-
Články
- Vzdělávání
- Časopisy
Top články
Nové číslo
- Témata
- Videa
- Podcasty
Nové podcasty
Reklama- Kariéra
Doporučené pozice
Reklama- Praxe
Evidence for Widespread Positive and Negative Selection in Coding and Conserved Noncoding Regions of
Selection affects patterns of genomic variation, but it is unclear how much the effects of selection vary across plant genomes, particularly in noncoding regions. To determine the strength and extent of selective signatures across the genome, we sequenced and analyzed genomes from 13 Capsella grandiflora individuals. Because C. grandiflora has experienced a large, stable effective population size, we expect that selection signatures will not be overly distorted by demographic effects. Our analysis shows that positive and negative selection acting on new mutations have broadly shaped patterns of genomic diversity in coding regions but not in most noncoding regions. However, when we focus only on noncoding regions that show evidence of constraint across species, we see evidence for strong positive and negative selection. In addition, we find that genes with high expression experience stronger negative selection than genes with low expression, but the extent of positive selection appears to be equivalent across expression categories.
Published in the journal: . PLoS Genet 10(9): e32767. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1004622
Category: Research Article
doi: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1004622Summary
Selection affects patterns of genomic variation, but it is unclear how much the effects of selection vary across plant genomes, particularly in noncoding regions. To determine the strength and extent of selective signatures across the genome, we sequenced and analyzed genomes from 13 Capsella grandiflora individuals. Because C. grandiflora has experienced a large, stable effective population size, we expect that selection signatures will not be overly distorted by demographic effects. Our analysis shows that positive and negative selection acting on new mutations have broadly shaped patterns of genomic diversity in coding regions but not in most noncoding regions. However, when we focus only on noncoding regions that show evidence of constraint across species, we see evidence for strong positive and negative selection. In addition, we find that genes with high expression experience stronger negative selection than genes with low expression, but the extent of positive selection appears to be equivalent across expression categories.
Introduction
Determining the amount of positive and negative selection and how it varies across the genome has wide-ranging implications for understanding genome function and the maintenance of genetic variation [1]. Current evidence suggests that both positive and negative selection are common in coding and some noncoding sequences in several model systems [2]–[8]. However our understanding of genome-wide selection in plants remains relatively limited [6], particularly in noncoding regions.
One key question concerns the extent to which both positive and negative selection act in noncoding regions of the genome compared with coding regions [2], [5]–[8]. For example, it has been suggested that the majority of adaptive evolution may occur in noncoding regulatory regions, where new mutations may have fewer deleterious pleiotropic effects [9], [10] but see [11]. Halligan and colleagues [8] showed that there have been many more adaptive substitutions in noncoding DNA than in coding regions in house mice, although adaptive substitutions in coding regions may experience stronger positive selection. Moreover, studies in Drosophila species and vertebrates have found that, although noncoding regions as a whole are generally less conserved than coding regions, there is more functional noncoding sequence than constrained coding sequence by a considerable margin [2], [12].
Comparing these results to noncoding selection across plant genomes is of particular interest because it has been hypothesized that in plants, regulatory evolution may occur more often through gene duplication than cis-regulatory change [13], possibly leading to lower levels of functional constraint and positive selection on plant noncoding DNA. Consistent with this prediction, Haudry and colleagues [14] recently compared the genomes of nine Brassicaceae species, and showed that approximately one quarter of the conserved sites in the Arabidopsis thaliana genome were in noncoding regions, a much smaller fraction than found to date in studies of vertebrates and Drosophila. However, the strength of selection on these noncoding sites, the extent of species-specific selection in noncoding regions, and the extent of positive selection in noncoding regions compared with coding regions have not been quantified.
While the strength of selection is expected to vary between coding and noncoding sequence, it also varies between genes. Gene expression level is one of the major determinants of rates of nonsynonymous evolution in coding regions in many species [15]–[17], including plants [18]–[21]. Variation in the strength of selection on genes could reflect differences in the relative importance of gene products for organism fitness, or it may simply relate to inherent properties of expression [22]. For example, deleterious mutations that cause misfolding or mis-interaction have more opportunity to interfere with cellular function when they occur in high expression genes [23]–[25]. Regardless of the underlying selective mechanisms, the negative correlation between expression level and nonsynonymous divergence could reflect relaxed purifying selection in lowly expressed genes, increased positive selection in lowly expressed genes, or both.
Here, we use population genomics to quantify the strength of both positive and negative selection inside and outside of coding regions and within highly and lowly expressed genes in a species-wide sample of 13 outbred Capsella grandiflora individuals. C. grandiflora is an obligately outcrossing member of the Brassicaceae family with a large effective population size (Ne∼600,000) and relatively low population structure [26], [27]. We estimate the strength of negative selection by fitting polymorphism data to a model of the distribution of negative fitness effects of mutations. We then quantify the contribution of positive selection to divergence in C. grandiflora using two complementary approaches: an extension of the McDonald-Kreitman test [28] and an analysis of neutral variation linked to lineage-specific fixed substitutions [29]. Our results demonstrate that both positive and negative selection are pervasive in coding regions, 5′ and 3′ untranslated regions (UTRs), and constrained noncoding regions of the C. grandiflora genome, but also that a large proportion of noncoding DNA may evolve neutrally. In addition, we find stronger negative selection in high expression genes compared to low expression genes, suggesting that differences in negative selection drive differences in rates of molecular evolution.
Results
Genome wide patterns of polymorphism
We sequenced 13 outbred C. grandiflora individuals (26 sampled haploid chromosomes; ∼140 Mb genome assembly) sampled from across the species' range in northern Greece using single-end Illumina GAII sequencing (Table S1). The resulting 108 bp reads were mapped to the Capsella rubella reference genome [30] using the Stampy aligner resulting in a median coverage of 34 reads per sample per site. Genotypes were called using the Genome Analysis Toolkit's Unified Genotyper [31]. After filtering for quality and depth (see Methods), we were left with ∼27 million sites, ∼1.5 million of which were single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) (Table S2). Sites from across the genome were identified as 0-fold degenerate, 4-fold degenerate, intronic, 5′ UTR, 3′ UTR, or intergenic, based on the annotation of the C. rubella reference genome [30]. To avoid comparing sites that do not have equivalent mutation profiles, we excluded sites in coding regions that were neither 4-fold nor 0-fold degenerate. After filtering, our analysis includes 30–40% of coding and noncoding sites, except in intergenic regions where only approximately 10% of sites are retained due to the higher repeat content in these regions and the removal of highly repetitive pericentromeric DNA (Figure S1).
Consistent with previous estimates made using a much smaller set of loci (257 Sanger-sequenced loci) and a different range-wide sample [32], average nucleotide diversity at 4-fold degenerate sites (Watterson's Θw) was 0.022 and there was evidence for an excess of rare variants genome-wide at 4-fold degenerate sites compared with the standard neutral model (Tajima's D = −0.512). Introns (Θw = 0.020) and intergenic regions (Θw = 0.019) showed only slightly lower levels of nucleotide diversity than 4-fold degenerate sites, suggesting that the large majority of sites in these regions are effectively neutral, or subject to comparable levels of purifying selection as 4-fold degenerate sites. 5′ and 3′ UTRs showed a much stronger diversity reduction (Θw = 0.015 and 0.014 respectively), while 0-fold degenerate nonsynonymous sites showed the strongest reduction (Θw = 0.005).
Neutral diversity at 4-fold degenerate sites near centromeric regions was elevated on most chromosomes, similar to observations made in A. thaliana [33], Arabidopsis lyrata [34], [35] and Medicago truncatula [36], (Figure S2). As with these other species, this effect is not obviously caused by higher mutation rates, since divergence between Capsella and Neslia is not clearly elevated in these regions (Figure S2). Although elevated error rates in repetitive regions may contribute to high diversity, our observation of high diversity in these regions is still apparent after extensive filtering (see Methods). This increase in neutral diversity in pericentromeric regions may reflect a weakening of background selection in regions of low gene density, as recently shown in models of background selection applied to Arabidopsis [37]. Furthermore, diversity generally declines towards the ends of the chromosomes, potentially reflecting the stronger effects of background selection and/or selective sweeps in regions of relatively low recombination but high gene density, where the effects of linked selection are expected to be strongest. Consistent with these interpretations, we see an increase in diversity in regions of low coding density (Figure S3).
We also examined individual heterozygosity in sliding windows along each chromosome. A number of individuals showed large stretches of homozygosity indicative of biparental inbreeding (Figure S4 and Figure S5). Consistent with these regions reflecting local biparental inbreeding, no such regions are found in our sample that is derived from a between-population cross, called AXE. These regions of identity-by-descent (IBD) in our data highlight that, despite being self-incompatible and obligately outcrossing, local biparental inbreeding can still generate excess homozygosity in stretches across the genome. To avoid biased estimation of species-wide allele frequencies in these regions, we subsampled the data to treat all IBD regions as haploid rather than diploid sequence for the purposes of allele frequency estimation, although treating these regions as diploid does not qualitatively change our conclusions (Figure S6).
