-
Články
Top novinky
Reklama- Vzdělávání
- Časopisy
Top články
Nové číslo
- Témata
Top novinky
Reklama- Videa
- Podcasty
Nové podcasty
Reklama- Kariéra
Doporučené pozice
Reklama- Praxe
Top novinky
ReklamaUncoupling of Molecular Maturation from Peripheral Target Innervation in Nociceptors Expressing a Chimeric TrkA/TrkC Receptor
Neurotrophins and their receptors control a number of cellular processes, such as survival, gene expression and axonal growth, by activating multiple signalling pathways in peripheral neurons. Whether each of these pathways controls a distinct developmental process remains unknown. Here we describe a novel knock-in mouse model expressing a chimeric TrkA/TrkC (TrkAC) receptor from TrkA locus. In these mice, prospective nociceptors survived, segregated into appropriate peptidergic and nonpeptidergic subsets, projected normally to distinct laminae of the dorsal spinal cord, but displayed aberrant peripheral target innervation. This study provides the first in vivo evidence that intracellular parts of different Trk receptors are interchangeable to promote survival and maturation of nociceptors and shows that these developmental processes can be uncoupled from peripheral target innervation. Moreover, adult homozygous TrkAC knock-in mice displayed severe deficits in acute and tissue injury-induced pain, representing the first viable adult Trk mouse mutant with a pain phenotype.
Published in the journal: . PLoS Genet 10(2): e32767. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1004081
Category: Research Article
doi: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1004081Summary
Neurotrophins and their receptors control a number of cellular processes, such as survival, gene expression and axonal growth, by activating multiple signalling pathways in peripheral neurons. Whether each of these pathways controls a distinct developmental process remains unknown. Here we describe a novel knock-in mouse model expressing a chimeric TrkA/TrkC (TrkAC) receptor from TrkA locus. In these mice, prospective nociceptors survived, segregated into appropriate peptidergic and nonpeptidergic subsets, projected normally to distinct laminae of the dorsal spinal cord, but displayed aberrant peripheral target innervation. This study provides the first in vivo evidence that intracellular parts of different Trk receptors are interchangeable to promote survival and maturation of nociceptors and shows that these developmental processes can be uncoupled from peripheral target innervation. Moreover, adult homozygous TrkAC knock-in mice displayed severe deficits in acute and tissue injury-induced pain, representing the first viable adult Trk mouse mutant with a pain phenotype.
Introduction
Sensory neurons of the dorsal root ganglia (DRG) represent a powerful model for studying neuronal survival, fate determination and neuronal circuit assembly during development. Indeed, after initial fate specification, these neurons establish connections with neurons in the spinal cord and with the appropriate targets in the periphery, such as various structures in the skin or muscle. Extracellular cues that are encountered by a developing sensory neuron, both en route and in the final destination tissue, then in turn control its survival and maturation. Neurotrophins (NTs) and their receptors (Trk) play key roles in this intricately balanced dialog between growing axons and their surroundings by controlling multiple aspects of development.
Neurotrophin NGF controls survival of nociceptors, which are pain and temperature sensing neurons expressing NGF receptor TrkA during development and projecting to dorsal spinal cord centrally and to skin in the periphery [1], [2]. Indeed, mice lacking TrkA or NGF exhibit massive apoptosis of these neurons as early as embryonic day 13.5 [3]. However, when survival of nociceptors from mice lacking NGF or TrkA was rescued by concomitant deletion of a pro-apoptotic protein Bax, these neurons failed to express such nociceptor-specific protein markers as CGRP and substance P, suggesting that NGF/TrkA signaling also controls gene expression in nociceptors [4]. Moreover, the postnatal maturation of nociceptive neurons also requires NGF signaling cascade [5].
In addition to controlling survival and maturation of cutaneous nociceptors, NGF is critical for axonal extension and peripheral target innervation by these neurons. Indeed, neurites from DRG explants grew towards NGF source in vitro [6] and beads containing NGF or other neurotrophins directed growth of sensory nerves in slice cultures of mouse embryos [7]. Moreover, after initially normal axonal extension, nociceptive neurons from NGF/Bax double mutants failed to branch and innervate the epidermis normally [4], [8].
Finally, it has been shown that expression of NT3 receptor TrkC from TrkA locus engaged a subset of former TrkA nociceptors to become TrkC-expressing proprioceptors [9]. Did these neurons switch fate because they responded to NT3 instead of NGF or because they were lacking intracellular TrkA signaling to confer the nociceptive fate? How can downstream signaling pathways activated by the same ligand/receptor complex, NGF/TrkA, control such distinct outcomes as survival, cell fate acquisition, maturation and target innervation? In order to answer these questions, we generated knock-in mice expressing a chimeric receptor TrkAC, composed of the extracellular part of TrkA and the intracellular part of TrkC, from TrkA locus. As result, we show for the first time that intracellular parts of Trk receptors are interchangeable in vivo to control a number of NGF/TrkA-dependent processes, such as survival, fate acquisition and postnatal maturation of nociceptive neurons. Moreover, we find that NGF-dependent survival and fate determination can be completely uncoupled from target innervation. Finally, our study describes the first viable mouse model with perturbed NGF/TrkA signalling that leads to severe deficits in pain sensation.
Results
Replacing TrkA with TrkAC supports survival of nociceptive neurons
To distinguish between the influence of extracellular cues and intracellular developmental programs in neurotrophin-dependent survival, cell fate specification and neuronal circuit establishment of nociceptors, we generated a mouse line expressing a chimeric TrkA/TrkC receptor (TrkAC) from TrkA (Ntrk1) locus. In these mice, the extracellular part of the chimeric Trk receptor is encoded by endogenous TrkA (Ntrk1) (exons 1–10), while the transmembrane and intracellular parts are encoded by TrkC (Ntrk3) cDNA (Figure S1A–D), thus leaving a large portion of the Ntrk1 locus intact in order to maximize the expression of the transgene. Unlike previously generated NGF and TrkA mutant mice [1], [2], [4], [9], homozygous TrkATrkAC/TrkAC (TrkAC-KI) mice survived till adulthood, were fertile and exhibited no obvious deficits, indicating that a functional Trk receptor is expressed from the TrkA locus.
We first verified that endogenous TrkA is completely replaced with TrkAC chimeric receptor in TrkAC-KI mice. In embryonic DRGs, TrkA-positive neurons are of small diameter and represent the vast majority of DRG neurons, while TrkC neurons are of large diameter and are small-numbered. In situ hybridization labeling with a probe specific to endogenous TrkA, but not to TrkAC, demonstrated lack of staining in E15.5 DRGs from TrkAC-KI animals, while staining the majority of DRG neurons from wild type littermates (control) (Figures 1A and B). A probe specific to the mRNA region corresponding to the intracellular part of TrkC labelled only TrkC expressing neurons in control DRGs, while showing a TrkA-like staining pattern in addition to that of TrkC in TrkAC-KI DRGs (Figures 1C and 1D). TrkA-expressing neurons are completely absent by this stage in mice lacking TrkA, causing drastic decrease of DRG size due to 75% loss of all DRG neurons by E15.5 [3]. Remarkably, DRGs from TrkAC-KI mice appeared normal, suggesting that survival of neurons expressing TrkAC instead of TrkA was not affected.
Fig. 1. Replacing TrkA with TrkAC is compatible with grossly normal survival of sensory neurons in TrkAC-KI mice. 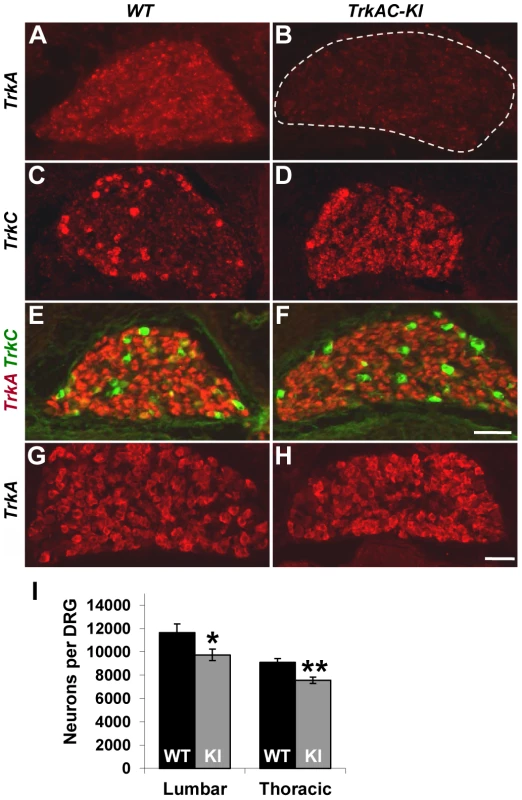
(A,B) An in situ probe recognizing endogenous TrkA, but not chimeric TrkAC is labeling the majority of wild type E15.5 DRG neurons, while mutant DRGs lack any staining. (C,D) An in situ probe specific to both TrkC and chimeric TrkAC is labeling few TrkC-positive neurons in wild type embryos and the majority of neurons in the E15.5 mutant DRGs. (E,F) Immunostaining with a TrkA antibody recognizing both TrkA and TrkAC (red) and a TrkC-specific antibody (green) showing normal pattern of TrkC expression and comparable TrkA antibody immunoreactivity in E15.5 mutant DRG. (G,H) There is normal TrkA antibody immunoreactivity in DRGs from P0 TrkAC-KI mutant mice. (I) Total number of lumbar (L3–4) and thoracic (T11–12) DRG neurons is reduced by 16% and 18% respectively in TrkAC-KI mice. Data represent mean ± s.e.m. Lumbar counts: 9 mutant and 8 wild type DRGs from 4 animals for each genotype, p = 0.041; thoracic counts: 8 mutant and 6 wild type DRGs from 3 and 2 animals respectively, p = 0.0019. * p<0.05, ** p<0.01. Scale bar is 50 µm. We then tested TrkAC expression during several developmental time points. Immunofluorescent labeling with an antibody recognizing the extracellular part of TrkA, the common part of both TrkA and TrkAC receptors, showed a similar level of immunoreactivity of extracellular part of TrkA in control and TrkAC in TrkAC-KI DRGs at embryonic stages (Figures 1E, 1F) and at birth (Figures 1G and 1H). Consistent with the normal appearance of DRGs during embryonic development, the total number of sensory neurons in adult DRGs was only modestly reduced (Figures 1I).
