-
Články
Top novinky
Reklama- Vzdělávání
- Časopisy
Top články
Nové číslo
- Témata
Top novinky
Reklama- Videa
- Podcasty
Nové podcasty
Reklama- Kariéra
Doporučené pozice
Reklama- Praxe
Top novinky
ReklamaPelle Modulates dFoxO-Mediated Cell Death in
In the present study we report a Toll pathway independent function of Pll in modulating apoptotic cell death. Our major findings include: 1) loss of pll generates Toll pathway-independent wing phenotypes, which are caused by a reduction in cell number but not cell size; 2) depletion of pll up-regulates the transcription of pro-apoptotic genes hid, reaper and grim, and triggers caspase-mediated cell death, whereas cell proliferation remains unaffected; 3) pll modulates caspase activation and cell death through the transcription factor dFoxO; 4) loss of pll promotes dFoxO translocation from cytoplasm to nucleus, and activates the transcription of dFoxO target gene Thor/4E-BP; 5) Pll physically interacts with dFoxO and phosphorylates dFoxO directly. Thus, this work characterizes a previously unknown physiological function of pll that is independent of the Toll pathway.
Published in the journal: . PLoS Genet 11(10): e32767. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1005589
Category: Research Article
doi: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1005589Summary
In the present study we report a Toll pathway independent function of Pll in modulating apoptotic cell death. Our major findings include: 1) loss of pll generates Toll pathway-independent wing phenotypes, which are caused by a reduction in cell number but not cell size; 2) depletion of pll up-regulates the transcription of pro-apoptotic genes hid, reaper and grim, and triggers caspase-mediated cell death, whereas cell proliferation remains unaffected; 3) pll modulates caspase activation and cell death through the transcription factor dFoxO; 4) loss of pll promotes dFoxO translocation from cytoplasm to nucleus, and activates the transcription of dFoxO target gene Thor/4E-BP; 5) Pll physically interacts with dFoxO and phosphorylates dFoxO directly. Thus, this work characterizes a previously unknown physiological function of pll that is independent of the Toll pathway.
Introduction
Interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinases (IRAKs) are evolutionarily conserved Serine/Threonine (Ser/Thr) kinases that modulates Toll-like receptors (TLRs) and interleukin-1 receptors (IL-1Rs) signaling in the immune and inflammation response [1–3]. IRAKs transduce TLR/IL-1R signals to regulate subcellular distribution and activity of NF-κB transcription factor family via highly conserved downstream signaling molecules, including IκB kinase (IκK) complex and IκB [4,5]. While there are four IRAK family members (IRAK-1, IRAK-2, IRAK-4 and IRAK-M) in mammals, Pelle (Pll) is the only IRAK homolog in Drosophila [6]. Although Tube was initially characterized as a Drosophila IRAK homolog, it lacks the catalytic domain and thus functions as an adaptor protein in the Toll pathway [7]. As such, Drosophila melanogaster offers unique opportunities to investigate the physiological functions of IRAK with reduced genetic redundancy.
The Toll pathway in Drosophila has been implicated as a crucial regulator in embryonic Dorsal/Ventral (D/V) patterning [8,9], innate immune response against Gram-positive bacteria and fungi [10], proper muscle development and axon guidance [11,12]. This pathway is equivalent to the mammalian IL-1R/TLR pathway, with Toll/Cactus/Dorsal representing the respective homologs of IL-1R/IκB/NF-κB [13]. However, the Drosophila IκK is not involved in the Toll pathway [14,15], and Pll has been shown to be the only kinase implicated in Cactus phosphorylation [6,16]. Besides its role in the conserved pathway, it remains unknown whether Pll performs any Toll pathway independent functions in vivo.
Programmed cell death (PCD) or apoptosis is an important physiological regulator for tissue homeostasis and correct development. Cancer cells generally obtain the ability to evade cell death signaling pathways, which act as a protective tumor suppressive mechanism to remove damaged cells from the tissue. The central roles of caspases (cysteine aspartate-specific proteinases) have been widely studied in the context of apoptosis, and the core machinery of caspases signaling pathway, including the initiator caspases and the effector caspases, has been conserved throughout evolution [17,18]. In Drosophila, apoptosis is activated by the intrinsic and extrinsic cell death signals through transcriptional up-regulation of three pro-apoptotic genes reaper (rpr), head involution defective (hid) and grim [19]. Rpr, Hid and Grim (RHG) proteins subsequently bind to and antagonize the Drosophila inhibitor of apoptosis protein 1 (DIAP1), which in turn dampens caspases [20,21]. DIAP1 functions as an E3-ubiquitin ligase to block cell death by targeting the initiator caspase Dronc (Drosophila caspase-9) for degradation, and thus suppresses the activation of the downstream effector caspase Drice (Drosophila caspase-3) [22,23]. Hence, apoptosis is the consequence of a train of complex interactions between RHG proteins, DIAP1 and caspases in Drosophila.
Forkhead Box O (FoxO) transcription factors were originally identified in C. elegans as DAF-16 for its role in aging, and have been highly conserved in Drosophila (dFoxO) and mammals (FoxO1, FoxO3a, FoxO4 and FoxO6) [24–28]. FoxO proteins are known to modulate various physiological processes including cell proliferation and differentiation, DNA repair, apoptosis, metabolism, oxidative stress and lifespan [25,26,28–33]. In general, the multiple functions of FoxO transcription factors are regulated by various post-translational modifications (PTMs), including methylation, acetylation, ubiquitination, glycosylation and phosphorylation [34]. For example, FoxOs are targeted for phosphorylation by a number of kinases in response to different cellular stresses, which in turn regulate the nuclear-cytoplasmic shuttling of FoxOs and their transcriptional activity [34]. In Drosophila, dFoxO was reported as a key modulator in the UV-induced caspase-mediated apoptotic response by directly regulating the expression of pro-apoptotic gene hid [30].
In this study, we examined the physiological function of pelle (pll) in Drosophila development, and found that pll negatively regulates FoxO-mediated apoptotic cell death in vivo. First, loss of pll in the developing wing generates Toll/NF-κB pathway independent phenotypes, which are caused by a reduction in cell number but not cell size. Secondly, depletion of pll triggers caspase-mediated cell death, whereas cell proliferation remains unaffected. Thirdly, pll modulates caspase activation and cell death through dFoxO. Fourthly, loss of pll results in activation of dFoxO, as manifested by its translocation from cytoplasm to nucleus and the expression of its target gene Thor/4E-BP. Finally, Pll physically interacts with and phosphorylates on dFoxO, which likely contributes to the cytoplasmic retention of dFoxO. Therefore, we have identified a previously uncharacterized physiological function of pll in cell death, which is independent of the canonical Toll/NF-κB pathway.
Results
Loss of pll produces Toll pathway-independent wing phenotype
As a crucial component of the Toll pathway, Pll is known to regulate the dorsal-ventral polarity in early embryos [35] and the immune response in fat body [10]. Despite its ubiquitous lower level expression throughout development [6], the post-embryonic functions of Pll remain poorly understood. To explore the physiological function of pll in late development, we employed the UAS/Gal4 binary system to knockdown pll in a specific temporal and spatial manner. We found that expression of a pll RNA interference (RNAi) driven by ptc-Gal4 (ptc>pll-IR) along the anterior/posterior (A/P) compartment boundary resulted in a consistent loss of anterior cross-vein (ACV) phenotype (Fig 1C and 1M), compared with ptc-Gal4 control (Fig 1A) or RFP expression (Fig 1B). To exclude the possibility that the phenotype is a result of RNAi’s off-target effect, we examined two additional pll RNAi that target distinct regions of the pll transcript, and observed the same loss-of-ACV phenotype (S1A, S1F and S1H Fig). In addition, this phenotype could be rescued by expression of Pll (Fig 1D and 1M; S1G and S1H Fig), which by itself has no effect on ACV development (Fig 1E and 1M). The knock-down efficiencies of three pll RNAi lines were verified by their abilities to suppress the GMR>Pll rough eye phenotype (S2A–S2E Fig) and by real-time quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) assay (S2L Fig). To further verify the physiological function of pll in ACV development, we examined two pll mutant alleles: pll2 and pll7. While the heterozygous mutants show no obvious ACV defect, they could significantly increase the percentage of loss-of-ACV phenotype in the ptc>pll-IRW background (S1A–S1E and S1H Fig). Together these data suggest that pll is physiologically required for ACV development in Drosophila wing.
Fig. 1. Loss of pll produces Toll/NF-κB pathway independent wing phenotype. 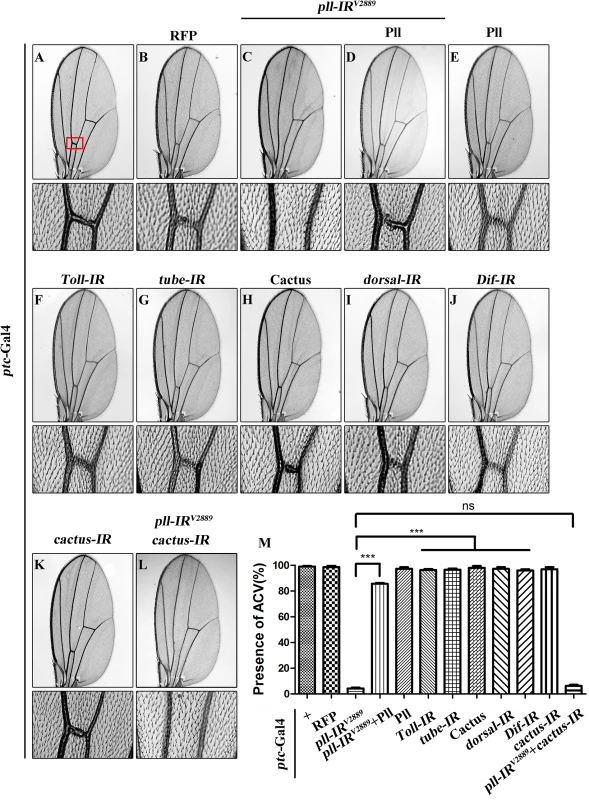
(A-L) Light micrographs showing Drosophila adult wings, anterior is to the left and distal up. Compared with ptc-Gal4 control (A), expression of pll RNAi (pll-IRV2889) induced a loss-of-ACV phenotype (C) that was rescued by expression of Pll (D), while expression of Pll alone showed no obvious defects (E). Expression of RFP was included as a negative control (B). Down-regulation of Toll/NF-κB pathway by expressing RNAi of Toll (F), tube (G), dorsal (I) or Dif (J), or the negative regulator Cactus (H), had no effect on wing development. ptc>pll-IRV2889 was not rescued by co-expressing a cactus RNAi (K and L). The lower panels show high magnification view of the ACV area, boxed in panel A, in upper panels. (M) Quantification of the ACV phenotype as shown in figures A-L. One-way ANOVA with Bonferroni multiple comparison test was used to compute P-values, significance is indicated with asterisks (*** P<0.001). ns stands for not significant. Detailed genotypes: (A) ptc-Gal4/+ (B) ptc-Gal4/+; UAS-RFP/+ (C) ptc-Gal4/UAS-pll-IRV2889 (D) ptc-Gal4/UAS-pll-IRV2889; UAS-Pll; (E) ptc-Gal4/+; UAS-Pll/+ (F) ptc-Gal4/+; UAS-Toll-IR/+ (G) ptc-Gal4/+; UAS-tube-IR/+ (H) ptc-Gal4/UAS-Cactus (I) ptc-Gal4/+; UAS-dorsal-IR/+ (J) ptc-Gal4/+; UAS-Dif-IR/+ (K) ptc-Gal4/+; UAS-cactus-IR/+ (L) ptc-Gal4/UAS-pll-IRV2889; UAS-cactus-IR/+. Pll has been implicated in the Toll/NF-κB pathway that directly phosphorylates the Drosophila IκB factor Cactus [36,37]. To examine whether the Toll/NF-κB pathway is required for the development of ACV, we down-regulated the pathway by knocking-down the positive regulators such as Toll, tube, dorsal and Dif, or ectopically expressing the negative regulator Cactus. At least two independent RNAi lines were tested for each gene, including a previously reported RNAi for Toll [38] and tube [39]. The knock-down efficacies of the RNAi lines were verified by their ability to suppress the rough eye phenotype of GMR>Toll10B (S2F–S2K Fig), which expresses the activated form of Toll in the developing eye. Intriguingly, down-regulation of the Toll/NF-κB pathway failed to recapitulate the loss-of-ACV phenotype produced by ptc>pll-IR (Fig 1F–1J and 1M), and this phenotype was not rescued by RNAi inactivation of cactus (Fig 1K–1M), the Drosophila I-κB homolog, implying that the physiological function of pll in wing development is independent of the canonical Toll/NF-κB pathway.
pelle regulates cell number, but not cell size in wing development
To further characterize the physiological function of pll in wing development, we knocked down pll in distinct regions of the wing disc by using additional wing specific Gal4 drivers: Optomotor-blind (Omb)-Gal4, Scalloped (Sd)-Gal4 and engrailed (en)-Gal4. We noted that loss of pll in the distal part (Omb>pll-IR), wing pouch (Sd>pll-IR) or posterior compartment (en>pll-IR) of the wing disc caused severe reduction in corresponding areas of the adult wing, which were rescued by co-expression of Pll, but not that of GFP (Fig 2A–2N and 2Q; S3 Fig), confirming that pll is required for proper wing development.
