-
Články
Top novinky
Reklama- Vzdělávání
- Časopisy
Top články
Nové číslo
- Témata
Top novinky
Reklama- Videa
- Podcasty
Nové podcasty
Reklama- Kariéra
Doporučené pozice
Reklama- Praxe
Top novinky
ReklamaElucidation of the RamA Regulon in Reveals a Role in LPS Regulation
Bacteria can rapidly evolve under antibiotic pressure to develop resistance, which occurs when target genes mutate, or when resistance-encoding genes are transferred. Alternatively, microbes can simply alter the levels of intrinsic proteins that allow the organism to “buy” time to resist antibiotic pressure. Klebsiella pneumoniae is a pathogen that causes significant blood stream or respiratory infections, but more importantly is a bacterium that is increasingly being reported as multidrug resistant. Our data demonstrate that RamA can trigger changes on the bacterial surface that allow Klebsiella to survive both antibiotic challenge, degradation by host immune peptides and resist phagocytosis. We demonstrate that the molecular basis of increased survival of ramA overexpressing K. pneumoniae, against host-derived factors is associated with RamA-driven alterations of the lipid A moiety of Klebsiella LPS. This modification is likely to be linked to Klebsiella’s ability to resist the host response so that it remains undetected by the immune system. The relevance of our work extends beyond RamA in Klebsiella as other pathogens such as Enterobacter spp and Salmonella spp. also produce this protein. Thus our overarching conclusion is that the intrinsic regulator, RamA perturbs host-microbe and microbe-drug interactions.
Published in the journal: . PLoS Pathog 11(1): e32767. doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1004627
Category: Research Article
doi: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1004627Summary
Bacteria can rapidly evolve under antibiotic pressure to develop resistance, which occurs when target genes mutate, or when resistance-encoding genes are transferred. Alternatively, microbes can simply alter the levels of intrinsic proteins that allow the organism to “buy” time to resist antibiotic pressure. Klebsiella pneumoniae is a pathogen that causes significant blood stream or respiratory infections, but more importantly is a bacterium that is increasingly being reported as multidrug resistant. Our data demonstrate that RamA can trigger changes on the bacterial surface that allow Klebsiella to survive both antibiotic challenge, degradation by host immune peptides and resist phagocytosis. We demonstrate that the molecular basis of increased survival of ramA overexpressing K. pneumoniae, against host-derived factors is associated with RamA-driven alterations of the lipid A moiety of Klebsiella LPS. This modification is likely to be linked to Klebsiella’s ability to resist the host response so that it remains undetected by the immune system. The relevance of our work extends beyond RamA in Klebsiella as other pathogens such as Enterobacter spp and Salmonella spp. also produce this protein. Thus our overarching conclusion is that the intrinsic regulator, RamA perturbs host-microbe and microbe-drug interactions.
Introduction
The microbial response to antimicrobial challenge is multifactorial and can be conferred by a combination of extrinsic or intrinsic mechanisms. Those intrinsic mechanisms that confer pleiotropic phenotypes can provide a “stepping stone” to surmounting both the host or drug response. Intrinsic proteins such as the AraC-transcriptional proteins e.g. MarA [1], SoxS [2], Rob [3], RamA [4] and RarA [5], directly regulate genes linked to microbial permeability barriers which results in reduced susceptibility [6] to multiple antibiotic classes. The perturbation of the permeability barrier is identified as a critical step in the development and emergence of higher levels of resistance [7].
The regulatory proteins, typified by the MarA protein, are unique, as unlike other members of the AraC family, these proteins bind DNA as monomers [8], interact with RNA polymerase via a process of pre-recruitment [9] and generally confer reduced antimicrobial susceptibility [10]. Microarray analyses has highlighted the wider effects of increased MarA [1], SoxS [2], RamA [4, 11] and RarA [5] levels in modulating gene expression particularly of those genes linked to virulence. This is further supported by studies reporting that either the inhibition or deletion of these regulators [12] can impair the ability of E. coli to colonise and cause infection in vivo [13]. Taken together, it is evident that these AraC proteins can confer bifunctional phenotypes of reduced drug susceptibility and increased virulence, which facilitate pathogen survival. These findings firstly, underscore the relative importance of these factors in microbial survival and secondly, provide a rationale for the development of “Anti-virulence-type” inhibitors against these transcription proteins.
The ramA gene which encodes the RamA protein is found in Klebsiella, Enterobacter [14], Salmonella [15] and Citrobacter spp [16] where the genetic organisation of the ram locus is conserved in most organisms, with the exception of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium (Fig. 1) which lacks romA, a putative metallo-beta-lactamase gene. The levels of both the romA-ramA genes are repressed at the transcriptional level by the TetR-type family regulator RamR, encoded by the ramR gene, which is divergently transcribed from the romA-ramA operon. In both Klebsiella and Salmonella, an increase in ramA expression can be mediated by inactivating mutations [16–18] or ligand mediated interactions [19] with the cognate repressor, RamR which binds to a highly conserved inverted repeat (atgagtgn6cactcat) [20] overlapping the promoter region of the romAramA operon (Fig. 1). Mutations within the ramR gene in K. pneumoniae resulting in ramA overexpression were initially reported as a result of tigecycline exposure [17, 21]. However, previous work evaluating clinical isolates that pre-date the use of tigecycline demonstrate that ramA overexpressing strains were already present within the nosocomial population of K. pneumoniae, suggesting a broader role for RamA mediated overexpression in antibiotic resistance [16]. Interestingly, studies evaluating the prevalence of ramA-mediated overexpression in clinical isolates of K. pneumoniae and Salmonella spp. indicate that these bacteria are more likely to overexpress ramA than marA or soxS, suggesting that elevated ramA levels may be more relevant to the development of antibiotic resistance in these organisms.
Fig. 1. Organisation of the ram locus in Klebsiella pneumoniae / Enterobacter spp. 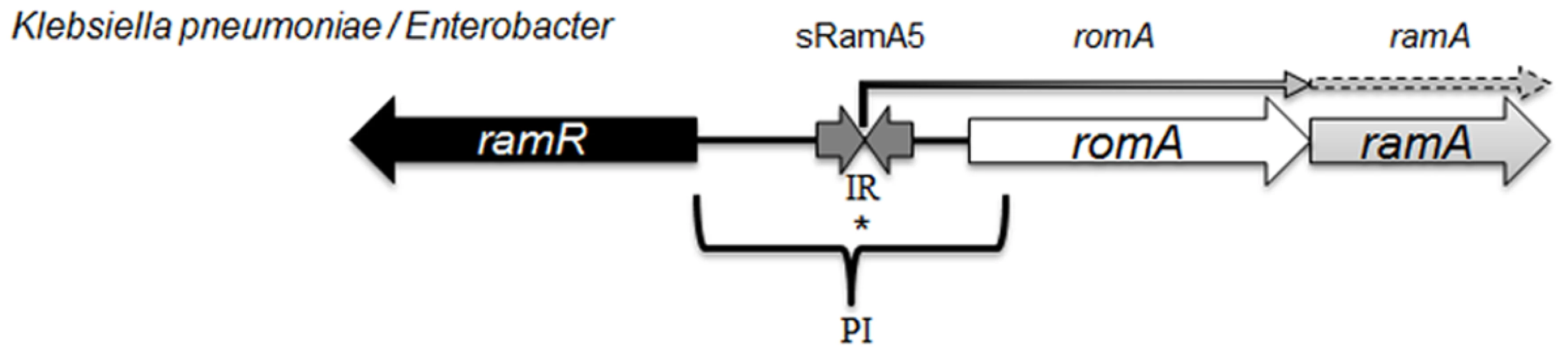
In K. pneumoniae romA and ramA are usually co-transcribed from the TSS depicted with *, under the control of the PI promoter. RamR can bind the inverted repeat (atgagtgn6cactcat), which in turn represses the transcription of both romA and ramA. Our analysis shows that the small regulatory RNA, sRamA5 and romA in Klebsiella pneumoniae share the TSS (depicted with *). Several studies [4, 11] have addressed the scope of the RamA regulon in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium using microarray profiling. These studies demonstrate that ramA overexpression results in reduced antimicrobial susceptibility due to the differential regulation of acrAB and micF genes, which consequently decrease OmpF levels. One study [4] suggests that genes linked to the Salmonella Pathogenicity Island (SPI-2) are also differentially expressed, leading to the initial observation that RamA may impact on Salmonella-specific virulence attributes. However this link was not corroborated in subsequent in vivo experiments. In K. pneumoniae, the wider impact of RamA-mediated regulation is not known. Despite the apparent similarities in genome structure, the microbial lifestyles of both K. pneumoniae [22] and Salmonella spp. differ. Importantly, the increasing multidrug resistance in Klebsiella spp. demands a thorough understanding of factors within this genus that contribute to the intrinsic microbial ‘resistome’ and survival under selective (host or drug) pressure. Therefore to define the broad effects of RamA-mediated expression on microbe-host and microbe-drug phenotypes we carried out transcriptome profiling using directional RNAseq with the wild type strain K. pneumoniae Ecl8 [23] and its isogenic derivatives Ecl8ΔramA and Ecl8ΔramR. Our key findings show the scope of RamA-mediated regulation significantly alters the transcriptional landscape of K. pneumoniae. This occurs by directly modulating the expression of different genes notably those associated with antimicrobial resistance and host-microbe interactions thereby resulting in the emergence of a less antibiotic susceptible and more virulent K. pneumoniae.
Results
Regulation of the ram Locus
The ram locus encodes a sRNA to maintain basal levels of ramA expression. RamR functions as the primary repressor of both romA-ramA expression in K. pneumoniae by binding the palindromic repeats of the IR element which flanks the TSS for romA at position -64T. ramR, itself, has two transcriptional start sites, located at the -83T and -167A positions where expression analyses using GFP fusions suggest that the primary promoter region for ramR transcription is located at the -83T start site (S1 and S2 Figs.). This site is also repressed 5-fold more than the vector only control by ramR in trans indicating that like other TetR-type regulators, RamR expression is autoregulated (S2 Fig.).
Previous work in Salmonella has shown that the regulatory RNA, StyR3, can control expression at the ram locus [24]. Given the expansive role of ramA in gene regulation, we sought to determine whether the K. pneumoniae ortholog of StyR3, denoted as sRamA5, would function as co-regulator of ramA expression in K. pneumoniae to promote basal ramA levels. The lack of similarity within the intergenic regions located between the ramR and romA-ramA genes or ramR and ramA genes in K. pneumoniae and Salmonella spp. respectively, excluded the possibility of using sequence analyses to identify the StyR3 ortholog. Direct northern blot analyses of RNA derived from K. pneumoniae strain Ecl8 and its derivatives did not produce a detectable signal for the putative regulatory RNA, sRamA5. Thus in order to demonstrate the presence of sRamA5, we cloned the entire intergenic region flanked by the ramR and romA genes and the partial romA open reading frame into the TA cloning vector pGEMTeasy to generate pGEMsRamA5. Northern blot analyses derived from the expression of sRamA5 encoded on pGEMsRamA5, using gene specific probes for sRamA5 and romA ORF, demonstrate the presence of sRamA5 (~ 60nt) (shown in Fig. 2A). Notably, the sRamA5 specific probe also detected a further two RNA molecules (Fig. 2A, arrowed bands 1 and 2). These fragments, detected by both the sRamA5 and romA specific probe, possibly represent primary transcripts initiated from the common start site as determined by 5’ RACE analyses for sRamA5 and romA (S1 Fig.). As expected the romA specific probe did not detect the 60nt sRamA5 molecule (Fig. 2A). Thus we surmise that sRamA5 and romA are co-transcribed into a primary RNA molecule, which undergoes further processing prior to excision proximal to the start of the romA gene, thereby producing sRamA5.