TrkA receptor is known to be present in different glycosylation forms in a cell, but only the mature (140 kD) form is targeted to the plasma membrane [10], [11]. We found that this mature form of TrkAC chimeric protein was present in DRGs from TrkAC-KI embryos (Figure S1E) Further biochemical characterization of the chimeric TrkAC receptor is depicted in figures S1F–H.To evaluate the ability of TrkAC receptor to transduce NGF-induced signals, lysates from three independent NGF-stimulated E14.5 DRG cultures were electrophoresed and probed with antibodies against TrkA, phospho-Akt, phospho-ERK (MAPK) and ERK (Figure S2A). Despite lower amounts of TrkAC protein in the cultured neurons, levels of phospho-ERK reached control levels after 5 min stimulation with 100 ng/ml NGF (Figures S2B and C), suggesting that the intracellular part of TrkAC chimeric protein is more efficient at activating this effectors than the intracellular part of TrkA. Another intriguing difference between these two receptors was the higher level of baseline Akt (but not ERK) activation in DRG neurons from TrkAC-KI embryos (Figure S2D). These results are consistent with the previously reported finding that TrkC signaling activates Akt more strongly than TrkA signalling [12]. These data show that TrkAC receptor is able to activate downstream signaling and suggest that this chimeric receptor could promote distinct outcomes in response to NGF stimulation in comparison to TrkA. Taken together, these data showed that despite certain differences in response to NGF stimulation, TrkAC receptor is able to activate downstream effectors that are sufficient to support normal survival of nociceptive neurons during development and through adulthood.
TrkAC induces normal segregation of nociceptors into peptidergic and nonpeptidergic neurons
Several recent studies have given new insights into the molecular control of nociceptive neuron maturation [5], [13]–[16]. These neurons, specialized in sensing a myriad of noxious thermal, mechanical and chemical stimuli, are classically divided into two major subtypes: peptidergic and nonpeptidergic neurons. Each of these two categories of neurons can be further subdivided into multiple subsets according to the sets of genes they specifically express. While all prospective nociceptors express TrkA during development, only peptidergic neurons continue expressing TrkA in adulthood, while nonpeptidergic neurons downregulate TrkA in early postnatal period and express GDNF receptor Ret [5], [17]. NGF is critical for both initial expression of multiple nociceptive markers and for postnatal maturation of nociceptors [4], [5]. To determine whether replacing the intracellular part of TrkA with that of TrkC would interfere with the maturation of prospective nociceptors, we analysed the expression patterns of a battery of nociceptive and proprioceptive markers in DRGs from adult mice. Quantification of CGRP and Ret positive neurons showed no difference between TrkAC-KI and control DRGs, suggesting that these neurons segregated normally into peptidergic and nonpeptidergic subsets (Figures 2A–D and M). Consistent with these results, nonpeptidergic marker IB4 was appropriately excluded from the peptidergic (CGRP-positive) subpopulation of nociceptors in mutant DRGs (Figures 2E and 2F). Expression of multiple other markers, with exception of TrpM8, was also normal in adult TrkAC-KI mice (Figures 2K–M and S3). Interestingly, while expression of many NGF-dependent genes, including GFRalpha1,2 and 3, RUNX1, TrpC3, MrgA1 and MrgA3 is completely abolished in developing and P0 DRGs from NGF/Bax double knockout mice [5], expression of these markers was not affected in TrkAC-KI DRGs (Figures S4A–P and data not shown).
Fig. 2. Postnatal maturation of nociceptive neurons is grossly normal in DRGs from adult TrkAC-KI mice. 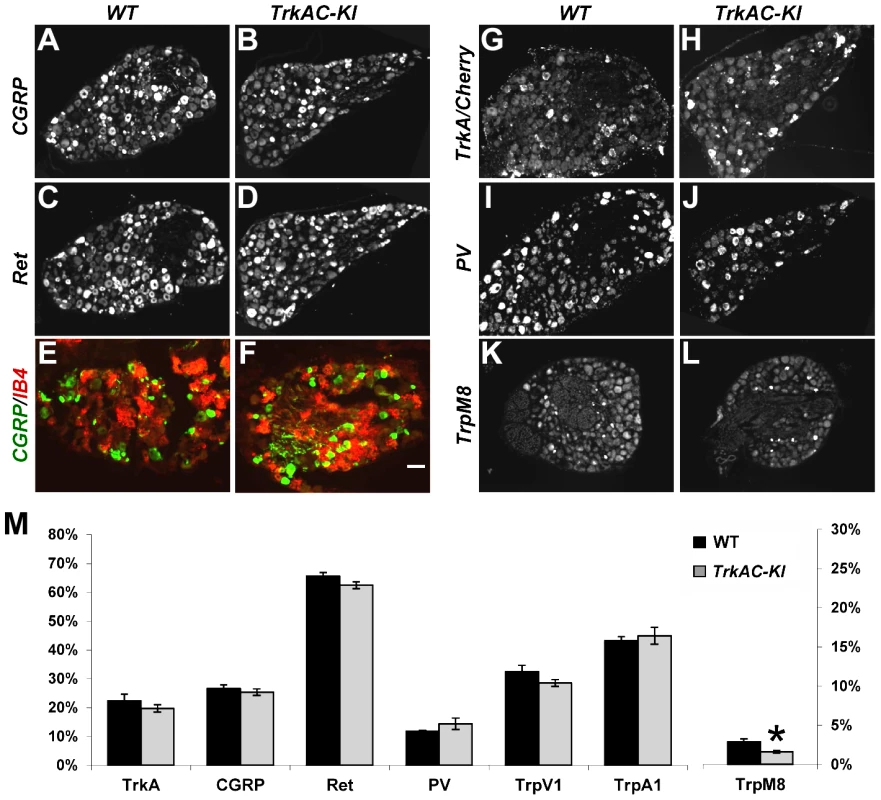
(A–D) CGRP and Ret immunostaining in lumbar DRG from adult TrkAC-KI and control mice show normal expression of peptidergic (A,B) and nonpeptidergic(C,D) markers in nociceptive neurons. n = 8–9 DRGs from 4 animals from each genotype. (E,F) Double fluorescent labeling with CGRP antibody and IB4 binding on adult thoracic DRGs from TrkAC-KI and wild type mice shows that segregation of peptidergic (CGRP) and nonpeptidergic(IB4) marker expression occurs normally in mutant mice. (G–J) In situ hybridization with TrkA (for wild type 5 DRGs from 4 animals) and Cherry (for TrkAC-KI 7 DRGs from 4 animals), as well as PV probes (8 mutant and 7 wild type DRGs from 4 and 3 animals respectively) on adult lumbar DRGs from TrkAC-KI and control animals show that fate specification of nociceptive (G,H) and proprioceptive (I,J) neurons is unaffected. (K,L) Expression of TrpM8 mRNA in adult thoracic DRGs from TrkAC-KI and control mice (7 DRGs from 3 mutant and 2 wild type animals). (M) Quantification of the percentage of neurons expressing indicated markers in (A–L and Figure S3, TrpA1 and TrpV1, 4–6 DRGs from 3 mutant and 2 wild type mice). Data represent mean ± s.e.m, * p<0.05. Scale bar is 50 µm. It has been previously shown that replacing endogenous TrkA with TrkC makes a subpopulation of former nociceptors to switch fate and become proprioceptors, leading to presence of increased numbers of PV positive neurons in DRGs [9]. We therefore quantified the number of neurons expressing parvalbumin (PV), a proprioceptive marker, as well as TrkA (or TrkAC) neurons in DRGs from control and TrkAC-KI mice. There was no difference, suggesting that TrkAC-expressing neurons retained their nociceptive fate (Figures 2I, 2J and 2M). Thus, replacing the intracellular part of TrkA with that of TrkC, not only promoted survival of most presumptive nociceptors, but also activated genetic programs that engaged these neurons towards normal nociceptive molecular fates, followed by normal postnatal maturation of these neurons.
Peripheral, but not central, projections are drastically reduced in TrkAC-KI mice
Anatomically, peptidergic and nonpeptidergic nociceptors innervate distinct peripheral and central targets in the body. In the periphery, nonpeptidergic fibers mainly innervate the skin, whereas peptidergic fibers project to most parts of the body in addition to skin. Moreover, in the glabrous skin, they innervated distinct layers of epidermis. Centrally, peptidergic and nonpeptidergic fibers terminate in distinct lamina in the dorsal horn of the spinal cord [18]. Since NGF/TrkA signalling is critical for peripheral target innervation [4], [8], we then questioned whether expression of TrkAC chimeric protein in nociceptors would have an effect on axonal extension in vivo. Surprisingly, despite normal survival and maturation of nociceptors described above, we observed a drastic decrease in peptidergic (CGRP-positive) fibers both in thin (Figures 3A, 3B and 3E) and thick (Figures 3F, 3G, and 3J) glabrous skin of adult TrkAC-KI mice comparing to wild type littermate controls. Since the number of CGRP-positive DRG neurons is normal in these mice (Figures 2A and 2B), the observed innervation deficit is due to target innervation defect and not due to cell death. Nonpeptidergic neurons depend on NGF/TrkA signalling during early development and thus could also be affected in TrkAC-KI mice. We therefore used pan-axonal marker PGP9.5 on skin sections from TrkAC-KI and control mice. Indeed, the reduction in PGP9.5-positive fibers in thin glabrous skin from TrkAC-KI mice was even greater than reduction in CGRP fibers, suggesting that target innervation by nonpeptidergic neurons was also affected (Figure 3J). The peripheral innervation defect was also observed in hairy skin, where both CGRP and PGP9.5 positive fibers appeared disorganized and drastically reduced in numbers (Figures S5A–D).
