-
Články
Top novinky
Reklama- Vzdělávání
- Časopisy
Top články
Nové číslo
- Témata
Top novinky
Reklama- Videa
- Podcasty
Nové podcasty
Reklama- Kariéra
Doporučené pozice
Reklama- Praxe
Top novinky
ReklamaA Genome-Wide Association Study of Upper Aerodigestive Tract Cancers Conducted within the INHANCE Consortium
Genome-wide association studies (GWAS) have been successful in identifying common genetic variation involved in susceptibility to etiologically complex disease. We conducted a GWAS to identify common genetic variation involved in susceptibility to upper aero-digestive tract (UADT) cancers. Genome-wide genotyping was carried out using the Illumina HumanHap300 beadchips in 2,091 UADT cancer cases and 3,513 controls from two large European multi-centre UADT cancer studies, as well as 4,821 generic controls. The 19 top-ranked variants were investigated further in an additional 6,514 UADT cancer cases and 7,892 controls of European descent from an additional 13 UADT cancer studies participating in the INHANCE consortium. Five common variants presented evidence for significant association in the combined analysis (p≤5×10−7). Two novel variants were identified, a 4q21 variant (rs1494961, p = 1×10−8) located near DNA repair related genes HEL308 and FAM175A (or Abraxas) and a 12q24 variant (rs4767364, p = 2×10−8) located in an extended linkage disequilibrium region that contains multiple genes including the aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 (ALDH2) gene. Three remaining variants are located in the ADH gene cluster and were identified previously in a candidate gene study involving some of these samples. The association between these three variants and UADT cancers was independently replicated in 5,092 UADT cancer cases and 6,794 controls non-overlapping samples presented here (rs1573496-ADH7, p = 5×10−8; rs1229984-ADH1B, p = 7×10−9; and rs698-ADH1C, p = 0.02). These results implicate two variants at 4q21 and 12q24 and further highlight three ADH variants in UADT cancer susceptibility.
Published in the journal: . PLoS Genet 7(3): e32767. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1001333
Category: Research Article
doi: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1001333Summary
Genome-wide association studies (GWAS) have been successful in identifying common genetic variation involved in susceptibility to etiologically complex disease. We conducted a GWAS to identify common genetic variation involved in susceptibility to upper aero-digestive tract (UADT) cancers. Genome-wide genotyping was carried out using the Illumina HumanHap300 beadchips in 2,091 UADT cancer cases and 3,513 controls from two large European multi-centre UADT cancer studies, as well as 4,821 generic controls. The 19 top-ranked variants were investigated further in an additional 6,514 UADT cancer cases and 7,892 controls of European descent from an additional 13 UADT cancer studies participating in the INHANCE consortium. Five common variants presented evidence for significant association in the combined analysis (p≤5×10−7). Two novel variants were identified, a 4q21 variant (rs1494961, p = 1×10−8) located near DNA repair related genes HEL308 and FAM175A (or Abraxas) and a 12q24 variant (rs4767364, p = 2×10−8) located in an extended linkage disequilibrium region that contains multiple genes including the aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 (ALDH2) gene. Three remaining variants are located in the ADH gene cluster and were identified previously in a candidate gene study involving some of these samples. The association between these three variants and UADT cancers was independently replicated in 5,092 UADT cancer cases and 6,794 controls non-overlapping samples presented here (rs1573496-ADH7, p = 5×10−8; rs1229984-ADH1B, p = 7×10−9; and rs698-ADH1C, p = 0.02). These results implicate two variants at 4q21 and 12q24 and further highlight three ADH variants in UADT cancer susceptibility.
Introduction
560,000 cases of upper aerodigestive tract (UADT) cancers (encompassing of the oral cavity, pharynx, larynx and esophagus) are estimated to occur each year world-wide [1]. Exposure to alcohol and tobacco [1] are the major UADT cancer risk factors in Europe and the Americas, with infection with human papillomavirus also playing an important role [2].
Elevated familial relative risks are consistently reported for UADT cancers [3]-[7]. While this implies that genetics contributes to UADT cancer susceptibility, the identity of the specific genes involved remains unclear. Studies of common genetic variation and UADT cancer susceptibility have mostly employed a candidate gene approach, with a particular focus on the genes that metabolize alcohol [8]. The metabolism of alcohol releases the carcinogen acetaldehyde as an intermediate [9]. As genetic variation in alcohol metabolism genes appears to influence their rate of function [10], [11], variants that lead to a relative increase in exposure to acetaldehyde are expected to confer carriers to an increased risk of UADT cancers [12]. Consistent with this hypothesis, genetic variation in the alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH) 1B, and the aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 (ALDH2) genes in Asian populations have been associated with UADT cancer risk [8], [12], [13]. Three independent variants ADH1B, ADH7 and ADH1C variants have also been associated with UADT cancer risk in European populations [14]. Common genetic variation in additional genetic pathways have also been considered, although with some exceptions, such as DNA repair [15], [16], the results have been inconsistent [3].
The candidate gene based studies have tested only a very small proportion of common human genetic variation in relation to UADT cancer risk. To further investigate common genetic variation and susceptibility to UADT cancers, we have performed a genome-wide association study within the International Head and Neck Cancer Epidemiology (INHANCE) consortium, comprising genome wide analysis of 2,091 UADT cancer cases and 8,334 controls and replication analysis of the nineteen top ranked variants in an independent series consisting of 6,514 UADT cancer cases and 7,892 controls from thirteen additional studies.
Results
Genome-wide results
After exclusion of suboptimal DNA based on QC criteria, data from 2,091 cases and 3,513 study specific controls and 4,821 generic controls were available for statistical analyses (Table S1) with 294,620 genetic variants. The overall results did not show a large deviation from what was expected by chance (λ = 1.07) (Figure 1). One genetic variant, rs971074, was strongly associated with UADT cancers (p<1×10−8). rs971074 is positioned in the ADH7 locus on chromosome 4q23 and is highly correlated (r2 = 1.0 CEU hapmap) with the SNP in ADH7, rs1573496, that we have described previously to be associated with UADT cancer risk [14]. Similarly, rs1789924, which is highly correlated (r2 = 0.97 CEU hapmap) with ADH1C rs698, was also highly ranked (p = 2×10−6).