Genome-wide measures of purifying selection
In order to quantify the amount of negative selection acting on different categories of sites, we used the methods of Eyre-Walker & Keightley [1] to compare the allele frequency spectrum (AFS) and divergence of various site categories to those for 4-fold degenerate sites, which are putatively neutral (Figure 1A). Consistent with the patterns of diversity described above, negative selection is generally much stronger in coding regions than noncoding regions (Figure 1A). This pattern is most clearly seen in 0-fold degenerate sites, the only site category with a sizable fraction of sites in the strongest category of negative selection (41%). Of the noncoding categories, UTRs show much stronger negative selection than other regions. In C. grandiflora ∼55% of both 5′ and 3′ UTRs are under moderate levels of purifying selection (Nes>1), but a considerably larger fraction of UTR sites are effectively neutral (45%) than 0-fold degenerate sites (14%). Additionally while the UTRs and CNSs (see below) show a signal of strong purifying selection (Nes>10), they experience less strong selection than 0-fold degenerate sites.
Fig. 1. Estimates of negative and positive selection on coding and noncoding sites in C. grandiflora. 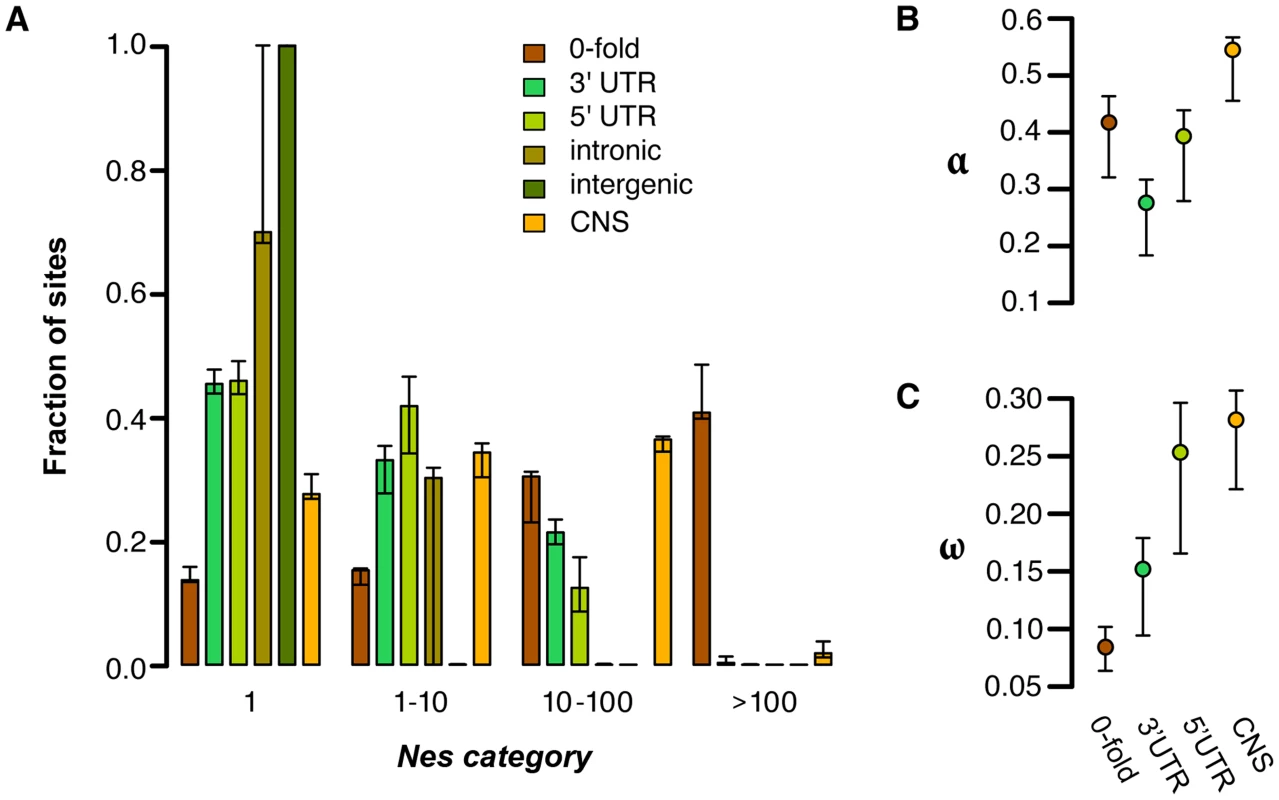
A) The proportion of sites found in each bin of purifying selection strength, separated by site type, B) The proportion of divergent sites fixed by positive selection, and C) the rate of adaptive substitution relative to neutral divergence. Error bars represent 95% bootstrap confidence intervals. Genome-wide, we estimate that the proportion of intergenic sites that are nearly neutral approaches 100% and that approximately 70% of intronic sites are effectively neutral. Furthermore, bootstrapping results suggest that there is not significant support for less than 100% of intronic sites being effectively neutral. The large confidence intervals around estimates of selection on intronic sites may be due to strong selection at splice site junctions [14] coupled with typically weak to no selection outside of splice junctions. To test for selection near splice junctions, we quantified selection acting on the first and last 30 bp of each intron separately from sites in the middle of introns. While 100% of sites in the middle of introns are estimated to be effectively neutral, only 68% of sites in junctions are, suggesting that our wide confidence intervals around intronic sites can be partially explained by variance caused by sampling sites in these different regions between bootstraps. These generally low estimates of Nes in (non-junction) intronic and intergenic sites imply a general lack of purifying selection in most noncoding regions, a lack of sensitivity to detect small proportions of selected sites, and/or nearly equivalent purifying selection to synonymous sites.
Although our analysis suggests very low levels of purifying selection in noncoding regions other than UTRs and splice junctions, these global analyses may miss signatures of purifying selection on a small proportion of noncoding sites. One candidate set of sites that may have different signatures of selection are conserved noncoding sequences (CNSs); these are regions that show evidence of cross-species conservation, and are therefore prime candidates for functional noncoding sequences subject to selection. We identified CNSs across nine Brassicaceae genomes, following the implementation in Haudry et al. [14]. For this study, we used the Capsella genome as a reference for alignment, but excluded Capsella when identifying CNSs in order to avoid circularity when quantifying selection from diversity [8]. This method allows our analysis of selection on noncoding sites using polymorphism to be more independent of the comparative analysis. When we look at only these conserved regions in our C. grandiflora sample we see a small proportion of effectively neutral sites (28%) compared to the noncoding regions as whole, suggesting that the majority of CNS sequences are subject to purifying selection (Figure 1). However, estimates suggest that CNSs are generally under weaker purifying selection than nonsynonymous (0-fold) sites and experience primarily weak and intermediate purifying selection (Figure 1).
Although CNSs as a whole retain a considerable proportion of effectively neutral sites, it is of interest to examine whether particular classes of CNS show stronger selection. To examine differences between categories we quantified selection on the different types of CNSs separately (Figure S7). In most categories, about 25% of sites are nearly neutral, a slightly stronger signal of purifying selection than when we pool all CNSs. Intronic CNSs have a larger proportion of effectively neutral sites than other categories, in agreement with the general neutrality of intronic sites (Figure 1). In contrast, small noncoding RNAs (sncCNSs) have a stronger signal of selection than the other CNS categories. However, the number of sites used to make the AFS for each of these categories varies substantially (Table S2), and our sample of sncCNSs has very little polymorphism (155 segregating sites). Nevertheless, despite the wide confidence intervals, sncCNSs still show a significantly (p<0.001) smaller fraction of sites that are nearly neutral (Nes<1) than the pooled CNSs, which could be due to strong selection for sequence specificity to obtain the proper secondary structure important for RNA activity [38]. This effect is consistent with sncCNSs showing a higher degree of conservation across the Brassicaceae [14] and having traceable orthologs in other plants.
Genome-wide estimates of positive selection
We used the approach of Eyre-Walker and Keightley [28] to estimate the proportion of fixations driven by positive selection (α) and the rate of positive selection (ω) while taking into account the effect of slightly deleterious mutations, which can bias estimates of positive selection downwards. To do this, we estimated divergence using whole genome alignments of C. rubella, A. thaliana, and Neslia paniculata (estimate of 4-fold synonymous divergence Ks between C. rubella and N. paniculata is Ks = 0.14). Because the large majority of noncoding sites are estimated to be effectively neutral, and because of alignment concerns between species in unconstrained noncoding regions, we focus our estimates of positive selection on 0-fold degenerate sites, CNS sites, and UTRs. We found that 0-fold degenerate sites show a very high proportion of divergence driven by positive selection (Figure 1B; α = 0.417) and estimates of the rate of adaptive substitution relative to synonymous substitution (Figure 1C; ω = 0.08). Similarly, UTRs and CNS sites show evidence for positive selection (Figures 1B and 1C). These results generally suggest widespread positive selection in both nonsynonymous and functional noncoding genomic regions.
