-
Články
Top novinky
Reklama- Vzdělávání
- Časopisy
Top články
Nové číslo
- Témata
Top novinky
Reklama- Videa
- Podcasty
Nové podcasty
Reklama- Kariéra
Doporučené pozice
Reklama- Praxe
Top novinky
ReklamaTranscriptional Derepression Uncovers Cryptic Higher-Order Genetic Interactions
Some genetic polymorphisms have phenotypic effects that are masked under most conditions, but can be revealed by mutations or environmental change. The genetic and molecular mechanisms that suppress and uncover these cryptic genetic variants are important to understand. Here, we show that a single mutation in a yeast cross causes a major phenotypic change through its genetic interactions with two specific combinations of cryptic variants in six genes. This result suggests that in some cases cryptic variants themselves play roles in revealing their own phenotypic effects through their genetic interactions with each other and the mutations that reveal them. We also demonstrate that most of the genes harboring cryptic variation in our system are transcription factors, a finding that supports an important role for perturbation of gene regulatory networks in the uncovering of cryptic variation. As a final part of our study, we interrogate how a mutation exposes combinations of cryptic variants and obtain evidence that it does so by disrupting the silencing of one or more genes that must be expressed for the cryptic variants to exert their effects. To prove this point, we delete the transcriptional repressor that mediates this silencing and demonstrate that this deletion reveals a similar set of cryptic variants to the ones that were discovered in the initial mutant background. These findings advance our understanding of the genetic and molecular mechanisms that reveal cryptic variation.
Published in the journal: . PLoS Genet 11(10): e32767. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1005606
Category: Research Article
doi: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1005606Summary
Some genetic polymorphisms have phenotypic effects that are masked under most conditions, but can be revealed by mutations or environmental change. The genetic and molecular mechanisms that suppress and uncover these cryptic genetic variants are important to understand. Here, we show that a single mutation in a yeast cross causes a major phenotypic change through its genetic interactions with two specific combinations of cryptic variants in six genes. This result suggests that in some cases cryptic variants themselves play roles in revealing their own phenotypic effects through their genetic interactions with each other and the mutations that reveal them. We also demonstrate that most of the genes harboring cryptic variation in our system are transcription factors, a finding that supports an important role for perturbation of gene regulatory networks in the uncovering of cryptic variation. As a final part of our study, we interrogate how a mutation exposes combinations of cryptic variants and obtain evidence that it does so by disrupting the silencing of one or more genes that must be expressed for the cryptic variants to exert their effects. To prove this point, we delete the transcriptional repressor that mediates this silencing and demonstrate that this deletion reveals a similar set of cryptic variants to the ones that were discovered in the initial mutant background. These findings advance our understanding of the genetic and molecular mechanisms that reveal cryptic variation.
Introduction
Cryptic genetic variants are standing polymorphisms that only exhibit phenotypic effects under atypical conditions, such as when specific genes are compromised or the environment dramatically changes [1–3]. Work in Arabidopsis thaliana (e.g., [4–6]), Caenorhabditis elegans (e.g., [7–9]), Drosophila melanogaster (e.g., [10–14]), multiple budding yeasts (e.g., [15–19]), and a number of non-model organisms (e.g., [20–26]) has shown that cryptic variation is abundant within and between species. Because it is so prevalent, cryptic variation could plausibly contribute to adaptation and phenotypic novelty [2, 27–29], as well as to disease susceptibility [30]. Yet due to their entirely conditional phenotypic effects, cryptic variants have proven difficult to study and are not understood as well as other classes of polymorphisms. In particular, the genetic and molecular mechanisms that suppress and uncover cryptic variation have yet to be fully determined.
For the purposes of this paper, we focus on the mechanisms by which functional disruption of specific ‘capacitor’ genes exposes the phenotypic effects of cryptic variants. This phenomenon is often referred to as ‘phenotypic capacitance’ or ‘evolutionary capacitance’, though for simplicity we refer to it as ‘capacitance’ [11, 31]. The first described capacitor was Hsp90, a chaperone that assists in the folding and stabilization of other proteins [11, 32]. Early research on capacitance suggested that Hsp90 might have distinct biochemical features that cause cryptic variation to be uncovered when it is compromised [4, 11, 32]. However, subsequent theoretical work showed that capacitance most likely occurs as a general consequence of gene regulatory network perturbation and that many genes might be able to act as capacitors [31]. Supporting this finding, a number of genes involved in chromatin regulation have also been shown to be capacitors of cryptic variation [15, 33, 34] and to even phenocopy the effects of Hsp90 perturbation [34].
More recent work suggests that capacitance depends not only on the perturbation of capacitors but also on the specific cryptic variants that are present. This is because cryptic variants themselves can play an important role in capacitance by genetically interacting with and ‘potentiating’ the phenotypic effects of their capacitors [3, 17, 33, 35–37]. The genetic architecture of this potentiating cryptic variation has not been characterized in detail [38], but may involve complex epistatic interactions between multiple cryptic variants and capacitating mutations (i.e., higher-order genetic interactions) [39]. In such a scenario, the phenotypic effect of a given capacitating mutation would depend on the cryptic variants with which it co-occurs, with the mutation having an effect only in certain genetic backgrounds [40] (Fig 1). This possibility is not unfounded, as several recent studies suggest that genetic background effects can involve higher-order genetic interactions among de novo or induced mutations and sets of cryptic variants [41–43].
Fig. 1. Capacitance, higher-order genetic interactions, and genetic background effects might be related phenomena that involve interactions among capacitating mutations and cryptic variants. 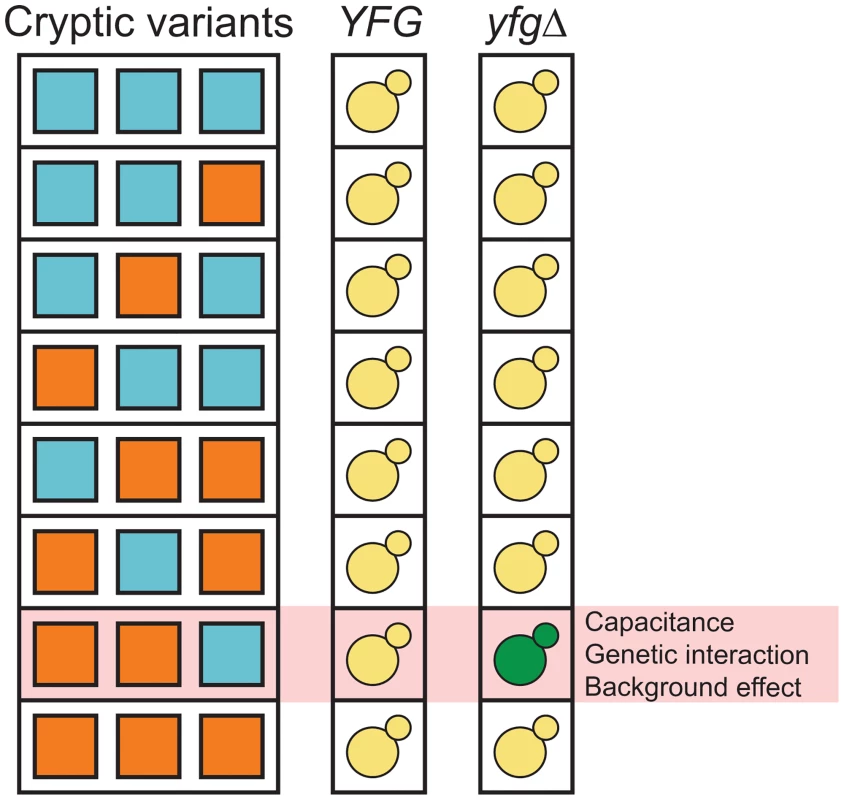
‘YFG’ and ‘yfgΔ’ refer to the wild type and mutant alleles of a gene that can genetically interact with cryptic variants. The green yeast indicates the combination of a capacitating mutation and cryptic variants that shows a phenotypic effect. We recently described an experimental system that can be used to study how higher-order genetic interactions among mutations and cryptic variants result in capacitance [42]. In our previous paper, we showed that a de novo mutation in IRA2, a negative regulator of the Ras-cAMP-PKA (Ras) pathway [44, 45], uncovers sets of interacting cryptic variants that influence colony morphology in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. This mutation (ira2Δ2933) occurred spontaneously while we were generating a cross of the lab strain BY4716 (‘BY’) and a derivative of the clinical isolate 322134S (‘3S’) [46, 47], and results in a truncated, partially functional Ira2 protein that lacks 117 amino acids relative to its wild type form. When the ira2Δ2933 lesion is present in specific haploid recombinants in the BYx3S cross, it causes a change in colony morphology from ‘smooth’ to ‘rough’ (Fig 2).