Fig. 2. pll regulates cell number, but not cell size in adult wing. 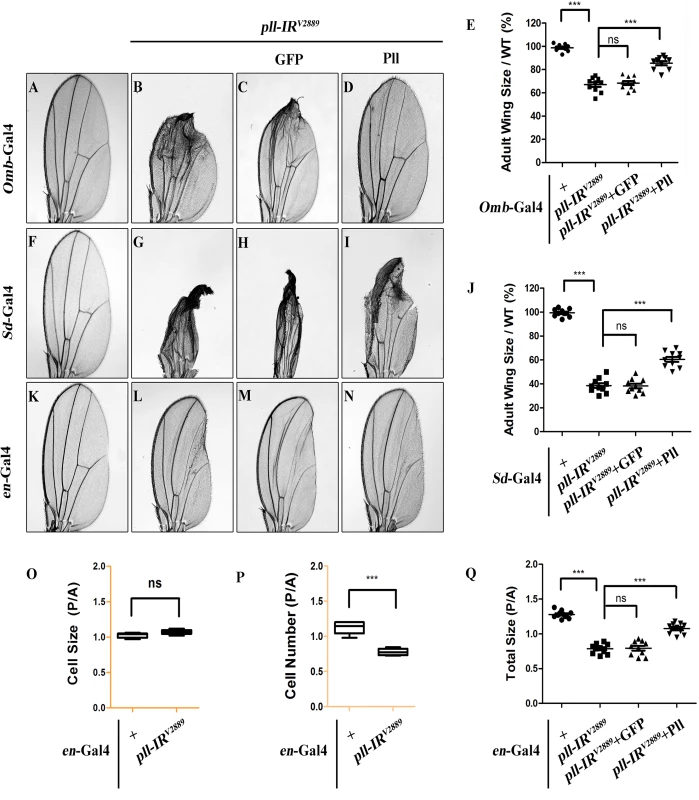
(A-D, F-I and K-N) Light micrographs of Drosophila adult wings are shown, anterior is to the left and distal up. Compared with the Gal4 controls (A, F and K), expression of pll RNAi (pll-IRV2889) driven by Omb-Gal4 (B), Sd-Gal4 (G) or en-Gal4 (L) resulted in reduced wing tissue in the corresponding areas, which were rescued by expression of Pll (D, I and N), but not that of GFP (C, H and M). (E and J) Quantifications of adult wing size/wild type (WT) ratio are shown for figures A-D and F-I respectively (n = 10). One-way ANOVA with Bonferroni multiple comparison test was used to compute P-values, significance is indicated with asterisks (*** P<0.001). (O and P) Quantifications of cell size (O) and cell number (P) in wings shown in K and L. The P/A ratio of cell size showed no difference while that of cell number decreased significantly when pll was knocked down in the P compartment by en-Gal4. Unpaired t test was used to calculate statistical significance, indicated with asterisks (*** P<0.001, n = 10 in each group). (Q) Statistic analysis of total size P/A ratio are shown for figures K-N. One-way ANOVA with Bonferroni multiple comparison test was used to compute P-values, significance is indicated with asterisks (*** P<0.001). ns stands for not significant. Detailed genotypes: (A) Omb-Gal4/+ (B) Omb-Gal4/+; UAS-pll-IRV2889/+ (C) Omb-Gal4/+; UAS-pll-IRV2889/+; UAS-GFP/+ (D) Omb-Gal4/+; UAS-pll-IRV2889/+; UAS-Pll/+ (F) Sd-Gal4/+ (G) Sd-Gal4/+; UAS-pll-IRV2889/+ (H) Sd-Gal4/+; UAS-pll-IRV2889/+; UAS-GFP/+ (I) Sd-Gal4/+; UAS-pll-IRV2889/+; UAS-Pll/+ (K) en-Gal4/+ (L) en-Gal4/UAS-pll-IRV2889 (M) en-Gal4/UAS-pll-IRV2889; UAS-GFP/+ (N) en-Gal4/UAS-pll-IRV2889; UAS-Pll/+. To investigate the underlying mechanism by which loss of pll results in reduced wing tissue, we compared the cell number and cell size in the posterior (P) compartment with that in the anterior (A) compartment of the adult wing. We found that when pll was specifically knock-down in the P compartment by en-Gal4 (Fig 2L), the P/A ratio of cell size remained unaffected (Fig 2O), whereas the P/A ratio of cell number and total size decreased significantly (Fig 2P and 2Q), suggesting that pll regulates cell number, but not cell size, in wing development. To further verify this conclusion, we generated pll loss-of-function clones in larvae and found that the size of clones, labeled by GFP expression, was significantly smaller than that of wild-type (WT) controls in wing discs (Fig 3A–3C), confirming the role of pll in regulating tissue growth. However, the sizes of cells inside the clones (marked by GFP expression) were similar to that of wild-type controls in fat body (FB) and salivary gland (SG) (Fig 3G and 3H). Furthermore, wing margin bristles in pll knock-down clones, marked by loss of the yellow (y) gene, are not statistically different in size from their wild-type neighbors (Fig 3D–3F). Together, these data indicate that pll modulates tissue growth via regulating cell number but not cell size.
Fig. 3. pll regulates cell number but not cell size in development. 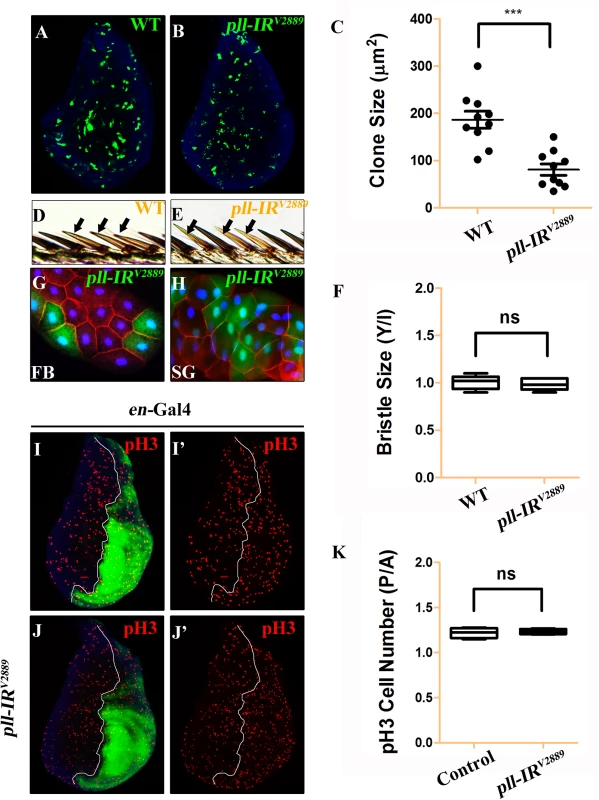
(A and B) Fluorescence micrographs of third instar larval wing discs with clones (marked by GFP) expressing no (A) or pll RNAi (B). Clones were induced by heat shock at 37°C for 1 hour and recovered at 25°C for 42 hours. Nuclei were labeled with DAPI (blue). (C) Quantification of clone size shown in A and B. Unpaired t test was used to calculate statistical significance, indicated with asterisks (*** P<0.001, n = 10 in each group). (D and E) Clones (marked by y-, yellow) expressing no (D) or pll RNAi (E) in adult wing margin bristles, 7 days after induction. (F) Quantification of bristle size as shown in D and E. The ratio of bristle size within clones (Y)/bristle size of internal control (I) remained unchanged when pll was knocked down in the clone. (G and H) Fluorescence micrographs of clones (marked by GFP) expressing pll RNAi in third instar larval fat body (FB, G) and salivary gland (SG, H) 42 hours after induction. Nuclei were labelled with DAPI (blue), cell membranes were stained by anti-Dlg antibody (red). (I and J) Fluorescence micrographs of wing discs are shown. The P compartment was labelled by GFP, while cell proliferation was detected by anti-pH3 staining (red) (I’ and J’), nuclei were labelled with DAPI (blue). (K) Quantification of pH3 positive cells shown in I and J. The P/A ratio of pH3 positive cells remained unchanged when pll was knocked down in the P compartment. ns stands for not significant. For all wing discs, anterior is to the left and dorsal up. Detailed genotypes: (A and D) y w hs-Flp/+; act>y+>Gal4 UAS-GFP/+ (B, E, G, H) y w hs-Flp/+; act>y+>Gal4 UAS-GFP/UAS-pll-IRV2889 (I) en-Gal4 UAS-GFP/+ (J) en-Gal4 UAS-GFP/UAS-pll-IRV2889. Loss of pll triggers caspase-mediated cell death
Loss of pll results in reduced cell number, which could be a consequence of decreased cell proliferation or increased cell death. To distinguish between the two possibilities, we first checked the cell proliferation rate by phospho-Histone H3 (pH3) staining in wing discs. We found that knock-down pll in the P compartment of wing discs (en>pll-IR) did not affect cell proliferation, as the P/A ratio of pH3 positive cells in such discs was not statistically different from that in control discs (Fig 3I–3K).
Apoptosis plays a crucial role in maintaining tissue homeostasis, making the decision between cell death and survival in response to various intracellular and extracellular stress [36,40]. To examine the role of pll in regulating cell death, we performed acridine orange (AO) staining and TdT-mediated dUTP nick end labelling (TUNEL) assay, both are commonly used to detect apoptosis [41,42]. We found that knock-down pll in the wing disc resulted in increased AO (Fig 4A, 4B, 4E and 4F; Fig 5A and 5B; S4A, S4B, S4K and S4L Fig) and TUNEL staining (Fig 4Q, 4R, 4U and 4V; S4G–S4J Fig) in the corresponding regions, which were soundly suppressed by the expression of Pll (Fig 4D, 4H, 4T and 4X), but not that of GFP (Fig 4C, 4G, 4S and 4W), indicating pll negatively regulates cell death in wing development.