Fig. 3. Peripheral, but not central innervation is drastically reduced in TrkAC-KI mice. 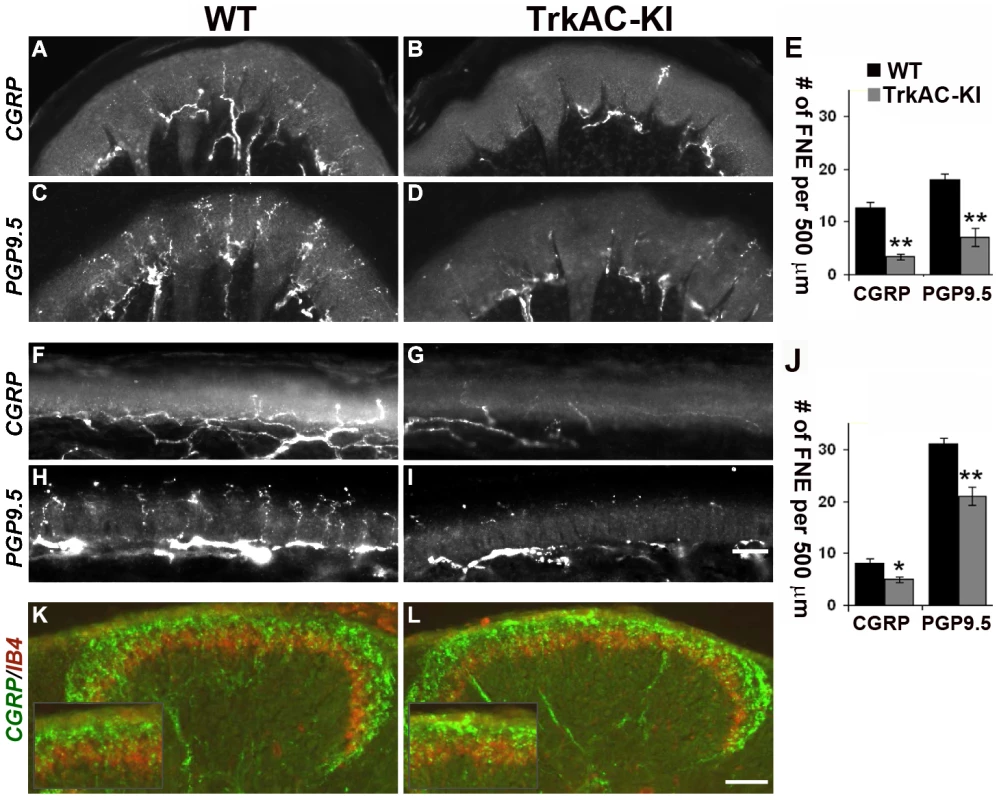
(A–D) Peptidergic (CGRP-positive) and total (PGP9.5-positive) fiber innervation is decreased in thick glabrous skin of adult TrkAC-KI hindlimbs. (E) Free nerve endings (FNE) counts in thick glabrous skin. Shown are means ± s.e.m. from 8–10 sections from two animals per genotype (* p>0.05, ** p<0.01). (F–I) Peptidergic (CGRP-positive) and total (PGP9.5-positive) fiber innervation is decreased in thin glabrous skin of adult TrkAC-KI hindlimbs. (J) Free nerve ending (FNE) counts in thin glabrous skin. Shown are means ± s.e.m. from 8–10 sections from two animals per genotype (* p>0.05, ** p<0.01). (K,L) Central projections are normal in TrkAC-KI mice. Peptidergic (CGRP-positive, green) and nonpeptidergic(IB4-positive, red) fibers normally innervate adult spinal cord in TrkAC-KI mice. Scale bar is 50 µm. Consistent with the observed skin innervation defect, sensory neurons from TrkAC-KI mice also showed abnormal NGF-dependent axonal extension in vitro. When exposed to NGF, embryonic DRG explants from TrkAC-KI mice grew out neurites at lower density comparing to DRG explants from wild type control embryos (Figures S6A–C). Neurites from mutant explants also appeared more tortuous comparing to neurites from wild type explants. However, this is most likely a consequence of difference in outgrowth density. A similar neurite outgrowth deficit was observed in cultured dissociated DRG neurons grown in presence of NGF. There were a significantly lower number of neurite-bearing cells in cultures from TrkAC-KI embryonic DRGs comparing to wild type dissociated neuron cultures (Figures S6D–F). In order to make sure that this difference was not due to differences in neuronal viability, the dissociated neurons were always labelled with anti-caspase-3 antibody. Only caspase-3 negative neurons were counted. Interestingly, the length and morphology of those TrkAC-KI neurons that did grow neurites were similar to that of wild type (Figure S6G), suggesting that TrkAC-expressing neurons are capable growing axons and that the basal axonogenesis process is intact in these cells.
Interestingly, both peptidergic (CGRP-positive, green) and nonpeptidergic (IB4-positive, red) fibers innervated adult spinal cord normally in TrkAC-KI mice (Figures 3K and 3L). This is not surprising, since DRG neurons projected to spinal cord even in Bax-deficient mice lacking NGF/TrkA signaling [4]. Thus, despite grossly normal survival and maturation of nociceptors in TrkAC-KI mice, innervation of adult skin by these neurons is specifically disrupted.
Abnormal adult skin innervation in TrkAC-KI mice is due to a developmental defect
We then investigated whether the reduced peripheral innervation in adult skin was due to a developmental defect or due to loss of axons at later stages. Immunofluorescent staining with anti-TrkA antibody showed robust labeling of DRGs and central projections in both TrkAC-KI and control E14.5 embryos, while drastic decrease in skin innervation was evident in TrkAC-KI comparing to control embryos (Figures 4A–D). Reduced skin innervation was also observed when stained with anti-PGP9.5 antibody, suggesting that the reduction in TrkA-positive fibers is due to defects in innervation and not due to lack of TrkA protein reactivity in axons (Figures 4E and 4F). Notably, skin innervation by mechanosensory TrkB positive fibers, known to innervate specialized structure in the dermis, was normal in TrkAC-KI embryos at this developmental stage (Figures 4G and 4H). Thus, even though TrkAC chimeric receptor supported survival, correct molecular maturation and normal central innervation of former TrkA-expressing neurons, it was not able to promote normal peripheral target innervation by these neurons during development.
Fig. 4. Peripheral innervation defect is evident during embryonic development. 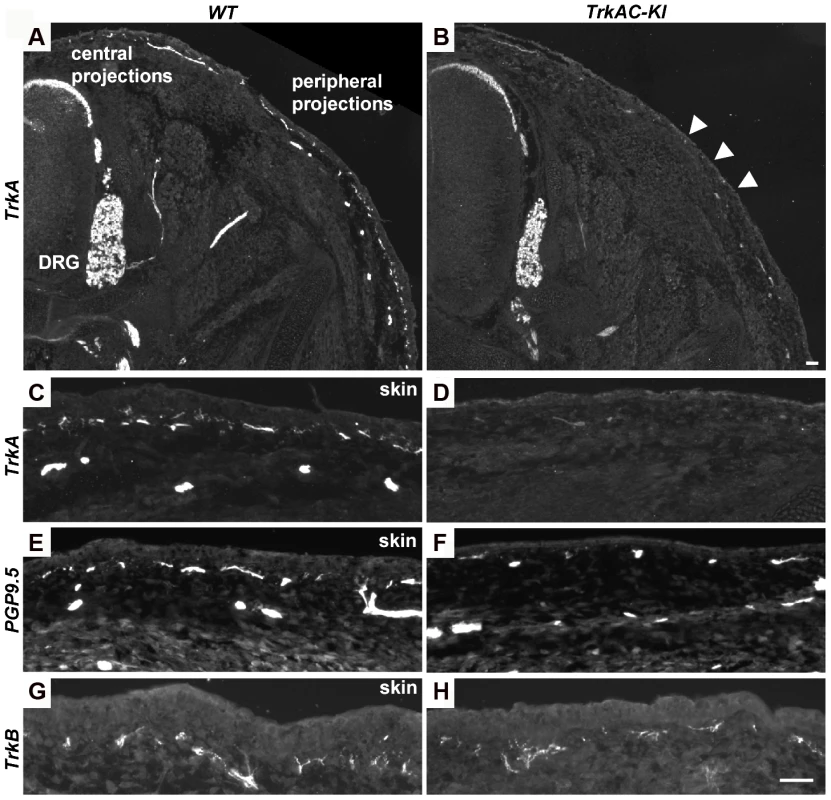
(A–D) Sections of E14.5 TrkAC-KI and control embryos stained with anti-TrkA antibody recognizing both TrkA and TrkAC proteins. Labeling of DRGs and projections to the spinal cord (central projections) is similar in both mutant and control animals while epidermal innervation is greatly decreased. (E and F) There are less PGP9.5 positive fibers in the skin of TrkAC-KI comparing to control embryos. (G and H) Skin innervation by TrkB-positive fibers is not changed in TrkAC-KI embryos. Scale bar is 50 µm. Expression of multiple axonal outgrowth molecules is affected in TrkAC-KI DRGs
Previous attempts to identify NGF-responsive genes yielded a large data set obtained from microarray experiments on neurotrophin mutants with defects in multiple NGF-dependent processes [19], [20]. In TrkAC-KI mice, however, the axonal growth deficit is accompanied by grossly normal survival and phenotypic differentiation of sensory neurons. Therefore, TrkAC-KI mice present a unique opportunity to identify genes specifically responsible for NGF-dependent axonal outgrowth without the confounding presence of genes controlling NGF-dependent survival and maturation. We seized this opportunity and performed a genome-wide screen comparing gene expression in DRGs from E14.5 TrkAC-KI and control embryos. A total number of 140 genes was identified by our microarray screen using FDR (False Discovery Rate) [21] cutoff 0.01 and fold-change of >1.5 (Table S1). Of interest, the 5 probes showing the highest downregulation in our screen corresponded to the endogenous TrkA-specific probes, expression of which is completely abolished in TrkAC-KI mice (Table S1 and Figure 1B). Remarkably, almost a third of genes (28%) that were up - or downregulated in TrkAC-KI DRGs encoded for proteins involved in cell-cell interaction and cell adhesion, processes critical for axonal pathfinding and growth (Figure 5A). Second largest (21%) group of genes encoded for proteins that are likely to play a role in trafficking and post-translational modification (Figure 5A). Dysfunction of the fine-tuned trafficking machinery needed to deliver building blocks to the extending tip of a growing axon could indeed be in part responsible for the peripheral innervation defect observed in TrkAC-KI mice. Interestingly, 16 out of 19 unknown genes identified in our screen encoded for transmembrane proteins, suggesting that they might also participate in these processes. A number of genes deregulated in TrkAC-KI mice have been previously identified in microarray screens for NGF-dependent genes, such as Cntn1, Cntn4, Mapk8, Rgs4 and Ret [19], [20]. Interestingly, while Ret expression was normal in DRGs from P0 and adult TrkAC-KI mice (Figures 5F, 5G and 2C, 2D), both protein and mRNA levels of Ret were decreased in small-diameter neurons at E14.5 (Figures 5B–E). The expression of Ret in large-diameter neurons, representing the “early Ret” population of rapidly adapting mechanoreceptors which do not express TrkA [22], remained unchanged (Figures S4Q–V). Ret is necessary for establishment and maintenance of epidermal innervation by nonpeptidergic sensory neurons [5], [22]. Thus, delayed expression of Ret or downregulation of other NGF-dependent axonal growth genes identified by our microarray screen could in part contribute to the target innervation phenotype observed in TrkAC-KI mice.