Fig. 2. Colony morphology phenotypes that occur in the BYx3S cross in the presence of ira2Δ2933. 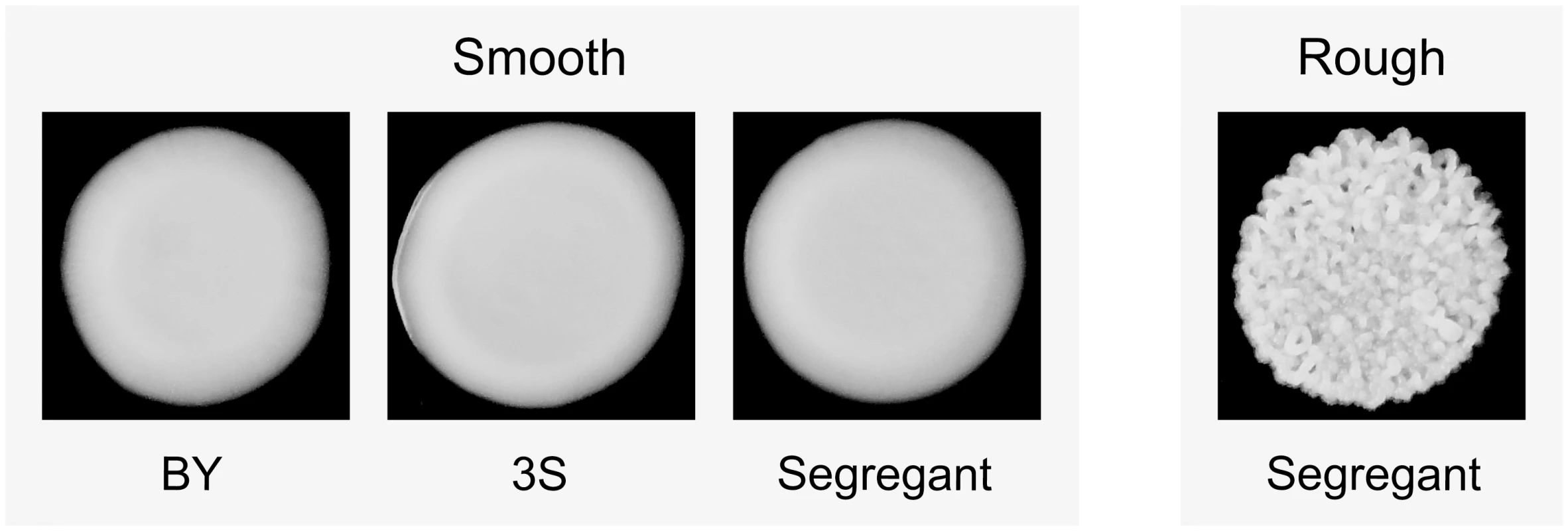
BY, 3S, and most segregants show a smooth phenotype, while a small fraction of segregants show a rough phenotype. Through comprehensive genetic mapping experiments, we showed that ira2Δ2933 induces the rough phenotype when it co-occurs with specific combinations of cryptic variants at four or more genes [42]. To better understand these higher-order genetic interactions, we cloned all of the genes involved in one of the combinations. This resulted in the identification of two transcriptional activators that heterodimerize and function downstream of the Ras pathway (FLO8 [48] and MSS11 [49]), a structural protein that plays a role in vesicle formation (END3 [50, 51]), and an enzyme that helps cells detoxify themselves of endogenous redox stress (TRR1 [52]). Most of the rough individuals in our past study had the genotype END3BY FLO83S ira2Δ2933 MSS11BY TRR13S. However, we also provided evidence for a more complex genotype involving END33S that requires specific alleles at two additional loci.
In this paper, we complete our efforts to determine the genetic basis of ira2Δ2933-dependent rough morphology in the BYx3S cross under our standard assay conditions. We show that in addition to the previously identified five-way genetic interaction, a six-way interaction can also cause the trait. Specifically, individuals with the genotype END33S FLO83S ira2Δ2933 MSS11BY exhibit the rough phenotype if they possess BY alleles at two other transcription factors that are regulated by the Ras pathway [53, 54]: the activator MGA1 [55] and the repressor SFL1 [56, 57]. This suggests that the rough phenotype arises due to genetically complex changes in the regulation of Ras target genes. We examine the role of ira2Δ2933 in these regulatory changes and find that it alleviates the silencing of FLO11, a gene that encodes a cell surface protein required for rough morphology. We also show that this ability to disrupt FLO11 repression is not unique to IRA2. These results illustrate how higher-order combinations of cryptic variants can confer the potential for capacitance to specific genetic backgrounds and indicate that capacitating mutations may reveal cryptic phenotypic potential by causing transcriptional derepression.
Results
END33S and ira2Δ2933 are involved in a six-way genetic interaction
To determine the specific combination of alleles involved in rough morphology in an END33S background, we generated new mapping populations by mating an END33S rough segregant from a (BYx3S)x3S backcross to BY and 3S (Methods). Throughout the paper, the term ‘backcross’ refers specifically to these ((BYx3S)x3S)xBY and ((BYx3S)x3S)x3S matings. Because END33S segregated in the BY backcross, we genotyped rough individuals recovered from this population to determine the allele of END3 they carried (Methods). In total, we obtained 63 and 88 rough END33S individuals from the BY and 3S backcrosses, respectively. We then pooled cells from these rough individuals by cross and performed bulk segregant mapping by sequencing [58, 59] (Methods). We found that the more complex genetic interaction involves a specific combination of alleles at six loci, with individual loci detected on Chromosomes V, VII, XIII, and XIV, and two loci identified on Chromosome XV (Fig 3A and 3B). The chromosome XIV locus corresponds to END33S, while allele replacements in a backcross segregant that carried the six-way interaction confirmed that FLO83S, MSS11BY, and ira2Δ2933 underlie the Chromosome V, XIII, and XV-1 loci, respectively (Fig 3C and S1 Fig; Methods). The new mapping data also allowed us to delimit the Chromosome VII and XV-2 loci, which we were unable to clone in our prior study [42], to a single gene (MGA1) and five genes (SFL1, ARP8, LSC1, SUF5, THI80), respectively. We used allele swaps to show that the BY alleles of MGA1 and SFL1, which respectively encode an activator and a repressor that are regulated by the Ras pathway, are the causal alleles at these loci (S1 Fig). These results show the six-way interaction occurs in individuals with the genotype END33S FLO83S ira2Δ2933 MGA1BY MSS11BY SFL1BY (Fig 3B). Thus, the differences between the five - and six-way interactions involve which END3 allele is involved and whether specific alleles of MGA1, SFL1, and TRR1 are required (Fig 3B).