If many of the amino acid changes between C. grandiflora and its nearest relatives are due to recent, strong positive selection from new mutations, we expect to see the signature of selective sweeps: reduced neutral diversity surrounding amino acid fixations [39], [40]. We tested for this signature by measuring the proportion of 4-fold degenerate sites in each window that were polymorphic (referred to hereafter as ‘4-fold diversity’) in non-overlapping 1 kb windows surrounding fixed replacement (n = 60,378), and silent (n = 83,812) substitutions in C. grandiflora. We found that 4-fold diversity surrounding fixed replacement substitutions was lower than 4-fold diversity surrounding fixed silent substitutions in the 4 kb window surrounding substitutions (Figure 2A). This result was robust to various window sizes from 500 kb to 2 kb (Figure S8) and a one-tailed test for reduced 4-fold diversity around replacement sites was significant (p<0.01 for 2 kb on either side of the substitution).
Fig. 2. Linked neutral diversity and divergence as a function of distance from fixed substitutions across the C. grandiflora genome. 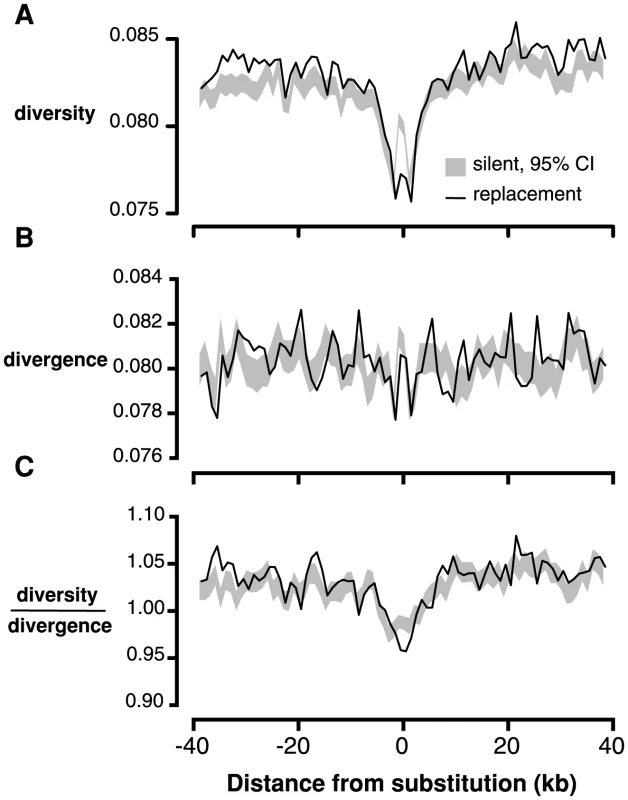
A) Diversity at 4-fold degenerate sites, B) Divergence at 4-fold degenerate sites, and C) Diversity/divergence at 4-fold degenerate sites. In all figures, black lines represent measures surrounding fixed replacement substitutions and gray shading represents 95% confidence intervals, from bootstrapping, surrounding silent substitutions. Patterns of diversity may be distorted by elevated mutation rates surrounding substitutions [39], which would increase diversity and divergence in C. grandiflora. Consistent with this prediction, divergence at 4-fold degenerate sites (‘4-fold divergence’) is elevated around synonymous and replacement substitutions (Figure 2B). To control for elevated mutation rate, we divided diversity by divergence at 4-fold degenerate sites (subsequently referred to as ‘4-fold diversity/divergence’). We observed a reduction in 4-fold diversity/divergence around replacement substitutions compared to silent substitutions, demonstrating that the signature of recurrent sweeps is not an artifact caused by variation in mutation rate (Figure 2C, p<0.01 for 1 kb on either side of the substitution).
An analogous test for selective sweeps around fixations in noncoding regions is challenging because the test depends on accurately identifying interspersed functional and neutral sites, a difficult task in noncoding regions [8]. Instead, we compared 4-fold diversity and divergence around fixed substitutions in CNS regions (n = 12,578) with 4-fold diversity and divergence around fixed substitutions in non-conserved intergenic, intronic, and UTR regions (n = 117,178). Interestingly, there is a reduction in both 4-fold diversity and divergence surrounding fixed substitutions in CNSs compared to non-conserved noncoding regions (Figure S9). It is not clear why 4-fold divergence decreases around CNS substitutions; it is possible that in genomic scans for conserved regions, large-scale constraint might span both coding and noncoding sequence, causing non-independence and reducing divergence at 4-fold degenerate sites near CNSs. However, there is still a reduction in 4-fold diversity/divergence around fixed substitutions in CNSs compared to those in non-conserved intergenic regions, consistent with the action of recurrent selective sweeps (Figure 3A).
Fig. 3. Linked neutral diversity/divergence surrounding conserved noncoding sequences (CNSs). 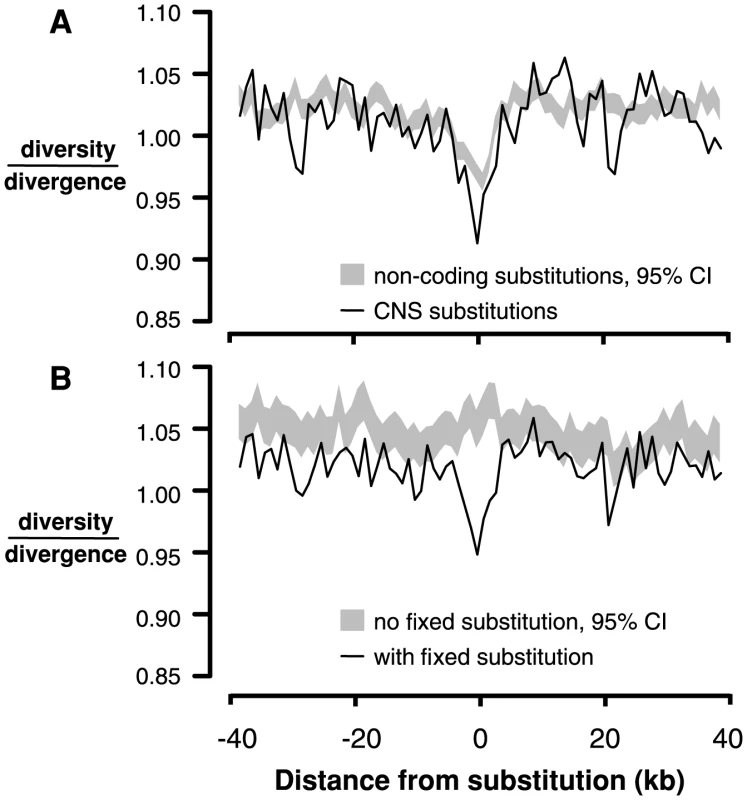
A) Diversity/divergence at 4-fold degenerate sites as a function of distance from fixed substitutions in CNSs (black lines) and fixed substitutions in non-conserved intergenic sequence (gray shading, 95% confidence interval). B) Diversity/divergence at 4-fold degenerate sites as a function of distance from CNSs containing fixed substitutions (black line) and CNSs without any fixed substitutions (gray shading, 95% confidence interval). The observed reduction in diversity/divergence around CNS substitutions could also reflect the action of background purifying selection; sites closer to CNSs may experience a reduction of neutral diversity due to greater purifying selection on mutations in CNSs. This effect is not a problem for comparisons between replacement and silent substitutions because they are interspersed within the same exons, so diversity and divergence around these sites experience the same background selection. To ensure that the reduction in diversity/divergence surrounding CNS substitutions compared to non-conserved noncoding substitutions is not due to differences in background selection between CNS and intergenic sites, we compared neutral diversity and divergence surrounding CNSs that contain at least one fixed substitution to neutral diversity and divergence around those that do not. There is a reduction in neutral diversity/divergence surrounding CNSs containing a fixed substitution (n = 12,884) compared to CNSs without fixed substitutions (n = 41,212), suggesting that this signature of recurrent sweeps is not driven by background selection specific to CNSs (Figure 3B).
Effects of expression and selection
We measured expression levels of all expressed genes using RNA extracted from leaf tissue of 10 of the 13 C. grandiflora individuals. Genes were sorted by mean expression level and split into four equally sized groups, which will be referred to as “high”, “mid-high”, “mid-low”, and “low” expression genes. We calculated polymorphism within C. grandiflora and lineage-specific divergence from N. paniculata and A. thaliana for sites within these genes. As expected from previous studies, dN/dS is considerably lower in high expression genes (0.15) than low expression genes (0.22). In addition, dN/dS is negatively correlated with expression level across all genes (correlation coefficient = −0.051, p<0.001).
To test whether the strength of negative selection differs between expression categories we compared the allele frequency spectra of sites in different expression categories. Replacement polymorphisms in high expression genes show a stronger skew towards rare alleles than those in low expression genes (Figure S10). In addition, a larger proportion of replacement sites are invariant in high expression genes (98.9%), than in low expression genes (97.8%), consistent with stronger negative selection. Comparisons of the distribution of fitness effects show that high expression genes have a much smaller proportion of effectively neutral sites (6.8%) than low expression genes (16%, randomization test [28], p<0.001) (Figure 4A).