Fig. 2. A: Northern blot analysis of sRamA5. 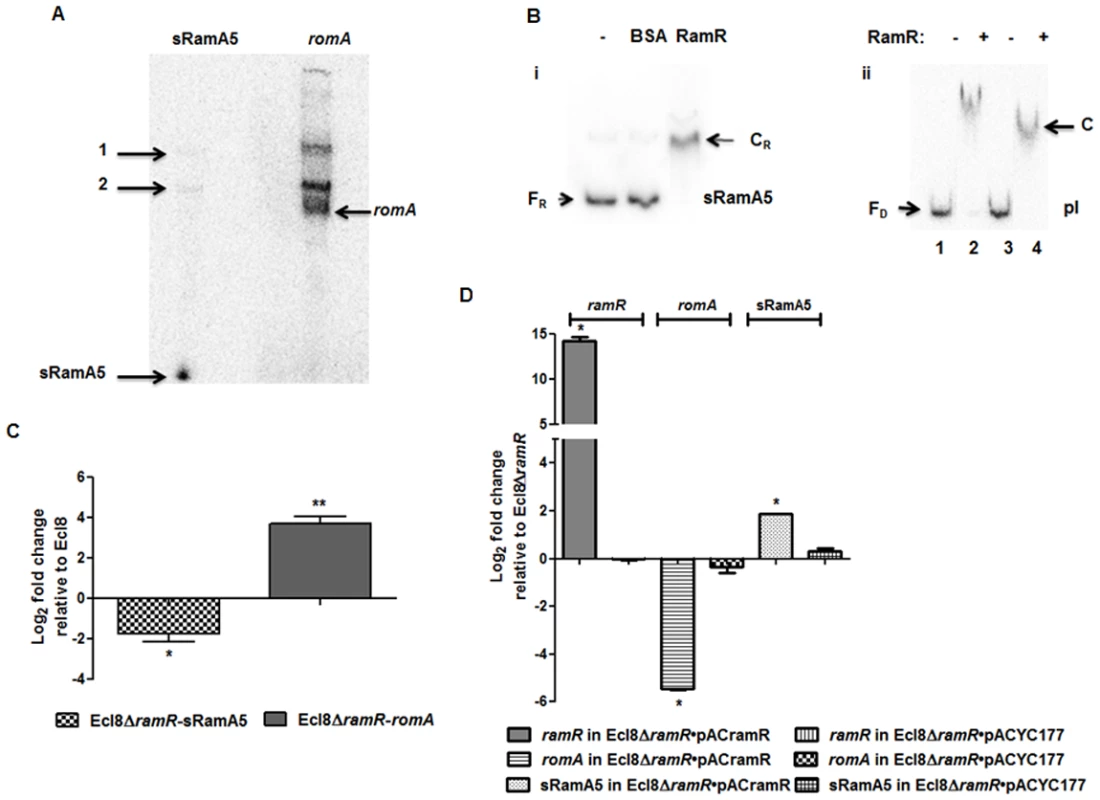
15 μg of total RNA extracted from Ecl8/pGEMTpI+romA were loaded into wells. The blots were either incubated with the 32P-end labelled sRamA5 specific DNA probe or romA specific DNA probe. The bands pointed as 1 and 2 are primary transcripts for both the RNA codes for sRamA5 and romA. The band referred to as sRamA5 is specifically detected by the sRamA5 DNA probe, sized at around 60 nucleotides; the band referred to as romA was specifically detected by the romA DNA probe. B: EMSA of RamR-sRamA5 or RamR-PI interaction in the presence of sRamA5. (i). RamR-sRamA5 interaction. The concentrations of sRamA5 and RamR were 40 nM and 1 μM respectively. (ii). RamR-pI interaction in the absence/presence of sRamA5. Radioactive labeled pI was 2 nM from lane 1 to 4. RamR’s concentrations from lane 1 to 4 were: 0, 2, 0, 2 μM. Cold sRamA5’s concentrations from lane 1 to 4 were: 0, 0, 1, 1 μM. FR = free RNA, CR = RNA-protein complex, FD = free DNA, C = RNA-DNA-protein complex. C: qPCR for the level of romA and sRamA5’s transcriptions in Ecl8ΔramR. qPCR using LNA probe for determining the levels of sRamA5 transcription in Ecl8 and Ecl8ΔramR. Despite sharing the same TSS, the transcript levels of sRamA5 are not linked to romA levels, thereby reducing the likelihood of sRamA5 being a 5’ untranslated region of romA. The log2 fold changes in Ecl8ΔramR displayed in the bar chart are relative to their transcript levels in Ecl8. One-way ANOVA analyses (P<0.001) were performed to demonstrate statistical significance. D: qPCR assay for the level of ramR, romA and sRamA5 in Ecl8ΔramR pACYCramR and Ecl8ΔramR pACYC177. The log2 fold changes in the two strains displayed in the bar chart are relative to their transcript levels in Ecl8ΔramR. sRamA5 levels are elevated in the presence of ramR, implying that RamR could stabilise the sRamA5 transcript. One-way ANOVA analyses (P<0.001) were performed to demonstrate statistical significance. As a classical TetR-family protein, RamR-mediated repression of the romA-ramA locus is likely to be perturbed through ligand-mediated interactions; therefore we hypothesized that to function as a co-regulator of romA-ramA expression RamR would interact with sRamA5. RNA-EMSA (S1 Text) analyses demonstrate that RamR and sRamA5 form a complex, suggesting direct interaction of the RNA (sRamA5) with RamR (Fig. 2B). In order to ascertain whether the interaction of sRamA5 and RamR is attributable to the presence of the highly conserved IR sequence in the ramR-romA inetrgenic region (ATGAGTGcgtactCACTCAT) and thus, act as a competitor for RamR-pI binding, we performed EMSA analyses using the pI promoter, sRamA5 and RamR. Our results show a reduction in affinity of RamR to sRamA5 in the presence of excess pI promoter (Fig. 2B). In contrast, competition experiments with excess sRamA5 show no perturbation of the pI+RamR interaction, suggesting that RamR has a higher affinity for the pI promoter compared to sRamA5 (Fig. 2B).
Simultaneous qPCR measurements utilizing an LNA probe to assess sRamA5 levels demonstrate firstly, that the transcription levels of sRamA5 and romA are not linked as sRamA5 levels are decreased in contrast to elevated romA levels (Fig. 2C). This suggests that despite being transcribed from the same TSS, sRamA5 and romA are likely subject to different rates of degradation. Secondly, the stability of sRamA5 may be dependent on the presence of a functional RamR. In order to investigate the requirement for a functional RamR in sRamA5 stability, we determined both the romA and sRamA5 levels in Ecl8ΔramR before and after complementation with ramR expressed in trans. As expected, our results show that the level of romA transcription was reduced (∼ 30-fold) in Ecl8ΔramR/pACramR compared to the plasmid only control (Ecl8ΔramR/pACYC177) (Fig. 2D). In contrast, the levels of sRamA5 were found upregulated by ∼ 2.8 fold in Ecl8ΔramR/pACramR relative to the plasmid only control (Ecl8ΔramR/pACYC177). Thus the increase in sRamA5 levels in the presence of a functional ramR supports our hypothesis that sRamA5 is stabilized by RamR. Our data also shows that sRamA5 does compete with pI for RamR binding, although this effect may be abrogated by the higher relative affinity of RamR to the pI promoter (Fig. 2B(ii)). Therefore, we surmise that the physiological relevance of RamR-sRamA5 interaction supports the basal level of ramA transcription detected in the wild type K. pneumoniae Ecl8.
Describing the Transcriptional Landscape of K. pneumoniae Ecl8 and Its Isogenic Derivatives Ecl8ΔramA, Ecl8ΔramR
To determine the effect of altered RamA levels on the whole transcriptome of K. pneumoniae strain Ecl8, we quantitatively compared the transcriptomes of the three strains (Ecl8, Ecl8ΔramA, Ecl8ΔramR) using the Kolmogorov-Smirnov (K-S) 2-sample test (S3 Fig.) as described in the supplementary data [25]. As expected, the distribution curve of Ecl8 and Ecl8ΔramA were more similar to each other compared to that observed for Ecl8ΔramR, suggesting that under normal growth conditions the deletion of ramA is less likely to perturb the transcriptional landscape as opposed to when it is overexpressed. This supports the notion that ramA functions as a pleiotropic regulator of gene expression in K. pneumoniae.
In all three strains, the 16S and 23S rRNA genes showed the highest number of mapped reads consistent with the lack of depletion for ribosomal RNA. However, pairwise comparisons of the normalized basemean values associated with these ribosomal regions were not differentially expressed between Ecl8 and Ecl8ΔramR or Ecl8 and Ecl8ΔramA. The lack of differential ribosomal gene expression is contrary to previous observations in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium [4]. Other non-ribosomal genes (e.g. fusA_1 (encoding translation elongation factor G), atpA (producing ATP synthase F1, α subunit) and aceE (encoding a pyruvate dehydrogenase)) were also found to have significantly high basemean values relative to most other genes within the genome. The increased expression of these genes is perhaps not surprising as atpA is associated with aerobic growth and aceE catalyses the production of precursors to the TCA cycle.
Potential regions of antisense transcription were also detected. However, in most cases, these regions appeared as antisense because of in silico errors in annotation or due to transcriptional noise from flanking genes within the chromosome. We did, however, identify antisense transcription, such as with BN373_16241 (producing an oxidoreductase) and BN373_02611, which were differentially expressed due to either elevated RamA levels or loss of the ramA gene (S4 Fig.). Coverage plots analyses indicate that the transcription associated with BN373_02611 may be associated with 3’UTR runoff transcription from the divergently transcribed treBC operon, in contrast to BN373_16241, which is upregulated when ramA was overexpressed and may be a “true” antisense RNA (S4 Fig.).
Genome analyses of K. pneumoniae strain Ecl8 [23] identified 11 unique predicted prophage genes encoding phage structural components (BN373_03311, BN373_09871, BN373_10091, BN373_14801, BN373_14811, BN373_14821, BN373_14841, BN373_14921, BN373_21511, BN373_37361, BN373_37371) which were not found to be differentially transcribed in the pairwise comparisons tested (Ecl8 vs Ecl8∆ramA, Ecl8 vs Ecl8∆ramR (S1 Table). However, pairwise comparisons of Ecl8ΔramA and Ecl8ΔramR detected the differential expression of Ecl8-genome specific genes, BN373_33401, BN373_33411, which were repressed (∼2–3 fold) in the ramA overexpressing strain Ecl8ΔramR (S2 Table). Of note, no differential gene expression was noted in the 233 plasmid-coding genes in the ramA null mutant or in the ramA overexpressor (Ecl8ΔramR) with respect to the wild type (Ecl8).
Defining the RamA Regulon
Transcriptome analyses underscores that perturbations in RamA levels can result in the differential expression of open reading frames, antisense transcripts and Ecl8-specific genes. As the majority of reads were mapped to open reading frames, the main focus of our analyses relates to the differential regulation of genes within K. pneumoniae. The RamA regulon in K. pneumoniae was identified by pairwise comparisons of Ecl8∆ramR versus Ecl8 (C) or Ecl8∆ramA (B). The pairwise comparisons of Ecl8 versus Ecl8∆ramA (A)(Fig. 3) indicate the cohort of genes (13) responsive to basal levels of RamA expression; the contrast between Ecl8 versus Ecl8∆ramR (35) specifies genes that are either affected by RamR or RamA, whereas the comparison between Ecl8∆ramR versus Ecl8∆ramA (77) identifies genes that largely react to altered RamA levels. As fewer genes are affected due to perturbations in ramR expression as opposed to RamA levels, we surmise that the majority of genes differentially expressed in our pairwise comparison (B) are associated with RamA-mediated regulation. Based on this assessment, the probable RamA regulon, Fig. 3, constitutes a total of 103 genes (as in genes in categories A, B, AB, BC, CA, ABC) (S2 Table). Of these, 68 genes were found to be activated and 35 were repressed (S2 Table) when levels of RamA is relatively higher.