Fig. 5. Microarray screen for differentially expressed genes in DRGs from E14.5 TrkAC-KI embryos reveal a number of genes potentially responsible for NGF-dependent axonal growth. 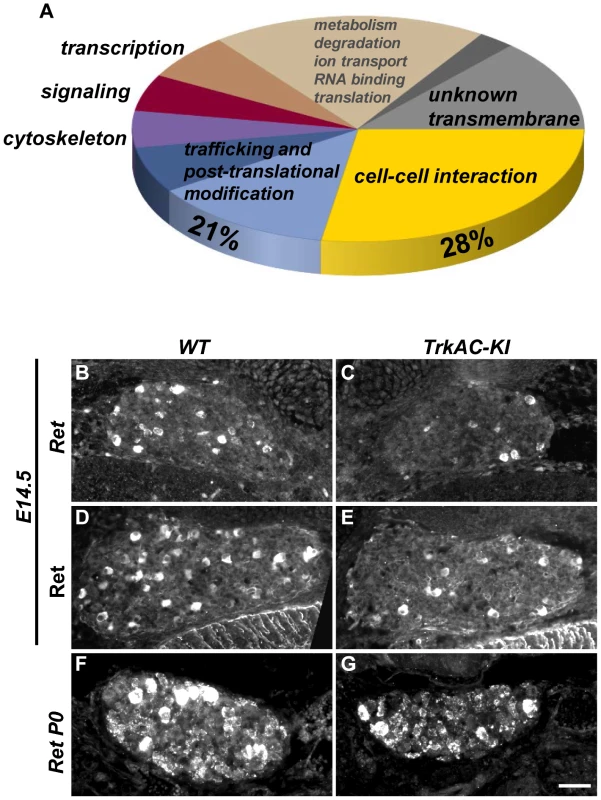
(A) Results of microarray experiment comparing gene expression between DRGs from TrkAC-KI and control E14.5 embryos. 28% of identified genes encoded for cell-cell interaction and cell adhesion molecules, and 21% for trafficking and post-translational modification proteins. Non-coding genes, as well as genes with both up- and down-regulated probes, were excluded from the data set presented in this figure (123 genes). Ret is downregulated 2 fold in our microarray. (B–G) Ret expression in small neurons is delayed in TrkAC-KI mice, as shown by in situ hybridization (B,C) and antibody labeling of E14.5 DRGs (D,E) and in situ hybridization of P0 DRGs (F,G) from mutant and control animals. Scale bar is 50 µm. Detection of temperature is moderately affected in TrkAC-KI mice
NGF/TrkA signaling is critical for development of nociceptive neurons which detect a variety of stimuli. However, behavioural analyses of mice mutant for NGF, TrkA, as well as NGF/Bax and TrkA/Bax double knockout mice have not been possible, since these animals die shortly after birth [1], [2], [4]. Unlike these mouse mutants, TrkAC-KI mice survived until adulthood and behaved normally in general locomotion and anxiety tests (Figures S7A and S7B), thus for the first time allowing behavioral analysis of mice with genetically altered NGF/TrkA signaling. We therefore subjected TrkAC-KI mice to a large battery of somatosensory tests. When tested on a hot plate at three different noxious temperatures, TrkAC-KI mice showed a decreased response at 52°C (Figure 6A), whereas heat threshold responses measured by the dynamic hot plate (Figure 6B), tail flick (Figure 6C) and Hargreaves protocols (Figure 7D) were not affected in TrkAC-KI mice. Since the number of TRPM8-expressing neurons is significantly decreased in TrkAC-KI mice, we tested the ability of these mice to respond to cold temperature. While rearing behavior and licking response latencies to cold stimuli were comparable between TrkAC-KI and control mice (Figures 6D and 6E), we observed a greater tolerance to cold (14°C) temperature during the thermal gradient protocol in TrkAC-KI compared to control mice. In this test, mice were allowed to move freely in a corridor with temperature gradient spanning from 14°C to 53°C for 1 hour. While attracted to the corner regions of the testing area, mice are generally repelled by the two extreme temperatures present in these parts. TrkAC-KI mice, however, spend a significant amount of time in the 14°C corner area during both periods: the exploration period (first 30 minutes) and the established preferred temperature period (second 30 minutes) (Figure 6F). To further examine this thermal selection phenotype, control and TrkAC-KI mice were subjected to series of two-temperature choice assays. In line with the decreased sensitivity to cold temperature observed in the gradient test, when given a choice between 20°C and 24°C, TrkAC-KI mice showed no preference for either side, whereas control mice displayed strong preference for the warmer area (Figure 6G). Mice of both genotypes behaved similarly when presented with other tested temperature choices (16°–20°, 30°C–34°C and 34°C–38°C) (Figure 6G). Together, these data showed that, despite drastic defects in skin innervation, temperature sensitivity is only moderately affected in TrkAC-KI mice.
Fig. 6. Abnormal temperature sensitivity in TrkAC-KI mice. 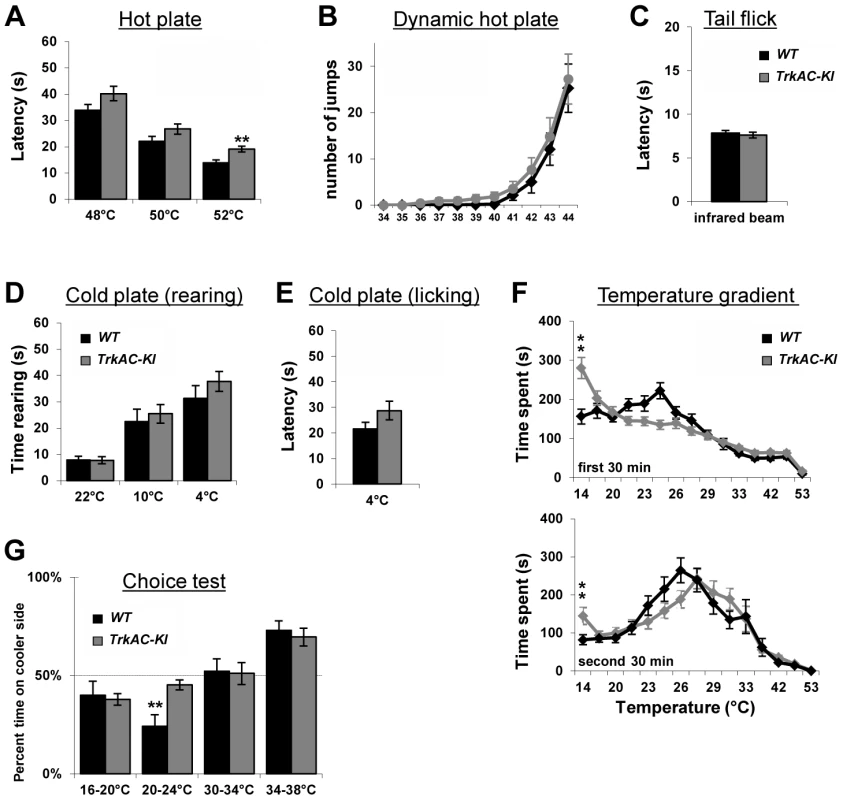
(A) TrkAC-KI mice showed increased latency of response at 52°C, but not at 48°C or 50°C (n = 9 for wild type and 11 for TrkAC-KI). (B–E) There was no difference between control and TrkAC-KI mice in the Dynamic Hot Plate (n = 14 for wild type and 16 for TrkAC-KI), Tail flick (n = 10 for wild type and 13 for TrkAC-KI), Cold Plate/Rearing (n = 10 for wild type and 8 for TrkAC-KI), or Cold Plate/Licking (n = 10 for wild type and 13 for TrkAC-KI) tests. (F) TrkAC-KI mice did not avoid cooler (14°C) area of the Temperature Gradient, suggesting that they were less sensitive to cool temperatures (n = 24 for wild type and 26 for TrkAC-KI). (G) TrkAC-KI mice spend significantly more time on cooler side during 20–24°C choice test (n = 11 for wild type and 15 for TrkAC-KI), while behaving similarly to control mice in 16–20°C (n = 11 for wild type and 15 for TrkAC-KI), 30–34°C (n = 11 for wild type and 16 for TrkAC-KI) or 34–38°C (n = 11 for wild type and 16 for TrkAC-KI) choice tests. Wild type: black bars, TrkAC-KI: gray bars. Data represent mean ± s.e.m. * p<0.05, ** p<0.01. Fig. 7. Abnormal mechanical and chemical pain response in TrkAC-KI mice. 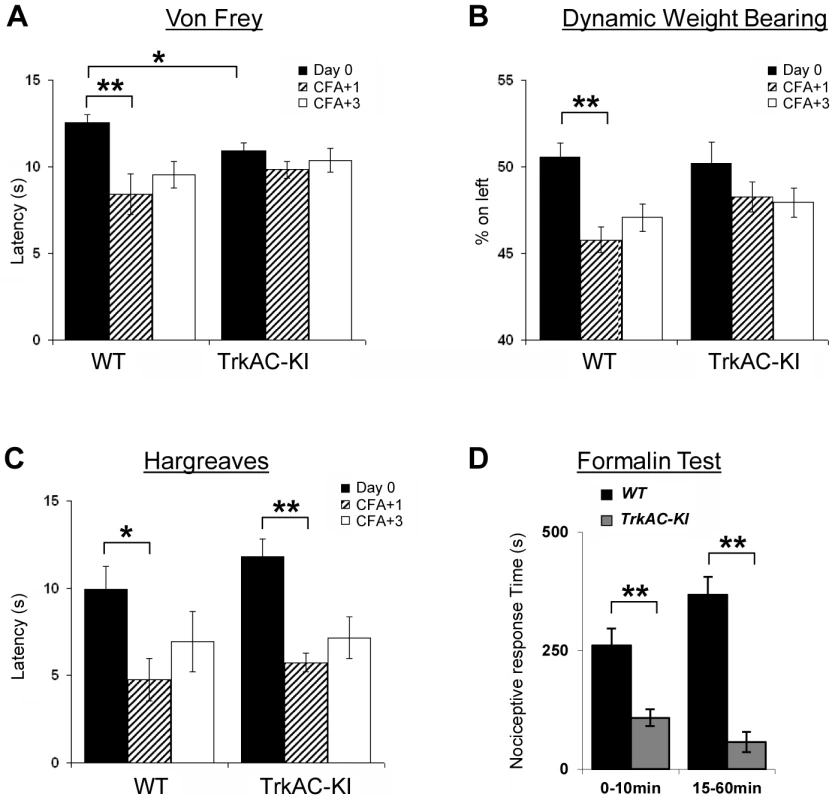
(A) Latency to mechanical stimulation using Von Frey apparatus was significantly lower in control mice one day after CFA injection, while TrkAC-KI mice did not show this response. Of note, the baseline latency to mechanical stimulation was lower in mutant mice (n = 9 for wild type and 13 for TrkAC-KI). (B) Lack of mechanical hypersensitivity after inflammation was also evident from a Dynamic Weight Bearing test. For TrkAC-KI mice, the weight distribution between inflamed and non-inflamed hindpaws was equal one day after CFA injection, while control mice favored the non-injected paw (n = 10 for wild type and 9 for TrkAC-KI). (C) Both TrkAC-KI and control mice developed thermal hyperalgesia one day after CFA injection (n = 8 for wild type and 6 for TrkAC-KI). The CFA effect (difference in latency between Day0 and day CFA+1) was significantly different between TrkAC-KI and wild type mice for Von Frey and DWB tests (A and B), but not for Hargreaves test (C). (D) TrkAC-KI mice exhibited severe deficit in pain from chemical injury when tested for nociceptive response after intraplantar injection of 10 µl of 2% formalin. Comparing to wild type littermates, TrkAC-KI mice had drastically reduced time of hindpaw shaking and biting during the first (0–10 min) and second (15–60 min) pain phases (n = 7 for each genotype). Data represent mean ± s.e.m * p<0.05, ** p<0.01. TrkAC-KI mice display severe deficit in response to noxious mechanical and chemical stimuli
In the last decade, growing evidence has implicated NGF/TrkA signalling as a major component contributing to many persistent pain states, especially those associated with inflammation [23]. We thus tested TrkAC-KI mice for ability to develop an inflammatory pain response to complete Freund's adjuvant (CFA) intraplantar injections, using automated Von Frey apparatus. One and three days after injections, CFA-induced mechanical hyperalgesia was highly pronounced in control but not in TrkAC-KI mice, when compared to the response before CFA injection (Figure 7A). However, since the latency of acute response to Von Frey stimulus before injection (Day 0) was lower in TrkAC-KI mice (Figure 7A), we also used another mechanical stimulation test, a newly engineered automated Dynamic Weight Bearing (DWB) device. This apparatus uses pressure captors that allow measuring the weight bore on paws of a freely moving mouse. In this test, mice are not acclimatized to the testing apparatus in order to maximize exploration behaviors. Before CFA-induced inflammation (day 0), the percentage of mouse weight distributed on both ipsilateral and contralateral hindpaws was equivalent between the two genotypes (Figure 7B). At one and three days post inflammation, control mice showed a marked disequilibrium towards the contralateral paw (the non-inflamed paw), while the hindpaw weight distribution of the TrkAC-KI mice was unchanged (Figure 7B). Surprisingly, post-inflammatory response to thermal stimulation was normal in TrkAC-KI mice (Figure 7C). In all experiments, paw swelling after CFA injection was comparable between TrkAC-KI and control mice. Together, the Von Frey and the DWB tests demonstrate that mechanical hypersensitivity response to tissue injury is disrupted in TrkAC-KI mice. To evaluate chemical sensitivity of TrkAC-KI mice, we opted for the formalin test. This test is a tonic model of continuous pain resulting from formalin-induced tissue injury. In rodents, intraplantar injection of formalin triggers a biphasic pain-like response characterized by flinching, licking and biting behaviors. It is generally admitted that the first phase results from activation of nociceptors at the site of injection while the second phase is largely due to central sensitization of spinal cord circuits as well as due to peripheral inflammation [24]. Injection of 10 µl of 2% formalin triggered robust first and second pain responses in the control mice, while these two behaviors were drastically reduced in TrkAC-KI mice, including an almost complete suppression of the second pain response (Figure 7D). These data demonstrate that tissue injury-induced chemical hypersensitivity is severely impaired in TrkAC-KI mice and highlight the importance of NFG/TrkA signaling in the development and function of nociceptive neurons.