Fig. 4. Estimates of negative and positive selection on nonsynonymous sites in genes of varying expression level. 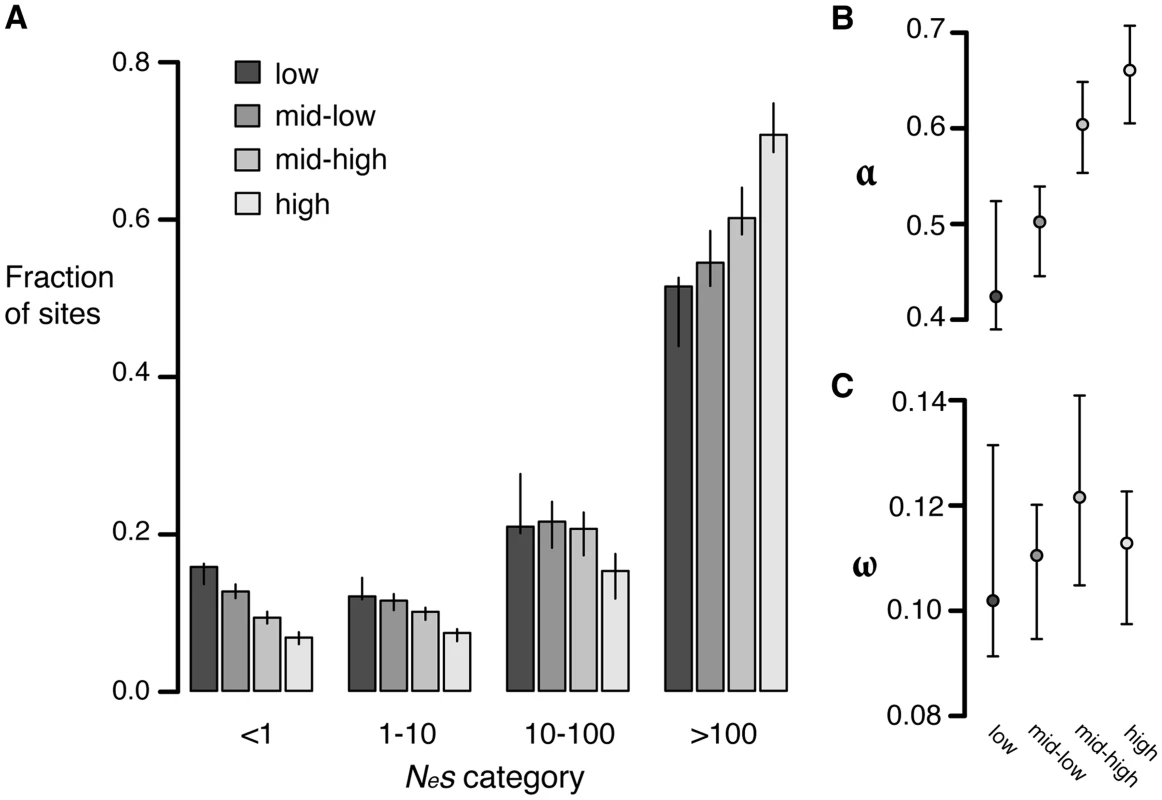
A) The proportion of sites found in each bin of purifying selection strength, separated by expression level. B) The proportion of divergent sites fixed by positive selection and C) The rate of adaptive substitution relative to neutral divergence. Error bars represent 95% bootstrap confidence intervals. Increased divergence in low expression genes relative to high expression genes could also be caused by increased positive selection in low expressed genes compared to highly expressed genes. To test this possibility, we calculated α and ω as described above. High expression genes have a significantly higher value of α (0.66) than low expression genes (0.42, p<0.01) but the ω value for both classes is similar (high: 0.11, low: 0.10, p = 0.38), suggesting that the rate of positive selection does not differ between high and low expression genes (Figure 4B, 4C). The difference in α between the two categories likely reflects the reduction in the number of weakly deleterious and effectively neutral mutations that are able to fix due to stronger purifying selection in high expression genes compared to low expression genes, causing a higher proportion of those amino acids that do reach fixation to be positively selected.
Discussion
In this population genomic survey of C. grandiflora, we demonstrated that positive and negative selection contribute to DNA sequence variation in protein-coding regions, UTRs, and CNSs. We also showed that differences in divergence between high and low expression genes are due to increased negative selection in high expression genes, not increased positive selection in low expression genes. In addition, we found a clear signature of recurrent selective sweeps contributing to divergence in coding regions as well as CNSs. Overall, our evidence for widespread positive and negative selection in C. grandiflora is in line with expectations, given its outcrossing mating system, large Ne, limited population structure, and lack of a recent whole genome duplication [6].
In contrast, selection appears to be very rare in intergenic and (non-junction) intronic regions that are not conserved across Brassicaceae species. In particular, we cannot detect significant evidence of purifying selection in intergenic or intronic regions as a whole, suggesting that selected sites within these regions must be rare or absent. However, when we only examine CNSs, we do see evidence of selection, indicating that at least 5% of sites in intergenic regions are selected, but the DFE approach is not sensitive enough to detect selection on such a small subset of intergenic sites. This result implies that this approach is likely to also be missing lineage-specific selection when it comprises a relatively small fraction of sites, and it highlights the importance of integrating additional evidence of function (comparative and experimental) for improved quantification of selection.
The general neutrality of noncoding regions, based on population genomic analysis, is consistent with the conclusions of Haudry and colleagues [14], who used comparative genomics approaches to estimate that only 5% of noncoding bases are under selection in the Arabidopsis genome. This result contrasts with Drosophila and humans, where a relatively large fraction of selected sites are found in noncoding regions [6]. For example, in Drosophila, only 30%–70% of intronic and intergenic regions are nearly neutral [2], [28], [29]. Similarly, Halligan et. al. [8] recently used information from the DFE to infer the number of adaptive substitutions in mice both in coding and noncoding regions. They show that the majority (approximately 80%) of the adaptive substitutions in the mouse genome are in noncoding regions and suggest that they may have regulatory function. In contrast, our data show that C. grandiflora has similar numbers of adaptive substitutions in 0-fold sites (50.6 kb) and noncoding sites (21.6 kb, 3′ UTR excluding CNSs; 10.2 kb, 5′ UTR excluding CNSs; 32.7 kb, CNS; 64.4 kb total). Additionally, the width of diversity reductions surrounding replacement substitutions and substitutions in CNS regions appear comparable, suggesting that there is little evidence for a difference in the strength of positive selection on substitutions in coding regions compared to conserved noncoding regions. Our results are consistent with previous suggestions that, unlike in animals, plant genomes may contain fewer noncoding regulatory sequences subject to positive and negative selection, possibly because gene expression can be modified through frequent gene duplication and functional divergence rather than through the evolution of novel regulatory elements [13]. In future work, it would be interesting to quantify the extent to which adaptive changes in gene expression in plants occur following gene duplication relative to between-species divergence at orthologous genes.
Unlike other classes of noncoding sequence, UTRs show relatively high levels of purifying selection, likely reflective of their function in post-transcriptional regulation [41]. UTRs are also under stronger negative selection than other noncoding regions in Drosophila [2], and this result is also in line with the previous study using comparative genomics in the Brassicaceae [14]. Interestingly, we infer that a large fraction of selected sites in UTRs may be outside of CNS regions identified in between-species comparisons. In particular, using estimates of the proportion of sites under selection, we estimate that 88% of 3′ UTR and 77% of 5′ UTR selected sites are outside of conserved regions. This result suggests that there may be many species-specific (i.e., non-CNS) functional regions in UTRs and they may therefore play an important role in recent or local adaptation.
One important consideration is the extent to which our analyses are truly reflective of genome-wide patterns of selection. Despite whole genome sequencing, our analyses are restricted to approximately 20% of the genome, and only 10% of intergenic sites, largely due to the fact that a large fraction of the genome is pericentromeric, repetitive and/or surrounds insertion/deletion events. It is important to recognize that our estimates of selection apply strictly to this ‘accessible’ genome and that the extent of purifying and positive selection on the repetitive regions remains difficult to assess. Nevertheless, we would expect that our conclusions about low levels of purifying and positive selection across most noncoding regions are likely conservative with respect to these filters because a large proportion of repetitive DNA is likely to be neutral. On the other hand, rates of positive selection may be elevated in coding regions of duplicate genes filtered out of our analysis [42], suggesting that our estimates of positive selection in protein-coding regions may also be a lower bound.
A second concern is the extent to which synonymous sites are neutrally evolving. Although analysis of codon usage bias from population genetic data does suggest the action of some purifying selection on synonymous sites in this species [43], the strength of selection inferred is close to effective neutrality. Furthermore, synonymous site selection is expected to be stronger in more high expression genes [23], [44], causing us to underestimate, rather than overestimate, the difference in the strength of purifying selection compared with low expression genes. Thus, while selection on synonymous sites may bias our estimates of selection slightly downward, our general conclusions are likely to be robust to violations of neutrality. Nevertheless, more investigation of the action of selection on synonymous sites is important, particularly given growing evidence for synonymous site selection that may reflect gene regulation, in addition to codon usage [45], [46].
At synonymous sites, we see an excess of rare variants, as indicated by a negative Tajima's D. The excess of rare variants is unlikely to be explained by a high Illumina error rate, as our observed value of −0.51 is nearly identical to a previous estimate (−0.52) from Sanger-sequenced loci and a comparable geographic sampling [27]. This previous study found that, while population subdivision was low compared to other herbaceous species studied, there were still three major geographic clusters (average between-population Fst of 0.11). If we restrict our dataset to one of the three geographic regions based on these previous results, Tajima's D approaches zero (−0.16 at 4-fold degenerate sites), suggesting that the excess of rare variants at synonymous sites may be largely due to population structure.