Fig. 1. Manhattan plot of the ARCAGE and CE UADT cancer GWAS discovery phase. 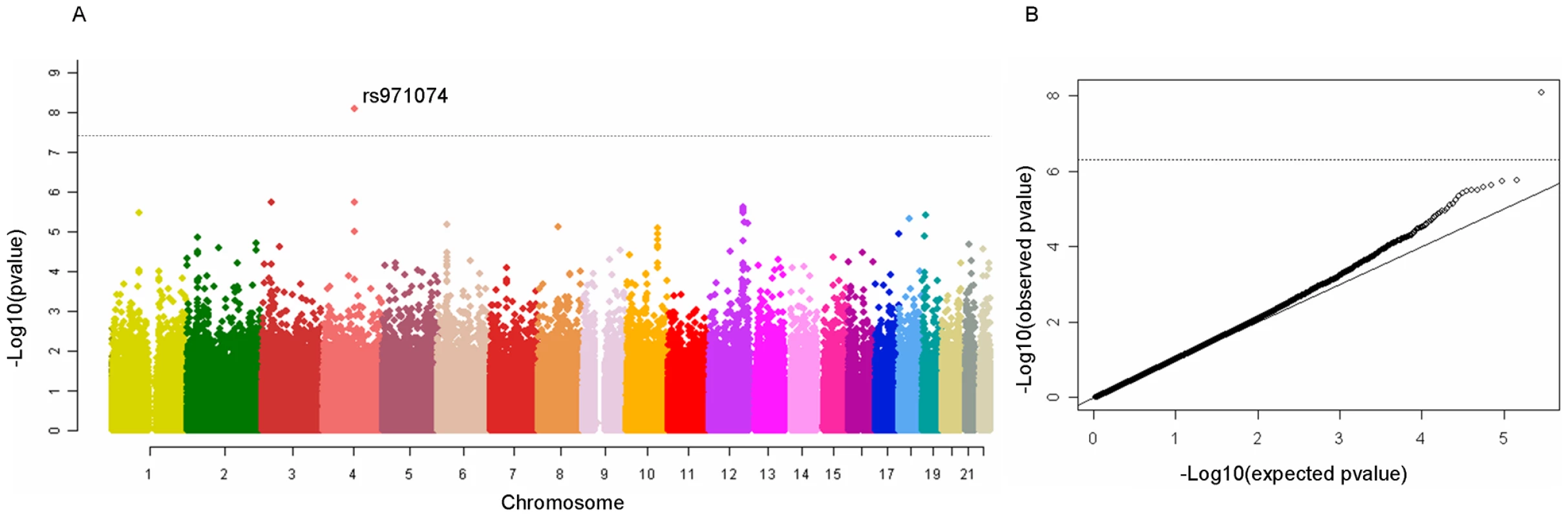
One clearly outlying marker, rs971074 is highly correlated with rs1573496, a SNP previously associated with UADT cancer risk. Right panel QQ plot for the UADT cancer GWAS. Variant selection for replication
For further analysis we selected the twenty top ranked genetic variants (including rs971074) for replication (Figure S1). These included those genetic variants in the discovery phase that achieved a p-value of ≤1×10−5 (12 variants) as well as nonsynonymous variants that achieved a p-value of ≤1×10−4 (5 additional variants). We also included variants that achieved a p-value of ≤5×10−7 when restricting the analysis to a specific UADT cancer site (1 variant), or heavy drinkers (1 variant) (Table 1). Only one variant from each high r2 group (r2>0.8) was included. We additionally included the non-synonymous ADH1B variant, rs1229984, that has been previously associated with UADT cancers [14] but not genotyped or tagged by a proxy variant on the HumanHap300 BeadChip. The association between the top ranked genetic variants selected for replication and UADT cancer was not sensitive to adjustment for population structure using principal component analysis, or exclusion generic controls (Table S2). rs1573496 was genotyped for replication as a proxy for rs971074 (r2 = 1.00) and rs698 for rs1789924 (r2>0.97) due to availability of Taqman assays. A TaqMan assay for rs12827056 could not be designed and no highly correlated (r2>0.95) proxy genetic variant was available, hence further investigation was not possible.
Tab. 1. Results from the UADT cancer genome-wide and replication analysis. 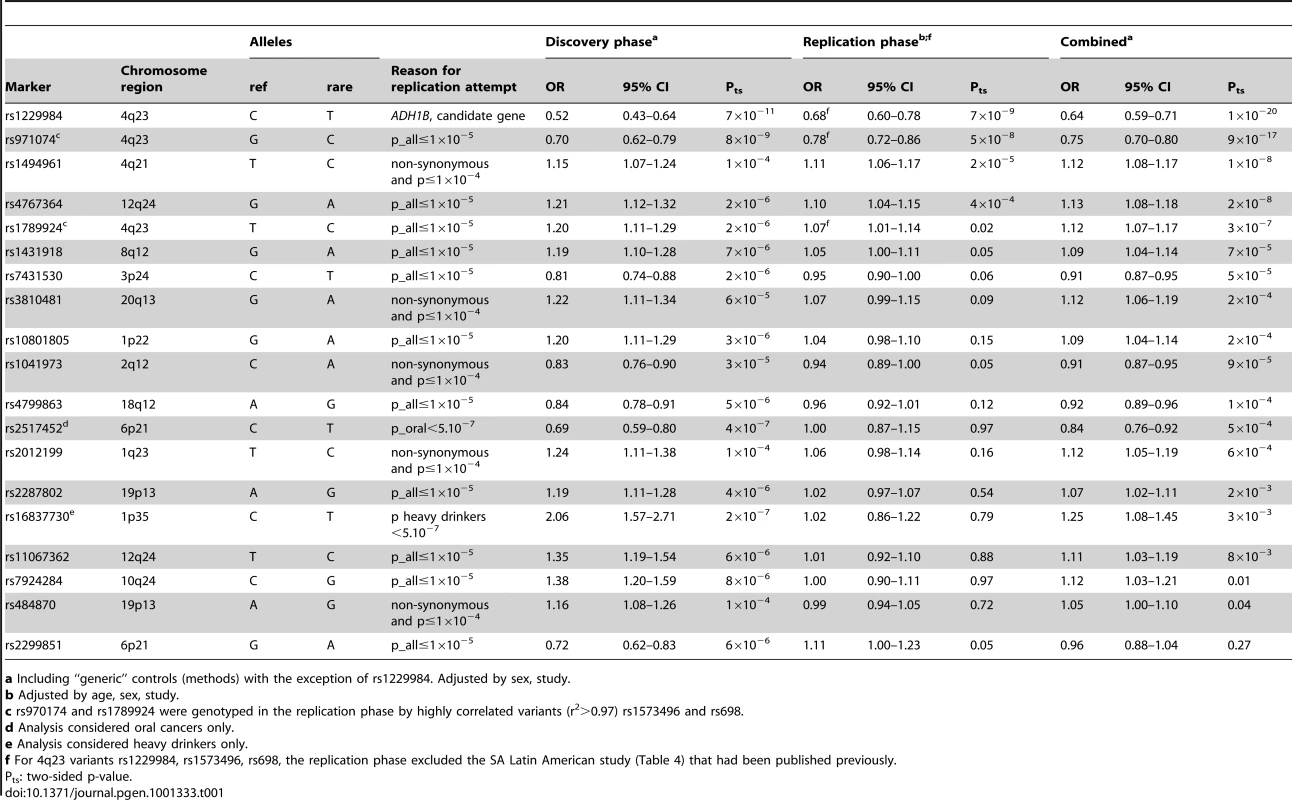
a Including “generic” controls (methods) with the exception of rs1229984. Adjusted by sex, study. Replication and combined results
Five genetic variants at three loci, 4q21, 4q23 and 12q24, were significantly associated with UADT cancer risk in the replication series (assuming Bonferroni correction for 19 comparisons or p≤0.003, or p = 0.05 for previously described variants) or in the combined analysis (p-value of ≤5×10−7) (Table 1) (Figure S2). Using imputed genotypes across the 4q21, 4q23 and 12q24 regions based on Caucasian individuals from the HapMap consortium, we did not identify any variants more strongly associated with UADT cancer risk than the SNPs genotyped on the beadchips directly (Figure 2).
Fig. 2. Imputation and LD patterns. 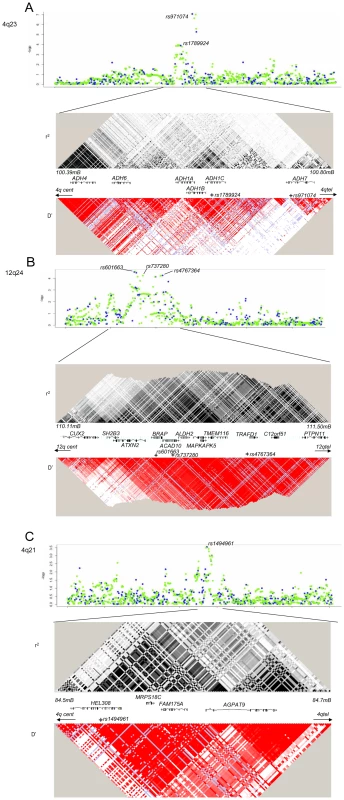
Imputation and LD patterns across the (a) 4q23 (ADH loci), (b) 12q24 (ALDH2), and (c) 4q21 (HEL308). Upper panel: Single marker association results for imputed (green) and directly genotyped variants (blue). Imputation performed on 2,091 cases and 3,513 study specific controls (excluded generic controls). After adjustment for the five variants that presented with replication, no variant had a p<0.0005 at any loci. Lower panel, pairwise LD estimates increasing intensities of black and red indicate higher r2 or D' statistics, respectively. Blue colour indicates that the pairwise comparison is not informative. Two novel variant loci were identified. rs4767364 located at 12q24 (preplication = 4×10−4; pcombined = 2×10−8) was one of multiple highly correlated SNPs (r2≥0.8) that presented evidence for association in the GWAS stage. It is located in a LD region including multiple genes including the aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 (ALDH2) (Figure 2), another key gene in alcohol metabolism (Figure 2). In stratified analysis in the combined 8,744 UADT cancer cases and 11,982 controls (Table S3), the association was more pronounced in esophageal cancers compared to other UADT cancer subsites (p heterogeneity = 0.01) and exhibited borderline heterogeneity when stratifying by alcohol use (Figure 3). Some heterogeneity was noted by when stratifying by country (p = 0.004), although there was no discernable geographic distribution that could explain this heterogeneity (data not shown). We noted little evidence for association between alcohol consumption and rs4767364 (Table 2), nor was there evidence for any gene-gene interactions between associated variants in ADH gene cluster and rs4767364 (data not shown).
