primers (forward: 5′-TAATACGACTCACTATAGGGTGATTGTGGTTGGTGCACTT-3′, reverse: 5′-TAATACGACTCACTATAGGGGACCAATGCGAACAGAAACA-3′). The GenBank accession numbers for Sm-tsp-1 and Sm-tsp-2 are AF521093 and AF521091, respectively. The PCR products were then utilized as templates for synthesis of dsRNAs using the T7 Megascript kit (www.ambion.com), following the manufacturer's instructions. An irrelevant negative control, firefly luciferase dsRNA derived from pGL3-basic (www.promega.com), was prepared as described previously [31].
dsRNA delivery in schistosomes
Adult schistosomes were cultured in vitro in Medium 199 (www.invitrogen.com) supplemented with 10% fetal calf serum (www.gembio.com), 1% antibiotic/antimycotic and 10 mM Hepes at 37°C under 5% CO2 atmosphere. Five pairs of adult worms were soaked in the presence of Sm-tsp-1, Sm-tsp-2 or luciferase dsRNAs at 1 µg/ml for 7 days with changes of media and dsRNAs every second day. Schistosomula were maintained at 37°C with 5% CO2 in Medium 169 [36] supplemented with 10% human AB serum (www.gembio.com) and mouse whole blood. Larval parasites (3 h old) were soaked in 1 µg/ml of Sm-tsp-1, Sm-tsp-2 or luciferase dsRNAs and cultured in vitro at 37°C under 5% CO2 atmosphere for 7, 14 and 21 days, with fresh changes of media, blood and dsRNAs every second day. Adult and larval parasites were washed in wash medium prior to RNA or protein extraction.
Infection of mice with dsRNA-treated schistosomula
Newly transformed schistosomula were incubated in wash medium at 37°C with 5% CO2 for 3 h. Parasites were then resuspended in 50 µl of wash medium with 100 µg/ml of Sm-tsp-1, Sm-tsp-2 or luciferase dsRNAs and electroporated in a 4 mm cuvette at 125 V for 20 ms using a square-wave BTX ECM 830 electroporator (www.btxonline.com). After three washes in wash medium, schistosomula were counted and 2000 were injected intramuscularly into each C57BL/6 female mouse (3 mice per group) using a 23-gauge needle. Adult worms were perfused 28 days later to assess the number of worms that had matured and reached the mesenteries.
Real-time quantitative RT-PCR
RNA was isolated from parasites using RNeasy Mini kit (www.qiagen.com) and then treated with Turbo DNA-free endonuclease (www.ambion.com) to remove contaminating genomic DNA. The quantity of RNA was measured on a Nanodrop Spectrophotometer (www.nanodrop.com) and 250 ng of total RNA, SuperScript II reverse transcriptase (www.invitrogen.com) and oligo dT15 primer (www.promega.com) were used to synthesize first strand cDNA.
The following primers were designed for real-time qRT-PCR; Sm-TSP-1 (forward: 5′-TGGTTGTGCTTATTGGGTTG-3′ and reverse: 5′-TGATGTCTTGTGCCTCTGGT-3′); Sm-TSP-2 (forward: 5′-CGAAATTGAACCCCCACTAC-3′ and revere: 5′-CATGCTCCAAACATCCCTAAA-3′); Sm-Paramyosin (forward: 5′-CGTGAAGGTCGTCGTATGGT-3′ and reverse 5′-GACGTTCAAATTTACGTGCTTG-3′) and Sm-α-tubilin (forward: 5′-CCAGCAAAATCAGATGGTGAA-3′ and reverse: 5′-TTGACATCCTTGGGGACAAC-3′). qRT-PCR was conducted in triplicate and each reaction underwent 40 amplification cycles using an Applied Biosystems 7500 real-time PCR system (www.appliedbiosystems.com) with cDNA equivalent to 20 ng of total RNA, 50 nM of primers and SYBR green PCR Master Mix (www.appliedbiosystems.com). Dissociation curves were generated for each sample to verify the amplification of a single PCR product. Sm-tsp transcript levels were calculated relative to Sm-paramyosin in test and irrelevant dsRNA treated parasites using the 2−ΔΔCt method [59], and data was expressed as percent differences. For relative endogenous expression of tsp mRNAs in schistosome life cycle stages, Sm-α-tubulin was used as the endogenous standard. Sm-paramyosin was used as the housekeeping gene for analyzing Sm-tsp expression in RNAi experiments.