Fig. 3. Venn diagram representing the RNA sequencing results. 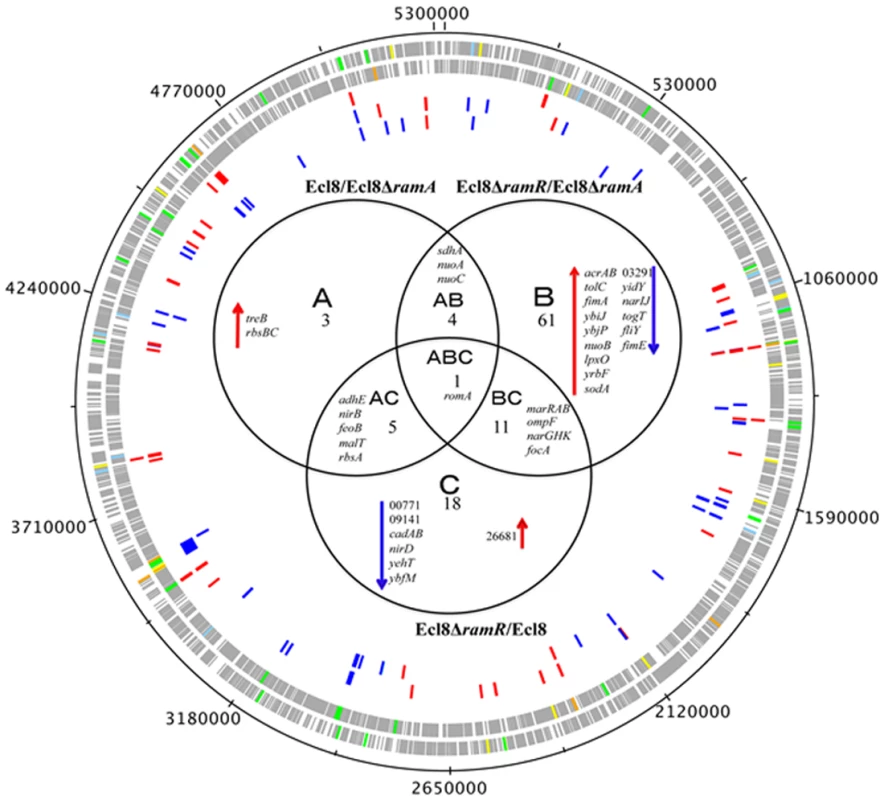
Ecl8ΔramA or Ecl8ΔramR were used as calibrators in the pairwise comparisons. The arrows ⬇ indicates a lower than 0.5 fold decrease in transcription compared to calibrator; ⬆ indicates a higher than 2 fold transcription compared to calibrator. The numbers beneath A, B and C indicate the number of transcripts showing higher or lower transcription (based on statistical cut-off) compared to calibrator. The genes under the different categories A, B and C represent pairwise comparisons between Ecl8/Ecl8ΔramA, Ecl8ΔramR/Ecl8ΔramA and Ecl8/Ecl8ΔramR comparison respectively; the genes in Area AB were found to be differentially transcribed in both the Ecl8/Ecl8ΔramA and the Ecl8ΔramR/Ecl8ΔramA comparisons; the genes in Area AC were found to be differentially transcribed in both the Ecl8/Ecl8ΔramA and the Ecl8/Ecl8ΔramR comparisons; the genes found in the area BC were found to be differentially transcribed in both the Ecl8/Ecl8ΔramR and Ecl8ΔramR/Ecl8ΔramA comparisons. The romA gene in Area ABC was found to be differentially transcribed in all the three comparisons. Genes associated with RamA-mediated regulation were initially mapped to the COG (clusters of orthologous groups) database to explore their biological function. COG functional classifications of the significantly differentially expressed genes reveal that RamA controls a myriad of cellular and metabolic processes (COG data presented in S2 Table). Generally, altered levels of RamA significantly modulate the expression of genes belonging to the COG functional group C (energy production and conversion). Specifically, when ramA is deleted, genes within the COG (G) (carbohydrate metabolism and transport) were also found to be differentially regulated. Pairwise comparison between Ecl8ΔramR versus Ecl8 indicates that COG families associated with transcription (K) and inorganic ion transport and metabolism (P) were also affected. Additionally, when ramA levels are elevated genes associated with cell wall membrane and envelope biogenesis (M), transcription (K) and Function UnknowN (FUN) categories were most differentially affected. Thus the resulting COG analyses also supports the observation where altered levels of RamA triggers a shift in gene functionality consistent with significant modulations in transcription patterns as predicted by the K-S test (S3 Fig.).
A closer analyses of the genes associated with pairwise comparisons of Ecl8ΔramA versus Ecl8ΔramR reveals that firstly, the highest number of genes (77) are differentially expressed and secondly genes (yhbW, nfnB, acrAB, ybhT, yrbB-F) associated with the previously characterized networks for MarA [1], SoxS [26] or Rob [3] in E. coli or RamA in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium [4, 11] are also affected. This is consistent with previous observations that demonstrate that these proteins exhibit considerable gene overlap within the regulons [1, 4, 11]. Importantly, RamA overexpression results in the modulation of efflux pump genes such as acrAB, oqxAB and yrbB-F, which is consistent with phenotypes linked to multidrug resistance [27] and susceptibility to toxic small molecules, which is associated with alterations in the lipid symmetry of the cell wall [28]. However, the pairwise comparisons for Ecl8 and Ecl8ΔramA also suggest that basal levels of RamA are sufficient to trigger the upregulation of genes such as the trehalose transporter operon treBC and the ribose ABC transporter, rbsACB. Uniquely, genes associated with biofilm formation (hha-ybaJ encodes a toxin-antitoxin system) and lipid A biosynthesis BN373_10601 (encodes lipid A biosynthesis lauroyl acyltransferase, lpxL_2) and the related dioxygenase protein encoding gene lpxO (BN373_36331) were also found to be upregulated by RamA.
A total of 51 genes were found to be downregulated. As expected, ompF was significantly repressed in the ramA overexpresser (Ecl8∆ramR) (Fig. 3) in addition to genes encoding the nitrate reductases (narGHJI operon and nirD), BN373_05601 encoding the LysR-type transcriptional regulator, elongation factor EF2 and the riboflavin synthase encoding gene ribH were also found to be significantly downregulated in the ramA overexpresser (Ecl8∆ramR).
Only a subset of those differentially regulated genes was chosen for validation using qPCR. As expected, both the romA and ramA genes were found to show 5.25-log2 fold and 14.5 - log2 fold increase in Ecl8∆ramR respectively compared to Ecl8∆ramA (S5A Fig.). When the activated genes (with the exception of romA, ramA) were assessed, increased expression of the following genes was noted (Fig. 4A): tolC (4.8 - log2 fold), acrA (4.6 - log2 fold), yhbW (1.8 - log2 fold), yrbC (2.8 - log2 fold), nfnB (3.3 - log2 fold), ybjP (3.95 - log2 fold), adhP (3.2 - log2 fold), BN373_36191 (encodes putative membrane protein, 2.95 - log2 fold), BN373_39031 (encodes oxidoreductase, aldo/keto reductase family, 1.5 - log2 fold), lpxO (2.8 - log2 fold) and lpxL-2 (3.6 - log2 fold). As expected, the levels of the ompF (4.2 - log2 fold down) and BN373_03291 (encodes conserved hypothetical protein, 1.1 - log2 fold down) were also downregulated (Fig. 4A).
Fig. 4. A: Quantitative real-time RT-PCR validation of differentially expressed genes in Ecl8∆ramR. 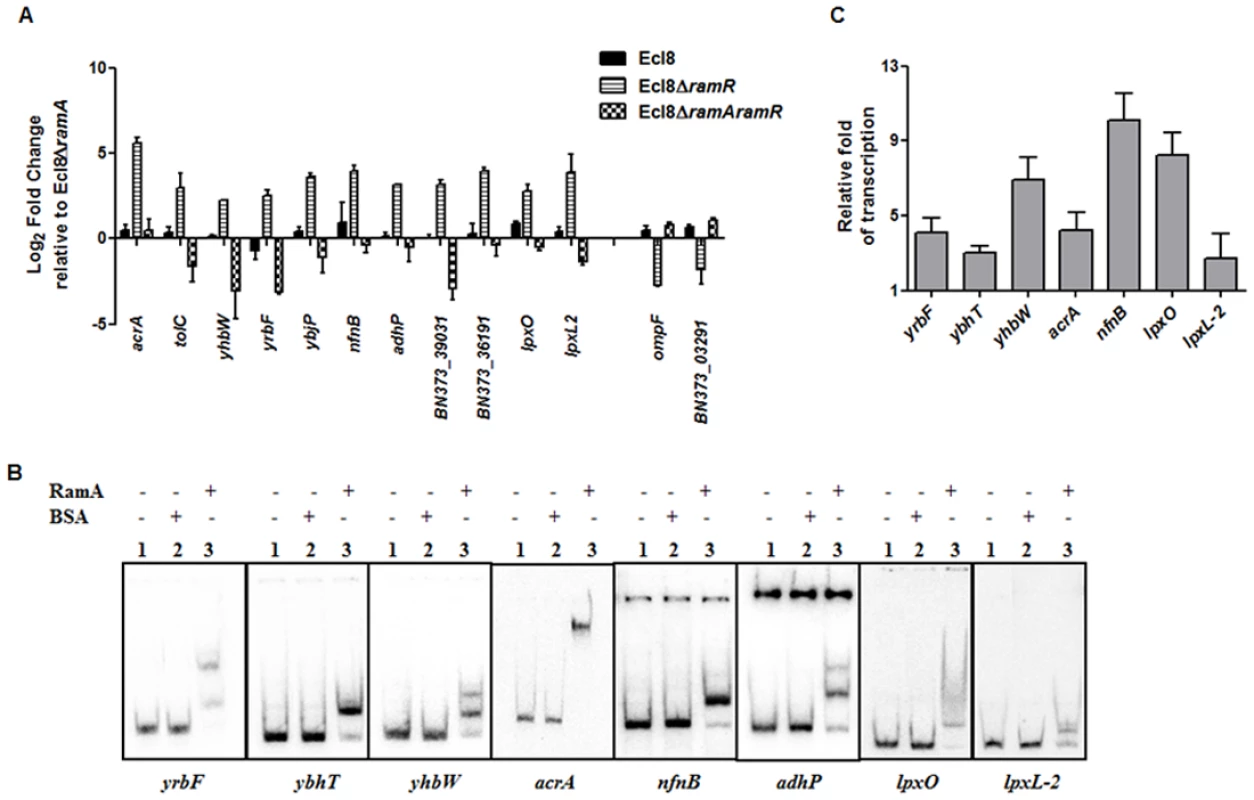
All qPCR experiments were performed as outlined in materials and methods. Expression levels were normalized to 16S levels, and fold change values were generated by calibrating against Ecl8∆ramA. Genes designated BN373_36191, BN373_39031, BN373_03291 encode a putative membrane protein, oxidoreductase family and conserved hypothetical protein respectively. All data is a mean of 3 experiments. B: Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay (EMSA) using purified RamA protein. Following PCR amplification, each promoter region was end-labelled with 32P-γ ATP. Purified RamA (200 nM) and the different labelled DNA probes (2 nM) were incubated on ice. All reactions were performed on ice prior to electrophoresis on 7.5% native gel. Lane 1 of each panel indicates the labelled DNA probe only, Lane 2 is the BSA control and Lane 3 contains RamA+DNA. C: Transcription in vitro assay of different promoters using the purified RamA protein. The test DNA (2 nM- yrbF, ybhT, yhbW, acrA, nfnB, lpxO and lpxC) with the control template (gnd) were incubated for transcription in vitro [32P]α-UTP with (+) or without (-) 200 nM purified RamA. Samples were fractionated by polyacrylamide/urea gel electrophoresis prior to drying and exposure to the phosphorimager. Relative fold increase was determined using densitometric analysis as described previously [55], by first normalizing all test transcription levels to the control promoter (gnd) prior to comparison to the no protein control. Statistics was done using One way ANOVA (P value < 0.05) where transcription levels were found to be statistically significant in the presence of purified RamA compared to the no protein control. Direct Regulation by RamA
In order to determine if some of these differentially expressed genes were under the direct or indirect control of RamA, we performed both EMSA and in vitro transcription (IVT) using purified recombinant RamA protein. The EMSA results show that RamA directly binds the yrbF, ybhT, yhbW, acrA, nfnB, adhP, lpxO and lpxL-2 promoters (Fig. 4B). Of note, our controls, showed no shift in the presence of the test promoters (Fig. 4B).
We then determined whether RamA would directly regulate the different promoters identified. By performing IVT experiments, we initially tested the effects of the RamA protein against the acrAB promoter to ascertain if RamA would function correctly as a transcriptional activator. As expected, the purified recombinant RamA activated the acrAB promoter directly (Fig. 4C) thereby confirming the biological activity of the purified RamA protein. Subsequently, we assessed the test promoters identified by the EMSA in our IVT assays. The results show that RamA upregulates yrbF (4-fold), ybhT (3-fold), yhbW (6.9-fold), acrA (4-fold), nfnB (10-fold), lpxO (8-fold) and lpxL-2 (∼3-fold) (Fig. 4C). Thus purified recombinant RamA alone can directly activate the expression of these promoters in vitro.