Fig. 3. Characterization of the six-way genetic interaction. 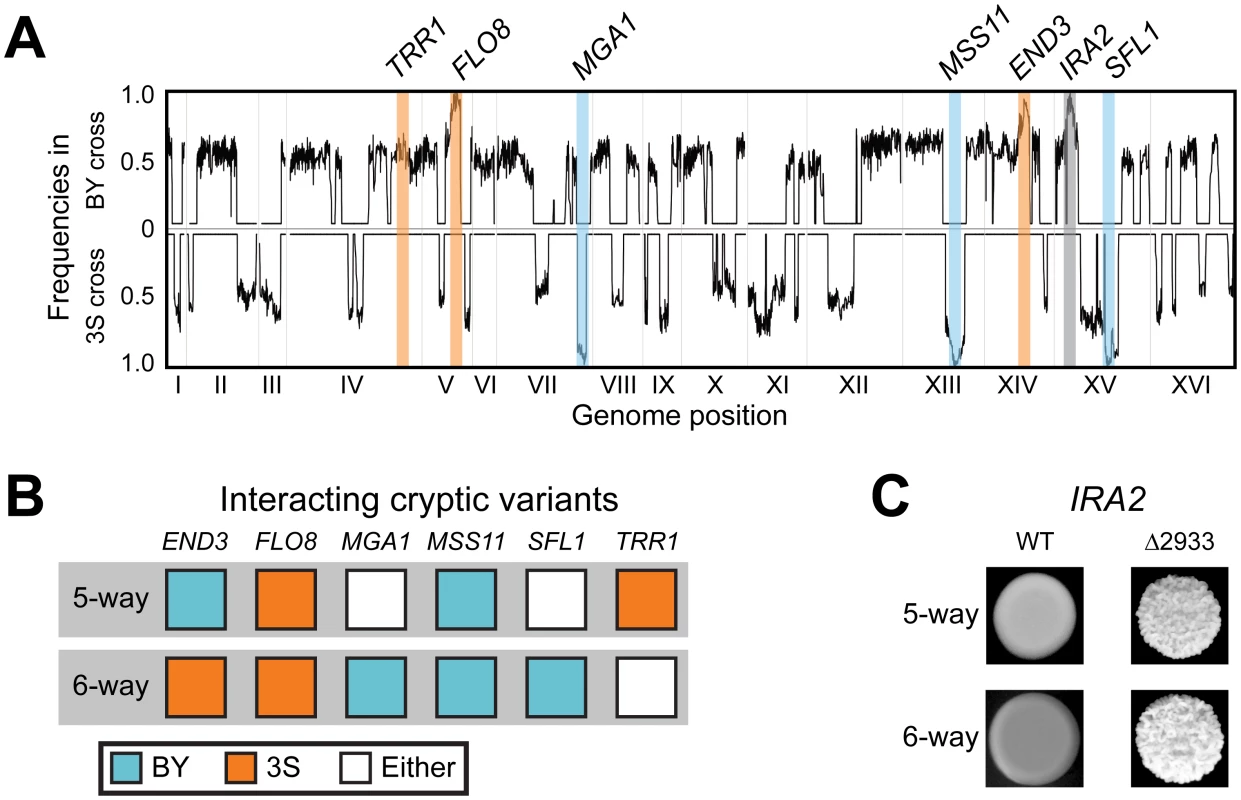
(A) Allele frequency plots for BY and 3S second iteration backcross populations of END33S rough strains. Fixed loci are denoted with a blue, orange, or grey bars depending on whether the BY, 3S, or mutant alleles, respectively, were detected at a locus. The allele frequencies were estimated by averaging data in sliding windows containing 10 SNPs. (B) Cryptic variants involved in the five- and six-way interactions. (C) Dependence of both genetic interactions on the ira2Δ2933 mutation. The two interactions fully account for rough morphology in the presence of ira2Δ2933
Based on our genetic mapping results in this paper and our past work [42], we have identified alleles of six genes (END3, FLO8, MGA1, MSS11, SFL1, TRR1) that genetically interact in two different combinations with ira2Δ2933 (Fig 3B and 3C). We tested whether these two allele combinations fully explain rough morphology in the BYx3S ira2Δ2933 cross by generating a new BYx3S cross in which 3S carried ira2Δ2933 (Methods). As our past work focused on matings of segregants to BY or 3S, this population enabled us to test for the first time the effects of all possible combinations of BY and 3S alleles in the presence of ira2Δ2933. Among 42 rough individuals that we recovered, 40 (95.2%) carried the five-way interaction, while two (4.8%) carried the six-way interaction. The five-way interaction should occur twice as often as the six-way interaction, yet the observed ratio was 20 : 1. This may be due to linkage between END3 and a locus at which the BY allele confers a strong selective advantage during random spore isolation (see Figure S2B from [42]). Alternatively, the enrichment of rough individuals carrying the five-way interaction could simply have occurred because the sample of rough individuals in this experiment was small. Nevertheless, our observation that all the examined rough individuals harbored either the five - or six-way interactions suggests that we have completely determined the genetic basis of rough morphology in the BYx3S ira2Δ2933 cross under our experimental conditions.
FLO11 expression is needed for rough morphology
Rough morphology in the BYx3S cross likely arises due to genetically complex changes in the regulation of Ras target genes. Such a possibility is supported by the finding that four Ras-regulated transcription factors [54] harbor cryptic variants involved in the rough phenotype, as well as by the fact that these cryptic variants are revealed by a capacitating mutation in IRA2, a negative regulator of Ras signaling. A gene that is likely influenced by these genetic factors is FLO11, which encodes a cell surface glycoprotein that facilitates cell-cell adhesion and is thought to be regulated by Flo8-Mss11, Mga1, and Sfl1 [60, 61]. To determine if expression of the rough phenotype due to the five - and six-way interactions requires FLO11, we deleted the gene from a nearly isogenic line possessing the five-way interaction and a backcross segregant carrying the six-way interaction (Methods). This was sufficient to convert both of these strains from rough to smooth (Fig 4A), indicating that both genetic interactions are FLO11-dependent. RT-PCR showed that FLO11 is expressed in individuals carrying the five - and six-way interactions, but not in BY or 3S (Fig 4B; Methods). These results suggest expression of the rough phenotype requires active transcription of FLO11.
Fig. 4. FLO11 is required for rough morphology and shows differential expression across genetic backgrounds. 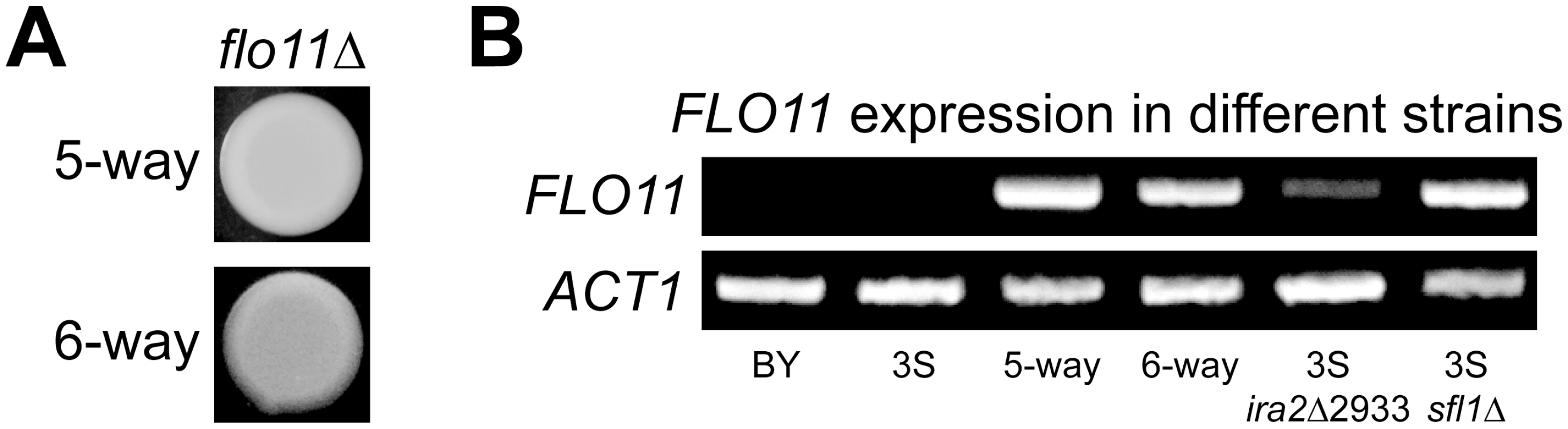
(A) Deletion of FLO11 leads to smooth morphology in both the five- and six-way genetic interaction backgrounds. (B) RT-PCR of FLO11 and the housekeeping gene ACT1 in multiple genetic backgrounds. FLO11 is not expressed in BY or 3S, but is expressed in recombinants that carry the five- and six-way genetic interactions. FLO11 is also expressed in 3S ira2Δ2933 and 3S sfl1Δ strains. ira2Δ2933 and SFL1 deletion cause FLO11 expression in 3S
We tested whether ira2Δ2933 influences FLO11 expression by introducing the lesion into BY and 3S, and conducting RT-PCR (Methods). Each strain remained smooth after this manipulation, which was expected because they both lack a complete set of alleles that can give rise to rough morphology. Furthermore, BY ira2Δ2933 did not express FLO11, likely because this strain carries a nonsense allele of FLO8, the major transcriptional activator of FLO11 [62]. However, introduction of ira2Δ2933 into 3S, which possesses a functional allele of FLO8, converted FLO11 from a silenced to an actively transcribed state (Fig 4B). Given that ira2Δ2933 alleviated repression of FLO11 in 3S, we hypothesized that it might do so by indirectly inhibiting Sfl1, which is thought to negatively regulate FLO11 and other targets of the Ras pathway when Ras signaling is low by recruiting the Ssn6-Tup1 corepressor complex [57], which in turn recruits the histone deacetylase Hda1 [63, 64]. To test this possibility, we deleted SFL1 from 3S. This knockout phenocopied the results of introducing ira2Δ2933 : 3S remained smooth, but expressed FLO11 (Fig 4B). This suggests that iraΔ2933 disrupts Sfl1-mediated transcriptional repression of Ras target genes.