Discussion
Neurotrophins control a number of different aspects of sensory neuron development [25]. Given its biological importance, numerous studies attempted to dissect the precise mechanisms of NGF/TrkA signaling, mostly by in vitro approaches using cultured neurons or neuron-like cell lines. However, our understanding of how this signaling affects the development of sensory neurons remains limited due to the challenging nature of experiments aimed at modulating Trk signaling in vivo. One study has previously addressed this issue by replacing the endogenous TrkA by TrkC using a knock in approach [9]. A subset of nociceptors in these mice developed into proprioceptors, which could be explained either by an instructive role of intracellular TrkC signaling or by a switch in responsiveness to an extracellular factor. We now report a novel mouse mutant expressing a chimeric TrkA/TrkC receptor in which the nociceptors respond to NGF but activate the intracellular signaling through TrkC intracellular domain. These mice show specific developmental target innervation defects in otherwise grossly normal nociceptive neurons. The fact that TrkAC-expressing sensory neurons retain their nociceptive fate argues against the hypothesis that activation of intracellular TrkC signaling can set in motion proprioceptor-specific developmental programs. Our results, therefore, highlight the critical role of extrinsic target derived factors in determining the fate of sensory neurons. It is likely that these factors are encountered by a growing sensory axon before it reaches its final destination, since TrkAC-positive nociceptors express most of the appropriate molecular markers even though they do not project to epidermis correctly.
Even though intracellular domains of TrkA and TrkC receptors share significant amino acid similarity, several differences in activation of downstream effectors as well as binding of interacting proteins have been reported [12], [26]–[28]. Remarkably, despite these differences, we show for the first time that the intracellular parts of these two receptors are interchangeable in vivo for supporting nociceptor survival and maturation.
It is well established that NGF/TrkA-dependent signaling controls nociceptors survival, specific marker expression and peripheral target innervation [1], [2], [4]. How can the same ligand/receptor complex activate downstream pathways controlling such distinct developmental outcomes? One hypothesis is that NGF-dependent signals instructing target innervation differ, either qualitatively or quantitatively, from signals controlling nociceptor survival and maturation. Currently available mouse mutants for neurotrophins and their receptors do not allow testing this hypothesis as these animals have deficits in multiple aspects of development [1]–[4]. We now show that survival and phenotypic maturation of nociceptors can be uncoupled from axonal growth by altering the intracellular part of the NGF receptor TrkA. What are the molecular mechanisms leading to uncoupling of these developmental processes in TrkAC-KI mice? One possibility is that the amount of NGF-activated signaling necessary for target innervation is higher than that required for supporting neuronal survival and expression of nociceptive markers. Indeed, our data show that replacing the intracellular part of TrkA with that of TrkC activated proteolytic processes leading to lower amount of the mature form of TrkAC receptor in mutant embryos. It has been recently shown DRG explant neurites are more responsive to an NGF gradient than to an absolute NGF concentration [29]. It is possible that interpretation of this gradient is defective in TrkAC-expressing neurons. Another explanation is that target innervation by nociceptors is controlled by TrkA-specific downstream transduction pathways, which could be specifically disrupted in TrkAC-KI mice. Given structural similarity of TrkA and TrkC, the vast majority of intracellular effector proteins interact with either receptor [25]. There are few proteins, however, that bind differentially to the intracellular domains of these two receptors, such as GIPC1 [27], Grit [28] and Nedd4L [26], possibly leading to activation or modulation of distinct downstream pathways. A recent study has also revealed fundamental differences between TrkA, TrkB and TrkC in instructing neuronal death both in vitro and in vivo [30]. Moreover, introducing a Sch site mutation in TrkB and TrkC receptors in vivo had distinct effects on vestibular and cochlear neurons respectively [31]. Finally, structural differences between TrkA and TrkAC receptors could lead to different activation levels of downstream effectors. Indeed, previous in vitro studies demonstrated that while both TrkA and TrkC receptors activated ERK and Akt pathways, they did so to a different extent, leading to distinct effects on axonal morphology [12]. Accordingly, our results on cultured sensory neurons from mutant and wild type embryos clearly show that the chimeric TrkAC receptor has different signaling properties comparing to that of TrkA, since lower amount of this receptor is able to activate wild type levels of pERK and pAkt. Regardless of the molecular mechanism, TrkAC-KI mice demonstrate for the first time that certain developmental processes, such as nociceptor survival and maturation, are less sensitive to qualitative and quantitative changes in Trk signaling, while other aspects of development, such as peripheral target innervation, might require precise levels of activation of specific pathways.
Both in humans and mice, loss-of-function mutations affecting NGF/TrkA signalling lead to marked insensitivity to pain [1], [2], [32] and sequestering NGF or TrkA has analgesic effects under various experimental conditions [23], [33]. However, the early lethality of NGF and TrkA mutant mice greatly impeded our understanding of the consequences of altered NGF/TrkA signalling in pain processing during postnatal stages. Our behavioural experiments revealed that TrkAC-KI mice have severe deficits in response to injury-induced mechanical and chemical pain. What are the mechanisms responsible for this phenotype? We favor the hypothesis that peripheral inflammation or chemical injury stimuli are not reaching the appropriate sensory fibers to generate an adequate response because of the drastic defects in skin innervation present in TrkAC-KI mice. In adult mice, injury-induced mechanical and chemical hypersensitivity require an intricate cross talk between peptidergic TrkA+ and nonpeptidergic Ret+ nociceptors. Indeed, genetic ablation of Nav1.8-expressing neuronal population, which included nearly all nonpeptidergic and a large fraction of peptidergic neurons, caused severe mechanical and chemical (formalin) hyposensitivity in mice [34]. Thus, it is most likely that the loss of injury-induced mechanical hypersensitivity and the decrease in response to formalin in TrkAC-KI mice is due to a dual defect: the developmental decrease in skin innervation by all nociceptors and the decreased amount of the chimeric TrkAC receptor in adult peptidergic neurons. Alternatively, the pain phenotypes could be caused by rewiring of the neuronal circuits in the spinal cord, present at the synaptic level despite the apparently normal central innervation morphology observed in TrkAC-KI mice. A combination of electrophysiological, behavioural and molecular studies of TrkAC-KI mice will distinguish between these possibilities and will greatly contribute to improving our understanding of the molecular mechanisms of nociception and pain.