Fig. 4. Loss of pll elicits apoptotic cell death. 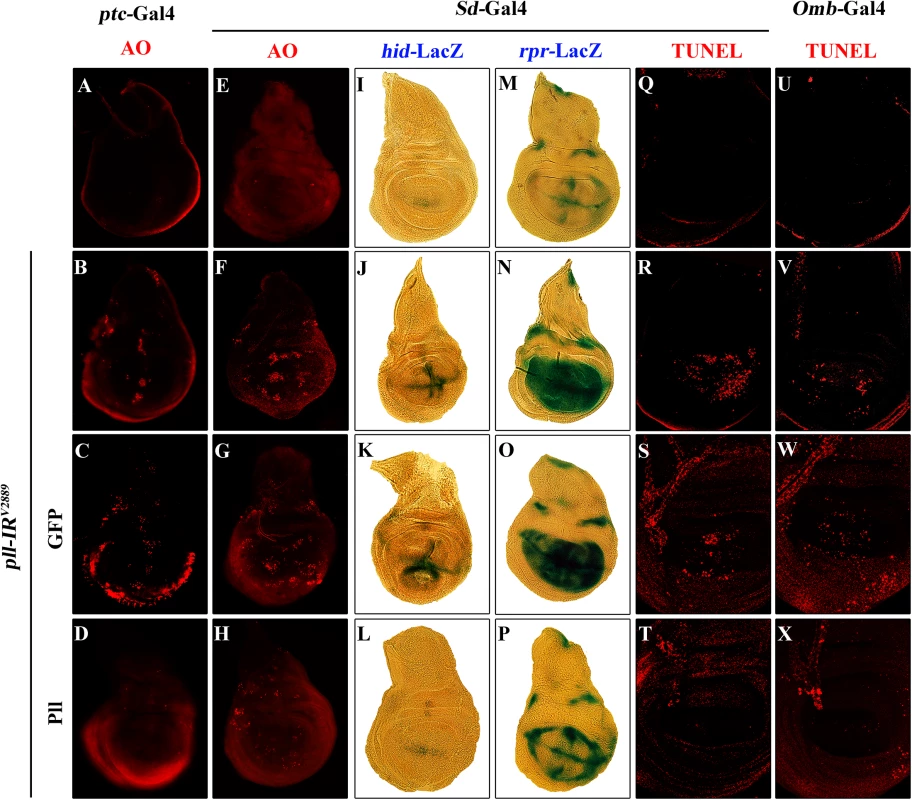
(A-H) AO staining of third instar larval wing discs. Compared with controls (A and E), knock down pll along the A/P boundary by ptc-gal4 (B) or in the wing pouch by Sd-Gal4 (F) triggered cell death in the corresponding areas, which was suppressed by expressing Pll (D and H), but not GFP (C and G). (I-P) X-Gal staining of a hid-LacZ and an rpr-LacZ reporters in wing discs. Compared with controls (I and M), knock down pll in the wing pouch induced hid (J) and rpr (N) transcription, which was blocked by expressing Pll (L and P), but not GFP (K and O). (Q-X) TUNEL staining of third instar larval wing discs. Compared with Gal4 controls (Q and U), knock down pll by Sd-Gal4 (R) or Omb-Gal4 (V) induced cell death in the corresponding areas, which was impeded by expressing Pll (T and X), but not GFP (S and W). In all figures, anterior is to the left and dorsal up. Detailed genotypes: (A) ptc-Gal4/+ (B) ptc-Gal4/UAS-pll-IRV2889 (C) ptc-Gal4/UAS-pll-IRV2889; UAS-GFP/+ (D) ptc-Gal4/UAS-pll-IRV2889; UAS-Pll/+ (E and Q) Sd-Gal4/+ (F and R) Sd-Gal4/+; UAS-pll-IRV2889/+ (G and S) Sd-Gal4/+; UAS-pll-IRV2889/+; UAS-GFP/+ (H and T) Sd-Gal4/+; UAS-pll-IRV2889/+; UAS-Pll/+ (I) Sd-Gal4/+; hid-LacZ/+ (J) Sd-Gal4/+; UAS-pll-IRV2889/+; hid-LacZ/+ (K) Sd-Gal4/+; UAS-pll-IRV2889/+; hid-LacZ/UAS-GFP (L) Sd-Gal4/+; UAS-pll-IRV2889/+; hid-LacZ/UAS-Pll (M) Sd-Gal4/+; rpr-LacZ/+ (N) Sd-Gal4/+; UAS-pll-IRV2889/+; rpr-LacZ/+ (O) Sd-Gal4/+; UAS-pll-IRV2889/+; rpr-LacZ/UAS-GFP (P) Sd-Gal4/+; UAS-pll-IRV2889/+; rpr-LacZ/UAS-Pll (U) Omb-Gal4/+ (V) Omb-Gal4/+; UAS-pll-IRV2889/+ (W) Omb-Gal4/+; UAS-pll-IRV2889/+; UAS-GFP/+ (X) Omb-Gal4/+; UAS-pll-IRV2889/+; UAS-Pll/+. Fig. 5. Loss-of-pll induces dFoxO-dependent cell death. 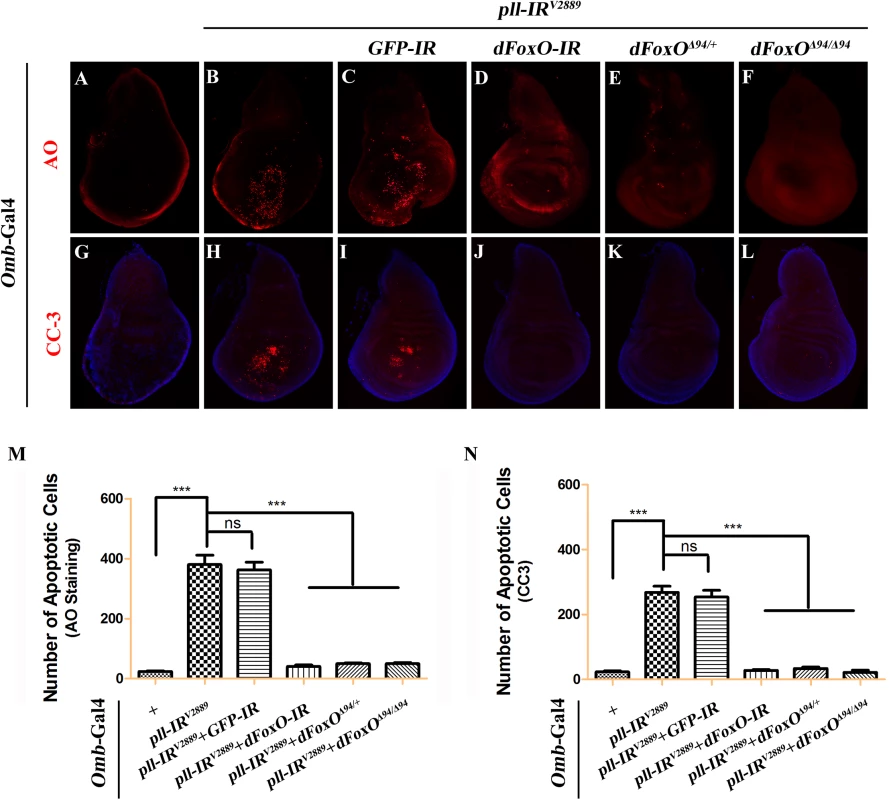
Fluorescence micrographs of third instar larval wing discs stained with AO (A-F) or anti-Cleaved Caspase-3 (CC-3) antibody (G-L), anterior is to the left and dorsal up. Compared with controls (A and G), loss of pll resulted in increased cell death (B) and caspase activity (H), both of which were suppressed by knocking-down dFoxO (D and J), or deleting one or both copies of endogenous dFoxO (E, F, K and L). GFP-IR was used here as a negative control (C and I). (M and N) Quantifications of cell death by AO (M) and CC-3 antibody (N) staining as shown in figures A-F and G-L respectively. One-way ANOVA with Bonferroni multiple comparison test was used to compute P-values, significance is indicated with asterisks (*** P<0.001). ns stands for not significant. Detailed genotypes: (A and G) Omb-Gal4/+ (B and H) Omb-Gal4/+; UAS-pll-IRV2889/+ (C and I) Omb-Gal4/+; UAS-pll-IRV2889/+; UAS-GFP-IR/+ (D and J) Omb-Gal4/+; UAS-pll-IRV2889/+; UAS-dFoxO-IR/+ (E and K) Omb-Gal4/+; UAS-pll-IRV2889/+; dFoxOΔ94/+ (F and L) Omb-Gal4/+; UAS-pll-IRV2889/+; dFoxOΔ94/Δ94. Apoptosis in Drosophila is triggered by transcriptional up-regulation of three pro-apoptotic genes rpr, hid and grim, and is mediated by the cleavage and activation of caspases [40]. Consistent with its role in cell death, loss of pll in the wing pouch results in up-regulated transcription of hid and rpr as revealed by X-gal staining of a hid-LacZ and an rpr-LacZ reporters (Fig 4I, 4J, 4M and 4N; S4C–S4F Fig), which is suppressed by expressing Pll, but not GFP (Fig 4K, 4L, 4O and 4P). Furthermore, we found that a ubiquitous knock-down of pll (act>pll-IR) was able to activate the transcription of endogenous hid, rpr and grim, as compared to the act-Gal4 control, via executing a real-time qRT-PCR assay (S4M Fig). In addition, depletion of pll leads to enhanced antibody staining for the activated form of Caspase-3 (CC-3, Fig 5G and 5H), a read-out of the initiator caspase Dronc activity [43]. Moreover, we found that the loss-of-ACV phenotype induced by ptc>pll-IR was suppressed partially by the deficiency Df(3L)H99 that deletes rpr, hid and grim (S5A–S5C Fig), and significantly by expressing the inhibitor of apoptosis protein DIAP1 or a dominant-negative form of Dronc (DroncDN), but not LacZ (Fig 6). Accordingly, the phenotype of reduced distal-most area in Omb>pll-IR wing is considerably rescued by Df(3L)H99 (S5D–S5F Fig). Thus, we conclude from these data that depletion of pll is sufficient to activate caspase-mediated cell death.
Fig. 6. Depletion of pll elicits caspases-dependent cell death in adult wing. 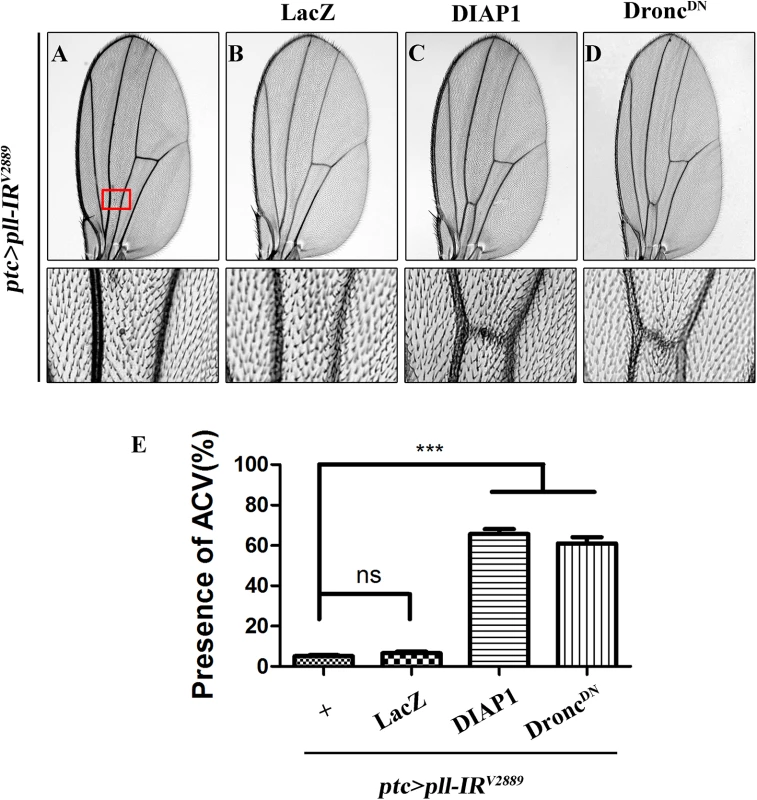
(A-D) Light micrographs showing Drosophila adult wings, anterior is to the left and distal up. The loss-of-ACV phenotype in ptc>pll-IRV2889 flies (A) was significantly suppressed by the expression of DIAP1 (C) or DroncDN (D), but not that of LacZ (B), which served as a negative control. The lower panels are high magnification of the boxed areas in upper panels (A-D). (E) Quantification of the ACV phenotypes as shown in figures A-D. One-way ANOVA with Bonferroni multiple comparison test was used to compute P-values, significance is indicated with asterisks (*** P<0.001). ns stands for not significant. Detailed genotypes: (A) ptc-Gal4/UAS-pll-IRV2889 (B) ptc-Gal4/UAS-pll-IRV2889; UAS-LacZ/+ (C) ptc-Gal4/UAS-pll-IRV2889; UAS-DIAP1/+ (D) ptc-Gal4/UAS-pll-IRV2889; UAS-DroncDN/+. dFoxO is required for loss-of-pll induced cell death
To understand the mechanism by which loss of pll induces caspase-dependent cell death, we considered the transcription factor dFoxO as a putative downstream factor negatively regulated by Pll. Firstly, dFoxO is known to be negatively regulated by other kinase, e.g. Akt [26,28]. Secondly, previous studies reported that dFoxO is required for the apoptotic response and regulates the expression of pro-apoptotic gene hid [30]. Thirdly, we have previously observed a similar loss-of-ACV phenotype resulted from dFoxO expression driven by ptc-Gal4 driver [33]. In support of the assumption, we found that loss-of-pll triggered cell death in the wing pouch, as detected by AO staining (Fig 5B and 5M) and cleaved caspase-3 (CC-3) antibody (Fig 5H and 5N), was notably blocked by RNAi-mediated depletion of dFoxO, and in heterozygous or homozygous dFoxOΔ94 mutants (Fig 5D–5F and 5J–5N). Furthermore, depletion of pll induced various wing defects are suppressed by loss of dFoxO, either by mutation or expression of RNAi (Fig 7; S6 Fig). A GFP RNAi was employed as a negative control (Fig 5C and 5I; Fig 7C, 7I and 7O). The knock-down efficiency of dFoxO RNAi lines and the dFoxO mRNA level in dFoxOΔ94 mutants have been previously verified [33,44,45]. Consistently, expression of dFoxO driven by ptc-Gal4 (ptc>dFoxO) recapitulates the loss-of-ACV phenotype in ptc>pll-IR flies (S7A Fig). However, the ptc>dFoxO triggered loss-of-ACV phenotype cannot be suppressed by co-expressing Pll (S7B and S7C Fig), confirming that dFoxO acts downstream of Pll. Therefore, we conclude that loss of pll induces dFoxO-dependent cell death in wing development.