Fig. 3. Stratified analysis of 4 replicated SNPs located near alcohol metabolism genes. 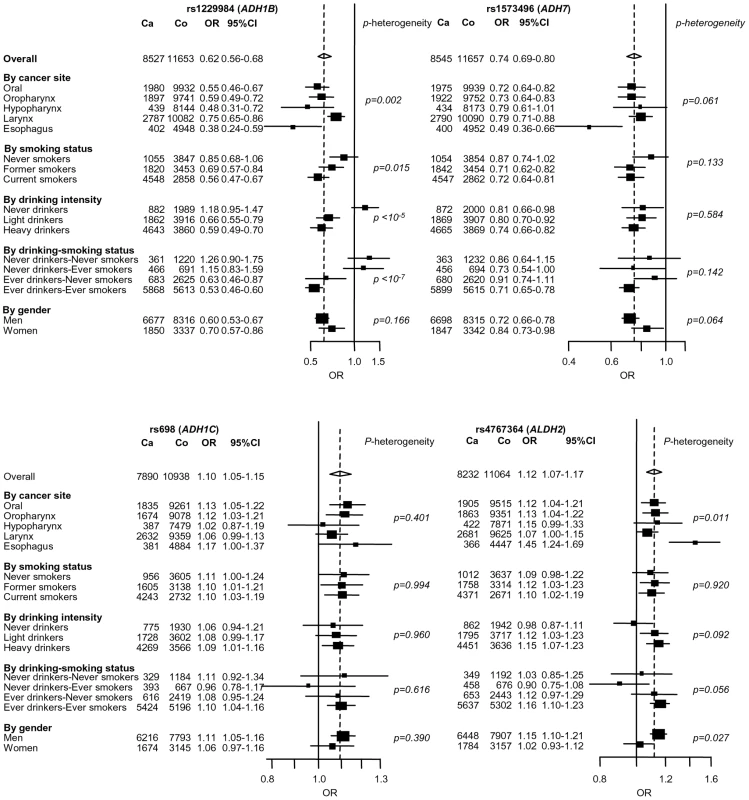
Estimates for rs1229984 (ADH1B), rs1573496 (ADH7), rs1042758 (ADH1C) and rs4767364 (ALDH2) were derived from a log-additive genetic model. ORs were adjusted by age, sex, study and were derived from fixed effects models. “Generic” controls were not included in this analysis. Tab. 2. Association between rs1229984, rs1573496, rs698, rs4767364, and drinking intensity in ever drinkers expressed as mean of ml of ethanol consumed per day. 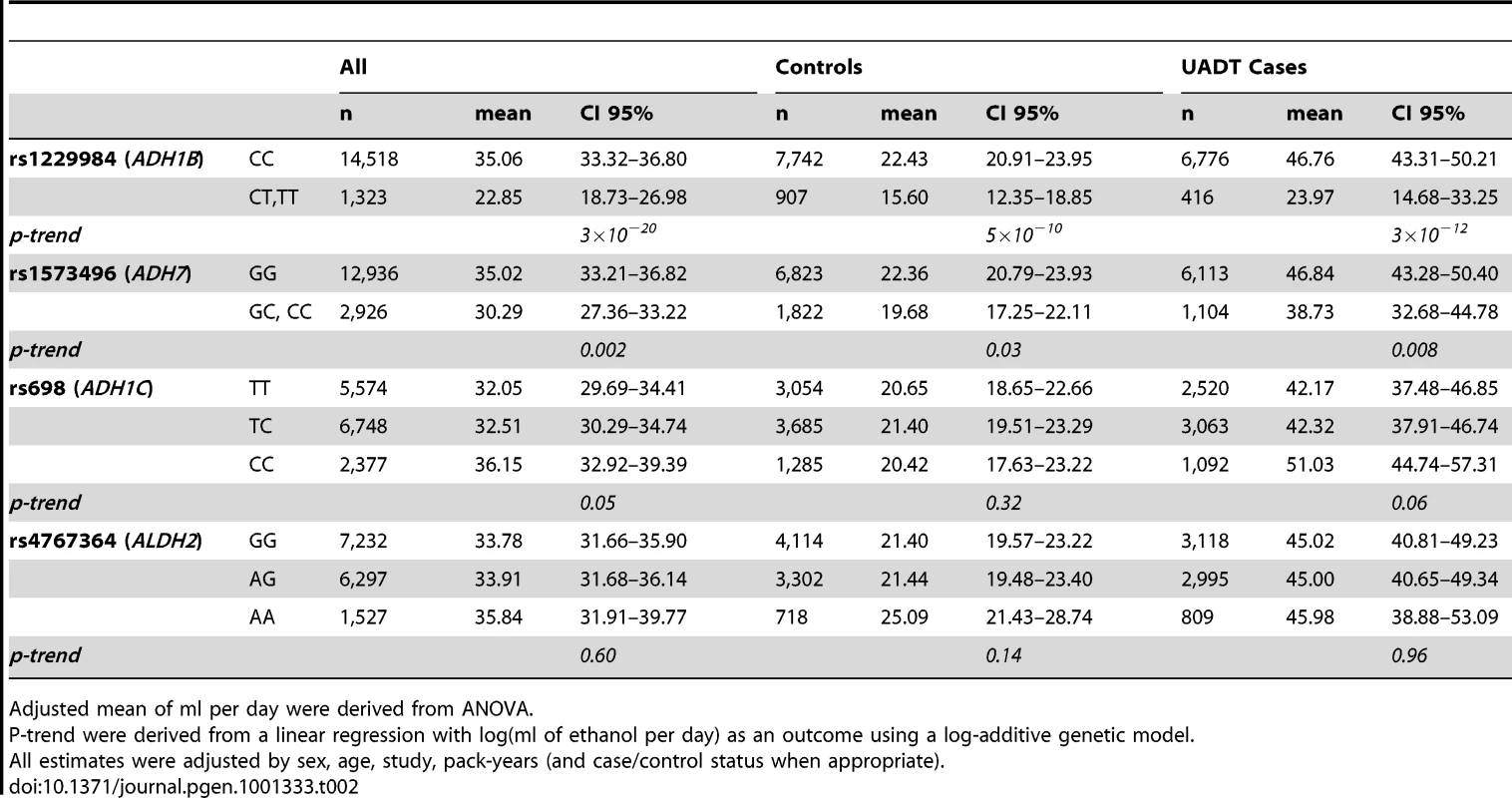
Adjusted mean of ml per day were derived from ANOVA. The second additional locus identified was at 4q21, with the nonsynonmous variant rs1494961 located in the HEL308 gene (preplication = 2×10−5, pcombined = 1×10−8) (Table 1). In combined analysis, the association tended to be more pronounced in younger ages and smokers (Figure 4). Given the possible role of the HEL308 in DNA repair, we also investigated the possibility that rs1494961 may play a role in lung cancer susceptibility by genotyping rs1494961 in a series of 5,652 lung cancer cases and 9,338 controls. We noted a similar association between rs1494961 and lung cancer (OR = 1.09, p = 3×10−4) from nine lung cancer studies, even when we excluded 1,844 cases and 2,735 controls where controls overlapped with the central European UADT study (OR = 1.09, p = 0.005).