Cryptic genetic variation uncovered by SFL1 deletion
To test whether loss of transcriptional repression by Sfl1 is sufficient to reveal the cryptic higher-order genetic interactions that specify rough morphology, we generated new BYx3S crosses. We first created a BYx3S cross that lacked the IRA2 mutation and screened for rough morphology among thousands of recombinants (Methods). All segregants in this cross were smooth. We then constructed a cross in which BY and 3S carried wild type alleles of IRA2, but had SFL1 deleted (Methods). Rough morphology, as well as a ‘bumpy’ intermediate phenotype that we previously reported (see Figure S4D and S1 Table in [42], as well as S1 Note), segregated in this sfl1Δ cross (Fig 5A). Genotyping of 44 rough sfl1Δ segregants showed that the rough phenotype is expressed in the ira2Δ2933 and sfl1Δ backgrounds largely due to the same cryptic variants (Methods). 43 (98%) of the rough sfl1Δ segregants possessed the genotype END3BY FLO83S MSS11BY TRR13S, which also potentiates the five-way interaction involving ira2Δ2933 (Fig 5B). The other rough sfl1Δ segregant had the genotype END3BY FLO83S MSS11BY TRR1BY, which does not give rise to rough morphology in the presence of ira2Δ2933 (Fig 5B). None of the rough sfl1Δ segregants had a genotype resembling the six-way interaction involving ira2Δ2933. This could have occurred because SFL1BY, which is required for the six-way interaction, is missing from the sfl1Δ cross; our sampling was biased due to the selectively advantageous locus that is linked to END3; or, as the detection of a rough sfl1Δ segregant with the END3BY FLO83S MSS11BY TRR1BY genotype also suggests, ira2Δ2933 and sfl1Δ have similar but not identical molecular effects. Despite these differences between the ira2Δ2933 and sfl1Δ crosses, our results clearly show that transcriptional repression normally suppresses rough morphology and that multiple genes can act as capacitors by disrupting this negative regulation.
Fig. 5. Deletion of SFL1 reveals interacting cryptic variants. 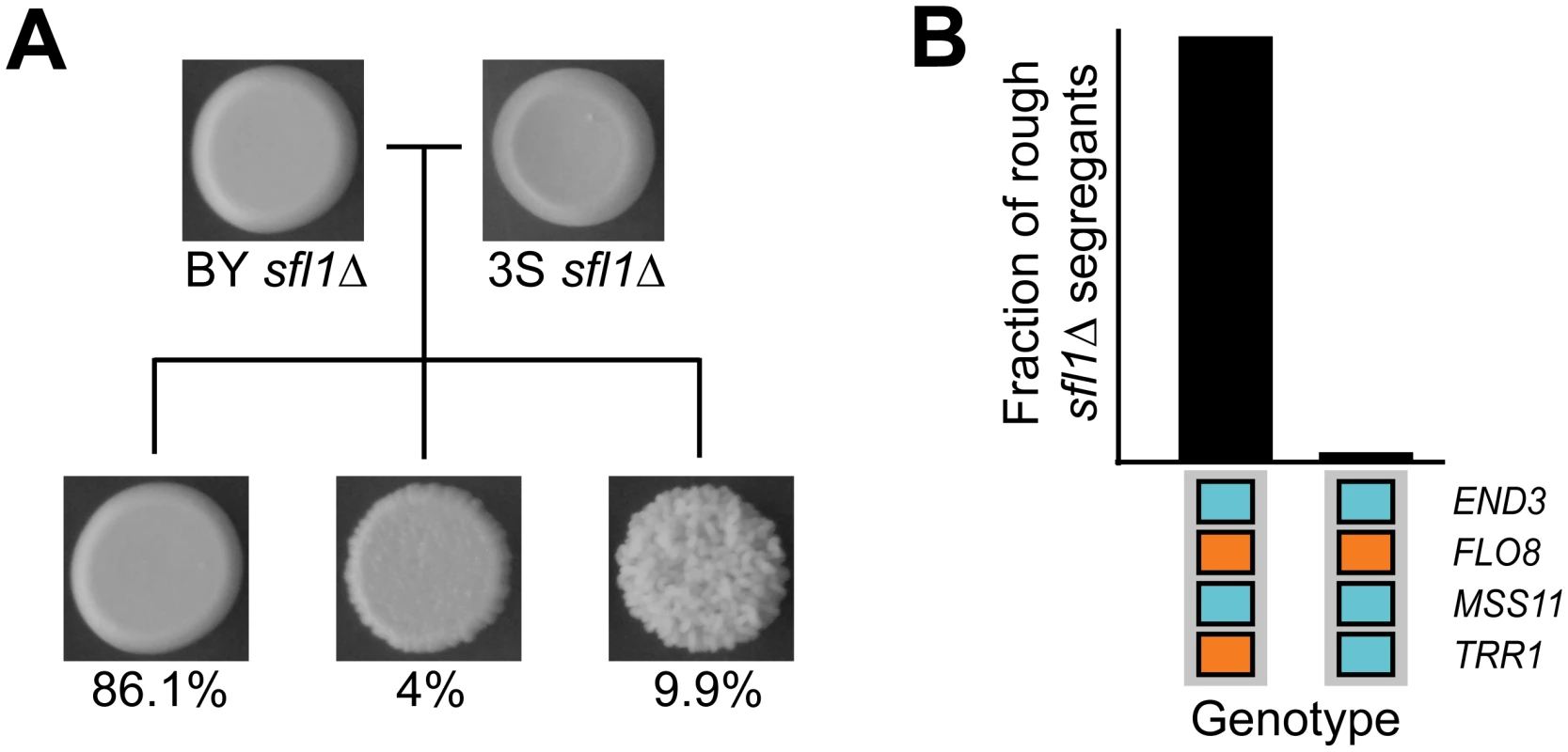
(A) Three phenotypic classes—smooth, bumpy, and rough—were observed among progeny from the BYx3S sfl1Δ cross. The proportion of segregants observed in each phenotypic class is shown below representative pictures for each class. (B) Genotypes observed among rough progeny from the BYx3S sfl1Δ cross. Discussion
Across this manuscript and our previous paper [42], we have cloned six genes that harbor cryptic variants that interact in two specific allele combinations to determine the phenotypic effect of ira2Δ2933. These two genetic backgrounds can be viewed as potentiating genotypes that facilitate the expression of rough morphology in the presence of a capacitating mutation, such as ira2Δ2933. This finding is important because it shows sets of cryptic variants can genetically interact with each other and their capacitating mutation, and implies a conceptual link between capacitance, higher-order genetic interactions, and genetic background effects (Fig 1).
Given that four of the identified genes encode transcription factors, our work suggests complex gene regulatory changes underlie the expression of rough morphology in the BYx3S cross. This finding is consistent with theoretical results that have shown an important role for gene regulatory network perturbation in capacitance [31] and higher-order genetic interactions [65]. In our specific case, the role of ira2Δ2933 is likely to cause transcriptional derepression, which may enable the involved cryptic variants to collectively alter the gene regulatory network underlying colony morphology. Supporting such a role for derepression in the rough phenotype, we have shown that IRA2 is not unique in its ability to act as a capacitor. Rather, SFL1 can also serve as a capacitor of rough morphology, presumably because its deletion also causes transcriptional derepression.
Moving forward, fully understanding capacitance in the BYx3S colony morphology system will likely require defining the gene regulatory network underlying rough morphology and determining how it changes across combinations of cryptic variants and capacitating mutations. Such work can shed light on the individual and collective contributions of the identified cryptic variants to the rough phenotype; may reveal why MGA1BY, SFL1BY, and TRR13S only have phenotypic effects in specific END3 backgrounds; and might further clarify how multiple genes can act as capacitors of the same cryptic variants and trait. More generally, research along these lines has the potential to provide basic insights into how genetically complex, cryptic phenotypes are suppressed and uncovered.
Additionally, to our knowledge, the present study, when considered with [42], represents the first comprehensive genetic characterization of a genetic background effect in any organism. Our work demonstrates how genetic background effects can arise due to complex epistatic relationships between mutations and cryptic variants at multiple modifier loci, as others have previously suggested [43]. Our findings also indicate that multiple epistatic configurations of cryptic variants may enable a given mutation to show a phenotypic effect. Although these results advance understanding of the causes of genetic background effects, determining the generality of these findings will require dissecting other genetic background effects that involve different mutations, species, and traits.