Measuring positive selection
In this study, we took advantage of the two detectable signatures expected to remain after recurrent classic selective sweeps from new mutations: 1) an excess of replacement substitutions relative to expectations based on polymorphism, and 2) reduced neutral diversity near fixed differences. Our findings strongly suggest that positive selection has been common in coding regions, UTRs and conserved noncoding regions in C. grandiflora and that classic selective sweeps contribute significantly to divergence in these regions. To our knowledge, this is the first time that the signature of recurrent selective sweeps has been observed in a non-Drosophila species, despite being tested in other species [8], [47]. Our ability to detect the signature of recurrent sweeps may be because C. grandiflora has relatively low linkage disequilibrium, increasing power.
However, many positively selected alleles may not follow the trajectory of a classic selective sweep. Soft sweeps — adaptation from an allele previously maintained in the population by mutation-selection-drift balance or the simultaneous fixation of multiple independently derived mutations at the same allele — may still increase the replacement to silent divergence ratio, but are expected to have a smaller effect on linked neutral diversity [48]–[50]. We expect that soft sweeps will also be common in C. grandiflora because of its large Ne [50], [51]. In addition, adaptation in genes that contribute to polygenic traits is often expected to occur without fixation of new mutations [52], and this will be missed by both of our tests for positive selection. These considerations suggest that both measures of positive selection are conservative and may miss many instances of positive selection acting in the genome.
Our conclusions about the prevalence of selective sweeps in C. grandiflora may seem to conflict with our observation that diversity and Tajima's D are slightly higher at 4-fold degenerate sites than intergenic sites, since frequent sweeps in coding regions should reduce diversity more strongly in sites near and within genes. There are two likely contributors to this discrepancy. First, recurrent sweeps may in fact reduce average diversity in 4-fold degenerate sites and, by using these sites to set neutral expectations, we are underestimating the strength of purifying selection in intergenic regions. Second, because recombination rates are relatively high, and intergenic regions near coding regions relatively small in Capsella, the average impact of linked selection may be similar at 4-fold degenerate sites and intergenic sequences.
Expression level and selection
Highly expressed genes diverge less than genes with low expression in many species [15]–[17], [19], [24], [53]–[55]. This pattern could be due to stronger positive selection in low expression genes or stronger negative selection in high expression genes, or both. Our results suggest that variation in divergence rates between high and low expression genes is largely due to increased negative selection in high expression genes compared to low expression genes. This result is consistent with previous studies that have suggested that new nonsynonymous mutations that cause protein mis-folding or mis-interaction will have stronger deleterious effects in high expression genes than low expression genes and that new mutations that cause mRNA mis-folding are under stronger negative selection in high expression genes than low expression genes [23]–[25]. In addition, our results agree with a similar study in Medicago truncatula that found stronger purifying selection in genes that were expressed than in genes that were not expressed [20].
Methods
Sampling and sequencing
Population samples for C. grandiflora represented a ‘scattered’ sample of one individual per population for twelve populations from across the geographic range in Greece, plus a thirteenth sample that was the product of a cross of two additional populations (Table S1). Plants were grown for several months at the University of Toronto greenhouse, and genomic DNA was extracted from leaf tissue using a modified CTAB protocol. Library preparation and single-end genomic sequencing were conducted at the Genome Quebec Innovation Centre at McGill University on the Illumina GAII platform. Each sample was sequenced in 2 to 3 lanes and with a read length of 108 bp.
Leaves from 10 of the 13 individuals were collected and flash frozen for RNA extraction using Qiagen's RNAeasy plant extraction kit. This RNA was sequenced at the Genome Quebec Innovation Centre, on an Illumina GAII platform with one individual per lane, generating single-end 108 bp long reads. The RNA sequence from these 10 individuals was used for the annotation of the C. rubella reference genome, as reported in [30], but the raw sequence data was reanalyzed for this study (see below).
Genotyping
Genomic reads were aligned to the C. rubella reference genome [30] using the Stampy aligner 1.0.13 with default settings [56]. Sites around indels were realigned using the Genome Analysis Toolkit (GATK) v1.05777 indel realigner [31]. Genotype and SNP calls were conducted using the GATK UnifiedGenotyper with default parameters [57], after aligning and genotyping the median site quality was 89 and the median individual depth across all sites was 34.
To get a rough assessment of genotyping error rates, we conducted Sanger sequencing from nine coding regions in six of our individuals. From a total of 16,389 bp of Sanger sequence, we found 8 differences between Sanger and Illumina genotypes, giving an estimated error rate of 0.00049. Three of these disagreements were due to three segregating bases at a single site, which we excluded in our GATK genotyping protocol. As we suspect several of these disagreements may be due to Sanger sequencing errors due to variation in allelic representation of heterozygotes, this provides an upper bound estimate of error rate in coding regions, although higher indel rates and repetitive sequence in noncoding DNA may lead to a higher error rate in those regions.
AFSs were generated from counts of sites in the VCF. Invariant sites were excluded from the AFS if (1) the site quality score was below 90, (2) the fraction of reads containing spanning deletions was not 0 (i.e. the ‘Dels’ value was greater than zero), or (3) any individual's read depth was less than 20 or greater than 60. Additionally, polymorphic sites were excluded, based on filters 1–3, if (4) the most likely genotype of any individual did not have a phred scaled likelihood score of 0, and if (5) the second most likely genotype had a phred likelihood score less than 40. Additionally, entire regions of the genome were filtered out of the analysis if less than 30% of the sites in a 20 kb window passed all other filters. This final filter primarily eliminated pericentromeric regions that were highly repetitive, where we were not confident in genotype calls and observed high heterozygosity.
Our data showed evidence of identity by descent (IBD) in some samples (Figure S4). We identified these regions by splitting the genome into 200 kb windows, then calculating FIS (Figure S5). If FIS was greater than 0.5, the region was flagged as IBD. Across all samples no more than 3 of these regions overlapped. For further analyses we downsampled data in other regions down to 23 chromosomes treating any region of IBD as haploid to ensure that no IBD region was sampled twice from the same individual.
Divergence
We calculated lineage-specific divergence in two ways. First, we aligned the C. rubella reference sequence with sequence data from A. thaliana and N. paniculata using lastZ [58] with chaining, as previously described [14]. In order to get an estimate of divergence unique to the Capsella lineage, we called sites as diverged where A. thaliana and N. paniculata had the same nucleotide and this nucleotide differed in the C. rubella sequence. If any of the three species was missing data at a site, then that site, and sites 5 bp upstream and downstream of the site, were excluded from divergence analyses in order to avoid inflating divergence because of spurious alignments around indels.
We used a second method for calculating divergence for comparisons that included only coding sequences, particularly for the comparison of genes with different expression levels. We found orthologs between C. rubella, A. thaliana and N. paniculata genes using InParanoid [59] and MultiParanoid [60]. The peptide sequences of these orthologs were aligned using DialignTX [61], and reverse-translated into coding sequence. Whole-gene divergence at synonymous and nonsynonymous sites was calculated, using PAML [62], under a model where ω was allowed to vary in the Capsella lineage compared to other branches.
We conducted comparisons of estimates of the distribution of fitness effects using the two methods above with identical gene sets, and found a very strong concordance of results (see Figure 4 compared to Figure S11). Furthermore, while we don't predict a significant effect on results, it is important to note that the two methods also differed in how selected and nonselected classes were determined: the first distinguishes between 0-fold and 4-fold sites and discards other sites, while the second distinguishes between synonymous and nonsynonymous sites, including all data. However, both approaches gave comparable estimates of positive and negative selection.
Identifying conserved noncoding sequences
Conserved noncoding sequences (CNS) were identified in the C. rubella genome by first obtaining whole-genome multiple alignments, using a variant of the lastZ/Multiz pipeline previously described [14], [63] and using C. rubella as the reference genome. The C. rubella genome sequence was then neutralized (bases replaced with N) and the PhastCons tool used to quantify family-wide levels of conservation. CNSs were then identified, based on extended (>12 nt) near-continuous regions of high conservation as previously described [14].
Estimates of the distribution of fitness effects and α
Site categories were determined based on the Joint Genome Institute's gene annotation of the C. rubella reference genome [30]. The allele frequency spectra (AFS) and divergence values were calculated for each category of sites, and DFE-alpha [28], [64] was used to estimate the fraction of sites under negative selection and α, using 4-fold degenerate sites as the neutral reference. The genome was broken up into 10 kb regions and these regions were bootstrapped 200 times to generate 95% CIs for selection on each category of sites. We tested for a significant difference in selection between the pooled set of CNSs and each individual category of CNSs using a randomization test, as in Keightley & Eyre-Walker [28], by calculating the proportion of bootstraps where selection was higher in the pooled set of CNS versus the category of interest. Because this is a two-tailed test, we report twice this proportion as the p value.