Fig. 7. dFoxO is required for loss-of-pll induced wing phenotypes. 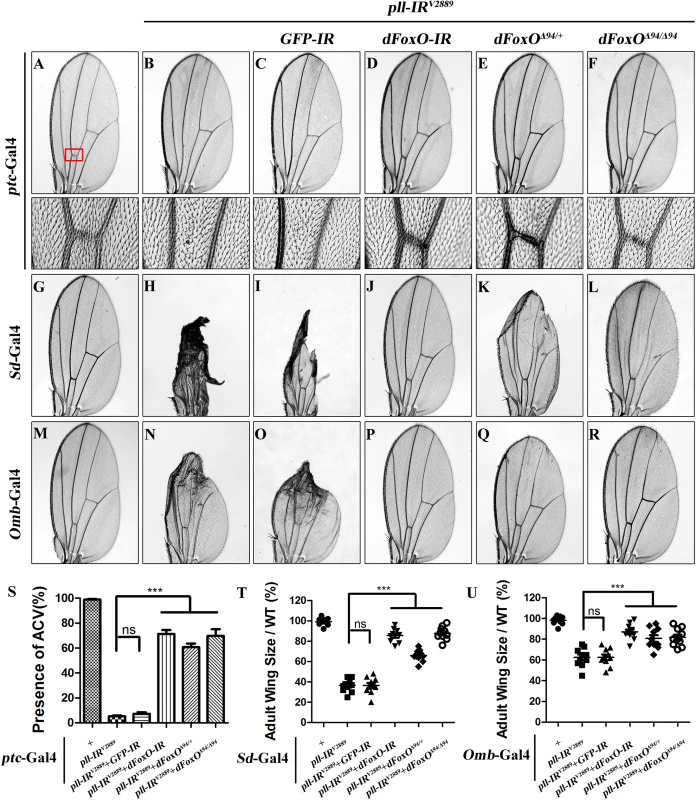
(A-R) Light micrographs showing Drosophila adult wings, anterior is to the left and distal up. Compared with controls (A, G and M), the wing phenotypes of ptc>pll-IRV2889 (B), Sd>pll-IRV2889 (H) and Omb>pll-IRV2889 (N) flies were suppressed by knocking-down dFoxO (D, J and P) or removing one or both copies of dFoxO (E, F, K, L, Q and R), but not by expressing a GFP-IR (C, I and O). In A-F, the lower panels are high magnification of the boxed areas in upper panels. (S-U) Statistical analysis of the ACV phenotype (S) and the adult wing size/wild type (WT) (T and U) as shown in figures A-F, G-L and M-R respectively. One-way ANOVA with Bonferroni multiple comparison test was used to compute P-values, significance is indicated with asterisks (*** P<0.001). ns stands for not significant. Detailed genotypes: (A) ptc-Gal4/+ (B) ptc-Gal4/UAS-pll-IRV2889 (C) ptc-Gal4/UAS-pll-IRV2889/+; UAS-GFP-IR/+ (D) ptc-Gal4/UAS-pll-IRV2889/+; UAS-dFoxO-IR/+ (E) ptc-Gal4/UAS-pll-IRV2889/+; dFoxOΔ94/+ (F) ptc-Gal4/UAS-pll-IRV2889/+; dFoxOΔ94/Δ94 (G) Sd-Gal4/+ (H) Sd-Gal4/+; UAS-pll-IRV2889/+ (I) Sd-Gal4/+; UAS-pll-IRV2889/+; UAS-GFP-IR/+ (J) Sd-Gal4/+; UAS-pll-IRV2889/+; UAS-dFoxO-IR/+ (K) Sd-Gal4/+; UAS-pll-IRV2889/+; dFoxOΔ94/+ (L) Sd-Gal4/+; UAS-pll-IRV2889/+; dFoxOΔ94/Δ94 (M) Omb-Gal4/+ (N) Omb-Gal4/+; UAS-pll-IRV2889/+ (O) Omb-Gal4/+; UAS-pll-IRV2889/+; UAS-GFP-IR/+ (P) Omb-Gal4/+; UAS-pll-IRV2889/+; UAS-dFoxO-IR/+ (Q) Omb-Gal4/+; UAS-pll-IRV2889/+; dFoxOΔ94/+ (R) Omb-Gal4/+; UAS-pll-IRV2889/+; dFoxOΔ94/Δ94. pll is ubiquitously expressed throughout development [6]. To investigate whether Pll modulates dFoxO-dependent cell death in other tissues, we knocked down pll in the notum by the pnr-Gal4 driver, and observed a loss-of-bristle phenotype in the notum (Fig 8A, 8B and 8H). This phenotype, most likely caused by cell death as expression of the apoptotic gene reaper in the notum produces a similar bristle-ablation phenotype [46], is significantly suppressed by expressing a dFoxO RNAi, or deleting one or both copies of endogenous dFoxO, or expressing Pll, but not a GFP RNAi (Fig 8C–8H). Thus, Pll negatively regulates dFoxO-dependent cell death in a non-tissue-specific manner.
Fig. 8. dFoxO is required for loss-of-pll induced bristle phenotype on notum. 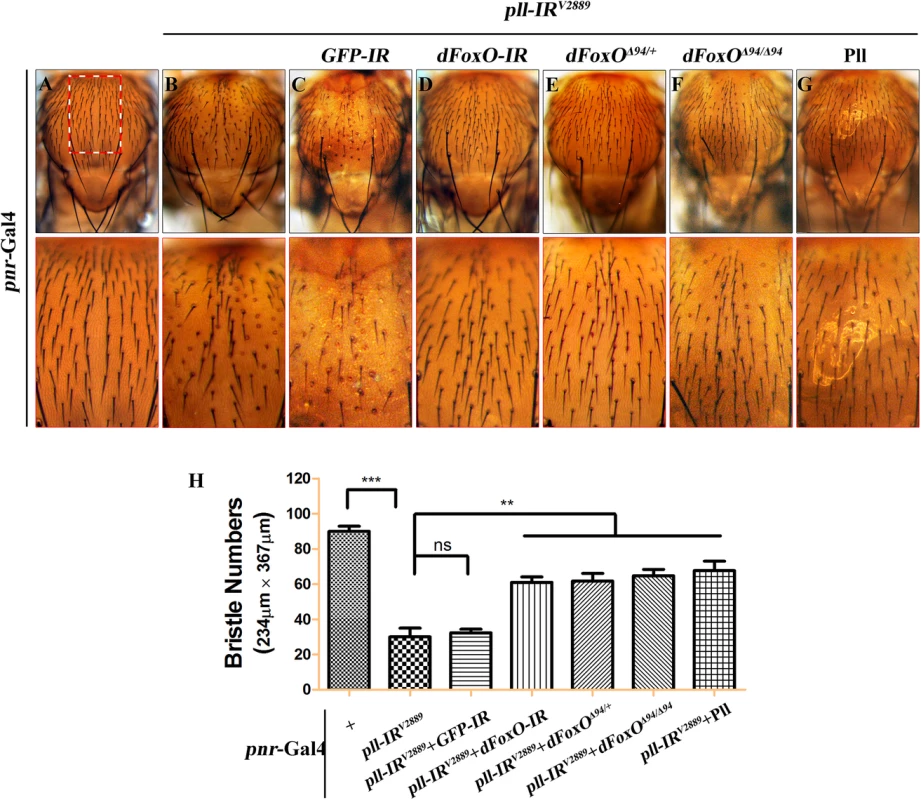
(A-G) Light micrographs showing bristles on the adult notum. Compared with the pnr-Gal4 control (A), RNAi-mediated depletion of pll in notum resulted in reduced bristle number (B), which was suppressed by knocking-down dFoxO (D), deleting one or both copies of endogenous dFoxO (E and F), or expressing Pll (G), but not by expressing a GFP RNAi that served as a negative control (C). The lower panels show high magnification view of the boxed areas in upper panels. (H) Quantification of bristles number in the boxed areas from A-G. One-way ANOVA with Bonferroni multiple comparison test was used to compute P-values, significance is indicated with asterisks (*** P<0.001, ** P<0.01). ns stands for not significant. Detailed genotypes: (A) pnr-Gal4/+ (B) UAS-pll-IRV2889/+; pnr-Gal4/+ (C) UAS-pll-IRV2889/+; pnr-Gal4/UAS-GFP-IR (D) UAS-pll-IRV2889/+; pnr-Gal4/UAS-dFoxO-IR (E) UAS-pll-IRV2889/+; pnr-Gal4/dFoxOΔ94 (F) UAS-pll-IRV2889/+; pnr-Gal4 dFoxOΔ94/dFoxOΔ94 (G) UAS-pll-IRV2889/+; pnr-Gal4/UAS-Pll. Pll regulates dFoxO subcellular localization and transcriptional activity
To address how Pll modulates dFoxO activity, we first checked whether Pll regulates dFoxO transcription by executing a real-time qRT-PCR assay. We found that a ubiquitous knockdown of pll (act>pll-IR) did not affect the mRNA level of dFoxO, as compared to the act-Gal4 control (Fig 9A), suggesting that pll does not regulate dFoxO transcription. Previous studies indicate that the nuclear localization of dFoxO is regulated by a series of post-translational modifications, including phosphorylation by different kinases [34]. To examine whether Pll modulates the nuclear-cytoplasmic shuttling of dFoxO, we checked the sub-cellular localization of a dFoxO-GFP fusion protein in the fat body. We found that the nuclear localization of dFoxO-GFP was significantly increased when pll was knocked down in fat body cells by Cg-Gal4 (Fig 9B–9D), which drives Gal4 expression specifically in fat body and hemocytes under the control of collagen (Cg25C) promoter [47]. To monitor the dFoxO activity directly, we detected the expression of its well-characterized target gene Thor/4E-BP by a Thor-LacZ reporter [26,28,48,49]. We found that Thor-LacZ expression was distinctly induced in the wing pouch by RNAi inactivation of pll under the control of Sd-Gal4 (Fig 9E and 9F). In addition, qRT-PCR assay confirmed that depletion of pll resulted in up-regulated Thor/4E-BP transcription (Fig 9G). Thus, we conclude that Pll regulates dFoxO subcellular localization and transcriptional activity.