Functional Relevance of RamA-Mediated Overexpression
RamA regulates genes involved in lipid A biosynthesis. Having established that purified RamA directly binds and activates the expression of lpxL-2 and lpxO gene promoters (Fig. 4B and 4C), we sought to determine whether RamA could regulate other genes associated with the lipid A biosynthetic pathway. The lipid A biosynthetic pathway is governed by nine enzymes encoded by lpxA, lpxC, lpxD, lpxB, lpxK, lpxl, lpxM and lpxO genes [29]. Gene expression analyses using qPCR showed that with the exception of lpxC, none of the other lpx genes showed significant differential expression in Ecl8ΔramR in comparison to Ecl8 or Ecl8ΔramA (Fig. 5A). We then chose to assess whether RamA would directly interact with the lpxC and lpxK promoter regions. Subsequent EMSA analyses demonstrate that RamA directly interacts with the lpxC but not the lpxK promoter (Fig. 5Bi) and increased lpxC transcription (9-fold) in the presence of purified RamA and RNA polymerase (Fig. 5Bii). Previous work has shown that the control of lipid A biosynthetic genes is mediated by the PhoPQ or PmrAB systems [30]. Further interrogation of the transcriptome data and subsequent qPCR analyses shows that the levels for phoP and pmrA levels remained unchanged in K. pnuemoniae Ecl8, Ecl8ΔramA and Ecl8ΔramR. Thus the differential modulation of the lpxO, lpxC and lpxL-2 genes is directly linked to increased RamA levels.
Fig. 5. A. Gene Expression analyses of lpx genes. 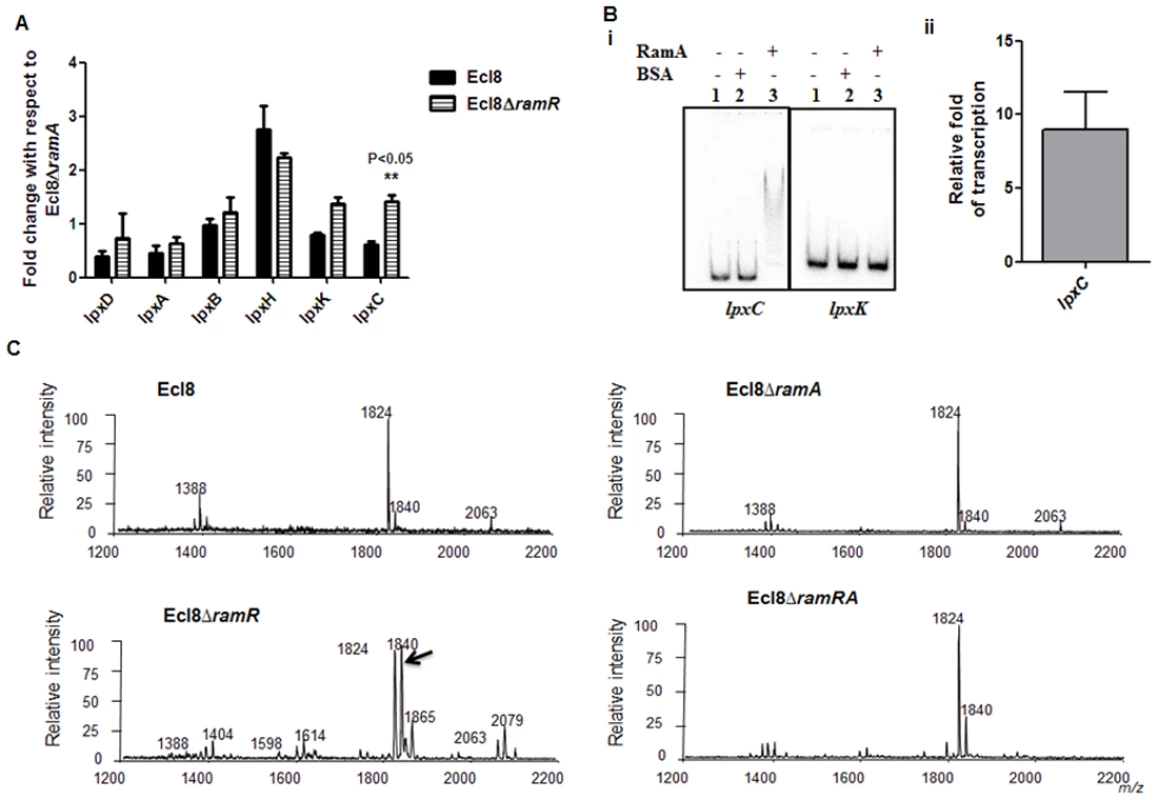
All qPCR experiments were performed as outlined in materials and methods. Expression levels were normalized to 16S levels, and fold change values were generated by calibrating against Ecl8∆ramA. Two-way ANOVA analyses (P<0.05) were performed to demonstrate statistical significance. B. Regulation of lpx genes. (i) EMSA using lpxC and lpxK promoter regions. Purified RamA (200nM) and the different labelled DNA probes (2 nM) were incubated on ice. All reactions were performed on ice prior to electrophoresis on 7.5% native gel. (ii) Transcription in vitro of lpxC promoter region. Relative fold increase was determined using densitometric analysis as described previously [55]. Fold increases in the presence of RamA were determined by first normalising to the control promoter (gnd) prior to comparison to the no protein control. C: Lipid A analysis from K. pneumoniae Ecl8 (WT), Ecl8ΔramA, Ecl8ΔramR and Ecl8ΔramRA. Lipid A analysis was undertaken as described before [31]. Negative ion MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry of lipid A isolated from K. pneumoniae Ecl8 and its derivatives. Peaks in bold correspond to LpxO dependent 2’ secondary chain modifications. To ascertain whether RamA-mediated transcriptional activation of lpxC, lpxL-2 and lpxO would actually result in modifications within the lipid A moiety, we performed MALDI TOF mass spectrometry (S1 Text for details). The mass spectrometry analyses confirm alterations in lipid A structure of the ramA overexpresser, Ecl8ΔramR compared to the wild type (Ecl8), the null mutant (Ecl8ΔramA) or the double mutant (Ecl8ΔramRA) (Fig. 5C) where peaks (m/z 1840, 1866 and 2079) were found to be elevated. Previous studies in K. pneumoniae [31, 32] indicate that those peaks correspond to LpxO hydroxylated lipid A species containing a hydroxymyristate group at position 2’ as secondary acyl substitution. Therefore, we surmise that RamA mediated activation of the different lipid A biosynthetic genes leads to alterations within the lipid A moiety in K. pneumoniae.
Antibiotic Susceptibility
Phenotype microarray analyses. In order to assign phenotypes linked to the differentially regulated genes, Biolog phenotype assays were undertaken for K. pneumoniae Ecl8 and its isogenic derivatives Ecl8ΔramA and Ecl8ΔramR. A comparison of Biolog phenotypic profiles of both Salmonella [11] and K. pneumoniae generally indicates a significant overlap in the susceptibilities to antimicrobial and toxic compounds (S3 Table). As expected, the overexpression of ramA resulted in increased tolerance of Ecl8ΔramR in the presence of antimicrobials such as tetracyclines (doxycycline, chlortetracycline, minocycline), macrolides (erythromycin, spiramycin, troleandomycin), beta-lactams (1st, 2nd, 3rd generation cephalosporins, penams) and (fluoro)quinolones (ciprofloxacin, ofloxacin, nalidixic acid, novobiocin), fungicides (such as chloroxylenol, dodine, domiphen bromide) and toxic anions (potassium tellurite, sodium metasilicate) (S3 Table, S6 Fig.). Notably, comparisons of the Biolog data also indicate that ramA overexpression results in altered polymyxin B susceptibility levels in both K. pneumoniae and Salmonella.
Susceptibilities to the Polymyxins and the Cationic Antimicrobial Peptides (cAMPs)
Lipid A synthesis in Gram-negative bacteria is controlled at both the transcriptional and translational levels, where alterations in the lipid A profile can result in perturbations in host-microbe interactions as well as reductions in susceptibility to both the polymyxins and the cationic antimicrobial peptides (cAMPs) [33]. Accordingly, we tested the strain Ecl8 and its isogenic derivatives Ecl8ΔramA, Ecl8ΔramR against colistin, polymyxin B and the cAMP LL-37. The relative survival assays for colistin, polymyxin B and LL-37 demonstrated that the ramA overexpressing strain, Ecl8ΔramR strain was significantly (P < 0.05) less susceptible to polymyxin B, colistin and LL-37 (Fig. 6 A, B, C) compared to the wild type Ecl8 and the null mutant Ecl8ΔramA. The reduction in polymyxin susceptibility, as noted in the survival assays, is also supported by the Biolog data (S3 Table). Taken together these results suggest that RamA-dependent regulation provides an alternative pathway for reduced susceptibility to polymyxins and cAMPs.
Fig. 6. Survival assay of K. pneumoniae (Ecl8, Ecl8∆ramA, Ecl8∆ramR, Ecl8∆ramRA) to polymyxin B, colistin and the antimicrobial peptide LL-37. 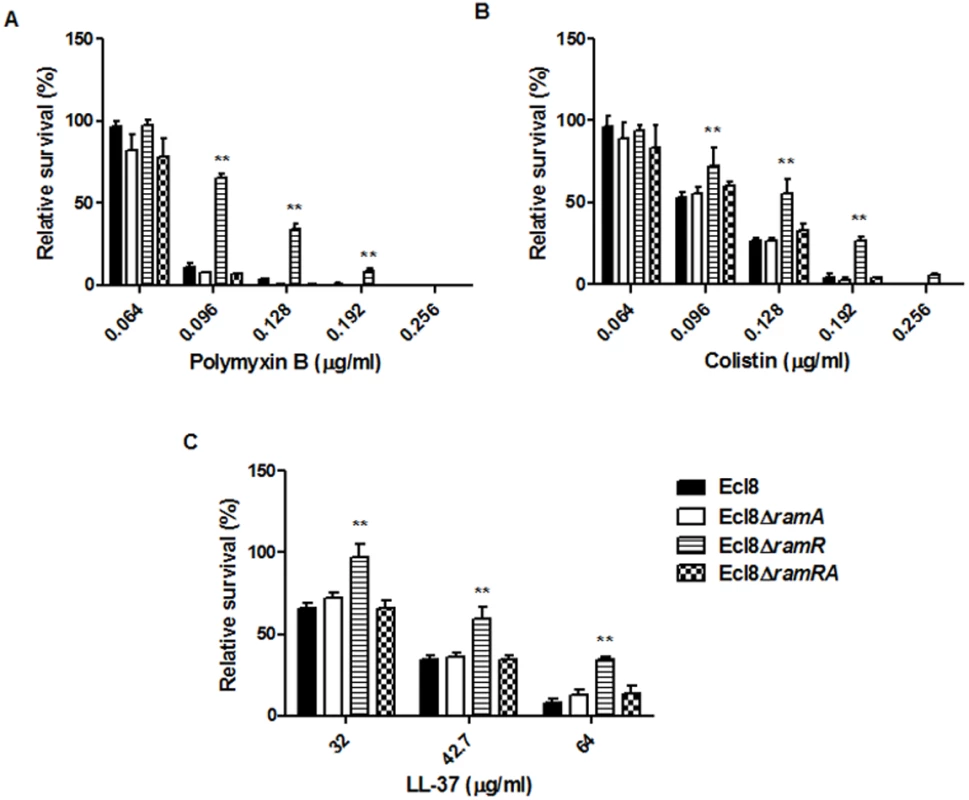
The relative survival of bacteria (expressed as a percentage of the number of colonies obtained from the unexposed control of the same strain) in the presence of different concentrations of polymyxin B (A), colistin (B) and LL-37 (C) are shown. Asterisks indicate that results obtained for the ramA expresser, Ecl8ΔramR is significantly different (P < 0.05 by Two-way ANOVA) compared to Ecl8, Ecl8ΔramA and Ecl8∆ramRA. Effect of RamA Overexpression on Host-Microbe Interactions
Macrophage-Klebsiella interaction. To ascertain whether RamA-mediated alterations can have an impact on microbe-macrophage interactions, we examined if Ecl8 and its isogenic derivatives, Ecl8ΔramR, Ecl8ΔramA and Ecl8ΔramRA would exhibit differential interactions in adherence and intracellularization into murine RAW macrophages. In the adhesion and intracellularization assays, the ramA overexpresser, Ecl8ΔramR, was significantly attenuated in its ability (approximately 50% decrease) to attach to and internalise into the RAW murine macrophage cells compared to wild type K. pneumoniae Ecl8, the mutants Ecl8ΔramA and Ecl8ΔramRA (Figs. 7A, B and C). Two possible explanations exist for the reduction in adherence and intracellularization of Ecl8ΔramR; the first, where altered RamA levels confers resistance to phagocytosis and the second, is due to accelerated killing by the macrophage. In order to ascertain whether the reduced intracellularization of Ecl8ΔramR was linked to accelerated killing by macrophages, we determined the levels of extracellular non-phagocytosed bacteria in our experiments and found significantly higher numbers of recovered bacteria for Ecl8ΔramR compared to the wild type Ecl8, Ecl8ΔramA and Ecl8ΔramRA (Fig. 7D). In previous work [34], resistance to phagocytosis by K. pneumoniae has been linked to bacterial surface structures which include the capsular polysaccharide (cps). However, ugd gene transcription, representative of the cps cluster [35], was not found to be altered in Ecl8, Ecl8ΔramA, Ecl8ΔramR and Ecl8ΔramRA (S5B Fig.), consistent with the RNAseq data. Thus our results underscore that reduced phagocyte adhesion and uptake is linked to RamA-mediated alterations, particularly those associated with lipid A.