Evaluation of protein expression
RNAi-treated adult parasites and schistosomula were harvested after 7 days and then lysed with 1% Triton X-100 in Tris buffered saline supplemented with complete protease inhibitor cocktail EASYpacks (www.roche.com). Protein concentrations of lysates were determined using a BCA protein assay kit (www.pierce.com), and lysates were electrophoresed in 12% SDS-PAGE gels at concentrations of 2, 1, 0.5 and 0.25 µg total protein per well. Proteins were transferred to nitrocellulose membrane (Hybond-ECL, www.gehealthcare.com) and then probed with either anti-Sm-TSP-2 (3H5/2) monoclonal antibody supernatants (L. Cooper, M. Tran and A. Loukas, unpublished) diluted 1∶1,000 followed by anti-mouse Ig-HRP (www.chemicon.com) diluted 1∶5,000. Reactive proteins were detected by ECL (www.gehealthcare.com) as per the manufacturer's instructions. To assess equal protein loading, nitrocellulose membranes were stripped after reacting with anti-TSP-2 antibodies and then re-probed with anti-paramyosin (Sm4B1) monoclonal antibody supernatants [60] diluted at 1∶1,000 followed by anti-mouse Ig-HRP. Experiments were repeated three times and protein quantities in gel bands were determined using Syngene Tools and software (www.syngene.com).
Electron microscopy
Adult parasites and schistosomula were soaked in 1 µg/ml of Sm-tsp or luciferase dsRNAs for 7 days at 37°C under 5% CO2 atmosphere, washed three times in wash medium and then fixed in 3% glutaradehyde in 0.1M phosphate buffer at pH 7.4, followed by fixation in potassium ferricyanide-reduced osmium tetroxide. After fixation, parasites were dehydrated in acetone and embedded in Epon Resin (ProSciTech). Ultrathin sections were mounted onto copper grids, contrasted in uranyl acetate and lead citrate and examined and photographed using a JEM 1011 transmission electron microscope operated at 80 kV and equipped with a digital camera.
A morphometric approach was employed to quantify possible changes to tegument structure in schistosomula treated with Sm-tsp-2 relative to those treated with luciferase dsRNA. Point counting stereology [61], [62] was used to measure the volume of tegument occupied by vacuolar compartments or tegument invaginations in the tegument. Such regions were evident as clear spaces in TEM sections. Twenty individual schistosomula were selected at low magnification in the TEM. For each parasite, the first region of tegument observed that fulfilled the two criteria below was photographed at ×10,000 magnification. Criteria for selection were, firstly, that the region photographed was from the lateral aspect of a parasite that was clearly longer than wide and in which internal organs were present, and secondly, that the region was not excessively spinous. Volume density of vacuolar compartments of tegument were estimated using grids generated by Image J analysis software (NIH Besthesda), and were calculated as the number of points on the grid intersecting a vacuolar space divided by the number of points intersecting the tegument. This was measured across the entire profile of the tegument in each electron micrograph, so that only one measure was obtained for each schistosomulum. In addition to the volume density measure, the thickness of the tegument was measured at 10 different points using the line tool in Image J. For each measure, a line was drawn digitally on each micrograph from the basal membrane of the tegument to the apical membrane. Regions where the tegument was excessively invaginated, and those containing isolated spines and sensory receptors were not measured. The 10 thickness measurements were averaged for each schistosomulum.
Statistical analyses
All data are presented as the mean±standard error. Differences between groups were assessed for statistical significance using Student t-test (GraphPad Prism Software, www.graphpad.com). A statistically significant difference for a particular comparison was defined as p<0.050.