Materials and Methods
Phenotyping of yeast colony morphology
All phenotyping experiments were performed on agar plates containing yeast extract and peptone (YP) with 2% ethanol as the carbon source (YPE). Prior to phenotyping, strains were grown to stationary phase in liquid YP with 2% dextrose (YPD). Cultures were manually pinned onto YPE and allowed to grow for five days at 30°C, and were then imaged using a standard digital camera.
Generation of backcross segregants
Strains with opposite mating types were mixed together on a YPD plate and incubated for four hours at 30°C. A zygote from each cross was obtained by microdissection. To generate segregants, diploids were sporulated at room temperature using standard yeast sporulation procedures [66]. Once sporulation had completed, spore cultures were digested with β-glucuronidase and then plated onto YPE plates at a density of roughly 100 to 200 colonies per plate. Approximately 10 plates were screened per backcross.148 (BY backcross) and 88 (3S backcross) rough segregants were picked manually and streaked to obtain single cell isolates. The mating type of each of these strains was checked to confirm that they were indeed haploid. Segregants from the BY backcross could be either END3BY or END33S. In order to ensure sequenced strains possessed the END33S allele, each segregant was genotyped using a nearby restriction marker (S1 Table). 63 of the 148 BY backcross progeny possessed the END33S allele and were used for genetic mapping. We note that other multicellularity phenotypes (e.g., flocculation) segregated in the backcrosses, but were not strongly correlated with expression of the rough phenotype, implying they have different genetic architectures.
Generation of IRA2 wild type, ira2Δ2933, and sfl1Δ crosses
The BY and 3S strains used in the ira2Δ2933 and sfl1Δ crosses possessed the Synthetic Genetic Array marker system [67], which allowed for generation of large numbers of recombinant MATa progeny. Regarding the IRA2 wild type cross, we re-mated BY and 3S to produce a different diploid than the one used in [42]. For the ira2Δ2933 cross, the lesion was introduced into 3S using allele replacement techniques described below and then this 3S ira2Δ2933 strain was mated to a wild type BY strain. We designed the cross in this way because the ira2Δ2933 mutation originally occurred in the 3S allele of the gene. However, we note that we have never seen evidence for a genetic interaction between ira2Δ2933 and other genetic variants in IRA23S. As for the sfl1Δ cross, we constructed BY and 3S strains that lacked the entire coding region of SFL1 using genetic engineering techniques described below. A BY/3S sfl1Δ/sfl1Δ diploid was then used to generate a population of BYx3S sfl1Δ recombinants. For each of the three crosses described in this section, diploids were generated and sporulated as described for the backcrosses, but sporulations were plated at low density onto YNB plates containing canavanine to select for haploid progeny. These were then replica plated on YPE to phenotype colony morphology. For each cross, around 20 plates containing roughly 100 to 200 colonies were screened.
Bulk segregant mapping of rough morphology in the backcrosses
Each rough END33S segregant from the backcrosses was grown to stationary phase as an individual, clonal culture. Cells from these stationary cultures were then mixed in equimolar fractions by backcross and DNA was extracted from the two pools using Qiagen G-tip columns. Whole genome sequencing libraries were prepared using the Illumina Nextera kit, with each of the backcross segregant pools barcoded with a unique sequence tag. The libraries were mixed together in equimolar fractions and sequenced on an Illumina MiSeq machine by the company Laragen, Inc. using 250 base pair (bp) x 250 bp reads. These sequencing reads were then mapped to the S. cerevisiae S288c reference and 322134S draft genomes (http://www.yeastgenome.org). S288c is the progenitor of BY, and to ensure high quality read mapping, reads from the BY and 3S backcrosses were mapped to S288c and 3S, respectively. Alignments were performed using the Burrows-Wheeler Aligner (BWA) version 7 with options mem -t 20 [68]. Based on these alignments, we obtained 73 - and 122-fold genomic coverage, as determined by the average per site coverages, from the BY and 3S backcross populations, respectively. A custom Python script was used to assess genome-wide allele frequencies at 36,756 high confidence SNPs that had previously been identified by mapping Illumina sequencing reads for 3S to the S288c genome [42] (S2 Note; S2 Table). Loci influencing colony morphology were called as regions enriched at 95% frequency or higher when the data were averaged within running windows of 10 SNPs (S2 Note). Intervals containing causal genes were identified in the R statistical programming environment as the smallest regions that had mean allele frequencies above a threshold of 95% (S3 Note). Subsequent restriction typing experiments focused on individual segregants and the selected loci (see S1 Table) showed that the detected loci were in fact fixed, and that deviations from fixation occurred due to the presence of a small number of sequencing or read mapping errors. We note that Illumina data used for genetic mapping are available through the NCBI Sequence Read Archive under the study accession number SRP062432, as well as the sample accession numbers SAMN03956543 (BY backcross) and SAMN03956544 (3S backcross).
Genetic engineering experiments
To generate allele replacement strains for ARP8, LSC1, MGA1, SFL1, SUF5, and THI80, a backcross segregant that expressed rough morphology due to the six-way genetic interaction was transformed using a modified form of adaptamer-mediated allele replacement [69]. Also, adaptamer-mediated allele replacement was used to introduce the ira2Δ2933 lesion into 3S. Transformations were conducted with two partially overlapping PCR products—a full-length amplicon of the gene of interest that was tailed at the 3’ end with the 5’ portion of the kanMX cassette and a copy of the kanMX cassette that was tailed on the 3’ end with part of the intergenic region downstream of the gene (as shown in Figure S1 of [70]). Knock-ins were identified using selection on G418 and verified by Sanger sequencing. Deletions were constructed using the CORE cassette [71]. Homology tails matching the 60 bases immediately up - and downstream of each gene were attached to the CORE cassette through PCR and introduced into cells using the Lithium Acetate method [72]. Selection for G418 resistance was used to screen for integration of the CORE cassette; correct integration was then checked using PCR. SFL1 was deleted from BY and 3S, while FLO11 was deleted from a nearly isogenic line and a backcross segregant harboring the five - and six-way genetic interactions, respectively. All primers used for genetic engineering are provided in S1 Table.
Genotyping of causal alleles in ira2Δ2933 and sfl1Δ crosses
Markers within END3, FLO8, MGA1, MSS11, SFL1, and TRR1 were genotyped using PCR and restriction digestion (S1 Table). These markers were identified from among the 36,756 high confidence SNPs that differentiate BY and 3S.
RT-PCRs
Strains were grown to stationary phase in liquid YPD media at 30°C and pinned on to YPE agar plates. After four days of growth at 30°C, total RNA was extracted with the Qiagen RNeasy kit. cDNA was then generated with Superscript reverse transcriptase from Life Technologies. ACT1, a well-known housekeeping gene, was used as a control for our FLO11 RT-PCRs. Strains that were used in the RT-PCR experiments are described in the main text. The specific primers that we used were taken from [73] and are provided in S1 Table.
Supporting Information
Zdroje
1. Gibson G, Dworkin I. Uncovering cryptic genetic variation. Nature reviews Genetics. 2004;5(9):681–90. 15372091
2. Paaby AB, Rockman MV. Cryptic genetic variation: evolution's hidden substrate. Nature reviews Genetics. 2014;15(4):247–58. doi: 10.1038/nrg3688 24614309
3. Hermisson J, Wagner GP. The population genetic theory of hidden variation and genetic robustness. Genetics. 2004;168(4):2271–84. 15611191
4. Queitsch C, Sangster TA, Lindquist S. Hsp90 as a capacitor of phenotypic variation. Nature. 2002;417(6889):618–24. 12050657
5. Sangster TA, Salathia N, Lee HN, Watanabe E, Schellenberg K, Morneau K, et al. HSP90-buffered genetic variation is common in Arabidopsis thaliana. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2008;105(8):2969–74. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0712210105 18287064
6. Sangster TA, Salathia N, Undurraga S, Milo R, Schellenberg K, Lindquist S, et al. HSP90 affects the expression of genetic variation and developmental stability in quantitative traits. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2008;105(8):2963–8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0712200105 18287065
7. Felix MA. Cryptic quantitative evolution of the vulva intercellular signaling network in Caenorhabditis. Current biology: CB. 2007;17(2):103–14. 17240335
8. Milloz J, Duveau F, Nuez I, Felix MA. Intraspecific evolution of the intercellular signaling network underlying a robust developmental system. Genes & development. 2008;22(21):3064–75. 18981482
9. Duveau F, Felix MA. Role of pleiotropy in the evolution of a cryptic developmental variation in Caenorhabditis elegans. PLoS biology. 2012;10(1):e1001230. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1001230 22235190