Fig. 7. A: Attachment of K. pneumoniae Ecl8, Ecl8ΔramA, Ecl8ΔramR or Ecl8∆ramRA to murine macrophage RAW 264.7 cell line. 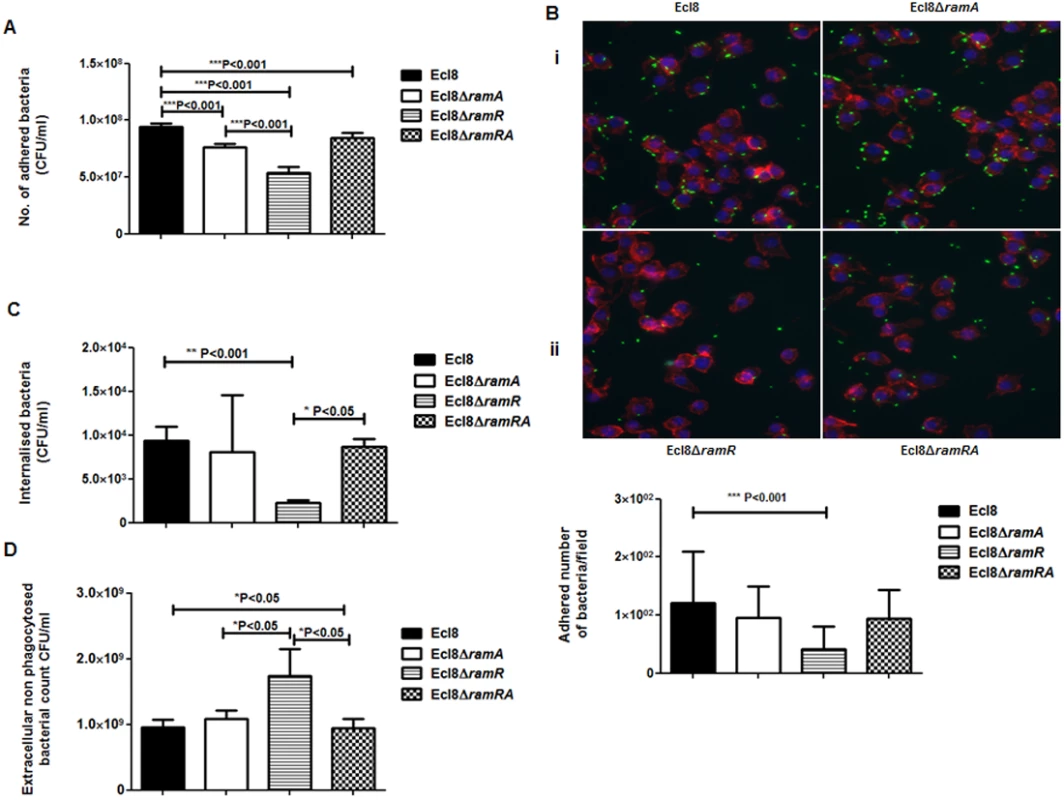
One-way ANOVA analyses were performed to demonstrate statistical significance. B: Microscopy to assess attachment to RAW 264.7 cell line. (i) Infection of the RAW264.7 cell line was carried out with K. pneumoniae Ecl8 (WT), Ecl8ΔramA, Ecl8∆ramR or Ecl8ΔramRA transformed with plasmid pRSMgfp. MOI was 1:100 and infections were carried out for 2 hrs. The actin cytoskeleton was stained with Acti stain 555 phalloidin (red) and host cell nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). Images are representative of 80 fields. (ii) Graph representating mean values are derived from 3 independent experiments. One-way ANOVA analyses (P<0.001) were performed to demonstrate statistical significance. C: Internalisation of K. pneumoniae Ecl8, Ecl8ΔramA, Ecl8ΔramR or Ecl8∆ramRA by RAW 264.7 cells. Bacterial internalisation was assessed by the gentamicin protection assay. One-way ANOVA analyses were performed to demonstrate statistical significance. D: Enumeration of the extracellular non-phagocytosed K. pneumoniae Ecl8, Ecl8ΔramA, Ecl8ΔramR or Ecl8∆ramRA. One-way ANOVA analyses were performed to demonstrate statistical significance. Infection In Vivo
In order to assign a broader relevance to altered Klebsiella-host interaction, we performed experiments to assess bacterial recovery using the intranasal inoculation method [36] as described previously. Following a 24-hour infection of 5–7 week old C57BL mice, organ homogenates (spleen and lung) were plated to determine bacterial counts. At 24 h post infection, bacterial recovery rates for the ramA overexpressor, Ecl8ΔramR were found to be significantly higher compared to the wild type Ecl8 or null mutant Ecl8ΔramA from the lung and spleen (Fig. 8(A) and 8(B)). The intranasal route of infection is expected to result in the primary infection of the lung prior to dissemination to other organs. Our results demonstrate that significantly higher levels of Ecl8ΔramR is recovered from both the lung and spleen highlighting that RamR-dependent RamA overexpression, confers reduced microbial clearance and increased systemic dissemination of K. pneumoniae in an intranasal infection model.
Fig. 8. Effect of RamA on bacterial recovery using an intranasal infection model. 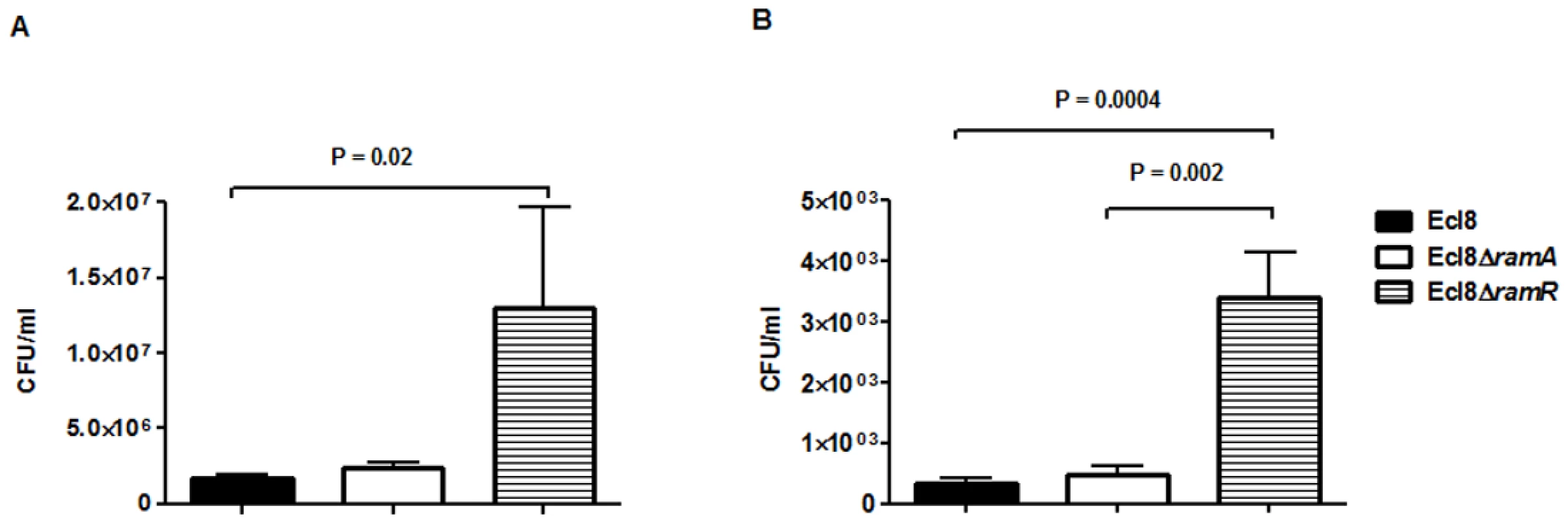
Bacterial recovery (cfu/ml) was determined from lung (A) and spleen (B) homogenates following a 24h infection of 5–7 week old, C57BL6, female mice (n = 5) using the previously described intranasal infection model. Unpaired t-test analyses were performed to demonstrate statistical significance. Discussion
The relevance of the MarA, SoxS, Rob, RamA and RarA regulators in microbial survival is attributed to their control of the antimicrobial resistance phenotype in a wide variety of Gram-negative bacteria [10, 37, 38]. Whilst the role of RamA in reduced antibiotic susceptibility is evident from multiple studies [16, 17, 37], its broader role in gene regulation is not known in Klebsiella pneumoniae. Using transcriptome profiling, we demonstrate that RamA-overexpression results in altered K. pneumoniae transcription patterns (S3 Fig.) compared to the null mutant or wild type strain thus highlighting its wider role in gene regulation in K. pneumoniae.
Our data suggests that RamA functions largely as a transcriptional activator of gene expression, where DNA-binding (Fig. 4B) and IVT assays (Fig. 4C) demonstrate that this regulation is direct and likely mediated via a mar/ram-box like element [39] located within the promoter region. Whilst our work is the first to demonstrate direct RamA-mediated activation of gene expression, other studies have shown that related proteins such as MarA, SoxS [40] and RarA [5] also exert explicit control of regulon genes. Comparative transcriptome data analyses suggests that RamA-mediated activation is dependent on regulator concentration (basal versus overexpressed, Fig. 2) in addition to the observation that identical RamA levels induce differential levels of promoter activation as supported by our in vitro data (Fig. 4C). The maintenance of basal ramA levels may be necessary for the K. pneumoniae stress response to a variety of agents as has been previously shown when selecting for fluoroquinolone resistant Salmonella [41] or Klebsiella in a ramA-deleted strain. In K. pneumoniae, basal levels of ramA expression is maintained due to titration of the absolute repressory effects of RamR by the RamR-sRamA5 interaction (S2 Fig.). Uniquely for tetracycline family regulators, RamR, directly interacts with the regulatory RNA, sRamA5, (Fig. 2B) which is produced as a cleaved by-product of the primary romA transcript (Fig. 2B). Whilst the sRamA5-RamR interaction, provides basal levels of ramA expression, ramA transcription as observed in the overexpressor, Ecl8ΔramR or clinical strains [16] are linked to loss of function mutations within RamR. Consequently, our data show that the maximal changes in gene expression profiles are observed when ramA is overexpressed as in Ecl8ΔramR (S3 Fig.). In this gene cohort, we demonstrate that RamA impacts on gene transcription linked to operons associated with efflux pumps, biofilm formation and lipid A biosynthesis (Fig. 3, S2 Table). Whilst it is possible that the differential regulation of these genes is not all directly linked to RamA, we demonstrate that purified RamA directly binds and activates the expression of multiple associated promoters (Fig. 4C & 4D).