Zdroje
1. FenwickA
RollinsonD
SouthgateV
2006 Implementation of human schistosomiasis control: Challenges and prospects. Adv Parasitol 61 567 622
2. GryseelsB
PolmanK
ClerinxJ
KestensL
2006 Human schistosomiasis. Lancet 368 1106 1118
3. SteinmannP
KeiserJ
BosR
TannerM
UtzingerJ
2006 Schistosomiasis and water resources development: systematic review, meta-analysis, and estimates of people at risk. Lancet Infect Dis 6 411 425
4. MillerP
WilsonRA
1980 Migration of the schistosomula of Schistosoma mansoni from the lungs to the hepatic portal system. Parasitology 80 267 288
5. JonesMK
GobertGN
ZhangL
SunderlandP
McManusDP
2004 The cytoskeleton and motor proteins of human schistosomes and their roles in surface maintenance and host-parasite interactions. Bioessays 26 752 765
6. SmithersSR
McLarenDJ
Ramalho-PintoFJ
1977 Immunity to schistosomes: the target. Am J Trop Med Hyg 26 11 19
7. SmithersSR
TerryRJ
1976 The immunology of schistosomiasis. Adv Parasitol 14 399 422
8. LoukasA
TranM
PearsonMS
2007 Schistosome membrane proteins as vaccines. Int J Parasitol 37 257 263
9. Verjovski-AlmeidaS
DeMarcoR
MartinsEA
GuimaraesPE
OjopiEP
2003 Transcriptome analysis of the acoelomate human parasite Schistosoma mansoni. Nat Genet 35 148 157
10. BerrimanM
HaasBJ
LoVerdePT
WilsonRA
DillonGP
2009 The genome of the blood fluke Schistosoma mansoni. Nature 460 352 358
11. BraschiS
CurwenRS
AshtonPD
Verjovski-AlmeidaS
WilsonA
2006 The tegument surface membranes of the human blood parasite Schistosoma mansoni: a proteomic analysis after differential extraction. Proteomics 6 1471 1482
12. GaugitschHW
HoferE
HuberNE
SchnablE
BaumrukerT
1991 A new superfamily of lymphoid and melanoma cell proteins with extensive homology to Schistosoma mansoni antigen Sm23. Eur J Immunol 21 377 383
13. SmythD
McManusDP
SmoutMJ
LahaT
ZhangW
2003 Isolation of cDNAs encoding secreted and transmembrane proteins from Schistosoma mansoni by a signal sequence trap method. Infect Immun 71 2548 2554
14. BraschiS
BorgesWC
WilsonRA
2006 Proteomic analysis of the schistosome tegument and its surface membranes. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz 101 Suppl 1 205 212
15. KovalenkoOV
MetcalfDG
DeGradoWF
HemlerME
2005 Structural organization and interactions of transmembrane domains in tetraspanin proteins. BMC Struct Biol 5 11
16. HemlerME
2001 Specific tetraspanin functions. J Cell Biol 155 1103 1107
17. StippCS
KolesnikovaTV
HemlerME
2003 Functional domains in tetraspanin proteins. Trends Biochem Sci 28 106 112
18. BoucheixC
DucGH
JasminC
RubinsteinE
2001 Tetraspanins and malignancy. Expert Rev Mol Med 2001 1 17
19. HemlerME
2003 Tetraspanin proteins mediate cellular penetration, invasion, and fusion events and define a novel type of membrane microdomain. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 19 397 422
20. WrightMD
MoseleyGW
van SprielAB
2004 Tetraspanin microdomains in immune cell signalling and malignant disease. Tissue Antigens 64 533 542
21. HigginbottomA
TakahashiY
BollingL
CoonrodSA
WhiteJM
2003 Structural requirements for the inhibitory action of the CD9 large extracellular domain in sperm/oocyte binding and fusion. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 311 208 214
22. LazoPA
2007 Functional implications of tetraspanin proteins in cancer biology. Cancer Sci 98 1666 1677
23. RubinsteinE
ZiyyatA
PrenantM
WrobelE
WolfJP
2006 Reduced fertility of female mice lacking CD81. Dev Biol 290 351 358
24. Barraud-LangeV
Naud-BarriantN
BomselM
WolfJP
ZiyyatA