Test for signatures of recurrent selective sweeps
We used the multiple species alignments of orthologous genes, generated as described above, to identify silent and replacement single-nucleotide sites that were the same in A. thaliana and N. paniculata but differed in the C. rubella reference, suggesting that the substitution had most likely occurred in the Capsella lineage after divergence from N. paniculata. From these substitutions, we identified those that did not diverge between C. rubella and C. grandiflora and were fixed in C. grandiflora.
We calculated neutral diversity in sliding windows around fixed substitutions by calculating the proportion of 4-fold degenerate sites within these windows that were polymorphic in C. grandiflora (i.e., the proportion of segregating sites). Neutral divergence was measured by calculating the proportion of 4-fold sites within these windows that diverged in the Capsella lineage. Diversity/divergence was calculated by dividing diversity by divergence in each window. We conducted this analysis for windows of 500 bp, 1 kb, and 2 kb, extending 40 kb from each substitution. We chose this window size range to match analysis done in Sattath et al [39]. For each of the above measures, we bootstrapped by substitution (n = 1000) and removed the top and bottom 25 bootstraps to construct 95% confidence intervals. Following Hernandez and colleagues [47], we tested the null hypothesis that diversity/divergence around replacement and silent substitutions does not differ by calculating a one-tailed p value for each window, equal to (i+1)/(n+2) where i is the number of bootstraps in which diversity/divergence around silent sites is lower or equal to the actual diversity/divergence around replacement sites, and n is the total number of bootstraps.
To detect the effects of linked selection on noncoding DNA, we compared diversity around fixed substitutions within CNSs to diversity around fixed substitutions in non-conserved intergenic regions. To find these substitutions, we compared the multiple sequence alignments of the CNSs between C. grandiflora, N. paniculata, and A. thaliana and chose sites that differed between C. grandiflora and the other species and were fixed within C. grandiflora. Additionally, we compared neutral diversity around CNSs with at least one fixed substitution to neutral diversity around CNSs without any fixed substitutions.
Gene expression
Illumina sequencing generated 331,629,531 reads for 10 individuals, ranging from 31,267,774 to 35,552,133 reads per individual. This RNA sequence was mapped to the C. rubella reference genome using Tophat 1.2.0 [65], and expression level was quantified from these mapped reads using Cufflinks 1.3.0 [66]. Cufflinks standardizes expression levels by gene length and library size, returning values in units of ‘fragments per kilobase of exon per million fragments mapped’ (FPKM). We calculated the mean expression level for each gene across our 10 samples and removed those genes with <1 FKPM to eliminate genes that may have been mis-annotated. The remaining 11,564 genes were divided into four, roughly equally sized categories based on expression level: low (1–6.8 FPKM), mid-low (6.8–17.5 FPKM), mid-high (17.5–44.7 FPKM), and high (44.7–17,092 FPKM). The distribution of fitness effects, α, and ω were calculated for each gene set, using the same protocol described above. We bootstrapped each gene set by sampling genes with replacement 1000 times to generate 95% confidence intervals for selection strength. Using the same methods described for tests of differences within the CNSs categories above, we tested for a significant difference in selection strength between high and low expression genes.
Supporting Information
Zdroje
1. KeightleyPD, Eyre-WalkerA (2010) What can we learn about the distribution of fitness effects of new mutations from DNA sequence data? Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 365 : 1187–1193 doi:10.1098/rstb.2009.0266
2. AndolfattoP (2005) Adaptive evolution of non-coding DNA in Drosophila. Nature 437 : 1149–1152 doi:10.1038/nature04107
3. TorgersonDG, BoykoAR, HernandezRD, IndapA, HuX, et al. (2009) Evolutionary processes acting on candidate cis-regulatory regions in humans inferred from patterns of polymorphism and divergence. PLoS Genet 5: e1000592 doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1000592
4. Lindblad-TohK, GarberM, ZukO, LinMF, ParkerBJ, et al. (2011) A high-resolution map of human evolutionary constraint using 29 mammals. Nature 478 : 476–482 doi:10.1038/nature10530
5. ArbizaL, GronauI, AksoyBA, HubiszMJ, GulkoB, et al. (2013) Genome-wide inference of natural selection on human transcription factor binding sites. Nat Genet 45 : 723–729 doi:10.1038/ng.2658
6. HoughJ, WilliamsonRJ, WrightSI (2013) Patterns of selection in plant genomes. Annu Rev Ecol Evol Syst 44 : 3.1–3.19 doi:10.1146/annurev-ecolsys-110512-135851
7. Zhen Y, Andolfatto P (2012) Methods to detect selection on noncoding DNA. Methods in Molecular Biology. Totowa, NJ: Humana Press, Vol. 856. pp. 141–159. doi:10.1007/978-1-61779-585-5_6.
8. HalliganDL, KousathanasA, NessRW, HarrB, EőryL, et al. (2013) Contributions of protein-coding and regulatory change to adaptive molecular evolution in murid rodents. PLoS Genet 9: e1003995 doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1003995
9. WrayGA (2007) The evolutionary significance of cis-regulatory mutations. Nat Rev Genet 8 : 206–216 doi:10.1038/nrg2063
10. CarrollSB (2005) Evolution at two levels: on genes and form. PLoS Biol 3: e245 doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.0030245
11. HoekstraHE, CoyneJA (2007) The locus of evolution: evo devo and the genetics of adaptation. Evolution 61 : 995–1016 doi:10.1111/j.1558-5646.2007.00105.x
12. KeightleyPD, GaffneyDJ (2003) Functional constraints and frequency of deleterious mutations in noncoding DNA of rodents. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100 : 13402–13406 doi:10.1073/pnas.2233252100
13. LocktonS, GautBS (2005) Plant conserved non-coding sequences and paralogue evolution. Trends Genet 21 : 60–65 doi:10.1016/j.tig.2004.11.013
14. HaudryA, PlattsAE, VelloE, HoenDR, LeclercqM, et al. (2013) An atlas of over 90,000 conserved noncoding sequences provides insight into crucifer regulatory regions. Nat Genet 45 : 891–898 doi:10.1038/ng.2684
15. PálC, PappB, HurstLD (2001) Highly expressed genes in yeast evolve slowly. Genetics 158 : 927–931.
16. SubramanianS, KumarS (2004) Gene expression intensity shapes evolutionary rates of the proteins encoded by the vertebrate genome. Genetics 168 : 373–381 doi:10.1534/genetics.104.028944
17. DrummondDA, RavalA, WilkeCO (2006) A single determinant dominates the rate of yeast protein evolution. Mol Biol Evol 23 : 327–337 doi:10.1093/molbev/msj038
18. YangL, GautBS (2011) Factors that contribute to variation in evolutionary rate among Arabidopsis genes. Mol Biol Evol 28 : 2359–2369 doi:10.1093/molbev/msr058
19. SlotteT, BataillonT, HansenTT, St OngeK, WrightSI, et al. (2011) Genomic determinants of protein evolution and polymorphism in Arabidopsis. Genome Biol Evol 3 : 1210–1219 doi:10.1093/gbe/evr094
20. PaapeT, BataillonT, ZhouP, J Y KonoT, BriskineR, et al. (2013) Selection, genome-wide fitness effects and evolutionary rates in the model legume Medicago truncatula. Mol Ecol 22 : 3525–3538 doi:10.1111/mec.12329
21. RenautS, GrassaCJ, MoyersBT, KaneNC, RiesebergLH (2012) The population genomics of sunflowers and genomic determinants of protein evolution revealed by RNAseq. Biology (Basel) 1 : 575–596 doi:10.3390/biology1030575
22. GautB, YangL, TakunoS, EguiarteLE (2011) The patterns and causes of variation in plant nucleotide substitution rates. Annu Rev Ecol Evol Syst 42 : 245–266 doi:10.1146/annurev-ecolsys-102710-145119
23. ParkC, ChenX, YangJ-R, ZhangJ (2013) Differential requirements for mRNA folding partially explain why highly expressed proteins evolve slowly. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110: E678–E686 doi:10.1073/pnas.1218066110
24. YangJ-R, LiaoB-Y, ZhuangS-M, ZhangJ (2012) Protein misinteraction avoidance causes highly expressed proteins to evolve slowly. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109: E831–E840 doi:10.1073/pnas.1117408109
25. DrummondDA, WilkeCO (2008) Mistranslation-induced protein misfolding as a dominant constraint on coding-sequence evolution. Cell 134 : 341–352 doi:10.1016/j.cell.2008.05.042
26. GossmannTI, SongB-H, WindsorAJ, Mitchell-OldsT, DixonCJ, et al. (2010) Genome wide analyses reveal little evidence for adaptive evolution in many plant species. Mol Biol Evol 27 : 1822–1832.