10. Waddington CH. Genetic assimilation of an acquired character. Evolution. 1953;7(2):118–26.
11. Rutherford SL, Lindquist S. Hsp90 as a capacitor for morphological evolution. Nature. 1998;396(6709):336–42. 9845070
12. Gibson G, Hogness DS. Effect of polymorphism in the Drosophila regulatory gene Ultrabithorax on homeotic stability. Science. 1996;271(5246):200–3. 8539619
13. Gibson G, Wemple M, van Helden S. Potential variance affecting homeotic Ultrabithorax and Antennapedia phenotypes in Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics. 1999;151(3):1081–91. 10049924
14. Dworkin I, Palsson A, Birdsall K, Gibson G. Evidence that Egfr contributes to cryptic genetic variation for photoreceptor determination in natural populations of Drosophila melanogaster. Current biology: CB. 2003;13(21):1888–93. 14588245
15. Tirosh I, Reikhav S, Sigal N, Assia Y, Barkai N. Chromatin regulators as capacitors of interspecies variations in gene expression. Molecular systems biology. 2010;6 : 435. doi: 10.1038/msb.2010.84 21119629
16. Halfmann R, Jarosz DF, Jones SK, Chang A, Lancaster AK, Lindquist S. Prions are a common mechanism for phenotypic inheritance in wild yeasts. Nature. 2012;482(7385):363–8. doi: 10.1038/nature10875 22337056
17. Jarosz DF, Lindquist S. Hsp90 and environmental stress transform the adaptive value of natural genetic variation. Science. 2010;330(6012):1820–4. doi: 10.1126/science.1195487 21205668
18. True HL, Lindquist SL. A yeast prion provides a mechanism for genetic variation and phenotypic diversity. Nature. 2000;407(6803):477–83. 11028992
19. True HL, Berlin I, Lindquist SL. Epigenetic regulation of translation reveals hidden genetic variation to produce complex traits. Nature. 2004;431(7005):184–7. 15311209
20. Ledon-Rettig CC, Pfennig DW, Crespi EJ. Diet and hormonal manipulation reveal cryptic genetic variation: implications for the evolution of novel feeding strategies. Proceedings of the royal society. 2010;277(1700):3569–78. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2010.0877 20573627
21. Lauter N, Doebley J. Genetic variation for phenotypically invariant traits detected in teosinte: implications for the evolution of novel forms. Genetics. 2002;160(1):333–42. 11805068
22. Rohner N, Jarosz DF, Kowalko JE, Yoshizawa M, Jeffery WR, Borowsky RL, et al. Cryptic variation in morphological evolution: HSP90 as a capacitor for loss of eyes in cavefish. Science. 2013;342(6164):1372–5. doi: 10.1126/science.1240276 24337296
23. Rosas U, Barton NH, Copsey L, Barbier de Reuille P, Coen E. Cryptic variation between species and the basis of hybrid performance. PLoS biology. 2010;8(7):e1000429. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1000429 20652019
24. Suzuki Y, Nijhout HF. Evolution of a polyphenism by genetic accommodation. Science. 2006;311(5761):650–2. 16456077
25. Berger D, Bauerfeind SS, Blanckenhorn WU, Schafer MA. High temperatures reveal cryptic genetic variation in a polymorphic female sperm storage organ. Evolution. 2011;65(10):2830–42. doi: 10.1111/j.1558-5646.2011.01392.x 21967425
26. Kienle S, Sommer RJ. Cryptic variation in vulva development by cis-regulatory evolution of a HAIRY-binding site. Nature communications. 2013;4 : 1714. doi: 10.1038/ncomms2711 23591881
27. Moczek AP. On the origins of novelty in development and evolution. BioEssays. 2008;30(5):432–47.
28. Le Rouzic A, Carlborg O. Evolutionary potential of hidden genetic variation. Trends in ecology & evolution. 2008;23(1):33–7. 18079017
29. Ehrenreich IM, Pfennig DW. Genetic assimilation: a review of its potential proximate causes and evolutionary consequences. Annals of botany. 2015.
30. Gibson G. Decanalization and the origin of complex disease. Nature reviews Genetics. 2009;10(2):134–40. doi: 10.1038/nrg2502 19119265
31. Bergman A, Siegal ML. Evolutionary capacitance as a general feature of complex gene networks. Nature. 2003;424(6948):549–52. 12891357
32. Sangster TA, Lindquist S, Queitsch C. Under cover: causes, effects and implications of Hsp90-mediated genetic capacitance. BioEssays. 2004;26(4):348–62.
33. Richardson JB, Uppendahl LD, Traficante MK, Levy SF, Siegal ML. Histone variant HTZ1 shows extensive epistasis with, but does not increase robustness to, new mutations. PLoS genetics. 2013;9(8):e1003733. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1003733 23990806
34. Sollars V, Lu X, Xiao L, Wang X, Garfinkel MD, Ruden DM. Evidence for an epigenetic mechanism by which Hsp90 acts as a capacitor for morphological evolution. Nature genetics. 2003;33(1):70–4. 12483213
35. Cowen LE, Lindquist S. Hsp90 potentiates the rapid evolution of new traits: drug resistance in diverse fungi. Science. 2005;309(5744):2185–9. 16195452
36. Jarosz DF, Taipale M, Lindquist S. Protein homeostasis and the phenotypic manifestation of genetic diversity: principles and mechanisms. Annual review of genetics. 2010;44 : 189–216. doi: 10.1146/annurev.genet.40.110405.090412 21047258
37. Blount ZD, Borland CZ, Lenski RE. Historical contingency and the evolution of a key innovation in an experimental population of Escherichia coli. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2008;105(23):7899–906. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0803151105 18524956
38. Dworkin I. Towards a genetic architecture of cryptic genetic variation and genetic assimilation: the contribution of K. G. Bateman. Journal of genetics. 2005;84(3):223–6. 16385156
39. Taylor MB, Ehrenreich IM. Higher-order genetic interactions and their contribution to complex traits. Trends in genetics. 2015;31(1):34–40. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2014.09.001 25284288
40. Chandler CH, Chari S, Dworkin I. Does your gene need a background check? How genetic background impacts the analysis of mutations, genes, and evolution. Trends in genetics. 2013;29(6):358–66. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2013.01.009 23453263
41. Dowell RD, Ryan O, Jansen A, Cheung D, Agarwala S, Danford T, et al. Genotype to phenotype: a complex problem. Science. 2010;328(5977):469. doi: 10.1126/science.1189015 20413493
42. Taylor MB, Ehrenreich IM. Genetic interactions involving five or more genes contribute to a complex trait in yeast. PLoS genetics. 2014;10(5):e1004324. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1004324 24784154
43. Chandler CH, Chari S, Tack D, Dworkin I. Causes and consequences of genetic background effects illuminated by integrative genomic analysis. Genetics. 2014;196(4):1321–36. doi: 10.1534/genetics.113.159426 24504186
44. Tanaka K, Nakafuku M, Satoh T, Marshall MS, Gibbs JB, Matsumoto K, et al. S. cerevisiae genes IRA1 and IRA2 encode proteins that may be functionally equivalent to mammalian ras GTPase activating protein. Cell. 1990;60(5):803–7. 2178777
45. Tanaka K, Nakafuku M, Tamanoi F, Kaziro Y, Matsumoto K, Toh-e A. IRA2, a second gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae that encodes a protein with a domain homologous to mammalian ras GTPase-activating protein. Molecular and cellular biology. 1990;10(8):4303–13. 2164637
46. Liti G, Carter DM, Moses AM, Warringer J, Parts L, James SA, et al. Population genomics of domestic and wild yeasts. Nature. 2009;458(7236):337–41. doi: 10.1038/nature07743 19212322
47. Schacherer J, Shapiro JA, Ruderfer DM, Kruglyak L. Comprehensive polymorphism survey elucidates population structure of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nature. 2009;458(7236):342–5. doi: 10.1038/nature07670 19212320
48. Kobayashi O, Suda H, Ohtani T, Sone H. Molecular cloning and analysis of the dominant flocculation gene FLO8 from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Molecular & general genetics. 1996;251(6):707–15. 8757402