Fig. 4. Association between 4q21 variant (rs1494961) and UADT and lung cancers. 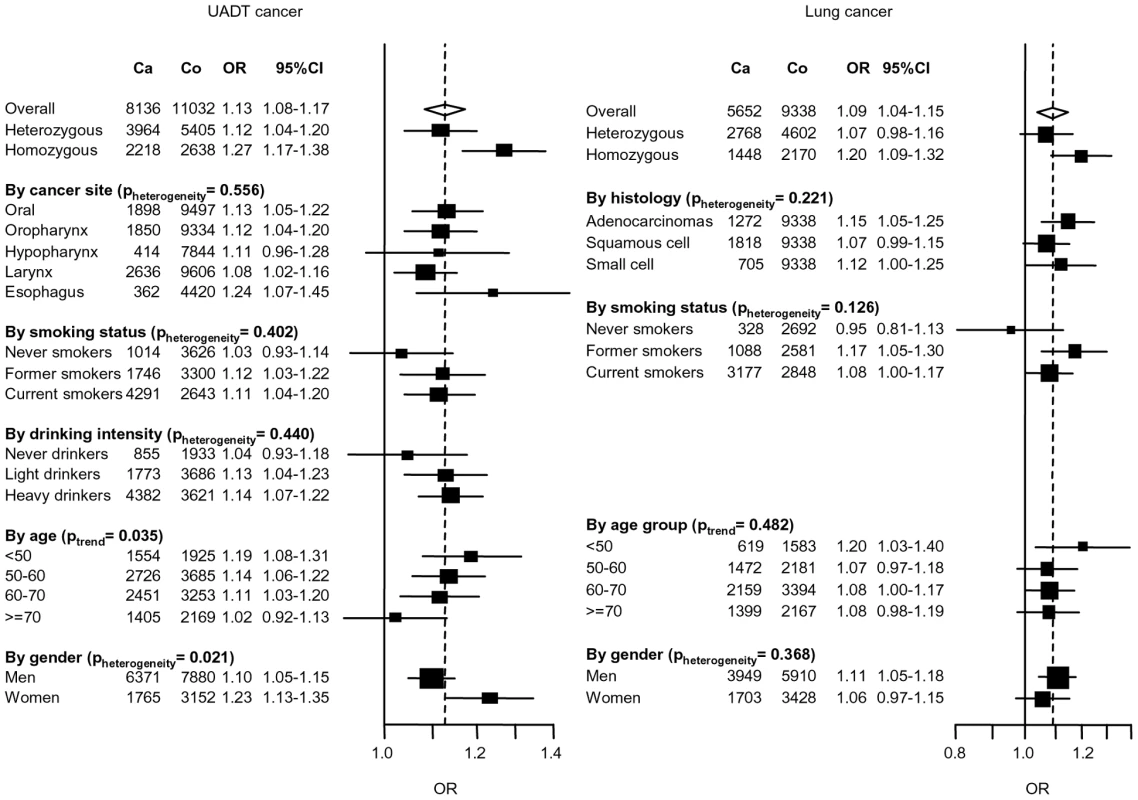
Estimates were derived from a log-additive model. ORs were adjusted by age, sex, study and were derived from fixed effects models. “Generic” controls were not included in this analysis. Replication of ADH genes associations
The association between the ADH variants, rs1573496, rs1229984 and rs698 at 4q23 and UADT cancer was described previously [14] in the CE, ARCAGE (excluding Bremen) and SA studies. When excluding these studies, the association with these variants was independently replicated in the additional 5,092 UADT cancer cases and 6,794 controls presented here (p = 5×10−8, 7×10−9 and 0.02 for rs1573496, rs1229984 and rs698, respectively) (Table 1). We combined all studies totaling 8,744 UADT cancer cases and 11,982 study specific controls to investigate effects of the ADH variants among different strata (Figure 3). For both the ADH1B and ADH7 variants heterogeneity was noted by UADT cancer subsite (p heterogeneity = 0.002, and 0.06 respectively). The rs1229984 ADH1B variant showed strong heterogeneity when stratifying by alcohol, with little evidence for association in never drinkers. By contrast, there was little evidence for heterogeneity noted with rs1573496 and rs698, but a statistically significant association with the ADH7 variant rs1573496 was observed never drinkers (p = 0.03).
Among ever drinkers in this pooled analysis, the minor allele carriers of rs1229984 reported consuming less alcohol than non-carriers (p = 3×10−20). rs1573496 minor allele carriers similarly were noted to consume somewhat less alcohol (p = 0.002), while rs698 minor allele carriers consumed slightly more (p = 0.05) (Table 2). Adjustment for alcohol consumption made little difference to the risk estimates for UADT cancer with all three variants (Table S4).
Association in African Americans
We additionally genotyped the five variants significantly associated with UADT cancer in 537 African American UADT cancer cases and 539 controls noting a significant association for the 12q24 variant rs4767364 (p = 0.004) (Table 3). Nevertheless, the smaller sample size and potential differences in genetic architecture between European and African American populations (both in terms of allele frequencies and LD structure) limits our ability to assess these five alleles in African-Americans.
Tab. 3. Comparison of results from the genome-wide analysis with analysis in a UADT case-control series of African-American origin. 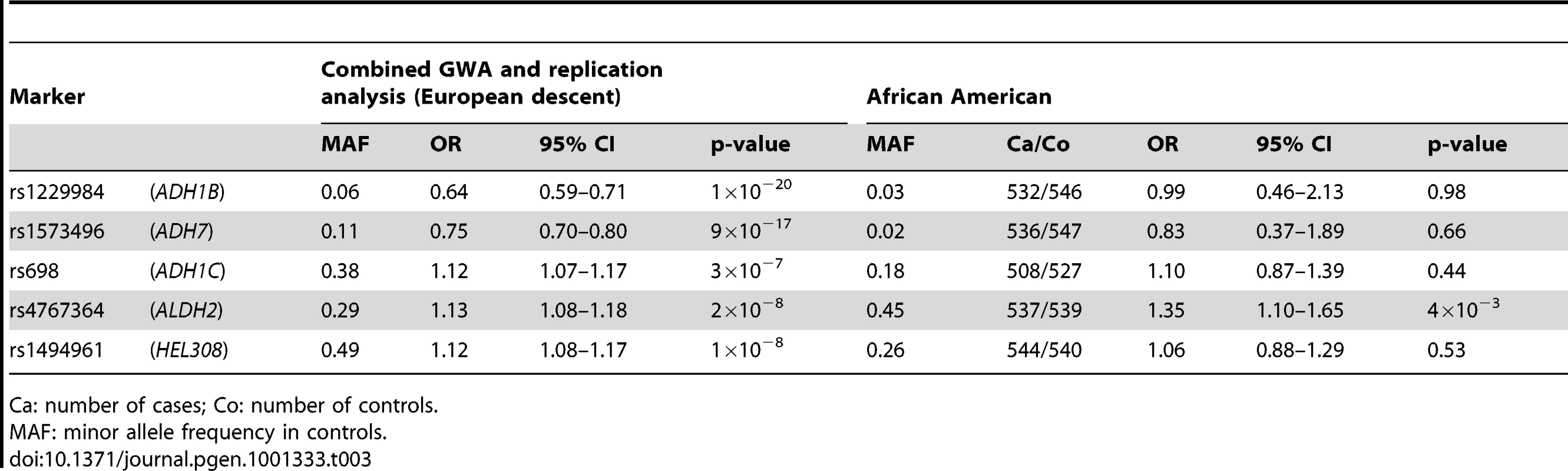
Ca: number of cases; Co: number of controls. Discussion
Five genetic variants at three loci, 4q23, 12q24 and 4q21, were significantly associated with UADT cancers in the independent replication series or after correction for multiple testing at a genome wide level in combined analysis (p≤5×10−7). The risk effects noted with all five variants were less prominent in the replication series when compared with the initial finding in the discovery series, consistent with the notion of “winner's curse” [17]. In combination we estimate these 5 variants are likely to explain only a small proportion (approximately 4%) of the UADT cancer familial risk.