2007 Transfer of oocyte membrane fragments to fertilizing spermatozoa. FASEB J 21 3446 3449
25. Gordon-AlonsoM
Yanez-MoM
BarreiroO
AlvarezS
Munoz-FernandezMA
2006 Tetraspanins CD9 and CD81 modulate HIV-1-induced membrane fusion. J Immunol 177 5129 5137
26. BartoschB
VitelliA
GranierC
GoujonC
DubuissonJ
2003 Cell entry of hepatitis C virus requires a set of co-receptors that include the CD81 tetraspanin and the SR-B1 scavenger receptor. J Biol Chem 278 41624 41630
27. YalaouiS
ZougbedeS
CharrinS
SilvieO
ArduiseC
2008 Hepatocyte permissiveness to Plasmodium infection is conveyed by a short and structurally conserved region of the CD81 large extracellular domain. PLoS Pathog 4 e1000010 doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1000010
28. TranMH
PearsonMS
BethonyJM
SmythDJ
JonesMK
2006 Tetraspanins on the surface of Schistosoma mansoni are protective antigens against schistosomiasis. Nature Med 12 835 840
29. van BalkomBW
van GestelRA
BrouwersJF
KrijgsveldJ
TielensAG
2005 Mass spectrometric analysis of the Schistosoma mansoni tegumental sub-proteome. J Proteome Res 4 958 966
30. BraschiS
WilsonRA
2006 Proteins exposed at the adult schistosome surface revealed by biotinylation. Mol Cell Proteomics 5 347 356
31. CorrentiJM
PearceEJ
2004 Transgene expression in Schistosoma mansoni: introduction of RNA into schistosomula by electroporation. Mol Biochem Parasitol 137 75 79
32. SkellyPJ
Da'daraA
HarnDA
2003 Suppression of cathepsin B expression in Schistosoma mansoni by RNA interference. Int J Parasitol 33 363 369
33. FreitasTC
JungE
PearceEJ
2007 TGF-beta signaling controls embryo development in the parasitic flatworm Schistosoma mansoni. PLoS Pathog 3 e52 doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.0030052
34. BoyleJP
WuXJ
ShoemakerCB
YoshinoTP
2003 Using RNA interference to manipulate endogenous gene expression in Schistosoma mansoni sporocysts. Mol Biochem Parasitol 128 205 215
35. HockleyDJ
McLarenDJ
1973 Schistosoma mansoni: changes in the outer membrane of the tegument during development from cercaria to adult worm. Int J Parasitol 3 13 25
36. BaschPF
1981 Cultivation of Schistosoma mansoni in vitro. I. Establishment of cultures from cercariae and development until pairing. J Parasitol 67 179 185
37. SchmidtJ
BodorO
GohrL
KunzW
1996 Paramyosin isoforms of Schistosoma mansoni are phosphorylated and localized in a large variety of muscle types. Parasitology 112 459 467
38. CousinCE
StirewaltMA
DorseyCH
WatsonLP
1986 Schistosoma mansoni: comparative development of schistosomules produced by artificial techniques. J Parasitol 72 606 609
39. Da'daraAA
LiYS
XiongT
ZhouJ
WilliamsGM
2008 DNA-based vaccines protect against zoonotic schistosomiasis in water buffalo. Vaccine 26 3617 3625
40. NdegwaD
Krautz-PetersonG
SkellyPJ
2007 Protocols for gene silencing in schistosomes. Exp Parasitol 117 284 291
41. PearceEJ
FreitasTC
2008 Reverse genetics and the study of the immune response to schistosomes. Parasite Immunol 30 215 221
42. CorrentiJM
BrindleyPJ
PearceEJ
2005 Long-term suppression of cathepsin B levels by RNA interference retards schistosome growth. Mol Biochem Parasitol 143 209 215
43. MoralesME
RinaldiG
GobertGN
KinesKJ
TortJF
2008 RNA interference of Schistosoma mansoni cathepsin D, the apical enzyme of the hemoglobin proteolysis cascade. Mol Biochem Parasitol 157 160 168
44. FaghiriZ
SkellyPJ
2009 The role of tegumental aquaporin from the human parasitic worm, Schistosoma mansoni, in osmoregulation and drug uptake. FASEB J 23 2780 2789
45. HemlerME