A comparison of RamA-mediated regulation in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium [4] and K. pneumoniae establishes key similarities in the genes associated with the respective RamA regulons; particularly in the control of genes associated with antimicrobial resistance acrAB and ompF [4, 11]. Additionally, RamA-dependent direct activation of acrAB is also consistent with phenotypic studies [10, 16–18] which consistently demonstrate that ramA overexpression is linked to increased elevated efflux via acrAB and decreased outer membrane protein levels (OmpF). Given its role in conferring reduced antimicrobial susceptibility, it is perhaps not surprising that we demonstrate that RamA directly regulates other efflux related operons specifically; the AcrAB linked inner periplasmic protein, YbhT [42] associated with detergent sensitivity, the Yrb operon which encodes an ABC transporter linked to the export of quinolones [27] and also lipid asymmetry [30]. The combined effect of the efflux or influx levels and membrane alterations associated with transport and structural variations likely contributes to the substrate range of compounds impacted by ramA overexpression (S3 Table). However, in the absence of a functional acrAB efflux pump, RamA-overexpression does not confer reduced susceptibility to most antibiotics in K. pneumoniae. This observation is consistent with previous studies for the MarA and RarA [38] proteins.
Therefore, it is likely that a functional AcrAB pump is crucial in mediating decreased antimicrobial susceptibility. However, a recent study [43] also suggests that acrAB may play a role in decreased antimicrobial peptide susceptibility and increased virulence in K. pneumoniae. Our findings support this observation and further demonstrate that increased RamA levels can also mediate LPS alterations, which likely contribute towards increased survival to both polymyxins and cationic AMPs (Fig. 5, 6).
Structurally, LPS is composed of three domains, the serovar dependent O-antigen chain, core oligosaccharide consisting of sugars and lipid A which is a phosphorylated disaccharide decorated with multiple fatty acids which anchor the LPS into the bacterial membrane [29]. The endotoxic lipid A component of LPS constitutes the outermost layer of the outer membrane of Gram-negative bacteria thereby playing a critical role in host-microbe interactions in addition to promoting reduced susceptibility to cAMPs [44] such as polymyxins [30] and host derived factors LL-37, HBD-1 [30]. Studies have shown that lipid A modifications can result in multiple outcomes such as reduced polymyxin susceptibility [45] in addition to directly facilitating microbial evasion by reduced immune recognition [46]. Our work suggests that the molecular basis for the modified lipid A structure is linked to the differential regulation of the biosynthesis genes e.g. lpxO, lpxL-2 and lpxC identified in this screen. Despite being constitutively produced the regulation of lpxC, lpxL-2 and lpxO, is still subject to either transcriptional or translational control [44, 46]; generally in response to stress, where, lpxC and lpxL-2 are regulated by the two-component systems, PhoPQ and PmrAB [44]. In contrast, lpxO is not subject to PhoPQ regulation in Salmonella [44, 46].
In Salmonella Typhimurium, the modulation of LpxO levels results in the remodeling of the outer membrane which reduces the net negative charge whilst simultaneously increasing membrane integrity resulting in increased virulence [47]. A similar phenotype is exhibited by the K. pneumoniae Ecl8ΔramR strain, which has altered LpxO levels (Fig. 8). Thus we surmise that the altered host-microbe and polymyxin-microbe interactions are in part attributable to the lipid A modifications.
Macrophages represent a key innate host defence strategy against microbial infections as phagocytosis of incoming pathogens is a trigger for the inflammatory response. Our data show that ramA overexpression protects against macrophage uptake and internalization (Fig. 7) thus providing a basis for the greater dissemination of the ramA overexpressing strain, Ecl8ΔramR in an in vivo infection model. Taken together, these RamA-linked phenotypes underscore its’ role in Klebsiella virulence and survival in vivo.
The molecular basis for phenotypes associated with reduced antimicrobial peptide susceptibility and increased virulence can be attributed to several key loci such as the acrAB pump and lipid A biosynthesis genes, lpxC, lpxL-2 and lpxO. This is supported by studies that demonstrate the involvement of acrAB [48] and lipid A modifications [30, 44] in host-microbe interactions. However to definitively pinpoint the exact contribution of the lipid A biosynthetic genes or acrAB to phenotypes associated with host-pathogen interactions would require the deletion of genes encoding lpxC [49], lpxL-2 and lpxO [50], acrAB individually or in combination with ramA overexpression. We note that previous studies [32, 50] have shown that strains deleted for these genes, result in avirulent microbes and as such, this phenotype would obscure any RamA-associated effects. Nevertheless, our work is first to demonstrate that firstly, RamA functions as an alternate regulator of certain lipid A biosynthesis genes and secondly, these alterations perturb microbe-host interaction.
The significance of our findings lies in the broader implications of RamA-mediated regulation in Enterobacteriaceae. In this work, we describe roles for RamA in both protection against antibiotic challenge but also against the innate host immune response thus resulting in Klebsiellae that are less susceptible to antibiotics and simultaneously more virulent. Notably, our findings highlight that RamA mediated overexpression via both increased acrAB expression and lipid A alterations can result in reduced susceptibility to the last line drugs e.g. tigecycline and polymyxins. This highlights the broader consequences in selecting for ramA overexpression in K. pneumoniae or other members of Enterobacteriaceae. Finally, our study underscores and highlights the importance of intrinsic proteins such as RamA, which regulate survival strategies in K. pneumoniae and likely other Enterobacteriaceae, specifically in priming the microbial population in surviving drug and host immune pressure. This proposes the notion where microbial immune evasive strategies contribute to the development and persistence of antimicrobial resistance.
Materials and Methods
Growth Conditions
Bacteria (Table 1) were cultured in Luria-Bertani (LB) medium (10 g/L tryptone, 5 g/L yeast extract, 10 g/L NaCl). Typically, a strain was first grown on an LB plate at 37°C from frozen -80°C stocks. A single colony was picked and inoculated into 5 ml of LB and incubated in a 37°C shaker overnight. A 1 in 100 dilution was made in LB and incubated in a 37°C shaker until the OD600 reached 0.6 unless otherwise stated. Antibiotics such as ampicillin (100 µg/ml) and chloramphenicol (20 µg/ml) were added as required.
Tab. 1. Strains used in this study. 
Antimicrobial Susceptibility and Peptide Survival Assay
The assay was as described previously by Moranta et al [51]. Briefly, bacteria were grown at 37°C in 5 ml LB medium, harvested (5,000 × g, 15 min, 5°C) and washed thrice with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS). A suspension containing approximately 105 CFU/ml was prepared in 10 mM PBS (pH 6.5), 1% tryptone soy broth (TSB; Oxoid), and 100 mM NaCl. Aliquots (5 μl) of this suspension were mixed in tubes with various concentrations of polymyxin B, colistin (0.064 µg/ml to 0.256 µg/ml) and LL-37 (32 µg/ml to 85.3 µg/ml) to a final volume of 30 µl. Following incubation for an hour at 37°C with polymyxin B (Sigma, UK), colistin (Sigma, UK) and LL-37 (Sigma, UK) the samples were diluted 1 : 10 with PBS prior to plating (100 μl) on LB agar. Colony counts were determined after overnight incubation, where results are expressed as percentages of the colony count of bacteria that were not exposed to the antibiotics or the antimicrobial peptide. Sensitivity profiles of the different mutants using the phenotypic microarray analyses were determined described in S1 Text.
RNA Extraction, RNA-Seq Sample Preparation and Sequencing
Overnight cultures of strains Ecl8, Ecl8ΔramA, Ecl8ΔramR were inoculated (1/100 dilution) into LB media and incubated at 37 ºC with vigorous shaking. Cell pellets were harvested at OD600 = 0.6 and RNA was extracted using the RNAeasy Extraction Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany), which enriches for RNA molecules larger than 200 nucleotides. No depletion of ribosomal RNA was carried out prior to the synthesis of single-stranded cDNA (sscDNA) as previously reported [52]. RNAseq DNA libraries were constructed as previously described [53]. For RNAseq, independent biological samples in triplicate were assessed for each strain. The resulting sscDNA libraries were sequenced in an Illumina HISeq 2000 sequencer. An average of 0.715 Gb of sequence data was obtained per sample, in 75 bp paired reads (Details of RNAseq analyses are outlined in S1 Text). The RNAseq read data has been deposited under the ENA data repository and ArrayExpress with the accession numbers ERP001994 and E-ERAD-122, respectively.
RNA for quantitative Real-Time PCR experiments was extracted from K. pneumoniae strains (Table 1) using the TRIzol extraction method [16]. Briefly, cells were grown to mid-log phase (OD600 = 0.6) at 37 ºC with shaking and then harvested by centrifugation at 3000g (PK121R, ALC) at 4 ºC. The cell pellet was then resuspended in TRIzol reagent (Invitrogen, Paisley, UK) and chloroform prior to centrifugation to separate the phases. The upper phase was then precipitated using 3 M sodium acetate, glycogen (5 mg/ml), and 100% ethanol.
Both RNA preparations were washed and resuspended in 50 µl DEPC treated water. RNA was treated with TurboDNase to remove DNA contamination (Ambion, New York, USA). All samples were assessed for RNA integrity and quantification using both the Bioanalyzer 2100 RNA nanochip (Agilent, UK) and the ND-1000 (Nanodrop Technologies) [4]. Only those samples with integrity level 9 were taken forward for library construction or qPCR analyses.
Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qPCR)
In order to validate the RNAseq data, quantitative Real-Time PCR experiments were undertaken. After the removal of contaminating DNA, cDNA synthesis was generated using the AffinityScript cDNA synthesis kit (Agilent, UK). Gene specific primers (S4 Table) were designed using the Primer3 (http://frodo.wi.mit.edu/) software and were tested to produce standard curves with amplification efficiencies ranging from 95–110%. qPCR analyses using the locked nucleic acid probe is detailed in S1 Text. Quantitative Real Time RT-PCR (RT-PCR) was performed using the synthesized cDNA with gene specific primers using the Brilliant III Ultra-fast SYBR Green Kit (Agilent, UK) in the Agilent Mx3005P. All data were analyzed using Agilent MxPro software, which is based on the efficiency corrected method (Pfaffl) of comparative quantification that utilizes the ΔΔCt approach, also taking into account primer efficiency. The relative fold increases in expression levels were determined by firstly normalizing gene expression levels to 16S rDNA and using either Ecl8 or Ecl8∆ramA as calibrators. All comparative analyses were done using the MxPro software (Agilent, UK).
DNA EMSA
DNA fragments that represent the promoter regions of the genes that were differentially regulated in the presence or absence of RamA or RamR were subjected to the electrophoretic gel shift mobility assay (EMSA) as described previously [54]. Briefly, DNA templates ranging from 250–150bp upstream of the start site were produced by PCR, and purified by StrataPrep PCR Purification kits (Agilent UK). The purified templates were end-labelled with [γ32P]-ATP by T4 Kinase (New England Biolabs, USA). The unincorporated, labelled ATP was removed using Biospin P6 spin columns (Biorad, UK) as per manufacturer’s instructions. Purified RamA was extracted from the recombinant pETramA construct using metal chelation chromatography on superflow nickel / nitrilotriacetate agarose (Qiagen, Germany) (James Hastie, Dundee University). His-tagged RamA (200 nM) and labelled DNA (2 nM) were mixed in binding buffer (125 mM Tris-HCl, 250 mM KCl, 5 mM DTT 5% glycerol) and incubated on ice for 15 min prior to electrophoresis at 75 V on a prechilled 7.5% native polyacrylamide gel in 1 × TBE buffer.
Transcription In Vitro
Transcription (IVT) experiments were performed as described previously [55]. Briefly 5 × IVT Buffer, 2 nM PCR product of the test and control (E. coli gnd [56]) promoters, RNA polymerase, RNAseOUT (Invitrogen, UK) was incubated for 15 minutes at 37°C prior to the addition of the transcription mix containing × 5 IVT buffer (50 mM Tris-HCl, 0.1 mM EDTA, 3 mM magnesium acetate, 0.1 mM dithiothreitol, 20 mM sodium chloride, and 250 μg/ml bovine serum albumin at pH 7.8), heparin (1.2 µg/ml), NTPS, and α32P-UTP (Perkin Elmer, UK). The reaction was stopped 5 minutes later followed by the addition of Gel loading buffer II (Ambion, UK). The resulting products were electrophoresed on a 7% polyacrylamide / 8 M urea gel. Quantification was determined by densitometric analysis using Fujifilm Multigauge Software where an increase or decrease in transcription levels is after normalization to the endogenous gnd levels and calibration to the no protein control.