Fig. 9. Loss of pll promotes dFoxO nuclear localization and transcriptional activity. 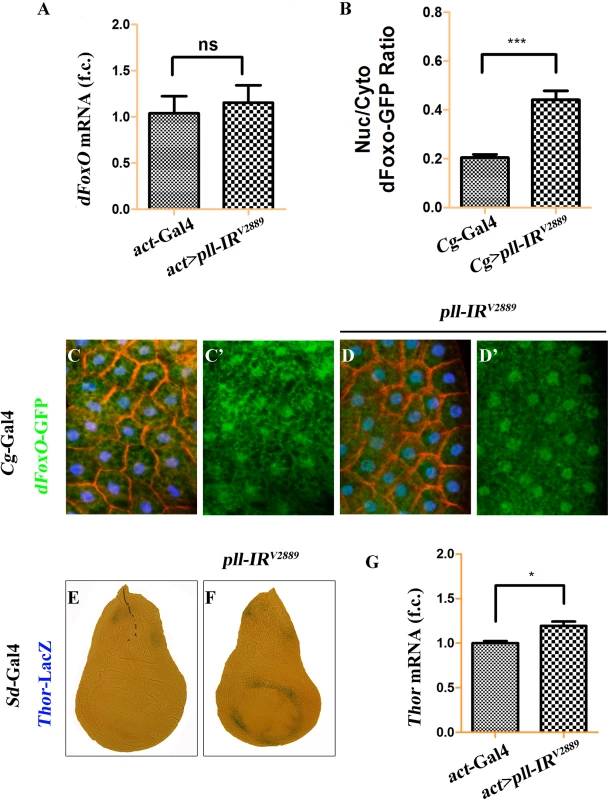
(A) Loss of pll does not affect the transcription of dFoxO. Histogram showing the levels of dFoxO mRNAs measured by quantitative RT-PCR. Total RNA of Drosophila third instar larvae were extracted and normalized for cDNA synthesis. Error bars represents standard deviation from three independent experiments. ns stands for not significant. (B-D) Loss of pll promotes nuclear localization of dFoxO. (B) Quantification of the nuclear/cytoplasmic ratio of dFoxO-GFP fusion protein in the fat body shown in C and D. dFoxO-GFP intensities were measured in pixels using Image J. Error bars showed standard deviation from measurement of at least 15 cells for each genotype. Unpaired t test was used to calculate statistical significance, indicated with asterisks (*** P<0.001). (C and D) Fluorescence micrographs of fat body cells are shown. Compared with the control (C), loss of pll promotes the translocation of dFoxO-GFP from cytoplasm to nucleus (D). Nuclei were marked with DAPI (blue), cell membranes were stained by anti-Dlg antibody (red). (E and F) X-Gal staining of a Thor-LacZ reporter in third instar larval wing discs. Compared with the control (E), knock-down pll in the wing pouch induced Thor transcription (F). (G) Loss of pll up-regulated the level of Thor mRNA, as measured by quantitative RT-PCR. Total RNA of Drosophila third instar larvae were extracted and normalized for cDNA synthesis. Error bars represented standard deviation from three independent experiments. Unpaired t test was used to calculate statistical significance, indicated with asterisks (* P<0.05). Detailed genotypes: (A) Left: act-Gal4/+, Right: UAS-pll-IRV2889/+; act-Gal4/+ (B) Left: Cg-Gal4/+, Right: Cg-Gal4/UAS-pll-IRV2889 (C) Cg-Gal4/+; dFoxO-GFP/+ (D) Cg-Gal4/UAS-pll-IRV2889; dFoxO-GFP/+ (E) Sd-Gal4/+; Thor-LacZ/+ (F) Sd-Gal4/+; Thor-LacZ/UAS-pll-IRV2889 (G) Left: act-Gal4/+, Right: UAS-pll-IRV2889/+; act-Gal4/+. Pll physically interacts with and phosphorylates dFoxO
To investigate the underlying mechanism by which Pll regulates dFoxO activity, we expressed HA-tagged Pll (HA-Pll) and Flag-tagged dFoxO (Flag-dFoxO) in Drosophila S2R+ cells, and examined the phosphorylation of dFoxO through Calf Intestine Phosphatase (CIP) assay. We found that co-expression of Pll resulted in a mobility shift of dFoxO, which was abolished upon CIP treatment (Fig 10A), suggesting that dFoxO could be phosphorylated by Pll. Next, we performed the in vitro kinase assay to confirm the phosphorylation of dFoxO by Pll. Since Pll could be auto-phosphorylated (Fig 10B), to better distinguish the phosphorylated dFoxO from auto-phosphorylated Pll, we divided the full-length dFoxO (1-622aa) into two segments: the N-terminal (NT, 1-304aa) and the C-terminal (CT, 305-622aa). Indeed, bacterially purified GST-Pll was able to phosphorylate dFoxO in vitro, heavily on the NT and lightly on the CT (Fig 10B), suggesting Pll might phosphorylate dFoxO at multiple sites, most of which are located in the N-terminal half of dFoxO. Furthermore, Co-IP assay demonstrated a physical interaction between HA-Pll and Flag-dFoxO in S2R+ cells (Fig 10C). Finally, we performed the GST-pulldown assay and confirmed a direct binding between Pll and dFoxO (Fig 10D). Together, these data suggest that Pll could phosphorylate dFoxO through direct interaction, thus negatively regulates dFoxO activity by preventing its nuclear translocation.
Fig. 10. Pll binds to and phosphorylates dFoxO. 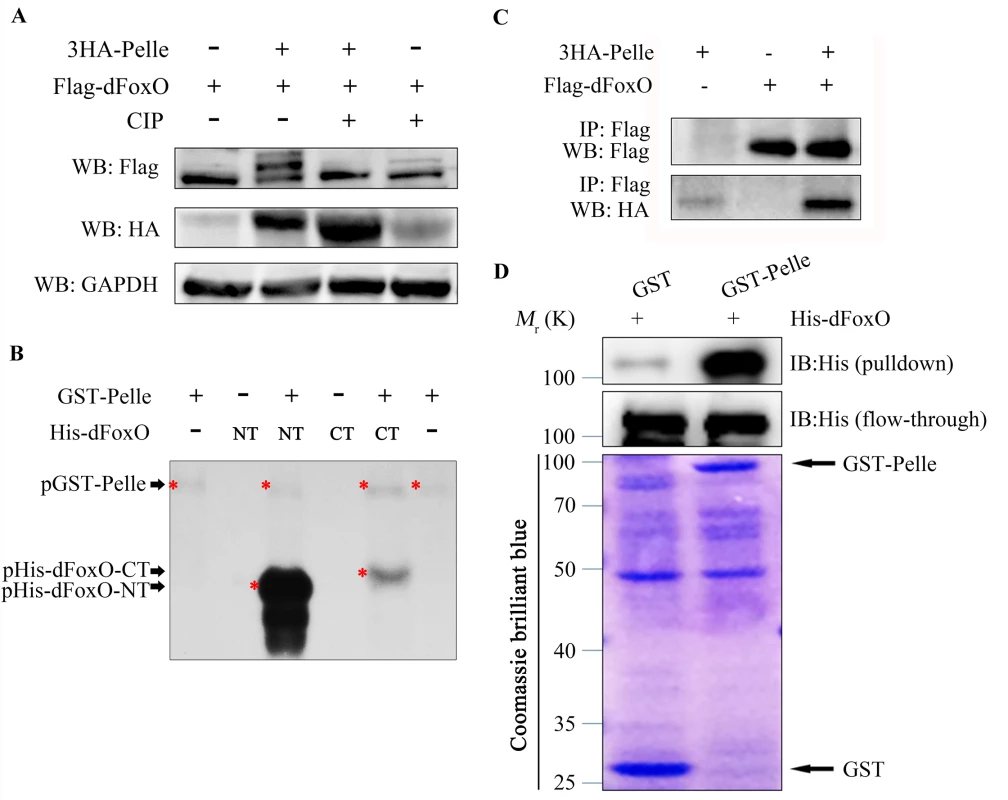
(A) Expression of Pll induced mobility shift of dFoxO, which was abolished by CIP treatment. Cell lysis was prepared from S2R+ cells expressing Flag-dFoxO alone or with HA-Pelle, treated with or without calf intestine phosphatase (CIP), followed by western blotting. (B) Kinase assay shows Pll phosphorylates the N- and C- terminal parts of dFoxO. (C) Co-immunoprecipitation experiment shows dFoxO interacts with Pelle in S2R+ cells. (D) GST pull-down assay shows direct binding between bacterially expressed His–dFoxO and GST–Pll in vitro. Discussion
Drosophila melanogaster has emerged as an excellent model organism to study apoptotic cell death and has made significant contribution to understand cell death regulation and its role in development. While mammalian IRAKs function as the mediator of IL-1Rs/TLRs signal transduction in the immune and inflammatory responses [1,2], Pll, the sole Drosophila orthologue of IRAKs, has been implicated as a central regulator of Toll pathway involved in embryonic dorsal/ventral patterning, innate immune response, muscle development and axon guidance. In this work, we identified a Toll pathway independent function of Pll in modulating caspase-mediated cell death in animal development.
Previous studies have suggested that Drosophila wing vein formation is a result of cell fate specification regulated by multiple signaling pathways including Notch, Hedgehog, EGF (epidermal growth factor) and BMP (bone morphogenetic proteins) pathways [50,51]. In the present study, we found that knock-down pll along the A/P compartment boundary of the developing wing (ptc>pll-IR) resulted in extensive cell death in the wing disc (Fig 4B) and a loss-of-ACV phenotype in the adult wing (Fig 1C; S1A and S1F Fig), implying a potential role of cell death in vein patterning. Consistent with this notion, the loss-of-ACV phenotype is rescued by blocking apoptotic cell death (Fig 6C–6E; S5B and S5C Fig), suggesting cell death is responsible for the loss of ACV. To investigate whether cell death is able to impede vein patterning, we initiated apoptosis by expressing the pro-apoptotic protein Grim under the control of ptc-Gal4. ptc>Grim caused extensive cell death in tissue ablation between L3 and L4 in the adult wing. In most cases, L3 and L4 were fused in the proximal area where ACV is located (S8A Fig). To adjust Grim expression and cell death, we added Tub-Gal80ts that represses Gal4 activity in a temperature sensitive manner. At 25°C, Tub-Gal80ts partially blocks ptc-Gal4 activity and allows limited Grim expression and therefore, cell death, between L3 and L4. Intriguingly, under this condition, we observed the loss-of-ACV phenotype accompanied by a slight reduction of area between L3 and L4 (S8B Fig), suggesting that both reduced area and loss-of-ACV phenotypes are consequences of cell death. From our experience, the loss-of-ACV phenotype is more sensitive to cell death, since weak cell death is sufficient to generate the phenotype, whereas stronger cell death is required to delete tissue between L3 and L4. Consistent with this notion, while ptc>pll-IR flies reared at 25°C only displayed the loss-of-ACV phenotype (Fig 1C), those raised at 29°C also showed reduced area between L3 and L4 (S8D and S8G Fig), which was caused by a reduction in cell number, but not cell size (S8E and S8F Fig).
We show that Pll regulates caspase activation and cell death through dFoxO. Mechanistically, loss of pll promotes the nuclear translocation of dFoxO, which otherwise is retained in the cytoplasm by phosphorylation. A number of kinases, including AKT, IκK and JNK, have been reported to phosphorylate FoxO and regulate its nuclear-cytoplasmic trafficking [52–54]. Here we provide evidence that Pll is another dFoxO kinase that phosphorylates dFoxO and inhibits its nuclear localization. Thus, it would be very interesting to check whether a similar interaction is conserved between IRAKs and FoxOs in mammal.
The FoxO family proteins have been implicated in multiple important biological processes, including cell death and tumor suppression. It has been reported that conditional deletion of FoxO1, FoxO3 and FoxO4 simultaneously results in the development of hemangiomas and thymic lymphomas [55], and IκB kinase represses FoxO3a activity to promote human breast tumorigenesis and acute myeloid leukemia (AML) [52,53]. IRAKs also show altered expression level in tumors and surrounding stroma [43,56], and participate in tumor initiation and progression [57], yet the underlying mechanisms remain poorly understood. Thus, the inhibitory effect of Pll on dFoxO activity in Drosophila provides a beneficial framework for a better understanding of mammalian IRAKs’ crucial roles in tumor development.
As the Toll/NF-κB pathway is not implicated in loss-of-pll triggered dFoxO-dependent cell death, we are curious about what are the pathways or factors act upstream of Pll to regulate its role in cell death? Since dFoxO has been reported as a downstream transcription factor in the JNK and Insulin pathways in Drosophila (S9P Fig; S10O Fig) [58–61], we wondered whether Pll is also involved in these pathways. Activation of JNK signaling between L3 and L4 by expressing Egr (Drosophila TNF) or Hep (Drosophila JNK Kinase), or depleting puc (encoding a JNK inhibitor), produced similar loss-of-ACV and reduced area phenotypes as that of pll depletion, yet the phenotypes were not affected by gain or loss of pll (S9 Fig). Inactivation of the Insulin pathway by expressing a dominant negative form of PI3K, or knocking-down PI3K or Akt, resulted in diminished area between L3 and L4, which remained unaffected by gain or loss of pll (S10 Fig). We also examined the Hippo pathway known to play a crucial role in regulating cell death and organ size [62]. Up-regulation of Hippo pathway in distinct wing areas by different Gal4 drivers led to various small wing or wing tissue ablation phenotypes, which were not altered by changing Pll level (S11 Fig). Finally, we checked dMyc, the fly homolog of c-Myc that regulates cell growth and cell death in Drosophila [63–65], and the cell polarity gene scribble (scrib), whose depletion promotes cell death [66–69]. We found that depletion of dMyc triggered wing phenotype and loss of scrib induced cell death are both independent of Pll (S12 Fig). Thus, while Pll directly regulates dFoxO-mediated caspase-dependent cell death in development, the upstream factors modulating Pll activity remain unknown, which deserve further investigation.