2008 Targeting of tetraspanin proteins - potential benefits and strategies. Nature Rev Drug Discov 7 747 758
46. MoribeH
YochemJ
YamadaH
TabuseY
FujimotoT
2004 Tetraspanin protein (TSP-15) is required for epidermal integrity in Caenorhabditis elegans. J Cell Sci 117 5209 5220
47. YamadaM
SumidaY
FujibayashiA
FukaguchiK
SanzenN
2008 The tetraspanin CD151 regulates cell morphology and intracellular signaling on laminin-511. FEBS J 275 3335 3351
48. SzollosiJ
HorejsiV
BeneL
AngelisovaP
DamjanovichS
1996 Supramolecular complexes of MHC class I, MHC class II, CD20, and tetraspan molecules (CD53, CD81, and CD82) at the surface of a B cell line JY. J Immunol 157 2939 2946
49. KropshoferH
SpindeldreherS
RohnTA
PlataniaN
GrygarC
2002 Tetraspan microdomains distinct from lipid rafts enrich select peptide-MHC class II complexes. Nature Immunol 3 61 68
50. ShengKC
van SprielAB
GartlanKH
SofiM
ApostolopoulosV
2009 Tetraspanins CD37 and CD151 differentially regulate Ag presentation and T-cell co-stimulation by DC. Eur J Immunol 39 50 55
51. SherA
HallBF
VadasMA
1978 Acquisition of murine major histocompatibility complex gene products by schistosomula of Schistosoma mansoni. J Exp Med 148 46 57
52. Le NaourF
AndreM
GrecoC
BillardM
SordatB
2006 Profiling of the tetraspanin web of human colon cancer cells. Mol Cell Proteomics 5 845 857
53. LiuL
HeB
LiuWM
ZhouD
CoxJV
2007 Tetraspanin CD151 promotes cell migration by regulating integrin trafficking. J Biol Chem 282 31631 31642
54. YangXH
RichardsonAL
Torres-ArzayusMI
ZhouP
SharmaC
2008 CD151 accelerates breast cancer by regulating alpha 6 integrin function, signaling, and molecular organization. Cancer Res 68 3204 3213
55. DeisslerH
KuhnEM
LangGE
2007 Tetraspanin CD9 is involved in the migration of retinal microvascular endothelial cells. Int J Mol Med 20 643 652
56. JamesER
TaylorMG
1976 Transformation of cercariae to schistosomula: a quantitative comparison of transformation techniques and of infectivity by different injection routes of the organisms produced. J Helminthol 50 223 233
57. SalafskyB
FuscoAC
WhitleyK
NowickiD
EllenbergerB
1988 Schistosoma mansoni: analysis of cercarial transformation methods. Exp Parasitol 67 116 127
58. LazdinsJK
SteinMJ
DavidJR
SherA
1982 Schistosoma mansoni: rapid isolation and purification of schistosomula of different developmental stages by centrifugation on discontinuous density gradients of Percoll. Exp Parasitol 53 39 44
59. LivakKJ
SchmittgenTD
2001 Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 25 402 408
60. PearceEJ
JamesSL
DaltonJ
BarrallA
RamosC
1986 Immunochemical characterization and purification of Sm-97, a Schistosoma mansoni antigen monospecifically recognized by antibodies from mice protectively immunized with a nonliving vaccine. J Immunol 137 3593 3600
61. GriffithsG
1993 Fine Structure Immunocytochemistry Berlin Springer 459
62. BartleyPB
RammGA
JonesMK
RuddellRG
LiY
McManusDP
2006 A contributory role for activated hepatic stellate cells in the dynamics of Schistosoma japonicum egg-induced fibrosis. Int J Parasitol 36 993 1001
Štítky
Hygiena a epidemiologie Infekční lékařství Laboratoř
Článek Novel Riboswitch Ligand Analogs as Selective Inhibitors of Guanine-Related Metabolic PathwaysČlánek The Physical Relationship between Infectivity and Prion Protein Aggregates Is Strain-DependentČlánek Rhomboid 4 (ROM4) Affects the Processing of Surface Adhesins and Facilitates Host Cell Invasion by
Článek vyšel v časopisePLOS Pathogens
Nejčtenější tento týden
2010 Číslo 4- Jak souvisí postcovidový syndrom s poškozením mozku?