It has been recently shown that acute deletion of Ret in adult mice leads to almost complete retraction of nonpeptidergic fibers from epidermis within two weeks [22], suggesting that nociceptive innervation of mammalian skin might be much more dynamic than previously thought. This plasticity in innervation is likely to play a significant role in pain perception in both normal and pathological states. Indeed, subcutaneous perfusion with NGF-sequestering molecules induced hyposensitivity to noxious thermal stimuli only after 5 days, with a similar latent period for recovery of sensitivity after the perfusion was stopped [35]. Retraction or reorganization of nociceptive axonal arbors could be responsible for this delayed effect. Major pain deficits in TrkAC-KI mice exhibiting drastic reduction in skin innervation are consistent with this hypothesis. NGF, a key player in the establishment of peripheral target innervation during embryonic development, has also been shown to alter the axonal arborisation in the adult skin [36]. Thus, it is likely that molecular mechanisms that govern the extension of embryonic sensory axons during development could also play a role in dynamics and plasticity of adult epidermal innervation. TrkAC-KI mice, therefore, represent an excellent model to study these processes, potentially leading to development of novel pain-controlling therapies. Finally, this mouse model also represents an invaluable tool to address the functions of other populations of neurons that respond to NGF/TrkA signalling such as sympathetic and cholinergic forebrain neurons.
Materials and Methods
Ethics Statement
The animal experiments were approved by the Comit? d ?thique de Marseille (reference number 14-08112010).
Generation of TrkATrkAC (TrkAC-KI) knock-in mice
See Protocol S1 for details.
Western blot on DRG extracts
For each genotype, DRGs were dissected from individual E14.5 embryos as well as from adult animals and lysed in the buffer containing 150 mM NaCl, 10 mM Tris PH7.4, 1 mM EDTA, 10 mM NaF, 1 mM Vanadine, 0.25% Na Deoxycholate, 1% NP40 and protease inhibitors. In order to quantify the amount of TrkA and TrkAC protein in embryonic DRGs, for each independent experiment (four total), lysates from individual control, heterozygous and TrkAC-KI embryos were run in parallel. Western blots were probed with anti-TrkA (generous gift from Dr. L. Reichardt, University of California San Francisco), recognizing both TrkA and TrkAC proteins, as well as anti-ERK (Cell Signaling, #9102), followed by revelation using ECL Plus kit (GE Healthcare Amersham) and MS Kodak film. Films were then scanned, making sure that the bands were not oversaturated. Intensities of TrkA or TrkAC bands, as well as corresponding loading control ERK bands were then measured using ImageJ program. After normalizing the intensity values of TrkA and TrkAC bands using the values obtained for ERK bands to control for loading differences, TrkAC amounts in heterozygous and homozygous embryos were quantified as percentage of TrkA in wild type embryos.
DRG explants and cultures of dissociated DRG neurons
For explant culturing, DRGs were dissected from E13.5 embryos obtained from a heterozygote cross, deposited on coverslips coated with poly-D-lysine(50 µg/ml, Sigma, P7405) and laminin (10 µg/ml, Sigma, L2020) and grown overnight in Neurobasal media (Invitrogen) supplemented with 2% B27 (Invitrogen), 2 mM glutamine and 1 mM Na pyruvate, in presence of 50 ng/ml NGF (Alomone Labs, N-240, lot # NF-11). DRG explants were then labeled with mouse anti-neurofilament antibody (NF (160 kD) NN18, Sigma, N5264) and photographed at 2.5× magnification. NIH ImageJ program was used to measure the neurite density in the area defined by two concentric circles 100 µm and 200 µm away from the explant border.
Dissociated DRG cultures were prepared following standard protocols. Briefly, DRG from E14.5 embryos were collected in cold DMEM. After trypsinization (10 min at 37°C), tissue was triturated using two fire-polished Pasteur pipettes and washed in Neurobasal media. Cells were then plated at low density (50 000–200 000 cells per well in a 4-well plate) on coverslips coated with poly-D-lysine/laminin, grown overnight (18 hours) in Neurobasal media containing 50 ng/ml NGF and 10 µM mix of FDU/U (5-Fluoro-2′-deoxyuridine, Sigma, F0503 and Uridine, Sigma, U3003) in order to prevent growth of non-neuronal cells. DRG neurons were then stained with mouse anti-neurofilament (Sigma) and rabbit anti-caspase3 (Cell Signaling) antibodies. In order to avoid bias in random field selection, an area of 25 fields (5×5) in the center of the coverslip was imaged at 10× magnification using MozaicX option on Apotome Z1. This area, corresponding to approximately 12 µm2, was divided into 12 1 µm2 areas in Photoshop. Neurons with and without neurites were identified by neurofilament staining and morphology. The length of neurites was measured using NeuronJ plug-in for NIH ImageJ program.
For cultures used in NGF-stimulation experiments, neurons were first grown overnight in presence of 50 ng/ml NGF and FDU/U, then washed twice in NGF-free Neurobasal medium and starved for 48 hours in NGF-free Neurobasal medium containing 2 µM caspase inhibitor Boc-D(Ome)-FMK (Biovision, #1160). DRG neurons were then stimulated with 100 ng/ml NGF for 5 and 15 minutes, by gently replacing half of the medium present in a well with equal amount of medium containing 200 ng/ml NGF. For non-stimulated cultures, half of the medium was replaced by an equal amount of NGF-free medium for 5 minutes. After stimulation, plates were immediately placed on ice, washed with ice-cold PBS and lysed in buffer containing 150 mM NaCl, 10 mM Tris PH7.4, 1 mM EDTA, 10 mM NaF, 1 mM Vanadine, 0.25% Na Deoxycholate, 1% NP40 and protease inhibitors. The following antibodies were used for Western blotting: anti-TrkA (generous gift from Dr. L. Reichardt, University of California San Francisco), anti-pErk1/2 (Cell Signaling, #9106), anti-pAkt (Cell Signaling, #9271S), anti-ERK (Cell Signaling, #9102).
In situ hybridization and immunofluorescence
In situ hybridization and immunofluorescence were carried out following standard protocols [9]. To obtain adult tissues, animals were deeply anesthetized with a mix of ketamine/xylazine and then transcardially perfused with an ice-cold solution of paraformaldehyde 4% in PBS (PAF). After dissection, DRGs were post-fixed for at least 24 hours in the same fixative at 4°C. Embryos were collected in ice-cold PBS, and fixed for 24 h in 4% PAF. Adult back skin and footpads were excised from deeply anesthetized animals and incubated in 5% formaldehyde, 15% v/v picric acid in PBS overnight at 4°C. Tissues were then transferred into a 30% (w/v) sucrose solution for cryoprotection before being frozen and stored at −80°C. Samples were sectioned at 10–30 µm using a standard cryostat (Leica).
RNA probes were synthesized using gene-specific PCR primers and cDNA templates from embryonic or adult mouse DRG. Double fluorescent in situ hybridization was carried out using a combination of digoxigenin and fluorescein/biotin labeled probes. Probes were hybridized overnight at 55°C and the slides incubated with the horseradish peroxidase anti-digoxigenin/fluorescein/biotin antibody (Roche). Final detection was achieved using fluorescein/cy3/cy5 TSA plus kit (Perkin Elmer). For double fluorescent in situ experiments, the first antibody was inactivated using H2O2 treatment.
For in situ probes, the following nucleotide positions were used. TrkA-Cterm, 2232–2573 of NM_001033124; TrkC-Cterm, 1360–1881 of NM_008746; PV, 80–594 of NM_013645; TrpM8, 1410–1980 of AF481480; TrpA1, 617–1518 of NM_177781, TrpV1, 1521–2065 of NM_031982; MrgB4, 1–860 of NM_205795; TrpC3, 2599–3514 of NM_019510; GFRalpha1, 1746–2913 of NM_010279; GFRalpha2, 2520–3287 of NM_008115; GFRalpha3, 1318–1952 of NM_010280; MrgA1, 89–917 of NM_153095; Ret, 1370–1845 of NM_009050.
For immunofluorescence, primary antibodies were diluted in PBS-10% donkey serum (Sigma)-3% bovine albumin (Sigma)-0.4% triton-X100 and incubated overnight at 4°C. Corresponding donkey anti-rabbit or anti-goat Alexa 488 or 555 (Molecular Probes) were used for secondary detection. Primary antibodies used in this study are as follows: rabbit anti-TrkA 1∶2000 (generous gift from Dr. L. Reichardt, University of California San Francisco), rabbit anti-Runx1 1∶4000 (generous gift from Dr. T. Jessell, New York University School of Medicine), goat anti-TrkC 1∶500 (R&D systems), goat anti-Ret 1∶500 (R&D systems) and rabbit anti-CGRP 1∶2000 (Chemicon).