Materials and Methods
Fly strains
All Drosophila stocks were raised on a standard cornmeal and agar media, and crosses were performed at 25°C according to standard protocols unless otherwise indicated. Drosophila strains used include: ptc-Gal4, Omb-Gal4, en-Gal4, act-Gal4, nub-Gal4, Cg-Gal4 (7011), Tub-Gal80ts (7017), UAS-RFP, UAS-LacZ, UAS-Dcr2, UAS-Toll10B, UAS-Cactus, UAS-DIAP1, UAS-dFoxO, UAS-GrimM146, UAS-Hep, UAS-GFP-IR, UAS-Toll-IR (31044, 31447 and 35628), UAS-dorsal-IR (27650, 32934 and 34938), UAS-Dif-IR (29514 and 30513), UAS-dFoxO-IR, UAS-puc-IR (3018), UAS-PI3K-IR (27690), Df(3L)H99, dFoxOΔ94, pll2 (3111), pll7 (3112), dFoxO-GFP (37585), hid-LacZ, Thor-LacZ (9558) and y w hs-Flp; act>y+>Gal4 UAS-GFP were obtained from Bloomington stock center, UAS-pelle-IR (2889 and 103774), UAS-dorsal-IR (45996 and 45998), UAS-Dif-IR (30578 and 30579), UAS-yki-IR (40497), UAS-dMyc-IR (2948) and UAS-scrib-IR (27424) were obtained from Vienna Drosophila RNAi Center (VDRC), UAS-tube-IR (10520R1 and 10520R3), UAS-dorsal-IR (6667R2 and 6667R5), UAS-cactus-IR (5848R3) and UAS-Akt-IR (4006R1) were obtained from Japanese National Institute of Genetics (NIG), UAS-Pelle (201696) was obtained from Drosophila Genetic Resource Center (DGRC). GMR-Gal4 [70], pnr-Gal4 [71–73], Sd-Gal4 [71–73], UAS-pelle-IRW [74], UAS-DroncDN [46], UAS-GFP [71–73], reaper-LacZ [75], UAS-EgrW [46], UAS-PI3KDN [76], UAS-Warts [77] and UAS-Hippo [78] were previously described.
Immunohistochemistry
Imaginal wing discs dissected from third instar larvae were collected in cold PBS and fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde. After proper washes, the wing discs were blocked in 10% horse serum, and stained with antibodies. The following antibodies were used: rabbit anti-pH3 (1 : 200 Cell Signaling Technology), rabbit anti-Cleaved Caspase-3 (1 : 200 Cell Signaling Technology) and mouse anti-Dlg (1 : 200). Secondary antibodies were anti-rabbit-Alexa (1 : 1000 Cell Signaling Technology) and anti-mouse-Cy3 (1 : 1000, Jackson Immuno Research).
AO staining
Wing discs were dissected from third instar larvae in PBST and incubated in 1×10−5 M AO for 5 min at room temperature prior to imaging as described [79].
X-Gal staining
Wing discs were dissected from third instar larvae in PBST (1×PBS pH 7.0, 0.1% Triton X-100) and stained for ß-galactosidase activity as described [80].
TUNEL staining
The wing discs of wandering third-instar were dissected out in PBS. Wing discs were fixed in 4% Paraformaldehyde for 30 min at room temperature (RT) and washed with PBS-Tx (0.3% Triton100) three times for 30 min. TUNEL staining was performed using the Fluorescein Cell Death Kit produced by Boster Company. Imaging of prepared sample was conducted by a Leica confocal microscope (Leica SP5).
qRT-PCR
Five third instar larvae of indicated genotypes were collected and total RNA was isolated using TRIzol (Invitrogen). qRT-PCR was performed as previously described [81] using following primers:
For rp49 Sense: 5’ - TACAGGCCCAAGATCGTGAA-3’
Antisense: 5’ - TCTCCTTGCGCTTCTTGGA-3’
For pelle Sense: 5’GTGGTAAGCCGTGCCTCGTCTA-3’
Antisense: 5’-CTGCCAGGTGAGTGCTGGTAGT-3’
For dFoxO Sense: 5’ - CAATCTCGAGTGCAATGTCGAGGA -3’
Antisense: 5’-CCCTGAGCATCAGCAACATTAGCA-3’
For Thor Sense: 5’-TCGGAGTTTGGATGCTGGGATCTT-3’
Antisense: 5’-AGTCACGTCGTCCTCATCGTTGTT-3’
For hid Sense: 5’-TGCGAAATACACGGGTTCA-3’
Antisense: 5’-CCAATATCACCCAGTCCCG-3’
For rpr Sense: 5’-GAGCAGAAGGAGCAGACGAT-3’
Antisense: 5’-CGATATTTGCCGGACTTTCT-3’
For grim Sense: 5’-TCGGAGTTTGGATGCTGGGATCTT-3’
Antisense: 5’-AGTCACGTCGTCCTCATCGTTGTT-3’
Western blotting, co-immunoprecipitation and phosphatase treatment
Drosophila S2R+ cells were cultured in Corning Insectagro DS2 with 10% FBS (HyClone). Plasmids pUAST-Flag-dFoxO, pUAST-3HA-Pelle and Actin-GAL4 were used for co-transfection as indicated using Effectene Transfection Reagent (QIAGEN). 48 hours after transfection, cells were lysed in RIPA buffer (CST) with PMSF and proceeded with the standard western blot and co-immunoprecipitation protocols. Proteins were probed or immunoprecipitated with following antibodies: Flag-Tag antibody [3A6] (CMCTAG), HA-Tag (C29F4) Rabbit mAb (CST), Anti dFoxO (Cosmo Bio), Anti-rabbit IgG, HRP-linked Antibody (CST), Anti-mouse IgG, HRP-linked Antibody (CST). For Phosphatase Treatment, cell extracts were incubated with calf intestine phosphatase (CIP) (New England BioLabs) for 40 mins at 37°C.
In vitro kinase assays
The GST-Pelle plasmid is a gift from Dr. Wasserman at UCSD. GST-Pelle protein was induced to express in BL21 cells and purified as described [37] except that cells were lysed by sonication. PCR amplified DNA fragments of dFoxO were constructed into pET.M.3C vector (gift from Dr. Long at Nankai University) for expressing proteins of full-length (1-622aa), N-terminal (1-304aa) and C-terminal (305-622aa) dFoxO, respectively. Each resulting protein contains 6ᵡHis-tag at N termini designed as His-dFoxO, His-dFoxONT or His-dFoxOCT. BL21 cells transformed with the constructs were grown for 15 hours at 16°C following 0.8mM IPTG induction, and 6ᵡHis-tagged proteins were purified as previously described [82].
The in vitro kinase assays were performed as described [37]. Briefly, GST-Pelle (30 μg) was pre-incubated for 45 mins at 30°C in 1×kinase buffer (10mM ATP, 10mM MgCl2, 50mM β-glycerophosphate, 25mM HEPES, pH6.5) to allow activation by auto-phosphorylation. The activated Pelle (6 μg) was then incubated with recombinant 6ᵡHis-tagged dFoxO/NT/CT (10 μg) in a volume of 40 μl in the presence of [γ-32P]-ATP (5 μ Curie, Perkin Elmer) in 1×kinase buffer. Following reaction for 5 mins at 30°C, samples were mixed with 10 μl 5×SDS loading sample buffer, boiled, and loaded (25 ml) on an 10% SDS protein gel.
GST-pulldown assays
The GST-pulldown assays were performed as previous described [83]. Recombinant GST-Pelle-λPPase and 6ᵡHis-dFoxo proteins were produced in BL21 cells and purified with glutathione-Sepharose 4B (GE Healthcare) or Ni-NTA resin (GE Healthcare) respectively according to standard protocols. 2 μg GST or 10 μg GST-fusion proteins was incubated at 4°C for 5 hours with 10 μg purified 6ᵡHis-dFoxo and 50 μl of glutathione-Sepharose beads. Supernatants were collected as input and the Sepharose beads were then extensively washed 5 times with lysis buffer and resuspended in SDS loading buffer and boiled. A quarter of the sample buffer was loaded in 12% SDS-PAGE for detection with anti-His antibody (Sungene Biotech).
Supporting Information
Zdroje
1. Flannery S, Bowie AG (2010) The interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinases: Critical regulators of innate immune signalling. Biochemical Pharmacology 80 : 1981–1991. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2010.06.020 20599782
2. Janssens S, Beyaert R (2003) Functional diversity and regulation of different interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase (IRAK) family members. Molecular Cell 11 : 293–302. 12620219
3. Gosu V, Basith S, Durai P, Choi S (2012) Molecular Evolution and Structural Features of IRAK Family Members. Plos One 7.
4. Silverman N, Maniatis T (2001) NF-kappaB signaling pathways in mammalian and insect innate immunity. Genes Dev 15 : 2321–2342. 11562344
5. Dunne A, O'Neill LA (2003) The interleukin-1 receptor/Toll-like receptor superfamily: signal transduction during inflammation and host defense. Sci STKE 2003: re3. 12606705
6. Shelton CA, Wasserman SA (1993) pelle encodes a protein kinase required to establish dorsoventral polarity in the Drosophila embryo. Cell 72 : 515–525. 8440018
7. Towb P, Sun H, Wasserman SA (2009) Tube Is an IRAK-4 homolog in a Toll pathway adapted for development and immunity. J Innate Immun 1 : 309–321. doi: 10.1159/000200773 19498957
8. Gerttula S, Jin YS, Anderson KV (1988) Zygotic expression and activity of the Drosophila Toll gene, a gene required maternally for embryonic dorsal-ventral pattern formation. Genetics 119 : 123–133. 2456252
9. Valanne S, Wang JH, Ramet M (2011) The Drosophila Toll signaling pathway. J Immunol 186 : 649–656. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1002302 21209287
10. Lemaitre B, Nicolas E, Michaut L, Reichhart JM, Hoffmann JA (1996) The dorsoventral regulatory gene cassette spatzle/Toll/cactus controls the potent antifungal response in Drosophila adults. Cell 86 : 973–983. 8808632
11. Halfon MS, Keshishian H (1998) The Toll pathway is required in the epidermis for muscle development in the Drosophila embryo. Dev Biol 199 : 164–174. 9676200
12. Mindorff EN, O'Keefe DD, Labbe A, Yang JP, Ou Y, et al. (2007) A gain-of-function screen for genes that influence axon guidance identifies the NF-kappaB protein dorsal and reveals a requirement for the kinase Pelle in Drosophila photoreceptor axon targeting. Genetics 176 : 2247–2263. 17603113
13. Akira S (2006) TLR signaling. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 311 : 1–16. 17048703
14. Rutschmann S, Jung AC, Zhou R, Silverman N, Hoffmann JA, et al. (2000) Role of Drosophila IKK gamma in a toll-independent antibacterial immune response. Nat Immunol 1 : 342–347. 11017107
15. Silverman N, Zhou R, Stoven S, Pandey N, Hultmark D, et al. (2000) A Drosophila IkappaB kinase complex required for Relish cleavage and antibacterial immunity. Genes Dev 14 : 2461–2471. 11018014
16. Towb P, Bergmann A, Wasserman SA (2001) The protein kinase Pelle mediates feedback regulation in the Drosophila Toll signaling pathway. Development 128 : 4729–4736. 11731453
17. Dick SA, Megeney LA (2013) Cell death proteins: an evolutionary role in cellular adaptation before the advent of apoptosis. Bioessays 35 : 974–983. doi: 10.1002/bies.201300052 23943356
18. Kumar S (2007) Caspase function in programmed cell death. Cell Death Differ 14 : 32–43. 17082813
19. Goyal L, McCall K, Agapite J, Hartwieg E, Steller H (2000) Induction of apoptosis by Drosophila reaper, hid and grim through inhibition of IAP function. EMBO J 19 : 589–597. 10675328
20. Holley CL, Olson MR, Colon-Ramos DA, Kornbluth S (2002) Reaper eliminates IAP proteins through stimulated IAP degradation and generalized translational inhibition. Nat Cell Biol 4 : 439–444. 12021770
21. Yoo SJ, Huh JR, Muro I, Yu H, Wang L, et al. (2002) Hid, Rpr and Grim negatively regulate DIAP1 levels through distinct mechanisms. Nat Cell Biol 4 : 416–424. 12021767
22. Wilson R, Goyal L, Ditzel M, Zachariou A, Baker DA, et al. (2002) The DIAP1 RING finger mediates ubiquitination of Dronc and is indispensable for regulating apoptosis. Nat Cell Biol 4 : 445–450. 12021771
23. Wang SL, Hawkins CJ, Yoo SJ, Muller HA, Hay BA (1999) The Drosophila caspase inhibitor DIAP1 is essential for cell survival and is negatively regulated by HID. Cell 98 : 453–463. 10481910
24. Lin K, Dorman JB, Rodan A, Kenyon C (1997) daf-16: An HNF-3/forkhead family member that can function to double the life-span of Caenorhabditis elegans. Science 278 : 1319–1322. 9360933
25. Greer EL, Brunet A (2005) FOXO transcription factors at the interface between longevity and tumor suppression. Oncogene 24 : 7410–7425. 16288288