12q24
The 12q24 variant, rs4767364, is positioned in an extended region of LD that contains multiple genes. Candidate genes include the aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 (ALDH2) (Figure 2), another key gene in alcohol metabolism. The minor allele carriers of ALDH2 variants rs737280 and rs4648328, in LD with rs4767364 (r2 = 0.86 and 0.67, respectively), have been associated with differences in alcohol metabolism in Europeans, leading some authors to hypothesise [18] that these alleles have a similar, albeit more modest, effect in European populations to that of the ALDH2 rs671 variant linked to alcohol metabolism differences [10] in Asian populations. The increased UADT cancer risk we observed with the minor allele of rs4767364 (and rs737280 by imputation, Figure 2) is similar to the UADT cancer risk effect observed for heterozygote rs671 carriers [12], [13] and is consistent with this hypothesis. Nevertheless, this region contains many additional plausable candidate genes. Other GWAS have implicated multiple variants in this region in many phenotypes (type 1 diabetes, arthritis, renal function, hemoglobin concentration/hematocrit, coronary artery disease and waist-to-hip ratio) [19]-[26] and therefore the nature of the actual causative allele and gene remains to be determined. The rs4767364 variant was also associated with UADT cancer risk in a smaller series of African Americans implying that this effect may be relevant to other populations.
4q21
The 4q21 variant significantly associated with UADT cancers was rs1494961 located (Table 1) 20 Mb proximal to the ADH gene cluster. There is no LD between rs1494961 and either rs1229984, rs1573496 or rs698 (r2<0.003). rs1494961 is a non-synonymous variant positioned in the HEL308 gene, a single stranded DNA-dependent ATPase and DNA helicase involved in DNA intra-strand cross-linking repair [27], although the residue involved, I306V, is not an evolutionary conserved site [28] suggesting that this alteration may not have a functional consequence. rs1494961 is in a LD region spanning approximately 90 kb, and is highly correlated (r2>0.95) with more than 20 common genetic variants. This region contains additional genes (Figure 2), notably a second DNA repair-related gene, FAM175A (or Abraxas and CCDC98), that interacts directly with the BRCT repeat region of BRCA1 [29]. That a comparable association was noted between this variant and lung cancer (p = 3×10−4) (Figure 4) suggests that the causal variant maybe relevant for cancers influenced by tobacco consumption in general.
4q23
The top two ranked variants (rs1573496 and rs698 and correlated variants) from the GWAS stage we have previously associated with UADT cancer risk [14]. The association between these variants, and a third variant, rs1229984, not included in the Humanhap300 beadchip but genotyped here based on our previous findings [14], and UADT cancer was independently replicated in the additional UADT cases and controls presented here (p = 1×10−7, 1×10−8 and 0.01 for rs1573496, rs1229984 and rs698, respectively).
The combined sample series presented here, totaling 8,774 UADT cancer cases and 11,982 controls, allowed further exploration of these genetic effects among UADT cancer subsites and strata defined by gender, drinking and smoking. The effects of these three variants were generally present for each UADT sub-sites but more pronounced in esophageal cancers and males (Figure 3). Strong heterogeneity was found with rs1229984 when stratifying by alcohol consumption. Notably, an association was observed in “Ever drinkers-Never smokers”, but not in “Never drinkers-Ever smokers”, suggesting the effect with the rs1229984 variant is mediated through alcohol drinking rather than tobacco smoking. In contrast, the lack of heterogeneity for rs1573496 when stratifying by alcohol use may imply differences in the mechanism of carcinogenesis among these ADH variants.
Several studies have suggested rs1229984 may influence alcohol consumption behaviour [30]-[33]. We have strongly replicated this association (p = 3×10−20). Similarly, minor allele carriers of rs1573496 and rs698 also consumed different amounts of alcohol compared with non-carriers (Table 2). Comparable to the observations made between 15q25 variants, propensity to smoke and lung cancer [34]-[36], adjustment for alcohol consumption did not fully explain the UADT cancer association with these variants (Table S4) suggesting, at least within the limits of this measurement of alcohol consumption, that these risks are unlikely to be explained by alcohol consumption behaviour patterns.
In conclusion, this study has identified two novel variants robustly associated with UADT cancers, and independently replicated three variants previously identified. All five variants variants are positioned near genes that appear relevant to etiology of UADT cancers, although further work is needed to identify the causative allele and gene at these loci.
Materials and Methods
Discovery phase study samples
Genome-wide genotyping was performed in two European based multi-centre UADT cancer case-control studies (Table 4), the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) central europe study [14], [37], [34] conducted from 2000 to 2002, in 6 centers from 5 countries; and the ARCAGE [14], [34], [38] (Alcohol-Related Cancers and Genetic susceptibility in Europe) multicentre case control study conducted by IARC from 2002 to 2005 in 12 centers from 9 European countries. DNA of sufficient quality and quantity for genome-wide genotyping was available for 2,230 UADT cancer cases (squamous cell carcinomas) and 4,090 controls from these two studies. We additionally included 4,983 generic controls to further increase statistical power. These generic controls included: 1,385 individuals from the 1958 birth cohort, (Wellcome Trust case control consortium[39]) as well as 1,823 French and 433 Norwegian controls genotyped by the Centre National Genotypage (CNG Evry France). We also included in our control series a separate group of 1,342 kidney cancer cases from the same centres as the central Europe study, inclusion or exclusion of these “controls” had no material effect on the results presented (Table S2). Both studies have been approved by local ethics committees as well as IARC IRB.
Tab. 4. The 15 UADT cancer studies participating in the genome-wide and replication analysis. 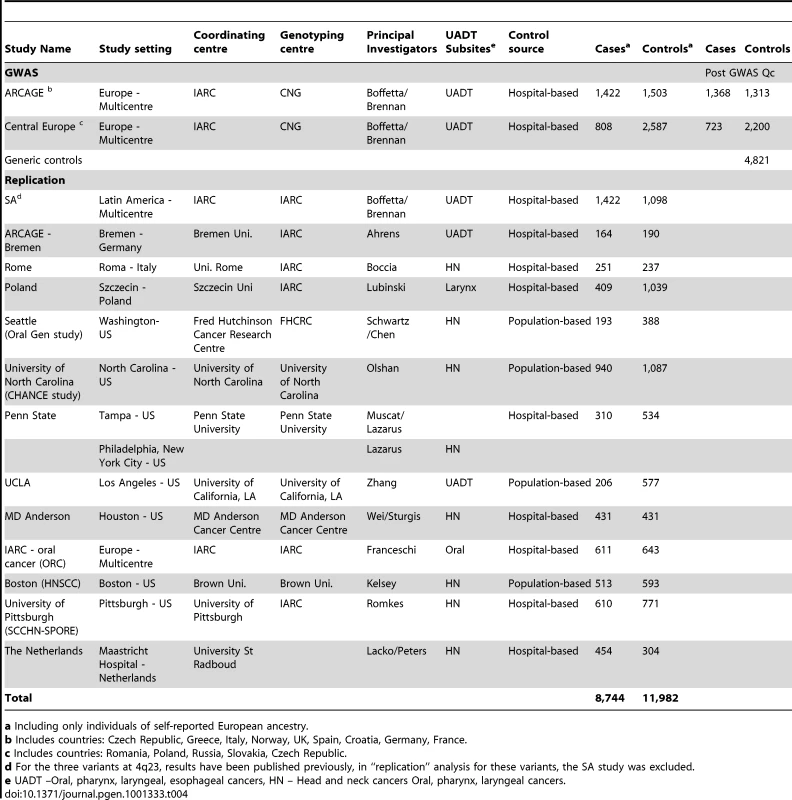
a Including only individuals of self-reported European ancestry. Genome-wide genotyping and quality control
The central Europe study and the ARCAGE study were genotyped using the Illumina Sentrix HumanHap300 BeadChip at the Centre d'Etude du Polymorphisme Humain (CEPH) and the CNG as described previously [34], [40].