Cell Culture
Murine RAW 264.7 macrophage cells (obtained from ATCC TIB-71) were cultured in Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle Medium (PAA, UK) supplemented with 10% endotoxin-free foetal bovine serum (PAA, UK) and penicillin and streptomycin (Invitrogen, UK) in 75-cm2 culture flasks in 5% CO2 for 24 h until subconfluent. Twelve well tissue culture plates were seeded with 5 × 105 cells per well and viability determined using trypan blue exclusion.
Bacterial Adhesion and Internalisation Assays
Bacterial adhesion and internalization experiments were performed as described previously [57, 58]. For the adhesion assays, RAW cells were washed with PBS and incubated for 2 h at 37°C in 5% CO2 with a suspension of 5 × 107 bacterial cells in DMEM medium alone. After incubation, wells were washed five times with PBS and adherent bacteria were released by addition of 0.5% Triton X-100 (Sigma, UK). Bacterial colonies were quantified by plating appropriate dilutions on LB agar plates. In the internalization assays, after the incubation of the RAW cells with the bacterial suspension, wells were washed twice with PBS and then incubated for 2 h with fresh DMEM medium containing gentamicin (100 µg/ml) to eliminate extracellular bacteria. After the incubation, an aliquot of the medium was plated to confirm killing of extracellular bacteria and the gentamicin-containing medium was washed again. RAW cells were lysed and intracellular bacteria were quantified as described above. To estimate levels of extracellular bacteria, the infection of the RAW cells was carried out as described previously for the adhesion assay. After incubation, the media with the non-phagocytosed extracellular bacteria was collected and quantified by plating appropriate dilutions on LB agar plates. All microscopy images were generated as outlined in S1 Text.
Ethics Statement
All mouse experiments were performed under the control of the UK Home Office legislation in accordance with the terms of the Project license (PPL2700) granted for this work under the Animals (Scientific Procedures) Act 1986 in addition to receiving formal approval of the document through Queen’s University Belfast Animal Welfare and Ethical Review Body.
Infection In Vivo
Overnight bacterial cultures were washed three times in sterile endotoxin free PBS. The bacteria was resuspended to an optical density of 0.2 and 20 μl (∼ 5 × 107 CFU/animal) and administered to anaesthetised 5–7 week old weight watched Harlan C57BL6 mice (n = 5 per group) using the intranasal inoculation method [36]. In order to ensure maximal delivery of the bacterial inoculation into the lungs the animals were held in a perpendicular position until cessation of laboured breathing. 24 h post inoculation the mice were sacrificed by lethal pentabarbitol injection. Perfused lungs and spleen were harvested and resuspended in 1 ml of sterile PBS. Following mechanical homogenisation dilutions were plated on LB agar plates and incubated at 37°C to establish the CFU/ml.
Supporting Information
Zdroje
1. Barbosa TM, Levy SB (2000) Differential Expression of Over 60 Chromosomal Genes in Escherichia coli by Constitutive Expression of MarA. J Bacteriol 182 : 3467–3474. doi: 10.1128/JB.182.12.3467-3474.2000 10852879
2. Pomposiello PJ, Bennik MH, Demple B (2001) Genome-wide Transcriptional Profiling of the Escherichia coli Responses to Superoxide Stress and Sodium Salicylate. J Bacteriol 183 : 3890–3902. doi: 10.1128/JB.183.13.3890-3902.2001 11395452
3. Bennik MH, Pomposiello PJ, Thorne DF, Demple B (2000) Defining a rob regulon in Escherichia coli by using transposon mutagenesis. J Bacteriol 182 : 3794–3801. doi: 10.1128/JB.182.13.3794-3801.2000 10850996
4. Bailey AM, Ivens A, Kingsley R, Cottell JL, Wain J, et al. (2010) RamA, a member of the AraC/XylS family, influences both virulence and efflux in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium. J Bacteriol 192 : 1607–1616. doi: 10.1128/JB.01517-09 20081028
5. De Majumdar S, Veleba M, Finn S, Fanning S, Schneiders T (2013) Elucidating the regulon of multidrug resistance regulator RarA in Klebsiella pneumoniae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 57 : 1603–1609. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01998-12 23318802
6. Martin RG, Rosner JL (2001) The AraC transcriptional activators. Curr Opin Microbiol 4 : 132–137. doi: 10.1016/S1369-5274(00)00178-8 11282467
7. Piddock LJ (2006) Multidrug-resistance efflux pumps—not just for resistance. Nat Rev Microbiol 4 : 629–636. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro1464 16845433
8. Dangi B, Pelupessey P, Martin RG, Rosner JL, Louis JM, et al. (2001) Structure and Dynamics of MarA-DNA Complexes: An NMR Investigation. J Mol Biol 314 : 113–127. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.2001.5106 11724537
9. Griffith KL, Shah IM, Myers TE, O’Neill MC, Wolf RE Jr. (2002) Evidence for “pre-recruitment” as a new mechanism of transcription activation in Escherichia coli: the large excess of SoxS binding sites per cell relative to the number of SoxS molecules per cell. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 291 : 979–986. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.2002.6559 11866462
10. Alekshun MN, Levy SB (1997) Regulation of Chromosomally Mediated Multiple Antibiotic Resistance: the mar Regulon. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 41 : 2067–2075. 9333027
11. Zheng J, Tian F, Cui S, Song J, Zhao S, et al. (2011) Differential gene expression by RamA in ciprofloxacin-resistant Salmonella Typhimurium. PLoS One 6: e22161. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0022161 21811569
12. Hung DT, Shakhnovich EA, Pierson E, Mekalanos JJ (2005) Small-molecule inhibitor of Vibrio cholerae virulence and intestinal colonization. Science 310 : 670–674. doi: 10.1126/science.1116739 16223984
13. Casaz P, Garrity-Ryan LK, McKenney D, Jackson C, Levy SB, et al. (2006) MarA, SoxS and Rob function as virulence factors in an Escherichia coli murine model of ascending pyelonephritis. Microbiology 152 : 3643–3650. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.2006/000604-0 17159217
14. Chollet R, Chevalier J, Bollet C, Pages JM, Davin-Regli A (2004) RamA is an alternate activator of the multidrug resistance cascade in Enterobacter aerogenes. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 48 : 2518–2523. doi: 10.1128/AAC.48.7.2518-2523.2004 15215103
15. Yassien MA, Ewis HE, Lu CD, Abdelal AT (2002) Molecular cloning and characterization of the Salmonella enterica Serovar Paratyphi B rma Gene, which confers multiple drug resistance in Escherichia coli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 46 : 360–366. doi: 10.1128/AAC.46.2.360-366.2002 11796342
16. Rosenblum R, Khan E, Gonzalez G, Hasan R, Schneiders T (2011) Genetic regulation of the ramA locus and its expression in clinical isolates of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Int J Antimicrob Agents 38 : 39–45. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2011.02.012 21514798
17. Hentschke M, Wolters M, Sobottka I, Rohde H, Aepfelbacher M (2010) ramR mutations in clinical isolates of Klebsiella pneumoniae with reduced susceptibility to Tigecycline. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 54 : 2720–2723. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00085-10 20350947
18. Abouzeed YM, Baucheron S, Cloeckaert A (2008) ramR mutations involved in efflux-mediated multidrug resistance in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 52 : 2428–2434. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00084-08 18443112
19. Yamasaki S, Nikaido E, Nakashima R, Sakurai K, Fujiwara D, et al. (2013) The crystal structure of multidrug-resistance regulator RamR with multiple drugs. Nat Commun 4 : 2078. doi: 10.1038/ncomms3078 23800819
20. Martin RG, Bartlett ES, Rosner JL, Wall ME (2008) Activation of the Escherichia coli marA/soxS/rob regulon in response to transcriptional activator concentration. J Mol Biol 380 : 278–284. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2008.05.015 18514222
21. Ruzin A, Visalli MA, Keeney D, Bradford PA (2005) Influence of transcriptional activator RamA on expression of multidrug efflux pump AcrAB and tigecycline susceptibility in Klebsiella pneumoniae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 49 : 1017–1022. doi: 10.1128/AAC.49.3.1017-1022.2005 15728897
22. Podschun R, Ullmann U (1998) Klebsiella spp. as nosocomial pathogens: epidemiology, taxonomy, typing methods, and pathogenicity factors. Clin Microbiol Rev 11 : 589–603.