26. Junger MA, Rintelen F, Stocker H, Wasserman JD, Vegh M, et al. (2003) The Drosophila forkhead transcription factor FOXO mediates the reduction in cell number associated with reduced insulin signaling. J Biol 2 : 20. 12908874
27. Kramer JM, Davidge JT, Lockyer JM, Staveley BE (2003) Expression of Drosophila FOXO regulates growth and can phenocopy starvation. BMC Dev Biol 3 : 5. 12844367
28. Puig O, Marr MT, Ruhf ML, Tjian R (2003) Control of cell number by Drosophila FOXO: downstream and feedback regulation of the insulin receptor pathway. Genes Dev 17 : 2006–2020. 12893776
29. Zhao J, Brault JJ, Schild A, Cao P, Sandri M, et al. (2007) FoxO3 coordinately activates protein degradation by the autophagic/lysosomal and proteasomal pathways in atrophying muscle cells. Cell Metab 6 : 472–483. 18054316
30. Luo X, Puig O, Hyun J, Bohmann D, Jasper H (2007) Foxo and Fos regulate the decision between cell death and survival in response to UV irradiation. EMBO J 26 : 380–390. 17183370
31. Giannakou ME, Goss M, Junger MA, Hafen E, Leevers SJ, et al. (2004) Long-lived Drosophila with overexpressed dFOXO in adult fat body. Science 305 : 361. 15192154
32. Hwangbo DS, Gershman B, Tu MP, Palmer M, Tatar M (2004) Drosophila dFOXO controls lifespan and regulates insulin signalling in brain and fat body. Nature 429 : 562–566. 15175753
33. Wang X, Wang Z, Chen Y, Huang X, Hu Y, et al. (2014) FoxO mediates APP-induced AICD-dependent cell death. Cell Death Dis 5: e1233. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2014.196 24832605
34. Zhao Y, Wang Y, Zhu WG (2011) Applications of post-translational modifications of FoxO family proteins in biological functions. J Mol Cell Biol 3 : 276–282. doi: 10.1093/jmcb/mjr013 21669942
35. Govind S, Steward R (1991) Dorsoventral pattern formation in Drosophila: signal transduction and nuclear targeting. Trends Genet 7 : 119–125. 2068782
36. Steller H (1995) Mechanisms and genes of cellular suicide. Science 267 : 1445–1449. 7878463
37. Daigneault J, Klemetsaune L, Wasserman SA (2013) The IRAK homolog Pelle is the functional counterpart of IkappaB kinase in the Drosophila Toll pathway. PLoS One 8: e75150. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0075150 24086459
38. Ligoxygakis P, Pelte N, Ji C, Leclerc V, Duvic B, et al. (2002) A serpin mutant links Toll activation to melanization in the host defence of Drosophila. EMBO J 21 : 6330–6337. 12456640
39. Naitza S, Rosse C, Kappler C, Georgel P, Belvin M, et al. (2002) The Drosophila immune defense against gram-negative infection requires the death protein dFADD. Immunity 17 : 575–581. 12433364
40. Steller H (2008) Regulation of apoptosis in Drosophila. Cell Death Differ 15 : 1132–1138. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2008.50 18437164
41. Abrams JM, White K, Fessler LI, Steller H (1993) Programmed cell death during Drosophila embryogenesis. Development 117 : 29–43. 8223253
42. Martin FA, Perez-Garijo A, Morata G (2009) Apoptosis in Drosophila: compensatory proliferation and undead cells. Int J Dev Biol 53 : 1341–1347. doi: 10.1387/ijdb.072447fm 19247932
43. Rodriguez-Berriguete G, Sanchez-Espiridion B, Cansino JR, Olmedilla G, Martinez-Onsurbe P, et al. (2013) Clinical significance of both tumor and stromal expression of components of the IL-1 and TNF-alpha signaling pathways in prostate cancer. Cytokine 64 : 555–563.
44. Slack C, Giannakou ME, Foley A, Goss M, Partridge L (2011) dFOXO-independent effects of reduced insulin-like signaling in Drosophila. Aging Cell 10 : 735–748. doi: 10.1111/j.1474-9726.2011.00707.x 21443682
45. Nechipurenko IV, Broihier HT (2012) FoxO limits microtubule stability and is itself negatively regulated by microtubule disruption. J Cell Biol 196 : 345–362. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201105154 22312004
46. Igaki T, Kanda H, Yamamoto-Goto Y, Kanuka H, Kuranaga E, et al. (2002) Eiger, a TNF superfamily ligand that triggers the Drosophila JNK pathway. EMBO J 21 : 3009–3018. 12065414
47. Asha H, Nagy I, Kovacs G, Stetson D, Ando I, et al. (2003) Analysis of Ras-induced overproliferation in Drosophila hemocytes. Genetics 163 : 203–215. 12586708
48. Mattila J, Kallijarvi J, Puig O (2008) RNAi screening for kinases and phosphatases identifies FoxO regulators. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105 : 14873–14878. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0803022105 18815370
49. Obata F, Kuranaga E, Tomioka K, Ming M, Takeishi A, et al. (2014) Necrosis-driven systemic immune response alters SAM metabolism through the FOXO-GNMT axis. Cell Rep 7 : 821–833. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2014.03.046 24746817
50. Fortini ME (2009) Notch signaling: the core pathway and its posttranslational regulation. Dev Cell 16 : 633–647. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2009.03.010 19460341
51. Perrimon N, Pitsouli C, Shilo BZ (2012) Signaling mechanisms controlling cell fate and embryonic patterning. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 4: a005975. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a005975 22855721
52. Hu MC, Lee DF, Xia W, Golfman LS, Ou-Yang F, et al. (2004) IkappaB kinase promotes tumorigenesis through inhibition of forkhead FOXO3a. Cell 117 : 225–237. 15084260
53. Chapuis N, Park S, Leotoing L, Tamburini J, Verdier F, et al. (2010) IkappaB kinase overcomes PI3K/Akt and ERK/MAPK to control FOXO3a activity in acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 116 : 4240–4250. doi: 10.1182/blood-2009-12-260711 20671123
54. Brunet A, Bonni A, Zigmond MJ, Lin MZ, Juo P, et al. (1999) Akt promotes cell survival by phosphorylating and inhibiting a Forkhead transcription factor. Cell 96 : 857–868. 10102273
55. Paik JH, Kollipara R, Chu G, Ji H, Xiao Y, et al. (2007) FoxOs are lineage-restricted redundant tumor suppressors and regulate endothelial cell homeostasis. Cell 128 : 309–323. 17254969
56. Rhyasen GW, Bolanos L, Starczynowski DT (2013) Differential IRAK signaling in hematologic malignancies. Exp Hematol 41 : 1005–1007. doi: 10.1016/j.exphem.2013.09.008 24084080
57. Guven Maiorov E, Keskin O, Gursoy A, Nussinov R (2013) The structural network of inflammation and cancer: merits and challenges. Semin Cancer Biol 23 : 243–251. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2013.05.003 23712403
58. Accili D, Arden KC (2004) FoxOs at the crossroads of cellular metabolism, differentiation, and transformation. Cell 117 : 421–426. 15137936
59. Essers MA, Weijzen S, de Vries-Smits AM, Saarloos I, de Ruiter ND, et al. (2004) FOXO transcription factor activation by oxidative stress mediated by the small GTPase Ral and JNK. EMBO J 23 : 4802–4812. 15538382
60. Oldham S, Hafen E (2003) Insulin/IGF and target of rapamycin signaling: a TOR de force in growth control. Trends Cell Biol 13 : 79–85. 12559758
61. Grewal SS (2009) Insulin/TOR signaling in growth and homeostasis: a view from the fly world. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 41 : 1006–1010. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2008.10.010 18992839
62. Yin M, Zhang L (2011) Hippo signaling: a hub of growth control, tumor suppression and pluripotency maintenance. J Genet Genomics 38 : 471–481. doi: 10.1016/j.jgg.2011.09.009 22035868
63. Johnston LA, Prober DA, Edgar BA, Eisenman RN, Gallant P (1999) Drosophila myc regulates cellular growth during development. Cell 98 : 779–790. 10499795
64. Bouchard C, Marquardt J, Bras A, Medema RH, Eilers M (2004) Myc-induced proliferation and transformation require Akt-mediated phosphorylation of FoxO proteins. EMBO J 23 : 2830–2840. 15241468
65. Benassayag C, Montero L, Colombie N, Gallant P, Cribbs D, et al. (2005) Human c-Myc isoforms differentially regulate cell growth and apoptosis in Drosophila melanogaster. Mol Cell Biol 25 : 9897–9909. 16260605
66. Bilder D, Perrimon N (2000) Localization of apical epithelial determinants by the basolateral PDZ protein Scribble. Nature 403 : 676–680. 10688207
67. Igaki T, Pastor-Pareja JC, Aonuma H, Miura M, Xu T (2009) Intrinsic tumor suppression and epithelial maintenance by endocytic activation of Eiger/TNF signaling in Drosophila. Dev Cell 16 : 458–465. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2009.01.002 19289090
68. Ohsawa S, Sugimura K, Takino K, Xu T, Miyawaki A, et al. (2011) Elimination of oncogenic neighbors by JNK-mediated engulfment in Drosophila. Dev Cell 20 : 315–328. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2011.02.007 21397843
69. Zhang S, Chen C, Wu C, Yang Y, Li W, et al. (2015) The canonical Wg signaling modulates Bsk-mediated cell death in Drosophila. Cell Death Dis 6: e1713. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2015.85 25855961
70. Li WZ, Li SL, Zheng HY, Zhang SP, Xue L (2012) A broad expression profile of the GMR-GAL4 driver in Drosophila melanogaster. Genet Mol Res 11 : 1997–2002. doi: 10.4238/2012.August.6.4 22911584
71. Ma X, Yang L, Yang Y, Li M, Li W, et al. (2013) dUev1a modulates TNF-JNK mediated tumor progression and cell death in Drosophila. Dev Biol 380 : 211–221. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2013.05.013 23726905
72. Ma X, Li W, Yu H, Yang Y, Li M, et al. (2014) Bendless modulates JNK-mediated cell death and migration in Drosophila. Cell Death Differ 21 : 407–415. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2013.154 24162658
73. Ma X, Shao Y, Zheng H, Li M, Li W, et al. (2013) Src42A modulates tumor invasion and cell death via Ben/dUev1a-mediated JNK activation in Drosophila. Cell Death Dis 4: e864. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2013.392 24136228
74. Ryu JH, Ha EM, Oh CT, Seol JH, Brey PT, et al. (2006) An essential complementary role of NF-kappaB pathway to microbicidal oxidants in Drosophila gut immunity. EMBO J 25 : 3693–3701. 16858400
75. Nordstrom W, Chen P, Steller H, Abrams JM (1996) Activation of the reaper gene during ectopic cell killing in Drosophila. Dev Biol 180 : 213–226. 8948586
76. Kim J, Neufeld TP (2015) Dietary sugar promotes systemic TOR activation in Drosophila through AKH-dependent selective secretion of Dilp3. Nat Commun 6 : 6846. doi: 10.1038/ncomms7846 25882208
77. Yin F, Yu J, Zheng Y, Chen Q, Zhang N, et al. (2013) Spatial organization of Hippo signaling at the plasma membrane mediated by the tumor suppressor Merlin/NF2. Cell 154 : 1342–1355. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2013.08.025 24012335
78. Wu S, Huang J, Dong J, Pan D (2003) hippo encodes a Ste-20 family protein kinase that restricts cell proliferation and promotes apoptosis in conjunction with salvador and warts. Cell 114 : 445–456. 12941273
79. Ma X, Huang J, Yang L, Yang Y, Li W, et al. (2012) NOPO modulates Egr-induced JNK-independent cell death in Drosophila. Cell Res 22 : 425–431. doi: 10.1038/cr.2011.135 21844890
80. Xue L, Noll M (2000) Drosophila female sexual behavior induced by sterile males showing copulation complementation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 97 : 3272–3275. 10725377