Microarray analysis
Spinal columns from E14 embryos from multiple litters were quickly dissected in Hank's Buffered Salt Solution (HBSS) and placed in RNAlater (Ambion) overnight at 4°C awaiting genotyping. DRGs were then dissected out and homogenized using glass beads in Precellys 24 (Bertin Technologies, France), followed by RNA extraction using RNeasy mini kit (Qiagen). RNA was then concentrated by precipitation with lithium chloride (2.5 M final concentration). The amount and quality of RNA was assessed using NanoDrop (NanoDrop Technologies) and Experion system (BIO-RAD). Three independent replicates, each containing DRGs from 6–8 embryos from multiple litters, were prepared for each genotype. RNA labeling, microarray hybridization and statistical analysis were carried out by MGX-Montpellier GenomiX platform. For the preparation of the labeled Cy3 - and Cy5 - aRNA target, one microgram of the total RNA samples were amplified and labeled using the Amino Allyl Message Amp II aRNA Amplification Kit (Ambion; Austin, Texas, USA), according to the manufacturer's instructions. The Cy3 - and Cy5-labeled aRNA samples were then added to Hybridization Buffer, hybridization component A and alignment oligo mix (Roche Nimblegen, Madison, Wisconsin), denatured at 95°C for three minutes and applied to an array on a 12×135K Nimblegen microarray slide. Each biological replicate sample (3wt+3ko for E14) was compared to the common reference twice. Hybridization was carried out at 42°C for 16 hours in the hybridization system 4 (Roche Nimblegen, Madison, Wisconsin). Hybridized slides were washed according to Nimblegen's protocols. Microarrays were immediately scanned at 1 µm resolution in both Cy3 and Cy5 channels with Innoscan900 scanner (Innopsys, Carbonne, France) using variable photo multiplier tube (PMT) settings to obtain maximal signal intensities. Nimblescan v2.5 software (Roche Nimblegen, Madison, Wisconsin) was used for feature extraction. To perform the analysis of the data, a script written in R language was used. R packages available in the BioConductor project [37] were used (R v2.12.2, bioconductor v2.7). The data were normalized using LOWESS (Locally Weighted Scatterplot Smoothing) method [38] from LIMMA package. 190 differentially expressed probes (corresponding to 140 genes) were identified by LIMMA (Linear Modeling of Microarray data) method [39], using FDR (False Discovery Rate) [21] cutoff 0.01 and fold-change of >1.5. Functional annotation to differentially expressed genes was assigned based on the Gene Ontology Project (http://www.geneontology.org/) and literature review.
Axonal projection counts
For each marker, 8–10 sections from 4–5 different areas of thick glabrous skin (1st–2nd hindpaw footpad) and 8–10 section of thin glabrous (skin adjacent to a footpad) were analyzed, 2 animals per genotype. At least 5 mm of skin was analyzed per each genotype.
Cell counts and statistical analysis
For adult tissues, we adopted a strategy that has been previously validated for DRG cell counts [13]. Briefly, serial sections of thoracic or lumbar DRG were distributed on 6 slides which were subjected to different markers including the pan-neuronal marker SCG10. This approach allowed us to represent all counts as percentage of the total number of neurons (SCG10+). All cell counts were conducted by an individual who was blind to the genotype of the animals. 8–12 week old mice were used for analysis. The number of DRGs counted for each marker is indicated in figure legends. Statistical significance was set to p<0.05 and assessed using unpaired t-test for all statistical tests in the manuscript.
Behavioral tests
Animals were maintained under standard housing conditions (25°C, 40% humidity, 12 h light cycles, and free access to food and water). Special effort was made to minimize the number as well as the stress and suffering of mice used in this study. All protocols are in agreement with European Union recommendations for animal experimentation. All behaviour analysis was conducted on littermate males 8–12 weeks old. Student's T-test was used for all statistical calculations. Detailed description of tests is provided in Protocol S1.
Supporting Information
Zdroje
1. CrowleyC, SpencerSD, NishimuraMC, ChenKS, Pitts-MeekS, et al. (1994) Mice lacking nerve growth factor display perinatal loss of sensory and sympathetic neurons yet develop basal forebrain cholinergic neurons. Cell 76 : 1001–1011.
2. SmeyneRJ, KleinR, SchnappA, LongLK, BryantS, et al. (1994) Severe sensory and sympathetic neuropathies in mice carrying a disrupted Trk/NGF receptor gene. Nature 368 : 246–249.
3. WhiteFA, Silos-SantiagoI, MolliverDC, NishimuraM, PhillipsH, et al. (1996) Synchronous onset of NGF and TrkA survival dependence in developing dorsal root ganglia. J Neurosci 16 : 4662–4672.
4. PatelTD, JackmanA, RiceFL, KuceraJ, SniderWD (2000) Development of sensory neurons in the absence of NGF/TrkA signaling in vivo. Neuron 25 : 345–357.
5. LuoW, WickramasingheSR, SavittJM, GriffinJW, DawsonTM, et al. (2007) A hierarchical NGF signaling cascade controls Ret-dependent and Ret-independent events during development of nonpeptidergic DRG neurons. Neuron 54 : 739–754.
6. Levi-MontalciniR, MeyerH, HamburgerV (1954) In vitro experiments on the effects of mouse sarcomas 180 and 37 on the spinal and sympathetic ganglia of the chick embryo. Cancer Res 14 : 49–57.
7. TuckerKL, MeyerM, BardeYA (2001) Neurotrophins are required for nerve growth during development. Nat Neurosci 4 : 29–37.
8. WickramasingheSR, AlvaniaRS, RamananN, WoodJN, MandaiK, et al. (2008) Serum response factor mediates NGF-dependent target innervation by embryonic DRG sensory neurons. Neuron 58 : 532–545.
9. MoqrichA, EarleyTJ, WatsonJ, AndahazyM, BackusC, et al. (2004) Expressing TrkC from the TrkA locus causes a subset of dorsal root ganglia neurons to switch fate. Nat Neurosci 7 : 812–818.
10. JullienJ, GuiliV, ReichardtLF, RudkinBB (2002) Molecular kinetics of nerve growth factor receptor trafficking and activation. J Biol Chem 277 : 38700–38708.
11. WatsonFL, PorcionattoMA, BhattacharyyaA, StilesCD, SegalRA (1999) TrkA glycosylation regulates receptor localization and activity. J Neurobiol 39 : 323–336.
12. MarkusA, ZhongJ, SniderWD (2002) Raf and akt mediate distinct aspects of sensory axon growth. Neuron 35 : 65–76.
13. ChenCL, BroomDC, LiuY, de NooijJC, LiZ, et al. (2006) Runx1 determines nociceptive sensory neuron phenotype and is required for thermal and neuropathic pain. Neuron 49 : 365–377.
14. GasconE, GaillardS, MalapertP, LiuY, Rodat-DespoixL, et al. (2010) Hepatocyte growth factor-Met signaling is required for Runx1 extinction and peptidergic differentiation in primary nociceptive neurons. J Neurosci 30 : 12414–12423.
15. GasconE, MoqrichA (2010) Heterogeneity in primary nociceptive neurons: from molecules to pathology. Arch Pharm Res 33 : 1489–1507.
16. WoolfCJ, MaQ (2007) Nociceptors–noxious stimulus detectors. Neuron 55 : 353–364.
17. MolliverDC, WrightDE, LeitnerML, ParsadanianAS, DosterK, et al. (1997) IB4-binding DRG neurons switch from NGF to GDNF dependence in early postnatal life. Neuron 19 : 849–861.
18. ZylkaMJ, RiceFL, AndersonDJ (2005) Topographically distinct epidermal nociceptive circuits revealed by axonal tracers targeted to Mrgprd. Neuron 45 : 17–25.
19. GuoT, MandaiK, CondieBG, WickramasingheSR, CapecchiMR, et al. (2011) An evolving NGF-Hoxd1 signaling pathway mediates development of divergent neural circuits in vertebrates. Nat Neurosci 14 : 31–36.
20. MandaiK, GuoT, St HillaireC, MeabonJS, KanningKC, et al. (2009) LIG family receptor tyrosine kinase-associated proteins modulate growth factor signals during neural development. Neuron 63 : 614–627.
21. Benjamini YHY (1995) Controlling the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J Roy Statist Soc Ser B (Methodological) 57 : 289–300.
22. LuoW, EnomotoH, RiceFL, MilbrandtJ, GintyDD (2009) Molecular identification of rapidly adapting mechanoreceptors and their developmental dependence on ret signaling. Neuron 64 : 841–856.
23. UgoliniG, MarinelliS, CovaceuszachS, CattaneoA, PavoneF (2007) The function neutralizing anti-TrkA antibody MNAC13 reduces inflammatory and neuropathic pain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104 : 2985–2990.
24. DickensonAH, SullivanAF (1987) Peripheral origins and central modulation of subcutaneous formalin-induced activity of rat dorsal horn neurones. Neurosci Lett 83 : 207–211.
25. ChaoMV (2003) Neurotrophins and their receptors: a convergence point for many signalling pathways. Nat Rev Neurosci 4 : 299–309.
26. ArevaloJC, WaiteJ, RajagopalR, BeynaM, ChenZY, et al. (2006) Cell survival through Trk neurotrophin receptors is differentially regulated by ubiquitination. Neuron 50 : 549–559.
27. KatoH, OhnoK, HashimotoK, SatoK (2004) Synectin in the nervous system: expression pattern and potential as a binding partner of neurotrophin receptors. FEBS Lett 572 : 123–128.
28. NakamuraT, KomiyaM, SoneK, HiroseE, GotohN, et al. (2002) Grit, a GTPase-activating protein for the Rho family, regulates neurite extension through association with the TrkA receptor and N-Shc and CrkL/Crk adapter molecules. Mol Cell Biol 22 : 8721–8734.
29. MortimerD, PujicZ, VaughanT, ThompsonAW, FeldnerJ, et al. (2010) Axon guidance by growth-rate modulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107 : 5202–5207.
30. NikoletopoulouV, LickertH, FradeJM, RencurelC, GiallonardoP, et al. (2010) Neurotrophin receptors TrkA and TrkC cause neuronal death whereas TrkB does not. Nature 467 : 59–63.
31. PostigoA, CalellaAM, FritzschB, KnipperM, KatzD, et al. (2002) Distinct requirements for TrkB and TrkC signaling in target innervation by sensory neurons. Genes Dev 16 : 633–645.
32. IndoY (2001) Molecular basis of congenital insensitivity to pain with anhidrosis (CIPA): mutations and polymorphisms in TRKA (NTRK1) gene encoding the receptor tyrosine kinase for nerve growth factor. Hum Mutat 18 : 462–471.
33. PezetS, McMahonSB (2006) Neurotrophins: mediators and modulators of pain. Annu Rev Neurosci 29 : 507–538.
34. AbrahamsenB, ZhaoJ, AsanteCO, CendanCM, MarshS, et al. (2008) The cell and molecular basis of mechanical, cold, and inflammatory pain. Science 321 : 702–705.
35. McMahonSB, BennettDL, PriestleyJV, SheltonDL (1995) The biological effects of endogenous nerve growth factor on adult sensory neurons revealed by a trkA-IgG fusion molecule. Nat Med 1 : 774–780.