23. Fookes M, Yu J, De Majumdar S, Thomson N, Schneiders T (2013) Genome Sequence of Klebsiella pneumoniae Ecl8, a Reference Strain for Targeted Genetic Manipulation. Genome Announc 1. doi: 10.1128/genomeA.00027-12
24. Chinni SV, Raabe CA, Zakaria R, Randau G, Hoe CH, et al. (2010) Experimental identification and characterization of 97 novel npcRNA candidates in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi. Nucleic Acids Res. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkq281
25. Yoder-Himes DR, Chain PS, Zhu Y, Wurtzel O, Rubin EM, et al. (2009) Mapping the Burkholderia cenocepacia niche response via high-throughput sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106 : 3976–3981. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0813403106 19234113
26. Pomposiello PJ, Demple B (2000) Identification of SoxS-regulated genes in Salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium. J Bacteriol 182 : 23–29. doi: 10.1128/JB.182.1.23-29.2000 10613858
27. Han X, Geng J, Zhang L, Lu T (2011) The role of Escherichia coli YrbB in the lethal action of quinolones. J Antimicrob Chemother 66 : 323–331. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkq427 21098540
28. Malinverni JC, Silhavy TJ (2009) An ABC transport system that maintains lipid asymmetry in the gram-negative outer membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106 : 8009–8014. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0903229106 19383799
29. Raetz CR, Guan Z, Ingram BO, Six DA, Song F, et al. (2009) Discovery of new biosynthetic pathways: the lipid A story. J Lipid Res 50 Suppl: S103–108. doi: 10.1194/jlr.R800060-JLR200 18974037
30. Gunn JS (2001) Bacterial modification of LPS and resistance to antimicrobial peptides. J Endotoxin Res 7 : 57–62. doi: 10.1177/09680519010070011001 11521084
31. Llobet E, Campos MA, Gimenez P, Moranta D, Bengoechea JA (2011) Analysis of the networks controlling the antimicrobial-peptide-dependent induction of Klebsiella pneumoniae virulence factors. Infect Immun 79 : 3718–3732. doi: 10.1128/IAI.05226-11 21708987
32. Clements A, Tull D, Jenney AW, Farn JL, Kim SH, et al. (2007) Secondary acylation of Klebsiella pneumoniae lipopolysaccharide contributes to sensitivity to antibacterial peptides. J Biol Chem 282 : 15569–15577. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M701454200 17371870
33. Campos MA, Vargas MA, Regueiro V, Llompart CM, Alberti S, et al. (2004) Capsule polysaccharide mediates bacterial resistance to antimicrobial peptides. Infect Immun 72 : 7107–7114. doi: 10.1128/IAI.72.12.7107-7114.2004 15557634
34. March C, Cano V, Moranta D, Llobet E, Perez-Gutierrez C, et al. (2013) Role of bacterial surface structures on the interaction of Klebsiella pneumoniae with phagocytes. PLoS One 8: e56847. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0056847 23457627
35. Shu HY, Fung CP, Liu YM, Wu KM, Chen YT, et al. (2009) Genetic diversity of capsular polysaccharide biosynthesis in Klebsiella pneumoniae clinical isolates. Microbiology 155 : 4170–4183. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.029017-0 19744990
36. Lawlor MS, Hsu J, Rick PD, Miller VL (2005) Identification of Klebsiella pneumoniae virulence determinants using an intranasal infection model. Mol Microbiol 58 : 1054–1073. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2005.04918.x 16262790
37. Schneiders T, Amyes SG, Levy SB (2003) Role of AcrR and ramA in fluoroquinolone resistance in clinical Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates from Singapore. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 47 : 2831–2837. doi: 10.1128/AAC.47.9.2831-2837.2003 12936981
38. Veleba M, Higgins PG, Gonzalez G, Seifert H, Schneiders T (2012) Characterization of RarA, a novel AraC family multidrug resistance regulator in Klebsiella pneumoniae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 56 : 4450–4458. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00456-12 22644028
39. Martin RG, Gillette WK, Rhee S, Rosner JL (1999) Structural requirements for marbox function in transcriptional activation of mar/sox/rob regulon promoters in Escherichia coli: sequence, orientation and spatial relationship to the core promoter. Mol Microbiol 34 : 431–441. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.1999.01599.x 10564485
40. Martin RG, Gillette WK, Rosner JL (2000) Promoter discrimination by the related transcriptional activators MarA and SoxS: differential regulation by differential binding. Mol Microbiol 35 : 623–634. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2000.01732.x 10672184
41. Ricci V, Tzakas P, Buckley A, Piddock LJ (2006) Ciprofloxacin-resistant Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium strains are difficult to select in the absence of AcrB and TolC. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 50 : 38–42. doi: 10.1128/AAC.50.1.38-42.2006 16377664
42. Hobbs EC, Yin X, Paul BJ, Astarita JL, Storz G (2012) Conserved small protein associates with the multidrug efflux pump AcrB and differentially affects antibiotic resistance. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109 : 16696–16701. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1210093109 23010927
43. Padilla E, Llobet E, Domenech-Sanchez A, Martinez-Martinez L, Bengoechea JA, et al. (2010) Klebsiella pneumoniae AcrAB efflux pump contributes to antimicrobial resistance and virulence. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 54 : 177–183. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00715-09 19858254
44. Raetz CR, Reynolds CM, Trent MS, Bishop RE (2007) Lipid A modification systems in gram-negative bacteria. Annu Rev Biochem 76 : 295–329. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biochem.76.010307.145803 17362200
45. Velkov T, Soon RL, Chong PL, Huang JX, Cooper MA, et al. (2013) Molecular basis for the increased polymyxin susceptibility of Klebsiella pneumoniae strains with under-acylated lipid A. Innate Immun 19 : 265–277. doi: 10.1177/1753425912459092 23008349
46. Needham BD, Trent MS (2013) Fortifying the barrier: the impact of lipid A remodelling on bacterial pathogenesis. Nat Rev Microbiol 11 : 467–481. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro3047 23748343
47. Gunn JS, Ryan SS, Van Velkinburgh JC, Ernst RK, Miller SI (2000) Genetic and functional analysis of a PmrA-PmrB-regulated locus necessary for lipopolysaccharide modification, antimicrobial peptide resistance, and oral virulence of Salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium. Infect Immun 68 : 6139–6146. doi: 10.1128/IAI.68.11.6139-6146.2000 11035717
48. Buckley AM, Webber MA, Cooles S, Randall LP, La Ragione RM, et al. (2006) The AcrAB-TolC efflux system of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium plays a role in pathogenesis. Cell Microbiol 8 : 847–856. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2005.00671.x 16611233
49. Mdluli KE, Witte PR, Kline T, Barb AW, Erwin AL, et al. (2006) Molecular validation of LpxC as an antibacterial drug target in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 50 : 2178–2184. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00140-06 16723580
50. Moreira CG, Herrera CM, Needham BD, Parker CT, Libby SJ, et al. (2013) Virulence and stress-related periplasmic protein (VisP) in bacterial/host associations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 110 : 1470–1475. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1215416110 23302685
51. Moranta D, Regueiro V, March C, Llobet E, Margareto J, et al. (2010) Klebsiella pneumoniae capsule polysaccharide impedes the expression of beta-defensins by airway epithelial cells. Infect Immun 78 : 1135–1146. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00940-09 20008534
52. Croucher NJ, Fookes MC, Perkins TT, Turner DJ, Marguerat SB, et al. (2009) A simple method for directional transcriptome sequencing using Illumina technology. Nucleic Acids Res 37: e148. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkp811 19815668
53. Quail MA, Kozarewa I, Smith F, Scally A, Stephens PJ, et al. (2008) A large genome center’s improvements to the Illumina sequencing system. Nat Methods 5 : 1005–1010. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.1270 19034268
54. Briggs GS, Mahdi AA, Wen Q, Lloyd RG (2005) DNA binding by the substrate specificity (wedge) domain of RecG helicase suggests a role in processivity. J Biol Chem 280 : 13921–13927. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M412054200 15695524
55. Schneiders T, Levy SB (2006) MarA-mediated transcriptional repression of the rob promoter. J Biol Chem 281 : 10049–10055. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M512097200 16478729
56. Barbosa TM, Levy SB (2002) Activation of the Escherichia coli nfnB gene by MarA through a highly divergent marbox in a class II promoter. Mol Microbiol 45 : 191–202. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2002.03006.x 12100559
57. Cano V, Moranta D, Llobet-Brossa E, Bengoechea JA, Garmendia J (2009) Klebsiella pneumoniae triggers a cytotoxic effect on airway epithelial cells. BMC Microbiol 9 : 156. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-9-156 19650888
58. Regueiro V, Campos MA, Pons J, Alberti S, Bengoechea JA (2006) The uptake of a Klebsiella pneumoniae capsule polysaccharide mutant triggers an inflammatory response by human airway epithelial cells. Microbiology 152 : 555–566. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.28285-0 16436443
59. George AM, Hall RM, Stokes HW (1995) Multidrug resistance in Klebsiella pneumoniae: a novel gene, ramA, confers a multidrug resistance phenotype in Escherichia coli. Microbiology 141 : 1909–1920. doi: 10.1099/13500872-141-8-1909 7551053
Štítky
Hygiena a epidemiologie Infekční lékařství Laboratoř
Článek Differential Reliance on Autophagy for Protection from HSV Encephalitis between Newborns and AdultsČlánek The Molecular Basis for Control of ETEC Enterotoxin Expression in Response to Environment and HostČlánek Different Infectivity of HIV-1 Strains Is Linked to Number of Envelope Trimers Required for EntryČlánek Preferential Use of Central Metabolism Reveals a Nutritional Basis for Polymicrobial Infection
Článek vyšel v časopisePLOS Pathogens
Nejčtenější tento týden
2015 Číslo 1- Jak souvisí postcovidový syndrom s poškozením mozku?
- Měli bychom postcovidový syndrom léčit antidepresivy?
- Farmakovigilanční studie perorálních antivirotik indikovaných v léčbě COVID-19
- 10 bodů k očkování proti COVID-19: stanovisko České společnosti alergologie a klinické imunologie ČLS JEP
-
Všechny články tohoto čísla
- The Importance of Pathogen Load
- Implication of Gut Microbiota in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
- Infections in Humans and Animals: Pathophysiology, Detection, and Treatment
- Helminth-Induced Immune Regulation: Implications for Immune Responses to Tuberculosis
- The M3 Muscarinic Receptor Is Required for Optimal Adaptive Immunity to Helminth and Bacterial Infection
- An Iron-Mimicking, Trojan Horse-Entering Fungi—Has the Time Come for Molecular Imaging of Fungal Infections?
- Modulates the Unfolded Protein Response in during Infection
- Differential Reliance on Autophagy for Protection from HSV Encephalitis between Newborns and Adults
- Identification of HNRNPK as Regulator of Hepatitis C Virus Particle Production
- Parasite Biomass-Related Inflammation, Endothelial Activation, Microvascular Dysfunction and Disease Severity in Vivax Malaria
- : Trypanosomatids Adapted to Plant Environments
- Early Virus-Host Interactions Dictate the Course of a Persistent Infection
- TLR3 Signaling in Macrophages Is Indispensable for the Protective Immunity of Invariant Natural Killer T Cells against Enterovirus 71 Infection
- The Epstein-Barr Virus Encoded BART miRNAs Potentiate Tumor Growth
- Macrophage-Derived Human Resistin Is Induced in Multiple Helminth Infections and Promotes Inflammatory Monocytes and Increased Parasite Burden
- Dissemination of a Highly Virulent Pathogen: Tracking The Early Events That Define Infection
- Variability in Tuberculosis Granuloma T Cell Responses Exists, but a Balance of Pro- and Anti-inflammatory Cytokines Is Associated with Sterilization
- The Shear Stress of Host Cell Invasion: Exploring the Role of Biomolecular Complexes
- The Molecular Basis for Control of ETEC Enterotoxin Expression in Response to Environment and Host
- Different Infectivity of HIV-1 Strains Is Linked to Number of Envelope Trimers Required for Entry
- Secreted Herpes Simplex Virus-2 Glycoprotein G Modifies NGF-TrkA Signaling to Attract Free Nerve Endings to the Site of Infection
- Preferential Use of Central Metabolism Reveals a Nutritional Basis for Polymicrobial Infection
- A New Family of Secreted Toxins in Pathogenic Neisseria Species
- A Human Type 5 Adenovirus-Based Therapeutic Vaccine Re-programs Immune Response and Reverses Chronic Cardiomyopathy
- Regulation of Oncogene Expression in T-DNA-Transformed Host Plant Cells
- GITR Intrinsically Sustains Early Type 1 and Late Follicular Helper CD4 T Cell Accumulation to Control a Chronic Viral Infection
- Cell Cycle-Independent Phospho-Regulation of Fkh2 during Hyphal Growth Regulates Pathogenesis
- Virus-Induced NETs – Critical Component of Host Defense or Pathogenic Mediator?
- Environmental Drivers of the Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Respiratory Syncytial Virus in the United States
- Protective Efficacy of Centralized and Polyvalent Envelope Immunogens in an Attenuated Equine Lentivirus Vaccine
- Transmitted Virus Fitness and Host T Cell Responses Collectively Define Divergent Infection Outcomes in Two HIV-1 Recipients
- Systemic Expression of Kaposi Sarcoma Herpesvirus (KSHV) Vflip in Endothelial Cells Leads to a Profound Proinflammatory Phenotype and Myeloid Lineage Remodeling
- Dengue Virus RNA Structure Specialization Facilitates Host Adaptation
- DNA Is an Antimicrobial Component of Neutrophil Extracellular Traps
- Uropathogenic Superinfection Enhances the Severity of Mouse Bladder Infection
- Well-Ordered Trimeric HIV-1 Subtype B and C Soluble Spike Mimetics Generated by Negative Selection Display Native-like Properties
- The Phylogenetically-Related Pattern Recognition Receptors EFR and XA21 Recruit Similar Immune Signaling Components in Monocots and Dicots
- Reprogramming of from Virulent to Persistent Mode Revealed by Complex RNA-seq Analysis
- Compartment-Specific and Sequential Role of MyD88 and CARD9 in Chemokine Induction and Innate Defense during Respiratory Fungal Infection
- Bacterial Flagella: Twist and Stick, or Dodge across the Kingdoms
- Elucidation of the RamA Regulon in Reveals a Role in LPS Regulation
- IL-1α Signaling Is Critical for Leukocyte Recruitment after Pulmonary Challenge
- Chronic Filarial Infection Provides Protection against Bacterial Sepsis by Functionally Reprogramming Macrophages
- Specificity and Dynamics of Effector and Memory CD8 T Cell Responses in Human Tick-Borne Encephalitis Virus Infection
- Promiscuous RNA Binding Ensures Effective Encapsidation of APOBEC3 Proteins by HIV-1
- Viral Activation of MK2-hsp27-p115RhoGEF-RhoA Signaling Axis Causes Cytoskeletal Rearrangements, P-body Disruption and ARE-mRNA Stabilization
- PLOS Pathogens
- Archiv čísel
- Aktuální číslo
- Informace o časopisu
Nejčtenější v tomto čísle- Infections in Humans and Animals: Pathophysiology, Detection, and Treatment
- : Trypanosomatids Adapted to Plant Environments
- Environmental Drivers of the Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Respiratory Syncytial Virus in the United States
- Dengue Virus RNA Structure Specialization Facilitates Host Adaptation
Kurzy
Zvyšte si kvalifikaci online z pohodlí domova
Současné možnosti léčby obezity
nový kurzAutoři: MUDr. Martin Hrubý
Všechny kurzyPřihlášení#ADS_BOTTOM_SCRIPTS#Zapomenuté hesloZadejte e-mailovou adresu, se kterou jste vytvářel(a) účet, budou Vám na ni zaslány informace k nastavení nového hesla.
- Vzdělávání