27. St OngeKR, KällmanT, SlotteT, LascouxM, PalméAE (2011) Contrasting demographic history and population structure in Capsella rubella and Capsella grandiflora, two closely related species with different mating systems. Mol Ecol 20 : 3306–3320 doi:10.1111/j.1365-294X.2011.05189.x
28. Eyre-WalkerA, KeightleyPD (2009) Estimating the rate of adaptive molecular evolution in the presence of slightly deleterious mutations and population size change. Mol Biol Evol 26 : 2097–2108 doi:10.1093/molbev/msp119
29. SellaG, PetrovDA, PrzeworskiM, AndolfattoP (2009) Pervasive natural selection in the Drosophila genome? PLoS Genet 5: e1000495 doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1000495
30. SlotteT, HazzouriKM, AgrenJA, KoenigD, MaumusF, et al. (2013) The Capsella rubella genome and the genomic consequences of rapid mating system evolution. Nat Genet 45 : 831–835 doi:10.1038/ng.2669
31. McKennaA, HannaM, BanksE, SivachenkoA, CibulskisK, et al. (2010) The Genome Analysis Toolkit: a MapReduce framework for analyzing next-generation DNA sequencing data. Genome Res 20 : 1297–1303 doi:10.1101/gr.107524.110
32. SlotteT, FoxeJP, HazzouriKM, WrightSI (2010) Genome-wide evidence for efficient positive and purifying selection in Capsella grandiflora, a plant species with a large effective population size. Mol Biol Evol 27 : 1813–1821.
33. ClarkRM, SchweikertG, ToomajianC, OssowskiS, ZellerG, et al. (2007) Common sequence polymorphisms shaping genetic diversity in Arabidopsis thaliana. Science 317 : 338–342 doi:10.1126/science.1138632
34. WrightSI, FoxeJP, DeRose-WilsonL, KawabeA, LooseleyM, et al. (2006) Testing for effects of recombination rate on nucleotide diversity in natural populations of Arabidopsis lyrata. Genetics 174 : 1421–1430 doi:10.1534/genetics.106.062588
35. KawabeA, ForrestA, WrightSI, CharlesworthD (2008) High DNA sequence diversity in pericentromeric genes of the plant Arabidopsis lyrata. Genetics 179 : 985–995 doi:10.1534/genetics.107.085282
36. BrancaA, PaapeTD, ZhouP, BriskineR, FarmerAD, et al. (2011) Whole-genome nucleotide diversity, recombination, and linkage disequilibrium in the model legume Medicago truncatula. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108: E864–E870 doi:10.1073/pnas.1104032108
37. SlotteT (2014) The impact of linked selection on plant genomic variation. Brief Funct Genomics 13 : 268–275 doi:10.1093/bfgp/elu009
38. EhrenreichIM, PuruggananMD (2008) Sequence variation of MicroRNAs and their binding sites in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 146 : 1974–1982 doi:10.1104/pp.108.116582
39. SattathS, ElyashivE, KolodnyO, RinottY, SellaG (2011) Pervasive adaptive protein evolution and diversity patterns around amino acid substitutions in Drosophila simulans. PLoS Genet 7: e1001302.
40. SmithJM, HaighJ (1974) The hitch-hiking effect of a favourable gene. Genet Res 23 : 23–35 doi:10.1017/S0016672308009579
41. KimY, LeeG, JeonE, SohnEJ, LeeY, et al. (2013) The immediate upstream region of the 5′-UTR from the AUG start codon has a pronounced effect on the translational efficiency in Arabidopsis thaliana. Nucleic Acids Res 42 : 485–498 doi:10.1093/nar/gkt864
42. HanMV, DemuthJP, McGrathCL, CasolaC, HahnMW (2009) Adaptive evolution of young gene duplicates in mammals. Genome Res 19 : 859–867 doi:10.1101/gr.085951.108
43. QiuS, ZengK, SlotteT, WrightS, CharlesworthD (2011) Reduced efficacy of natural selection on codon usage bias in selfing Arabidopsis and Capsella species. Genome Biol Evol 3 : 868–880 doi:10.1093/gbe/evr085
44. WrightSI, YauCBK, LooseleyM, MeyersBC (2004) Effects of gene expression on molecular evolution in Arabidopsis thaliana and Arabidopsis lyrata. Mol Biol Evol 21 : 1719–1726 doi:10.1093/molbev/msh191
45. DuretL, MouchiroudD (1999) Expression pattern and, surprisingly, gene length shape codon usage in Caenorhabditis, Drosophila, and Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96 : 4482–4487.
46. MaraisG, MouchiroudD, DuretL (2001) Does recombination improve selection on codon usage? Lessons from nematode and fly complete genomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98 : 5688–5692.
47. HernandezRD, KelleyJL, ElyashivE, MeltonSC, AutonA, et al. (2011) Classic selective sweeps were rare in recent human evolution. Science 331 : 920–924 doi:10.1126/science.1198878
48. PenningsPS, HermissonJ (2006) Soft sweeps II–molecular population genetics of adaptation from recurrent mutation or migration. Mol Biol Evol 23 : 1076–1084 doi:10.1093/molbev/msj117
49. PenningsPS, HermissonJ (2006) Soft sweeps III: the signature of positive selection from recurrent mutation. PLoS Genet 2: e186 doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.0020186
50. HermissonJ, PenningsPS (2005) Soft sweeps: molecular population genetics of adaptation from standing genetic variation. Genetics 169 : 2335–2352 doi:10.1534/genetics.104.036947
51. MesserPW, PetrovDA (2013) Population genomics of rapid adaptation by soft selective sweeps. Trends Ecol Evol 28 : 659–669 doi:10.1016/j.tree.2013.08.003
52. PavlidisP, MetzlerD, StephanW (2012) Selective sweeps in multilocus models of quantitative traits. Genetics 192 : 225–239 doi:10.1534/genetics.112.142547
53. LemosB, BettencourtBR, MeiklejohnCD, HartlDL (2005) Evolution of proteins and gene expression levels are coupled in Drosophila and are independently associated with mRNA abundance, protein length, and number of protein-protein interactions. Mol Biol Evol 22 : 1345–1354 doi:10.1093/molbev/msi122
54. Drosophila 12 Genomes Consortium, ClarkAG, EisenMB, SmithDR, BergmanCM, et al. (2007) Evolution of genes and genomes on the Drosophila phylogeny. Nature 450 : 203–218 doi:10.1038/nature06341
55. CarneiroM, AlbertFW, Melo-FerreiraJ, GaltierN, GayralP, et al. (2012) Evidence for widespread positive and purifying selection across the European rabbit (Oryctolagus cuniculus) Genome. Mol Biol Evol 29 : 1837–1849 doi:10.1093/molbev/mss025
56. LunterG, GoodsonM (2011) Stampy: a statistical algorithm for sensitive and fast mapping of Illumina sequence reads. Genome Research 21 : 936–939 doi:10.1101/gr.111120.110
57. DePristoMA, BanksE, PoplinR, GarimellaKV, MaguireJR, et al. (2011) A framework for variation discovery and genotyping using next-generation DNA sequencing data. Nature Genetics 43 : 491–498 doi:10.1038/ng.806