We conducted systematic quality control steps on the raw Illumina HumanHap300 genotyping data. Variants with a genotype call rate of less than 95% and also individuals where the overall genotype completion rate was less than 95% were excluded. We also conducted further exclusions where the genotype distribution clearly deviated from that expected by Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium (HWE) among controls (p-value of less than 10−7) and where there were discrepancies between sex based genotype and reported sex, as well as individuals with unlikely heterozygosity rates across genetic variants on the X chromosome (Table S1). Those genotyped were restricted to individuals of self – reported European ethnicity. To further increase the ethnic homogeneity of the series, we used the program STRUCTURE [41] to identify individuals of mixed ethnicity. Using a subseries of 12,898 genetic variants from the HumanHap 300 BeadChip panel evenly distributed across the genome and in low linkage disequilibrium (LD) (r2<0.004) [42], we estimated the genetic profile of the study participants compared with individuals of known ethnic origins (the Caucasian, African and east-Asian individuals genotyped by the HapMap project). We excluded 34 individuals because of some evidence of ethnic admixture (Figure S3), indicating that the extent of admixture within the central Europe and ARCAGE study centers is limited.
Genome-wide statistical analysis
The association between each genetic variant and the disease risk was estimated by the odds ratio (OR) per allele and ninety-five percent confidence intervals (CI) using multivariate unconditional logistic regression assuming a log-additive genetic model with sex and country of recruitment included in the regression model as covariates. Results that obtained a level of significance of a two sided p<5×10−7 were considered significant at a genome wide level [39]. All analyses were conducted using PLINK [43]. We also conducted analyses restricting to UADT cancer subtypes (oral/pharyngeal cancer, laryngeal cancer, esophageal cancer) and restricting to heavy (>median) drinkers and heavy (>median) smokers.
The potential for population stratification not accounted for by adjustment by country was also investigated by principal components analysis (PCA) undertaken with the EIGENSTRAT package [44] using 12,898 markers in low LD [42]. Adjustment for population stratification using the PCA was performed by including significant eigenvectors that were associated with case control status (p<0.05) as covariates in the logistic regression.
Genotypes for genetic variants across 4q21, 4q23 and 12q21 not genotyped on the Illumina HumanHap300 BeadChip, but genotyped by the HAPMAP consortium, were imputed using the program MACH with phased genotypes from the CEU Hapmap genotyping as a scaffold. Unconditional logistic regression using posterior haplotype probabilities (haplotype dosages) from MACH were carried out using ProbABEL [45] including age, sex, and country of origin in the regression as covariates. Linkage Disequilibirum (LD) statistics (D' and r2) were calculated using Haploview [46].
Replication study samples
The replication series consisted of 6,514 UADT cancer cases (squamous cell carcinomas) and 7,892 controls from 13 UADT cancer case-control studies (Table 4). With the exception of the Szczecin case-control study [16], all studies were part of the INHANCE consortium. As previously described [1], [3], [47], all INHANCE studies have extensive information on tumor site and histology, as well as lifestyle characteristics. The Szczecin, Seattle, UCLA and MD Anderson studies were only able to genotype a proportion of the variants (Table S5). Results for the three ADH variants, rs1229984, rs1573496 and rs698 have been published previously for the Latin American study (LA). For these variants, in “replication” analysis the Latin American study was excluded. All studies have been approved by local ethics committees as well as IARC IRB.
Replication genotyping
Replication genotyping was performed using the TaqMan genotyping platform in 8 participating genotyping laboratories (Table 4). The robustness of the Taqman assays (primers and probes are available upon request) were confirmed at IARC by re-genotyping the CEPH HapMap (CEU) trios and confirming concordance with HapMap genotypes. Any discordance between Hapmap and Taqman generated genotypes was resolved by direct DNA sequencing. All Taqman assays were found to be performing robustly. IARC supplied Taqman assays and a standardized Taqman genotyping protocol to each of the 8 participating genotyping laboratories. A common series of 90 standard DNAs were genotyped at each laboratory to ensure the quality and comparability of the genotyping results across the different studies. Concordance with the consensus genotype and the results produced at the eight genotyping laboratories for the standardized DNAs was 99.75%, and no individual centre had a overall concordance of less than 99.5%. If the assay produced 2 or more discordant genotypes relative to the consensus, the study genotypes for this genetic variant were not included in the statistical analysis. Assays that had a per-centre success rate of <90% or for which genotype distributions deviated from HWE (p<0.001) were also excluded (Table S5).
Replication statistical analysis
The association between the nineteen variants and UADT cancer risk was estimated by per allele ORs and their 95% CI derived from multivariate unconditional logistic regression, with age, sex, and study (and country of origin where appropriate) included in the regression model as covariates. Measures of alcohol consumption have been previously harmonized across INHANCE studies [48]. The association between ADH/ALDH2 variants and alcohol consumption was carried out in ever drinkers using multivariate linear regression using a log transformed milliliter of ethanol consumed per day as an outcome, adjusting for age, sex, study, packyears (and case-control status when appropriate). Milliliters of ethanol consumed per day was not available for 3 studies (Szczecin, Philadelphia/New York and The Netherlands study). Heterogeneity of ORs across the studies and across the stratification groups was assessed using the Cochran's Q-test. All replication and combined analyses were conducted using SAS 9.1 software. P values were two sided.
Investigation of the effects of 4q21 variant rs1494961 and lung cancer risk
The series of lung cancer cases and controls used to investigate 4q21 variant, rs1494961, and lung cancer risk included studies from central Europe (IARC), Toronto (McGill), HUNT2/Tromso, the CARET cohort, EPIC-lung, the Szczecin case-control study, Liverpool Lung Project (LLP), Paris France and Estonia as described previously [34], [40], [49]. All studies have been approved by local ethics committees as well as IARC IRB.
Genotyping protocol for 4q21 variant, rs1494961
Genotyping for rs1494691 was performed using the Illumina beadchips (Central Europe (IARC), Toronto (McGill), HUNT2/Tromso, the CARET cohort, France and Estonia) or the Applied Biosystems Taqman assays (EPIC-lung, the Szczecin case-control study, Liverpool Lung Project (LLP)) at IARC.
For the central European lung cancer study, the controls overlapped with the central European UADT cancer study for Bucharest (Romania), Lodz (Poland), Moscow (Russia), Banska Bystrika (Slovakia), and Olomouc and Prague (Czech Republic). We therefore performed analyses both including and excluding centres where controls overlapped.