- Měli bychom postcovidový syndrom léčit antidepresivy?
- Farmakovigilanční studie perorálních antivirotik indikovaných v léčbě COVID-19
- 10 bodů k očkování proti COVID-19: stanovisko České společnosti alergologie a klinické imunologie ČLS JEP
-
Všechny články tohoto čísla
- Innate Recognition of Fungal Cell Walls
- Suppression of mRNAs Encoding Tegument Tetraspanins from Results in Impaired Tegument Turnover
- Junín Virus Infection of Human Hematopoietic Progenitors Impairs Proplatelet Formation and Platelet Release via a Bystander Effect Involving Type I IFN Signaling
- The Endosymbiotic Bacterium Induces Resistance to Dengue Virus in
- Natural Regulatory T Cells in Malaria: Host or Parasite Allies?
- Keratinocytes Determine Th1 Immunity during Early Experimental Leishmaniasis
- Spatial and Temporal Association of Outbreaks of H5N1 Influenza Virus Infection in Wild Birds with the 0°C Isotherm
- Novel Riboswitch Ligand Analogs as Selective Inhibitors of Guanine-Related Metabolic Pathways
- RNA Polymerase Activity and Specific RNA Structure Are Required for Efficient HCV Replication in Cultured Cells
- The Physical Relationship between Infectivity and Prion Protein Aggregates Is Strain-Dependent
- Inadequate Clearance of Translocated Bacterial Products in HIV-Infected Humanized Mice
- Topology and Organization of the Type III Secretion Needle Complex Components
- Temperature Modulates Plant Defense Responses through NB-LRR Proteins
- Peptide Inhibitors of Dengue-Virus Entry Target a Late-Stage Fusion Intermediate
- Identification of Host-Dependent Survival Factors for Intracellular through an siRNA Screen
- Exposure to HIV-1 Directly Impairs Mucosal Epithelial Barrier Integrity Allowing Microbial Translocation
- Increased Asymmetric Dimethylarginine in Severe Falciparum Malaria: Association with Impaired Nitric Oxide Bioavailability and Fatal Outcome
- Reconstitution of SARS-Coronavirus mRNA Cap Methylation
- Induces Brain Microvascular Endothelial Cell Detachment from the Matrix and Cleavage of Occludin: A Role for MMP-8
- Two Coregulated Efflux Transporters Modulate Intracellular Heme and Protoporphyrin IX Availability in
- The Type I NADH Dehydrogenase of Counters Phagosomal NOX2 Activity to Inhibit TNF-α-Mediated Host Cell Apoptosis
- Rhomboid 4 (ROM4) Affects the Processing of Surface Adhesins and Facilitates Host Cell Invasion by
- Increased Monocyte Turnover from Bone Marrow Correlates with Severity of SIV Encephalitis and CD163 Levels in Plasma
- The RING-CH Ligase K5 Antagonizes Restriction of KSHV and HIV-1 Particle Release by Mediating Ubiquitin-Dependent Endosomal Degradation of Tetherin
- Molecular Mechanisms of Ethanol-Induced Pathogenesis Revealed by RNA-Sequencing
- Highly Frequent Mutations in Negative Regulators of Multiple Virulence Genes in Group A Streptococcal Toxic Shock Syndrome Isolates
- Emergence and Pathogenicity of Highly Virulent Genotypes in the Northwest United States
- Structural and Functional Analysis of Viral siRNAs
- Prion Shedding from Olfactory Neurons into Nasal Secretions