58. Harris RS (2007) Improved pairwise alignment of genomic DNA. PhD Thesis, Penn State Univ.
59. OstlundG, SchmittT, ForslundK, KostlerT, MessinaDN, et al. (2009) InParanoid 7: new algorithms and tools for eukaryotic orthology analysis. Nucleic Acids Res 38: D196–D203 doi:10.1093/nar/gkp931
60. AlexeyenkoA, TamasI, LiuG, SonnhammerELL (2006) Automatic clustering of orthologs and inparalogs shared by multiple proteomes. Bioinformatics 22: e9–e15 doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btl213
61. SubramanianAR, KaufmannM, MorgensternB (2008) DIALIGN-TX: greedy and progressive approaches for segment-based multiple sequence alignment. Algorithms Mol Biol 3 : 6 doi:10.1186/1748-7188-3-6
62. YangZ (2007) PAML 4: phylogenetic analysis by maximum likelihood. Mol Biol Evol 24 : 1586–1591 doi:10.1093/molbev/msm088
63. BlanchetteM, KentWJ, RiemerC, ElnitskiL, SmitAFA, et al. (2004) Aligning multiple genomic sequences with the threaded blockset aligner. Genome Res 14 : 708–715 doi:10.1101/gr.1933104
64. KeightleyPD, Eyre-WalkerA (2007) Joint inference of the distribution of fitness effects of deleterious mutations and population demography based on nucleotide polymorphism frequencies. Genetics 177 : 2251–2261 doi:10.1534/genetics.107.080663
65. TrapnellC, PachterL, SalzbergSL (2009) TopHat: discovering splice junctions with RNA-Seq. Bioinformatics 25 : 1105–1111 doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btp120
66. TrapnellC, WilliamsBA, PerteaG, MortazaviA, KwanG, et al. (2010) Transcript assembly and quantification by RNA-Seq reveals unannotated transcripts and isoform switching during cell differentiation. Nat Biotechnol 28 : 511–515 doi:10.1038/nbt.1621
Štítky
Genetika Reprodukční medicína
Článek An Evolutionarily Conserved Role for the Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor in the Regulation of MovementČlánek Requirement for Drosophila SNMP1 for Rapid Activation and Termination of Pheromone-Induced ActivityČlánek Co-regulated Transcripts Associated to Cooperating eSNPs Define Bi-fan Motifs in Human Gene NetworksČlánek Identification of a Regulatory Variant That Binds FOXA1 and FOXA2 at the Type 2 Diabetes GWAS LocusČlánek tRNA Modifying Enzymes, NSUN2 and METTL1, Determine Sensitivity to 5-Fluorouracil in HeLa CellsČlánek Derlin-1 Regulates Mutant VCP-Linked Pathogenesis and Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress-Induced ApoptosisČlánek A Genetic Assay for Transcription Errors Reveals Multilayer Control of RNA Polymerase II FidelityČlánek The Proprotein Convertase KPC-1/Furin Controls Branching and Self-avoidance of Sensory Dendrites inČlánek Regulation of p53 and Rb Links the Alternative NF-κB Pathway to EZH2 Expression and Cell SenescenceČlánek BMPs Regulate Gene Expression in the Dorsal Neuroectoderm of and Vertebrates by Distinct Mechanisms
Článek vyšel v časopisePLOS Genetics
Nejčtenější tento týden
2014 Číslo 9
-
Všechny články tohoto čísla
- Translational Regulation of the Post-Translational Circadian Mechanism
- An Evolutionarily Conserved Role for the Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor in the Regulation of Movement
- Eliminating Both Canonical and Short-Patch Mismatch Repair in Suggests a New Meiotic Recombination Model
- Requirement for Drosophila SNMP1 for Rapid Activation and Termination of Pheromone-Induced Activity
- Co-regulated Transcripts Associated to Cooperating eSNPs Define Bi-fan Motifs in Human Gene Networks
- Targeted H3R26 Deimination Specifically Facilitates Estrogen Receptor Binding by Modifying Nucleosome Structure
- Role for Circadian Clock Genes in Seasonal Timing: Testing the Bünning Hypothesis
- The Tandem Repeats Enabling Reversible Switching between the Two Phases of β-Lactamase Substrate Spectrum
- The Association of the Vanin-1 N131S Variant with Blood Pressure Is Mediated by Endoplasmic Reticulum-Associated Degradation and Loss of Function
- Identification of a Regulatory Variant That Binds FOXA1 and FOXA2 at the Type 2 Diabetes GWAS Locus
- Regulation of Flowering by the Histone Mark Readers MRG1/2 via Interaction with CONSTANS to Modulate Expression
- The Actomyosin Machinery Is Required for Retinal Lumen Formation
- Plays a Conserved Role in Assembly of the Ciliary Motile Apparatus
- Hidden Diversity in Honey Bee Gut Symbionts Detected by Single-Cell Genomics
- Ribosome Rescue and Translation Termination at Non-Standard Stop Codons by ICT1 in Mammalian Mitochondria
- tRNA Modifying Enzymes, NSUN2 and METTL1, Determine Sensitivity to 5-Fluorouracil in HeLa Cells
- Causal Variation in Yeast Sporulation Tends to Reside in a Pathway Bottleneck
- Tissue-Specific RNA Expression Marks Distant-Acting Developmental Enhancers
- WC-1 Recruits SWI/SNF to Remodel and Initiate a Circadian Cycle
- Clonal Expansion of Early to Mid-Life Mitochondrial DNA Point Mutations Drives Mitochondrial Dysfunction during Human Ageing
- Methylation QTLs Are Associated with Coordinated Changes in Transcription Factor Binding, Histone Modifications, and Gene Expression Levels
- Differential Management of the Replication Terminus Regions of the Two Chromosomes during Cell Division
- Obesity-Linked Homologues and Establish Meal Frequency in
- Derlin-1 Regulates Mutant VCP-Linked Pathogenesis and Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress-Induced Apoptosis
- Stress-Induced Nuclear RNA Degradation Pathways Regulate Yeast Bromodomain Factor 2 to Promote Cell Survival
- The MAPK p38c Regulates Oxidative Stress and Lipid Homeostasis in the Intestine
- Widespread Genome Reorganization of an Obligate Virus Mutualist
- Trans-kingdom Cross-Talk: Small RNAs on the Move
- The Vip1 Inositol Polyphosphate Kinase Family Regulates Polarized Growth and Modulates the Microtubule Cytoskeleton in Fungi
- Myosin Vb Mediated Plasma Membrane Homeostasis Regulates Peridermal Cell Size and Maintains Tissue Homeostasis in the Zebrafish Epidermis
- GLD-4-Mediated Translational Activation Regulates the Size of the Proliferative Germ Cell Pool in the Adult Germ Line
- Genome Wide Association Studies Using a New Nonparametric Model Reveal the Genetic Architecture of 17 Agronomic Traits in an Enlarged Maize Association Panel
- Translational Regulation of the DOUBLETIME/CKIδ/ε Kinase by LARK Contributes to Circadian Period Modulation
- Positive Selection and Multiple Losses of the LINE-1-Derived Gene in Mammals Suggest a Dual Role in Genome Defense and Pluripotency
- Out of Balance: R-loops in Human Disease
- A Genetic Assay for Transcription Errors Reveals Multilayer Control of RNA Polymerase II Fidelity
- Altered Behavioral Performance and Live Imaging of Circuit-Specific Neural Deficiencies in a Zebrafish Model for Psychomotor Retardation
- Nipbl and Mediator Cooperatively Regulate Gene Expression to Control Limb Development
- Meta-analysis of Mutations in Autism Spectrum Disorders: A Gradient of Severity in Cognitive Impairments
- The Proprotein Convertase KPC-1/Furin Controls Branching and Self-avoidance of Sensory Dendrites in
- Hydroxymethylated Cytosines Are Associated with Elevated C to G Transversion Rates
- Memory and Fitness Optimization of Bacteria under Fluctuating Environments
- Regulation of p53 and Rb Links the Alternative NF-κB Pathway to EZH2 Expression and Cell Senescence
- Interspecific Tests of Allelism Reveal the Evolutionary Timing and Pattern of Accumulation of Reproductive Isolation Mutations
- PRO40 Is a Scaffold Protein of the Cell Wall Integrity Pathway, Linking the MAP Kinase Module to the Upstream Activator Protein Kinase C
- Low Levels of p53 Protein and Chromatin Silencing of p53 Target Genes Repress Apoptosis in Endocycling Cells
- SPDEF Inhibits Prostate Carcinogenesis by Disrupting a Positive Feedback Loop in Regulation of the Foxm1 Oncogene
- RRP6L1 and RRP6L2 Function in Silencing Regulation of Antisense RNA Synthesis
- BMPs Regulate Gene Expression in the Dorsal Neuroectoderm of and Vertebrates by Distinct Mechanisms
- Unkempt Is Negatively Regulated by mTOR and Uncouples Neuronal Differentiation from Growth Control
- Atkinesin-13A Modulates Cell-Wall Synthesis and Cell Expansion in via the THESEUS1 Pathway
- Dopamine Signaling Leads to Loss of Polycomb Repression and Aberrant Gene Activation in Experimental Parkinsonism
- Histone Methyltransferase MMSET/NSD2 Alters EZH2 Binding and Reprograms the Myeloma Epigenome through Global and Focal Changes in H3K36 and H3K27 Methylation
- Bipartite Recognition of DNA by TCF/Pangolin Is Remarkably Flexible and Contributes to Transcriptional Responsiveness and Tissue Specificity of Wingless Signaling
- The Olfactory Transcriptomes of Mice
- Muscular Dystrophy-Associated and Variants Disrupt Nuclear-Cytoskeletal Connections and Myonuclear Organization
- Interplay of dFOXO and Two ETS-Family Transcription Factors Determines Lifespan in
- Evidence for Widespread Positive and Negative Selection in Coding and Conserved Noncoding Regions of
- Genome-Wide Association Meta-analysis of Neuropathologic Features of Alzheimer's Disease and Related Dementias
- Rejuvenation of Meiotic Cohesion in Oocytes during Prophase I Is Required for Chiasma Maintenance and Accurate Chromosome Segregation
- Admixture in Latin America: Geographic Structure, Phenotypic Diversity and Self-Perception of Ancestry Based on 7,342 Individuals
- Local Effect of Enhancer of Zeste-Like Reveals Cooperation of Epigenetic and -Acting Determinants for Zygotic Genome Rearrangements
- Differential Responses to Wnt and PCP Disruption Predict Expression and Developmental Function of Conserved and Novel Genes in a Cnidarian
- PLOS Genetics
- Archiv čísel
- Aktuální číslo
- Informace o časopisu
Nejčtenější v tomto čísle- Admixture in Latin America: Geographic Structure, Phenotypic Diversity and Self-Perception of Ancestry Based on 7,342 Individuals
- Nipbl and Mediator Cooperatively Regulate Gene Expression to Control Limb Development
- Genome Wide Association Studies Using a New Nonparametric Model Reveal the Genetic Architecture of 17 Agronomic Traits in an Enlarged Maize Association Panel
- Histone Methyltransferase MMSET/NSD2 Alters EZH2 Binding and Reprograms the Myeloma Epigenome through Global and Focal Changes in H3K36 and H3K27 Methylation
Kurzy
Zvyšte si kvalifikaci online z pohodlí domova
Současné možnosti léčby obezity
nový kurzAutoři: MUDr. Martin Hrubý
Všechny kurzyPřihlášení#ADS_BOTTOM_SCRIPTS#Zapomenuté hesloZadejte e-mailovou adresu, se kterou jste vytvářel(a) účet, budou Vám na ni zaslány informace k nastavení nového hesla.
- Vzdělávání