Web resources
http://inhance.iarc.fr/ (December 2010)
http://www.hapmap.org (December 2010)
http://www.sph.umich.edu/csg/abecasis/mach/index.html (December 2010)
Supporting Information
Zdroje
1. FerlayJ
BrayF
PisaniP
ParkinDM
2004 GLOBOCAN 2002 Cancer Incidence Mortality and Prevalence Worldwide. IARC Cancer Base No 5 version 20 IARC Press Lyon
2. HashibeM
BrennanP
BenhamouS
CastellsagueX
ChenC
2007 Alcohol drinking in never users of tobacco cigarette smoking in never drinkers and the risk of head and neck cancer: pooled analysis in the International Head and Neck Cancer Epidemiology Consortium. J Natl Cancer Inst 99 777 789
3. HerreroR
CastellsaguéX
PawlitaM
LissowskaJ
KeeF
2003 Human papillomavirus and oral cancer: the International Agency for Research on Cancer multicenter study. J Natl Cancer Inst 95 1772 1783
4. NegriE
BoffettaP
BerthillerJ
CastellsagueX
CuradoMP
2009 Family history of cancer: pooled analysis in the International Head and Neck Cancer Epidemiology Consortium. Int J Cancer 124 394 401
5. GoldsteinAM
BlotWJ
GreenbergRS
SchoenbergJB
AustinDF
1994 Familial risk in oral and pharyngeal cancer. Eur J Cancer B Oral Oncol 30 319 22
6. GoldgarDE
EastonDF
Cannon-AlbrightLA
SkolnickMH
1994 Systematic population-based assessment of cancer risk in first-degree relatives of cancer probands. J Natl Cancer Inst 86 1600 1608
7. GaravelloW
FoschiR
TalaminiR
La VecchiaC
RossiM
2008 Family history and the risk of oral and pharyngeal cancer. Int J Cancer 122 1827 31
8. BrennanP
LewisS
HashibeM
BellDA
BoffettaP
2004 Pooled analysis of alcohol dehydrogenase genotypes and head and neck cancer: a HuGE review. Am J Epidemiol 159 1 1 16
9. IARC
1988 Alcohol drinking IARC monographs on the evaluation of carcinogenic risks to humans. Vol 44 Lyon IARC
10. YoshidaA
HuangIY
IkawaM
1984 Molecular abnormality of an inactive aldehyde dehydrogenase variant commonly found in Orientals. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 81 258 261
11. EnomotoN
TakaseS
YasuharaM
TakadaA
1991 Acetaldehyde metabolism in different aldehyde dehydrogenase-2 genotypes. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 15 141 144
12. LewisSJ
SmithGD
2005 Alcohol ALDH2 and esophageal cancer: a meta-analysis which illustrates the potentials and limitations of a Mendelian randomization approach. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 14 1967 1971
13. BrooksPJ
EnochMA
GoldmanD
LiTK
YokoyamaA
2009 The alcohol flushing response: an unrecognized risk factor for esophageal cancer from alcohol consumption. PLoS Med 6 e50 doi:10.1371/journal.pmed.1000050
14. HashibeM
McKayJD
Curado OliveiraJ
KoifmanS
KoifmanR
2008 Multiple ADH genes are associated with upper aero-digestive cancers in three large independent studies. Nature Genetics 40 707 709
15. BrennanP
McKayJ
MooreL
ZaridzeD
MukeriaA
2007 Uncommon CHEK2 mis-sense variant and reduced risk of tobacco-related cancers: case control study. Hum Mol Genet 16 1794 801
16. CybulskiC
MasojcB
OszutowskaD
JaworowskaE
GrodzkiT
2008 Constitutional CHEK2 mutations are associated with a decreased risk of lung and laryngeal cancers. Carcinogenesis 29 762 765
17. XiaoR
BoehnkeM
2009 Quantifying and correcting for the winner's curse in genetic association studies. Genet Epidemiol. 33 453 62
18. DicksonPA
JamesMR
HeathAC
MontgomeryGW
MartinNG
2006 Effects of variation at the ALDH2 locus on alcohol metabolism sensitivity consumption and dependence in Europeans. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 30 1093 1100
19. CooperJD
SmythDJ
SmilesAM
PlagnolV
WalkerNM
2008 Meta-analysis of genome-wide association study data identifies additional type 1 diabetes risk loci. Nat Genet. 40 1399 401
20. BarrettJC
ClaytonDG
ConcannonP
AkolkarB
CooperJD
2009 Genome-wide association study and meta-analysis find that over 40 loci affect risk of type 1 diabetes. Nat Genet. 41 703 707
21. PrahaladS
HansenS
WhitingA
GutherySL
CliffordB
2009 Variants in TNFAIP3, STAT4, and C12orf30 loci associated with multiple autoimmune diseases are also associated with juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 60 2124 30
22. KöttgenA
PattaroC
BögerCA
FuchsbergerC
OldenM
2010 New loci associated with kidney function and chronic kidney disease. Nat Genet. 42 376 84
23. GaneshSK
ZakaiNA
van RooijFJ
SoranzoN
SmithAV
2009 Multiple loci influence erythrocyte phenotypes in the CHARGE Consortium. Nat Genet. 41 1191 8
24. SoranzoN
SpectorTD
ManginoM
KühnelB
RendonA
2009 A genome-wide meta-analysis identifies 22 loci associated with eight hematological parameters in the HaemGen consortium. Nat Genet. 41 1182 90
25. KamataniY
MatsudaK
OkadaY
KuboM
HosonoN
2010 Genome-wide association study of hematological and biochemical traits in a Japanese population. Nat Genet. 42 210 5
26. ChoYS
GoMJ
KimYJ
HeoJY
OhJH
2009 A large-scale genome-wide association study of Asian populations uncovers genetic factors influencing eight quantitative traits. Nat Genet. 41 527 34
27. MariniF
WoodRD
2002 A human DNA helicase homologous to the DNA cross-link sensitivity protein Mus308. J Biol Chem 277 8716 8723
28. MariniF
KimN
SchuffertA
WoodRD
2003 POLN a nuclear PolA family DNA polymerase homologous to the DNA cross-link sensitivity protein Mus308. J Biol Chem 278 32014 32019
29. WangB
MatsuokaS
BallifBA
ZhangD
SmogorzewskaA
2007 Abraxas and RAP80 form a BRCA1 protein complex required for the DNA damage response. Science 316 1194 1198
30. MacgregorS
LindPA
BucholzKK
HansellNK
MaddenPA
2009 Associations of ADH and ALDH2 gene variation with self report alcohol reactions consumption and dependence: an integrated analysis. Hum Mol Genet 18 580 593
31. TolstrupJS
NordestgaardBG
RasmussenS
Tybjaerg-HansenA
GrønbaekM
2008 Alcoholism and alcohol drinking habits predicted from alcohol dehydrogenase genes. Pharmacogenomics J 8 3 220 7
32. ZuccoloL
Fitz-SimonN
GrayR
RingSM
SayalK
2009 A non-synonymous variant in ADH1B is strongly associated with prenatal alcohol use in a European sample of pregnant women. Hum Mol Genet 15 4457 66
33. LuoX
KranzlerHR
ZuoL
WangS
SchorkNJ
2006 Diplotype trend regression analysis of the ADH gene cluster and the ALDH2 gene: multiple significant associations with alcohol dependence. Am J Hum Genet 78 973 87
34. HungRJ
McKayJD
GaborieauV
BoffettaP
HashibeM
2008 A susceptibility locus for lung cancer maps to nicotinic acetylcholine receptor subunit genes on 15q25. Nature 452 633 637
35. AmosCI
WuX
BroderickP
GorlovIP
GuJ
2008 Genome-wide association scan of tag SNPs identifies a susceptibility locus for lung cancer at 15q25.1. Nat Genet. 40 616 22
36. ThorgeirssonTE
GellerF
SulemP
RafnarT
WisteA
2008 A variant associated with nicotine dependence, lung cancer and peripheral arterial disease. Nature 452 638 42
37. SceloG
ConstantinescuV
CsikiI
ZaridzeD
Szeszenia-DabrowskaN
Occupational exposure to vinyl chloride acrylonitrile and styrene and lung cancer risk (Europe). Cancer Causes Control 2004 15 445 52
38. LagiouP
GeorgilaC
MinakiP
AhrensW
PohlabelnH
2009 Alcohol-related cancers and genetic susceptibility in Europe: the ARCAGE project: study samples and data collection. Eur J Cancer Prev 18 76 84