49. Gagiano M, Bester M, van Dyk D, Franken J, Bauer FF, Pretorius IS. Mss11p is a transcription factor regulating pseudohyphal differentiation, invasive growth and starch metabolism in Saccharomyces cerevisiae in response to nutrient availability. Molecular microbiology. 2003;47(1):119–34. 12492858
50. Benedetti H, Raths S, Crausaz F, Riezman H. The END3 gene encodes a protein that is required for the internalization step of endocytosis and for actin cytoskeleton organization in yeast. Molecular biology of the cell. 1994;5(9):1023–37. 7841519
51. Tang HY, Xu J, Cai M. Pan1p, End3p, and S1a1p, three yeast proteins required for normal cortical actin cytoskeleton organization, associate with each other and play essential roles in cell wall morphogenesis. Molecular and cellular biology. 2000;20(1):12–25. 10594004
52. Pedrajas JR, Kosmidou E, Miranda-Vizuete A, Gustafsson JA, Wright AP, Spyrou G. Identification and functional characterization of a novel mitochondrial thioredoxin system in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. The Journal of biological chemistry. 1999;274(10):6366–73. 10037727
53. Pan X, Heitman J. Protein kinase A operates a molecular switch that governs yeast pseudohyphal differentiation. Molecular and cellular biology. 2002;22(12):3981–93. 12024012
54. Robertson LS, Fink GR. The three yeast A kinases have specific signaling functions in pseudohyphal growth. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 1998;95(23):13783–7. 9811878
55. Lorenz MC, Heitman J. Regulators of pseudohyphal differentiation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae identified through multicopy suppressor analysis in ammonium permease mutant strains. Genetics. 1998;150(4):1443–57. 9832522
56. Fujita A, Kikuchi Y, Kuhara S, Misumi Y, Matsumoto S, Kobayashi H. Domains of the SFL1 protein of yeasts are homologous to Myc oncoproteins or yeast heat-shock transcription factor. Gene. 1989;85(2):321–8. 2697640
57. Conlan RS, Tzamarias D. Sfl1 functions via the co-repressor Ssn6-Tup1 and the cAMP-dependent protein kinase Tpk2. Journal of molecular biology. 2001;309(5):1007–15. 11399075
58. Michelmore RW, Paran I, Kesseli RV. Identification of markers linked to disease-resistance genes by bulked segregant analysis: a rapid method to detect markers in specific genomic regions by using segregating populations. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 1991;88(21):9828–32. 1682921
59. Ehrenreich IM, Torabi N, Jia Y, Kent J, Martis S, Shapiro JA, et al. Dissection of genetically complex traits with extremely large pools of yeast segregants. Nature. 2010;464(7291):1039–42. doi: 10.1038/nature08923 20393561
60. Lo WS, Dranginis AM. FLO11, a yeast gene related to the STA genes, encodes a novel cell surface flocculin. Journal of bacteriology. 1996;178(24):7144–51. 8955395
61. Bruckner S, Mosch HU. Choosing the right lifestyle: adhesion and development in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. FEMS microbiology reviews. 2012;36(1):25–58. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6976.2011.00275.x 21521246
62. Liu H, Styles CA, Fink GR. Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288C has a mutation in FLO8, a gene required for filamentous growth. Genetics. 1996;144(3):967–78. 8913742
63. Halme A, Bumgarner S, Styles C, Fink GR. Genetic and epigenetic regulation of the FLO gene family generates cell-surface variation in yeast. Cell. 2004;116(3):405–15. 15016375
64. Wu J, Suka N, Carlson M, Grunstein M. TUP1 utilizes histone H3/H2B-specific HDA1 deacetylase to repress gene activity in yeast. Molecular cell. 2001;7(1):117–26. 11172717
65. Gjuvsland AB, Hayes BJ, Omholt SW, Carlborg O. Statistical epistasis is a generic feature of gene regulatory networks. Genetics. 2007;175(1):411–20. 17028346
66. Sherman F. Guide to Yeast Genetics and Molecular. In: Guthrie C, Fink GR, editors. Methods in enzymology. San Diego, California: Elsevier Academic Press; 1991. p. 3–21.
67. Tong AH, Evangelista M, Parsons AB, Xu H, Bader GD, Page N, et al. Systematic genetic analysis with ordered arrays of yeast deletion mutants. Science. 2001;294(5550):2364–8. 11743205
68. Li H, Durbin R. Fast and accurate short read alignment with Burrows-Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics. 2009;25(14):1754–60. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp324 19451168
69. Erdeniz N, Mortensen UH, Rothstein R. Cloning-free PCR-based allele replacement methods. Genome research. 1997;7(12):1174–83. 9414323
70. Matsui T, Linder R, Phan J, Seidl F, Ehrenreich IM. Regulatory Rewiring in a Cross Causes Extensive Genetic Heterogeneity. Genetics. 2015. 26232408
71. Storici F, Lewis LK, Resnick MA. In vivo site-directed mutagenesis using oligonucleotides. Nature biotechnology. 2001;19(8):773–6. 11479573
72. Gietz RD, Woods RA. Transformation of yeast by lithium acetate/single-stranded carrier DNA/polyethylene glycol method. Methods in enzymology. 2002;350 : 87–96. 12073338
73. Fichtner L, Schulze F, Braus GH. Differential Flo8p-dependent regulation of FLO1 and FLO11 for cell-cell and cell-substrate adherence of S. cerevisiae S288c. Molecular microbiology. 2007;66(5):1276–89. 18001350
Štítky
Genetika Reprodukční medicína
Článek Evidence of Selection against Complex Mitotic-Origin Aneuploidy during Preimplantation DevelopmentČlánek A Novel Route Controlling Begomovirus Resistance by the Messenger RNA Surveillance Factor PelotaČlánek A Follicle Rupture Assay Reveals an Essential Role for Follicular Adrenergic Signaling in OvulationČlánek Canonical Poly(A) Polymerase Activity Promotes the Decay of a Wide Variety of Mammalian Nuclear RNAsČlánek FANCI Regulates Recruitment of the FA Core Complex at Sites of DNA Damage Independently of FANCD2Článek Hsp90-Associated Immunophilin Homolog Cpr7 Is Required for the Mitotic Stability of [URE3] Prion inČlánek The Dedicated Chaperone Acl4 Escorts Ribosomal Protein Rpl4 to Its Nuclear Pre-60S Assembly SiteČlánek Chromatin-Remodelling Complex NURF Is Essential for Differentiation of Adult Melanocyte Stem CellsČlánek A Systems Approach Identifies Essential FOXO3 Functions at Key Steps of Terminal ErythropoiesisČlánek Integration of Posttranscriptional Gene Networks into Metabolic Adaptation and Biofilm Maturation inČlánek Lateral and End-On Kinetochore Attachments Are Coordinated to Achieve Bi-orientation in OocytesČlánek MET18 Connects the Cytosolic Iron-Sulfur Cluster Assembly Pathway to Active DNA Demethylation in
Článek vyšel v časopisePLOS Genetics
Nejčtenější tento týden
2015 Číslo 10
-
Všechny články tohoto čísla
- Gene-Regulatory Logic to Induce and Maintain a Developmental Compartment
- A Decad(e) of Reasons to Contribute to a PLOS Community-Run Journal
- DNA Methylation Landscapes of Human Fetal Development
- Single Strand Annealing Plays a Major Role in RecA-Independent Recombination between Repeated Sequences in the Radioresistant Bacterium
- Evidence of Selection against Complex Mitotic-Origin Aneuploidy during Preimplantation Development
- Transcriptional Derepression Uncovers Cryptic Higher-Order Genetic Interactions
- Silencing of X-Linked MicroRNAs by Meiotic Sex Chromosome Inactivation
- Virus Satellites Drive Viral Evolution and Ecology
- A Novel Route Controlling Begomovirus Resistance by the Messenger RNA Surveillance Factor Pelota
- Sequence to Medical Phenotypes: A Framework for Interpretation of Human Whole Genome DNA Sequence Data
- Your Data to Explore: An Interview with Anne Wojcicki
- Modulation of Ambient Temperature-Dependent Flowering in by Natural Variation of
- The Ciliopathy Protein CC2D2A Associates with NINL and Functions in RAB8-MICAL3-Regulated Vesicle Trafficking
- PPP2R5C Couples Hepatic Glucose and Lipid Homeostasis
- DCA1 Acts as a Transcriptional Co-activator of DST and Contributes to Drought and Salt Tolerance in Rice
- Intermediate Levels of CodY Activity Are Required for Derepression of the Branched-Chain Amino Acid Permease, BraB
- "Missing" G x E Variation Controls Flowering Time in