- a GATA Transcription Factor That Directs Disparate Fates in Including Morphogenesis and Siderophore Biosynthesis
- Three Members of the 6-cys Protein Family of Play a Role in Gamete Fertility
- Complement as an Endogenous Adjuvant for Dendritic Cell-Mediated Induction of Retrovirus-Specific CTLs
- A Genomic Survey of Positive Selection in Provides Insights into the Evolution of Accidental Virulence
- Overcomes Stress of Azole Drugs by Formation of Disomy in Specific Multiple Chromosomes
- Blood Fluke Exploitation of Non-Cognate CD4 T Cell Help to Facilitate Parasite Development
- Antagonism of Tetherin Restriction of HIV-1 Release by Vpu Involves Binding and Sequestration of the Restriction Factor in a Perinuclear Compartment
- The Development of Therapeutic Antibodies That Neutralize Homologous and Heterologous Genotypes of Dengue Virus Type 1
- Deficiencies in Jasmonate-Mediated Plant Defense Reveal Quantitative Variation in Pathogenesis
- Interactions with Bacteria in the Context of Human Health and Disease
- Viral Capsid Is a Pathogen-Associated Molecular Pattern in Adenovirus Keratitis
- Electron Tomography Reveals the Steps in Filovirus Budding
- Selective Condensation Drives Partitioning and Sequential Secretion of Cyst Wall Proteins in Differentiating
- The Effect of Vaccination on the Evolution and Population Dynamics of Avian Paramyxovirus-1
- A Timescale for Evolution, Population Expansion, and Spatial Spread of an Emerging Clone of Methicillin-Resistant
- VacA Toxin/Subunit p34: Targeting of an Anion Channel to the Inner Mitochondrial Membrane
- Production of Extracellular Traps against and in Infected Lung Tissue Is Dependent on Invading Neutrophils and Influenced by Hydrophobin RodA
- A Differential Role for Macropinocytosis in Mediating Entry of the Two Forms of Vaccinia Virus into Dendritic Cells
- Impaired Innate Immunity in Mice but Preserved CD8 T Cell Responses against in -, -, - or -Deficient Mice
- SARS-CoV Pathogenesis Is Regulated by a STAT1 Dependent but a Type I, II and III Interferon Receptor Independent Mechanism
- Proteolysis of Human Thrombin Generates Novel Host Defense Peptides
- Multilayered Mechanism of CD4 Downregulation by HIV-1 Vpu Involving Distinct ER Retention and ERAD Targeting Steps
- PLOS Pathogens
- Archiv čísel
- Aktuální číslo
- Informace o časopisu
Nejčtenější v tomto čísle- The Effect of Vaccination on the Evolution and Population Dynamics of Avian Paramyxovirus-1
- Reconstitution of SARS-Coronavirus mRNA Cap Methylation
- Deficiencies in Jasmonate-Mediated Plant Defense Reveal Quantitative Variation in Pathogenesis
- A Timescale for Evolution, Population Expansion, and Spatial Spread of an Emerging Clone of Methicillin-Resistant
Kurzy
Zvyšte si kvalifikaci online z pohodlí domova
Současné možnosti léčby obezity
nový kurzAutoři: MUDr. Martin Hrubý
Všechny kurzyPřihlášení#ADS_BOTTOM_SCRIPTS#Zapomenuté hesloZadejte e-mailovou adresu, se kterou jste vytvářel(a) účet, budou Vám na ni zaslány informace k nastavení nového hesla.
- Vzdělávání