81. Wang MC, Bohmann D, Jasper H (2003) JNK signaling confers tolerance to oxidative stress and extends lifespan in Drosophila. Dev Cell 5 : 811–816. 14602080
82. Chu X, Qin X, Xu H, Li L, Wang Z, et al. (2013) Structural insights into Paf1 complex assembly and histone binding. Nucleic Acids Res 41 : 10619–10629. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt819 24038468
83. Ma B, Chen Y, Chen L, Cheng H, Mu C, et al. (2015) Hypoxia regulates Hippo signalling through the SIAH2 ubiquitin E3 ligase. Nat Cell Biol 17 : 95–103. doi: 10.1038/ncb3073 25438054
Štítky
Genetika Reprodukční medicína
Článek Evidence of Selection against Complex Mitotic-Origin Aneuploidy during Preimplantation DevelopmentČlánek A Novel Route Controlling Begomovirus Resistance by the Messenger RNA Surveillance Factor PelotaČlánek A Follicle Rupture Assay Reveals an Essential Role for Follicular Adrenergic Signaling in OvulationČlánek Canonical Poly(A) Polymerase Activity Promotes the Decay of a Wide Variety of Mammalian Nuclear RNAsČlánek FANCI Regulates Recruitment of the FA Core Complex at Sites of DNA Damage Independently of FANCD2Článek Hsp90-Associated Immunophilin Homolog Cpr7 Is Required for the Mitotic Stability of [URE3] Prion inČlánek The Dedicated Chaperone Acl4 Escorts Ribosomal Protein Rpl4 to Its Nuclear Pre-60S Assembly SiteČlánek Chromatin-Remodelling Complex NURF Is Essential for Differentiation of Adult Melanocyte Stem CellsČlánek A Systems Approach Identifies Essential FOXO3 Functions at Key Steps of Terminal ErythropoiesisČlánek Integration of Posttranscriptional Gene Networks into Metabolic Adaptation and Biofilm Maturation inČlánek Lateral and End-On Kinetochore Attachments Are Coordinated to Achieve Bi-orientation in Oocytes
Článek vyšel v časopisePLOS Genetics
Nejčtenější tento týden
2015 Číslo 10
-
Všechny články tohoto čísla
- Gene-Regulatory Logic to Induce and Maintain a Developmental Compartment
- A Decad(e) of Reasons to Contribute to a PLOS Community-Run Journal
- DNA Methylation Landscapes of Human Fetal Development
- Single Strand Annealing Plays a Major Role in RecA-Independent Recombination between Repeated Sequences in the Radioresistant Bacterium
- Evidence of Selection against Complex Mitotic-Origin Aneuploidy during Preimplantation Development
- Transcriptional Derepression Uncovers Cryptic Higher-Order Genetic Interactions
- Silencing of X-Linked MicroRNAs by Meiotic Sex Chromosome Inactivation
- Virus Satellites Drive Viral Evolution and Ecology
- A Novel Route Controlling Begomovirus Resistance by the Messenger RNA Surveillance Factor Pelota
- Sequence to Medical Phenotypes: A Framework for Interpretation of Human Whole Genome DNA Sequence Data
- Your Data to Explore: An Interview with Anne Wojcicki
- Modulation of Ambient Temperature-Dependent Flowering in by Natural Variation of
- The Ciliopathy Protein CC2D2A Associates with NINL and Functions in RAB8-MICAL3-Regulated Vesicle Trafficking
- PPP2R5C Couples Hepatic Glucose and Lipid Homeostasis
- DCA1 Acts as a Transcriptional Co-activator of DST and Contributes to Drought and Salt Tolerance in Rice
- Intermediate Levels of CodY Activity Are Required for Derepression of the Branched-Chain Amino Acid Permease, BraB
- "Missing" G x E Variation Controls Flowering Time in
- The Rise and Fall of an Evolutionary Innovation: Contrasting Strategies of Venom Evolution in Ancient and Young Animals
- Type IV Collagen Controls the Axogenesis of Cerebellar Granule Cells by Regulating Basement Membrane Integrity in Zebrafish
- Loss of a Conserved tRNA Anticodon Modification Perturbs Plant Immunity
- Genome-Wide Association Analysis of Adaptation Using Environmentally Predicted Traits
- Oriented Cell Division in the . Embryo Is Coordinated by G-Protein Signaling Dependent on the Adhesion GPCR LAT-1
- Disproportionate Contributions of Select Genomic Compartments and Cell Types to Genetic Risk for Coronary Artery Disease
- A Follicle Rupture Assay Reveals an Essential Role for Follicular Adrenergic Signaling in Ovulation
- The RNAPII-CTD Maintains Genome Integrity through Inhibition of Retrotransposon Gene Expression and Transposition
- Canonical Poly(A) Polymerase Activity Promotes the Decay of a Wide Variety of Mammalian Nuclear RNAs
- Allelic Variation of Cytochrome P450s Drives Resistance to Bednet Insecticides in a Major Malaria Vector
- SCARN a Novel Class of SCAR Protein That Is Required for Root-Hair Infection during Legume Nodulation
- IBR5 Modulates Temperature-Dependent, R Protein CHS3-Mediated Defense Responses in
- NINL and DZANK1 Co-function in Vesicle Transport and Are Essential for Photoreceptor Development in Zebrafish
- Decay-Initiating Endoribonucleolytic Cleavage by RNase Y Is Kept under Tight Control via Sequence Preference and Sub-cellular Localisation
- Large-Scale Analysis of Kinase Signaling in Yeast Pseudohyphal Development Identifies Regulation of Ribonucleoprotein Granules
- FANCI Regulates Recruitment of the FA Core Complex at Sites of DNA Damage Independently of FANCD2
- LINE-1 Mediated Insertion into (Protein of Centriole 1 A) Causes Growth Insufficiency and Male Infertility in Mice
- Hsp90-Associated Immunophilin Homolog Cpr7 Is Required for the Mitotic Stability of [URE3] Prion in
- Genome-Scale Mapping of σ Reveals Widespread, Conserved Intragenic Binding
- Uncovering Hidden Layers of Cell Cycle Regulation through Integrative Multi-omic Analysis
- Functional Diversification of Motor Neuron-specific Enhancers during Evolution
- The GTP- and Phospholipid-Binding Protein TTD14 Regulates Trafficking of the TRPL Ion Channel in Photoreceptor Cells
- The Gyc76C Receptor Guanylyl Cyclase and the Foraging cGMP-Dependent Kinase Regulate Extracellular Matrix Organization and BMP Signaling in the Developing Wing of
- The Ty1 Retrotransposon Restriction Factor p22 Targets Gag
- Functional Impact and Evolution of a Novel Human Polymorphic Inversion That Disrupts a Gene and Creates a Fusion Transcript
- The Dedicated Chaperone Acl4 Escorts Ribosomal Protein Rpl4 to Its Nuclear Pre-60S Assembly Site
- The Influence of Age and Sex on Genetic Associations with Adult Body Size and Shape: A Large-Scale Genome-Wide Interaction Study
- Parent-of-Origin Effects of the Gene on Adiposity in Young Adults
- Chromatin-Remodelling Complex NURF Is Essential for Differentiation of Adult Melanocyte Stem Cells
- Retinoic Acid Receptors Control Spermatogonia Cell-Fate and Induce Expression of the SALL4A Transcription Factor
- A Systems Approach Identifies Essential FOXO3 Functions at Key Steps of Terminal Erythropoiesis
- Protein O-Glucosyltransferase 1 (POGLUT1) Promotes Mouse Gastrulation through Modification of the Apical Polarity Protein CRUMBS2
- KIF7 Controls the Proliferation of Cells of the Respiratory Airway through Distinct Microtubule Dependent Mechanisms
- Integration of Posttranscriptional Gene Networks into Metabolic Adaptation and Biofilm Maturation in
- Lateral and End-On Kinetochore Attachments Are Coordinated to Achieve Bi-orientation in Oocytes
- Protein Homeostasis Imposes a Barrier on Functional Integration of Horizontally Transferred Genes in Bacteria
- A New Method for Detecting Associations with Rare Copy-Number Variants
- Histone H2AFX Links Meiotic Chromosome Asynapsis to Prophase I Oocyte Loss in Mammals
- The Genomic Aftermath of Hybridization in the Opportunistic Pathogen
- A Role for the Chaperone Complex BAG3-HSPB8 in Actin Dynamics, Spindle Orientation and Proper Chromosome Segregation during Mitosis
- Establishment of a Developmental Compartment Requires Interactions between Three Synergistic -regulatory Modules
- Regulation of Spore Formation by the SpoIIQ and SpoIIIA Proteins
- Association of the Long Non-coding RNA Steroid Receptor RNA Activator (SRA) with TrxG and PRC2 Complexes
- Alkaline Ceramidase 3 Deficiency Results in Purkinje Cell Degeneration and Cerebellar Ataxia Due to Dyshomeostasis of Sphingolipids in the Brain
- ACLY and ACC1 Regulate Hypoxia-Induced Apoptosis by Modulating ETV4 via α-ketoglutarate
- Quantitative Differences in Nuclear β-catenin and TCF Pattern Embryonic Cells in .
- HENMT1 and piRNA Stability Are Required for Adult Male Germ Cell Transposon Repression and to Define the Spermatogenic Program in the Mouse
- Axon Regeneration Is Regulated by Ets–C/EBP Transcription Complexes Generated by Activation of the cAMP/Ca Signaling Pathways
- A Phenomic Scan of the Norfolk Island Genetic Isolate Identifies a Major Pleiotropic Effect Locus Associated with Metabolic and Renal Disorder Markers
- The Roles of CDF2 in Transcriptional and Posttranscriptional Regulation of Primary MicroRNAs
- A Genetic Cascade of Modulates Nucleolar Size and rRNA Pool in
- Inter-population Differences in Retrogene Loss and Expression in Humans
- Cationic Peptides Facilitate Iron-induced Mutagenesis in Bacteria
- EP4 Receptor–Associated Protein in Macrophages Ameliorates Colitis and Colitis-Associated Tumorigenesis
- Fungal Infection Induces Sex-Specific Transcriptional Changes and Alters Sexual Dimorphism in the Dioecious Plant
- FLCN and AMPK Confer Resistance to Hyperosmotic Stress via Remodeling of Glycogen Stores
- MET18 Connects the Cytosolic Iron-Sulfur Cluster Assembly Pathway to Active DNA Demethylation in
- Sex Bias and Maternal Contribution to Gene Expression Divergence in Blastoderm Embryos
- Transcriptional and Linkage Analyses Identify Loci that Mediate the Differential Macrophage Response to Inflammatory Stimuli and Infection
- Mre11 and Blm-Dependent Formation of ALT-Like Telomeres in Ku-Deficient
- Genome Wide Identification of SARS-CoV Susceptibility Loci Using the Collaborative Cross
- Identification of a Single Strand Origin of Replication in the Integrative and Conjugative Element ICE of
- The Type VI Secretion TssEFGK-VgrG Phage-Like Baseplate Is Recruited to the TssJLM Membrane Complex via Multiple Contacts and Serves As Assembly Platform for Tail Tube/Sheath Polymerization
- The Dynamic Genome and Transcriptome of the Human Fungal Pathogen and Close Relative
- Secondary Structure across the Bacterial Transcriptome Reveals Versatile Roles in mRNA Regulation and Function
- ROS-Induced JNK and p38 Signaling Is Required for Unpaired Cytokine Activation during Regeneration
- Pelle Modulates dFoxO-Mediated Cell Death in
- PLOS Genetics
- Archiv čísel
- Aktuální číslo
- Informace o časopisu
Nejčtenější v tomto čísle- Single Strand Annealing Plays a Major Role in RecA-Independent Recombination between Repeated Sequences in the Radioresistant Bacterium
- The Rise and Fall of an Evolutionary Innovation: Contrasting Strategies of Venom Evolution in Ancient and Young Animals
- Genome Wide Identification of SARS-CoV Susceptibility Loci Using the Collaborative Cross
- DCA1 Acts as a Transcriptional Co-activator of DST and Contributes to Drought and Salt Tolerance in Rice
Kurzy
Zvyšte si kvalifikaci online z pohodlí domova
Současné možnosti léčby obezity
nový kurzAutoři: MUDr. Martin Hrubý
Všechny kurzyPřihlášení#ADS_BOTTOM_SCRIPTS#Zapomenuté hesloZadejte e-mailovou adresu, se kterou jste vytvářel(a) účet, budou Vám na ni zaslány informace k nastavení nového hesla.
- Vzdělávání