36. DiamondJ, HolmesM, CoughlinM (1992) Endogenous NGF and nerve impulses regulate the collateral sprouting of sensory axons in the skin of the adult rat. J Neurosci 12 : 1454–1466.
37. GentlemanRC, CareyVJ, BatesDM, BolstadB, DettlingM, et al. (2004) Bioconductor: open software development for computational biology and bioinformatics. Genome Biol 5: R80.
38. SmythGK, SpeedT (2003) Normalization of cDNA microarray data. Methods 31 : 265–273.
39. Smyth GK (2005) Limma: linear models for microarray data. Bioinformatics and Computational Biology Solutions using R and Bioconductor, R Gentleman, V Carey, S Dudoit, R Irizarry, W Huber. New York: Springer. pp. 397–420.
Štítky
Genetika Reprodukční medicína
Článek Natural Polymorphisms in Influence Negative Selection and CD4∶CD8 Lineage Commitment in the RatČlánek MicroRNAs Located in the Hox Gene Clusters Are Implicated in Huntington's Disease PathogenesisČlánek Comparative RNAi Screens in and Reveal the Impact of Developmental System Drift on Gene FunctionČlánek Mutation of SLC35D3 Causes Metabolic Syndrome by Impairing Dopamine Signaling in Striatal D1 Neurons
Článek vyšel v časopisePLOS Genetics
Nejčtenější tento týden
2014 Číslo 2
-
Všechny články tohoto čísla
- Fifteen Years Later: Hard and Soft Selection Sweeps Confirm a Large Population Number for HIV In Vivo
- The Same but Different: Worms Reveal the Pervasiveness of Developmental System Drift
- Serine Carboxypeptidase SCPEP1 and Cathepsin A Play Complementary Roles in Regulation of Vasoconstriction via Inactivation of Endothelin-1
- Coherent Functional Modules Improve Transcription Factor Target Identification, Cooperativity Prediction, and Disease Association
- A Long-Chain Flavodoxin Protects from Oxidative Stress and Host Bacterial Clearance
- Mammalian E-type Cyclins Control Chromosome Pairing, Telomere Stability and CDK2 Localization in Male Meiosis
- Influenza Virus Drug Resistance: A Time-Sampled Population Genetics Perspective
- Transcriptome-Wide Analyses of 5′-Ends in RNase J Mutants of a Gram-Positive Pathogen Reveal a Role in RNA Maturation, Regulation and Degradation
- Selective Disruption of Aurora C Kinase Reveals Distinct Functions from Aurora B Kinase during Meiosis in Mouse Oocytes
- X Chromosome Control of Meiotic Chromosome Synapsis in Mouse Inter-Subspecific Hybrids
- A Cohesin-Independent Role for NIPBL at Promoters Provides Insights in CdLS
- Extreme Population Differences in the Human Zinc Transporter ZIP4 (SLC39A4) Are Explained by Positive Selection in Sub-Saharan Africa
- Classic Selective Sweeps Revealed by Massive Sequencing in Cattle
- Genomic Networks of Hybrid Sterility
- Natural Polymorphisms in Influence Negative Selection and CD4∶CD8 Lineage Commitment in the Rat
- Oxidative Stress Is Not a Major Contributor to Somatic Mitochondrial DNA Mutations
- Molecular Identification of Collagen 17a1 as a Major Genetic Modifier of Laminin Gamma 2 Mutation-Induced Junctional Epidermolysis Bullosa in Mice
- Uncoupling of Molecular Maturation from Peripheral Target Innervation in Nociceptors Expressing a Chimeric TrkA/TrkC Receptor
- MicroRNAs Located in the Hox Gene Clusters Are Implicated in Huntington's Disease Pathogenesis
- Loss of Trabid, a New Negative Regulator of the Immune-Deficiency Pathway at the Level of TAK1, Reduces Life Span
- Targeted Ablation of Nesprin 1 and Nesprin 2 from Murine Myocardium Results in Cardiomyopathy, Altered Nuclear Morphology and Inhibition of the Biomechanical Gene Response
- Identification of Novel Genetic Loci Associated with Thyroid Peroxidase Antibodies and Clinical Thyroid Disease
- CEP-1, the p53 Homolog, Mediates Opposing Longevity Outcomes in Mitochondrial Electron Transport Chain Mutants
- Transcriptomics and Functional Genomics of ROS-Induced Cell Death Regulation by
- Quantitative Genome-Wide Genetic Interaction Screens Reveal Global Epistatic Relationships of Protein Complexes in
- Cascades of Genetic Instability Resulting from Compromised Break-Induced Replication
- Serine- and Threonine/Valine-Dependent Activation of PDK and Tor Orthologs Converge on Sch9 to Promote Aging
- Zfp322a Regulates Mouse ES Cell Pluripotency and Enhances Reprogramming Efficiency
- Insertional Mutagenesis and Deep Profiling Reveals Gene Hierarchies and a -Dependent Bottleneck in Lymphomagenesis
- DAAM Is Required for Thin Filament Formation and Sarcomerogenesis during Muscle Development in Drosophila
- Plasma Cholesterol–Induced Lesion Networks Activated before Regression of Early, Mature, and Advanced Atherosclerosis
- High-Resolution Profiling of Stationary-Phase Survival Reveals Yeast Longevity Factors and Their Genetic Interactions
- Comparative RNAi Screens in and Reveal the Impact of Developmental System Drift on Gene Function
- Accurate and Robust Genomic Prediction of Celiac Disease Using Statistical Learning
- Sex-Specific Embryonic Gene Expression in Species with Newly Evolved Sex Chromosomes
- Chromosome X-Wide Association Study Identifies Loci for Fasting Insulin and Height and Evidence for Incomplete Dosage Compensation
- Negative Feedback and Transcriptional Overshooting in a Regulatory Network for Horizontal Gene Transfer
- DNA Sequence Explains Seemingly Disordered Methylation Levels in Partially Methylated Domains of Mammalian Genomes
- Insights into the Genomic Landscape: Comparative Genomics Reveals Variations in Ploidy and Nutrient Utilisation Potential amongst Wine Isolates
- Molecular Evidence for the Inverse Comorbidity between Central Nervous System Disorders and Cancers Detected by Transcriptomic Meta-analyses
- The Centriolar Satellite Protein AZI1 Interacts with BBS4 and Regulates Ciliary Trafficking of the BBSome
- Fine-Mapping the Region Detects Common Variants Tagging a Rare Coding Allele: Evidence for Synthetic Association in Prostate Cancer
- Transmission Distortion Affecting Human Noncrossover but Not Crossover Recombination: A Hidden Source of Meiotic Drive
- A Variant in the Neuropeptide Receptor is a Major Determinant of Growth and Physiology
- Mutation of SLC35D3 Causes Metabolic Syndrome by Impairing Dopamine Signaling in Striatal D1 Neurons
- NSUN4 Is a Dual Function Mitochondrial Protein Required for Both Methylation of 12S rRNA and Coordination of Mitoribosomal Assembly
- MicroRNA-133 Inhibits Behavioral Aggregation by Controlling Dopamine Synthesis in Locusts
- Convergence of Light and ABA Signaling on the Promoter
- Arf4 Is Required for Mammalian Development but Dispensable for Ciliary Assembly
- Distinct Requirements for Cranial Ectoderm and Mesenchyme-Derived Wnts in Specification and Differentiation of Osteoblast and Dermal Progenitors
- Chk2 and P53 Regulate the Transmission of Healed Chromosomes in the Male Germline
- Ddc2 Mediates Mec1 Activation through a Ddc1- or Dpb11-Independent Mechanism
- Mapping the Fitness Landscape of Gene Expression Uncovers the Cause of Antagonism and Sign Epistasis between Adaptive Mutations
- Euchromatic Transposon Insertions Trigger Production of Novel Pi- and Endo-siRNAs at the Target Sites in the Germline
- miR-100 Induces Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition but Suppresses Tumorigenesis, Migration and Invasion
- Canine Hereditary Ataxia in Old English Sheepdogs and Gordon Setters Is Associated with a Defect in the Autophagy Gene Encoding
- Within-Host Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Plant Virus Infection at the Cellular Level
- Analysis of Meiosis in SUN1 Deficient Mice Reveals a Distinct Role of SUN2 in Mammalian Meiotic LINC Complex Formation and Function
- Genome-Wide Association Study of Metabolic Traits Reveals Novel Gene-Metabolite-Disease Links
- Mechanistically Distinct Mouse Models for -Associated Retinopathy
- DAF-16/FoxO Directly Regulates an Atypical AMP-Activated Protein Kinase Gamma Isoform to Mediate the Effects of Insulin/IGF-1 Signaling on Aging in
- Chromosome I Controls Chromosome II Replication in
- Integrated Genomic Characterization Reveals Novel, Therapeutically Relevant Drug Targets in FGFR and EGFR Pathways in Sporadic Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma
- The Iodotyrosine Deiodinase Ortholog SUP-18 Functions through a Conserved Channel SC-Box to Regulate the Muscle Two-Pore Domain Potassium Channel SUP-9
- The Genome of Highlights a Fish Pathogen Adapted to Fluctuating Environments
- Distinct DNA Binding Sites Contribute to the TCF Transcriptional Switch in and
- The Streamlined Genome of spp. Relative to Human Pathogenic Kinetoplastids Reveals a Parasite Tailored for Plants
- PLOS Genetics
- Archiv čísel
- Aktuální číslo
- Informace o časopisu
Nejčtenější v tomto čísle- Genome-Wide Association Study of Metabolic Traits Reveals Novel Gene-Metabolite-Disease Links
- A Cohesin-Independent Role for NIPBL at Promoters Provides Insights in CdLS
- Classic Selective Sweeps Revealed by Massive Sequencing in Cattle
- Arf4 Is Required for Mammalian Development but Dispensable for Ciliary Assembly
Kurzy
Zvyšte si kvalifikaci online z pohodlí domova
Současné možnosti léčby obezity
nový kurzAutoři: MUDr. Martin Hrubý
Všechny kurzyPřihlášení#ADS_BOTTOM_SCRIPTS#Zapomenuté hesloZadejte e-mailovou adresu, se kterou jste vytvářel(a) účet, budou Vám na ni zaslány informace k nastavení nového hesla.
- Vzdělávání