- The Rise and Fall of an Evolutionary Innovation: Contrasting Strategies of Venom Evolution in Ancient and Young Animals
- Type IV Collagen Controls the Axogenesis of Cerebellar Granule Cells by Regulating Basement Membrane Integrity in Zebrafish
- Loss of a Conserved tRNA Anticodon Modification Perturbs Plant Immunity
- Genome-Wide Association Analysis of Adaptation Using Environmentally Predicted Traits
- Oriented Cell Division in the . Embryo Is Coordinated by G-Protein Signaling Dependent on the Adhesion GPCR LAT-1
- Disproportionate Contributions of Select Genomic Compartments and Cell Types to Genetic Risk for Coronary Artery Disease
- A Follicle Rupture Assay Reveals an Essential Role for Follicular Adrenergic Signaling in Ovulation
- The RNAPII-CTD Maintains Genome Integrity through Inhibition of Retrotransposon Gene Expression and Transposition
- Canonical Poly(A) Polymerase Activity Promotes the Decay of a Wide Variety of Mammalian Nuclear RNAs
- Allelic Variation of Cytochrome P450s Drives Resistance to Bednet Insecticides in a Major Malaria Vector
- SCARN a Novel Class of SCAR Protein That Is Required for Root-Hair Infection during Legume Nodulation
- IBR5 Modulates Temperature-Dependent, R Protein CHS3-Mediated Defense Responses in
- NINL and DZANK1 Co-function in Vesicle Transport and Are Essential for Photoreceptor Development in Zebrafish
- Decay-Initiating Endoribonucleolytic Cleavage by RNase Y Is Kept under Tight Control via Sequence Preference and Sub-cellular Localisation
- Large-Scale Analysis of Kinase Signaling in Yeast Pseudohyphal Development Identifies Regulation of Ribonucleoprotein Granules
- FANCI Regulates Recruitment of the FA Core Complex at Sites of DNA Damage Independently of FANCD2
- LINE-1 Mediated Insertion into (Protein of Centriole 1 A) Causes Growth Insufficiency and Male Infertility in Mice
- Hsp90-Associated Immunophilin Homolog Cpr7 Is Required for the Mitotic Stability of [URE3] Prion in
- Genome-Scale Mapping of σ Reveals Widespread, Conserved Intragenic Binding
- Uncovering Hidden Layers of Cell Cycle Regulation through Integrative Multi-omic Analysis
- Functional Diversification of Motor Neuron-specific Enhancers during Evolution
- The GTP- and Phospholipid-Binding Protein TTD14 Regulates Trafficking of the TRPL Ion Channel in Photoreceptor Cells
- The Gyc76C Receptor Guanylyl Cyclase and the Foraging cGMP-Dependent Kinase Regulate Extracellular Matrix Organization and BMP Signaling in the Developing Wing of
- The Ty1 Retrotransposon Restriction Factor p22 Targets Gag
- Functional Impact and Evolution of a Novel Human Polymorphic Inversion That Disrupts a Gene and Creates a Fusion Transcript
- The Dedicated Chaperone Acl4 Escorts Ribosomal Protein Rpl4 to Its Nuclear Pre-60S Assembly Site
- The Influence of Age and Sex on Genetic Associations with Adult Body Size and Shape: A Large-Scale Genome-Wide Interaction Study
- Parent-of-Origin Effects of the Gene on Adiposity in Young Adults
- Chromatin-Remodelling Complex NURF Is Essential for Differentiation of Adult Melanocyte Stem Cells
- Retinoic Acid Receptors Control Spermatogonia Cell-Fate and Induce Expression of the SALL4A Transcription Factor
- A Systems Approach Identifies Essential FOXO3 Functions at Key Steps of Terminal Erythropoiesis
- Protein O-Glucosyltransferase 1 (POGLUT1) Promotes Mouse Gastrulation through Modification of the Apical Polarity Protein CRUMBS2
- KIF7 Controls the Proliferation of Cells of the Respiratory Airway through Distinct Microtubule Dependent Mechanisms
- Integration of Posttranscriptional Gene Networks into Metabolic Adaptation and Biofilm Maturation in
- Lateral and End-On Kinetochore Attachments Are Coordinated to Achieve Bi-orientation in Oocytes
- Protein Homeostasis Imposes a Barrier on Functional Integration of Horizontally Transferred Genes in Bacteria
- A New Method for Detecting Associations with Rare Copy-Number Variants
- Histone H2AFX Links Meiotic Chromosome Asynapsis to Prophase I Oocyte Loss in Mammals
- The Genomic Aftermath of Hybridization in the Opportunistic Pathogen
- A Role for the Chaperone Complex BAG3-HSPB8 in Actin Dynamics, Spindle Orientation and Proper Chromosome Segregation during Mitosis
- Establishment of a Developmental Compartment Requires Interactions between Three Synergistic -regulatory Modules
- Regulation of Spore Formation by the SpoIIQ and SpoIIIA Proteins
- Association of the Long Non-coding RNA Steroid Receptor RNA Activator (SRA) with TrxG and PRC2 Complexes
- Alkaline Ceramidase 3 Deficiency Results in Purkinje Cell Degeneration and Cerebellar Ataxia Due to Dyshomeostasis of Sphingolipids in the Brain
- ACLY and ACC1 Regulate Hypoxia-Induced Apoptosis by Modulating ETV4 via α-ketoglutarate
- Quantitative Differences in Nuclear β-catenin and TCF Pattern Embryonic Cells in .
- HENMT1 and piRNA Stability Are Required for Adult Male Germ Cell Transposon Repression and to Define the Spermatogenic Program in the Mouse
- Axon Regeneration Is Regulated by Ets–C/EBP Transcription Complexes Generated by Activation of the cAMP/Ca Signaling Pathways
- A Phenomic Scan of the Norfolk Island Genetic Isolate Identifies a Major Pleiotropic Effect Locus Associated with Metabolic and Renal Disorder Markers
- The Roles of CDF2 in Transcriptional and Posttranscriptional Regulation of Primary MicroRNAs
- A Genetic Cascade of Modulates Nucleolar Size and rRNA Pool in
- Inter-population Differences in Retrogene Loss and Expression in Humans
- Cationic Peptides Facilitate Iron-induced Mutagenesis in Bacteria
- EP4 Receptor–Associated Protein in Macrophages Ameliorates Colitis and Colitis-Associated Tumorigenesis
- Fungal Infection Induces Sex-Specific Transcriptional Changes and Alters Sexual Dimorphism in the Dioecious Plant
- FLCN and AMPK Confer Resistance to Hyperosmotic Stress via Remodeling of Glycogen Stores
- MET18 Connects the Cytosolic Iron-Sulfur Cluster Assembly Pathway to Active DNA Demethylation in
- Sex Bias and Maternal Contribution to Gene Expression Divergence in Blastoderm Embryos
- Transcriptional and Linkage Analyses Identify Loci that Mediate the Differential Macrophage Response to Inflammatory Stimuli and Infection
- Mre11 and Blm-Dependent Formation of ALT-Like Telomeres in Ku-Deficient
- Genome Wide Identification of SARS-CoV Susceptibility Loci Using the Collaborative Cross
- Identification of a Single Strand Origin of Replication in the Integrative and Conjugative Element ICE of
- The Type VI Secretion TssEFGK-VgrG Phage-Like Baseplate Is Recruited to the TssJLM Membrane Complex via Multiple Contacts and Serves As Assembly Platform for Tail Tube/Sheath Polymerization
- The Dynamic Genome and Transcriptome of the Human Fungal Pathogen and Close Relative
- Secondary Structure across the Bacterial Transcriptome Reveals Versatile Roles in mRNA Regulation and Function
- ROS-Induced JNK and p38 Signaling Is Required for Unpaired Cytokine Activation during Regeneration
- Pelle Modulates dFoxO-Mediated Cell Death in
- PLOS Genetics
- Archiv čísel
- Aktuální číslo
- Informace o časopisu
Nejčtenější v tomto čísle- Single Strand Annealing Plays a Major Role in RecA-Independent Recombination between Repeated Sequences in the Radioresistant Bacterium
- The Rise and Fall of an Evolutionary Innovation: Contrasting Strategies of Venom Evolution in Ancient and Young Animals
- Genome Wide Identification of SARS-CoV Susceptibility Loci Using the Collaborative Cross
- DCA1 Acts as a Transcriptional Co-activator of DST and Contributes to Drought and Salt Tolerance in Rice
Kurzy
Zvyšte si kvalifikaci online z pohodlí domova
Současné možnosti léčby obezity
nový kurzAutoři: MUDr. Martin Hrubý
Všechny kurzyPřihlášení#ADS_BOTTOM_SCRIPTS#Zapomenuté hesloZadejte e-mailovou adresu, se kterou jste vytvářel(a) účet, budou Vám na ni zaslány informace k nastavení nového hesla.
- Vzdělávání