39. The Wellcome Trust Case Control Consortium 2007 Genome-wide association study of 14000 cases of seven common diseases and 3000 shared controls. Nature 447 661 678
40. McKayJD
HungRJ
GaborieauV
BoffettaP
ChabrierA
2008 Lung cancer susceptibility locus at 5p15.33. 40 Nat Genet. 1404 6
41. FalushD
StephensM
PritchardJK
2003 Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data: linked loci and correlated allele frequencies. Genetics 164 1567 1587
42. YuK
WangZ
LiQ
WacholderS
HunterDJ
2008 Population substructure and control selection in genome-wide association studies. PLoS ONE 3 e2551 doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0002551
43. PurcellS
NealeB
Todd-BrownK
ThomasL
FerreiraMA
2007 PLINK: a tool set for whole-genome association and population-based linkage analyses. Am J Hum Genet 81 559 575
44. PriceAL
PattersonNJ
PlengeRM
WeinblattME
ShadickNA
2006 Principal components analysis corrects for stratification in genome-wide association studies. Nat Genet 38 904 909
45. AulchenkoYS
StruchalinMV
van DuijnCM
2010 ProbABEL package for genome-wide association analysis of imputed data. BMC Bioinformatics 11 134
46. BarrettJC
FryB
MallerJ
DalyMJ
2005 Haploview: analysis and visualization of LD and haplotype maps. Bioinformatics 21 263 5
47. ConwayDI
HashibeM
BoffettaP
Wunsch-FilhoV
INHANCE consortium 2009 Enhancing epidemiologic research on head and neck cancer: INHANCE - The international head and neck cancer epidemiology consortium. Oral Oncol 45 743 746
48. PurdueMP
HashibeM
BerthillerJ
La VecchiaC
Dal MasoL
2009 Type of alcoholic beverage and risk of head and neck cancer–a pooled analysis within the INHANCE Consortium. Am J Epidemiol. 169 132 42
49. LipsEH
GaborieauV
McKayJD
ChabrierA
HungRJ
2010 Association between a 15q25 gene variant smoking quantity and tobacco-related cancers among 17 000 individuals. Int J Epidemiol. 39 2 563 77
Štítky
Genetika Reprodukční medicína
Článek Genetic Regulation by NLA and MicroRNA827 for Maintaining Nitrate-Dependent Phosphate Homeostasis inČlánek c-di-GMP Turn-Over in Is Controlled by a Plethora of Diguanylate Cyclases and PhosphodiesterasesČlánek Viral Genome Segmentation Can Result from a Trade-Off between Genetic Content and Particle Stability
Článek vyšel v časopisePLOS Genetics
Nejčtenější tento týden
2011 Číslo 3
-
Všechny články tohoto čísla
- Whole-Exome Re-Sequencing in a Family Quartet Identifies Mutations As the Cause of a Novel Skeletal Dysplasia
- Origin-Dependent Inverted-Repeat Amplification: A Replication-Based Model for Generating Palindromic Amplicons
- Testing for an Unusual Distribution of Rare Variants
- Limited dCTP Availability Accounts for Mitochondrial DNA Depletion in Mitochondrial Neurogastrointestinal Encephalomyopathy (MNGIE)
- FUS Transgenic Rats Develop the Phenotypes of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis and Frontotemporal Lobar Degeneration
- Repeat Associated Non-ATG Translation Initiation: One DNA, Two Transcripts, Seven Reading Frames, Potentially Nine Toxic Entities!
- Initial Mutations Direct Alternative Pathways of Protein Evolution
- Dopamine Signalling in Mushroom Bodies Regulates Temperature-Preference Behaviour in
- Sensing of Replication Stress and Mec1 Activation Act through Two Independent Pathways Involving the 9-1-1 Complex and DNA Polymerase ε
- Genetic Regulation by NLA and MicroRNA827 for Maintaining Nitrate-Dependent Phosphate Homeostasis in
- Identification of a Novel Type of Spacer Element Required for Imprinting in Fission Yeast
- Chiasmata Promote Monopolar Attachment of Sister Chromatids and Their Co-Segregation toward the Proper Pole during Meiosis I
- Global Analysis of the Relationship between JIL-1 Kinase and Transcription
- H3K9me2/3 Binding of the MBT Domain Protein LIN-61 Is Essential for Vulva Development
- REVEILLE8 and PSEUDO-REPONSE REGULATOR5 Form a Negative Feedback Loop within the Arabidopsis Circadian Clock
- A Novel Unstable Duplication Upstream of Predisposes to a Breed-Defining Skin Phenotype and a Periodic Fever Syndrome in Chinese Shar-Pei Dogs
- Polycomb Repressive Complex 2 Controls the Embryo-to-Seedling Phase Transition
- A Role for Set1/MLL-Related Components in Epigenetic Regulation of the Germ Line
- Genome-Wide Association Analysis Identifies Variants Associated with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease That Have Distinct Effects on Metabolic Traits
- A Genome-Wide Association Study of Upper Aerodigestive Tract Cancers Conducted within the INHANCE Consortium
- Ancestral Mutation in Telomerase Causes Defects in Repeat Addition Processivity and Manifests As Familial Pulmonary Fibrosis
- Ultra-Deep Sequencing of Mouse Mitochondrial DNA: Mutational Patterns and Their Origins
- Phenotype Restricted Genome-Wide Association Study Using a Gene-Centric Approach Identifies Three Low-Risk Neuroblastoma Susceptibility Loci
- The Toll-Like Receptor Gene Family Is Integrated into Human DNA Damage and p53 Networks
- Polycomb Targets Seek Closest Neighbours
- Widespread Hypomethylation Occurs Early and Synergizes with Gene Amplification during Esophageal Carcinogenesis
- c-di-GMP Turn-Over in Is Controlled by a Plethora of Diguanylate Cyclases and Phosphodiesterases
- Estimating Divergence Time and Ancestral Effective Population Size of Bornean and Sumatran Orangutan Subspecies Using a Coalescent Hidden Markov Model
- Rif1 Supports the Function of the CST Complex in Yeast Telomere Capping
- A Tradeoff Drives the Evolution of Reduced Metal Resistance in Natural Populations of Yeast
- Quantifying the Underestimation of Relative Risks from Genome-Wide Association Studies
- Population-Based Resequencing of Experimentally Evolved Populations Reveals the Genetic Basis of Body Size Variation in
- Triplet Repeat–Derived siRNAs Enhance RNA–Mediated Toxicity in a Drosophila Model for Myotonic Dystrophy
- The FUN30 Chromatin Remodeler, Fft3, Protects Centromeric and Subtelomeric Domains from Euchromatin Formation
- Viral Genome Segmentation Can Result from a Trade-Off between Genetic Content and Particle Stability
- Environmental Sex Determination in the Branchiopod Crustacean : Deep Conservation of a Gene in the Sex-Determining Pathway
- Systematic Detection of Polygenic Regulatory Evolution
- The SUMO Isopeptidase Ulp2p Is Required to Prevent Recombination-Induced Chromosome Segregation Lethality following DNA Replication Stress
- Uncoupling Antisense-Mediated Silencing and DNA Methylation in the Imprinted Cluster
- Role of the Drosophila Non-Visual ß-Arrestin Kurtz in Hedgehog Signalling
- Differential Genetic Associations for Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Based on Anti–dsDNA Autoantibody Production
- COMPASS-Like Complexes Mediate Histone H3 Lysine-4 Trimethylation to Control Floral Transition and Plant Development
- H3 Lysine 4 Is Acetylated at Active Gene Promoters and Is Regulated by H3 Lysine 4 Methylation
- Diverse Roles and Interactions of the SWI/SNF Chromatin Remodeling Complex Revealed Using Global Approaches
- A Bow-Tie Genetic Architecture for Morphogenesis Suggested by a Genome-Wide RNAi Screen in
- Roles of () in Oocyte Nuclear Architecture, Gametogenesis, Gonad Tumors, and Genome Stability in Zebrafish
- A Molecular Phylogeny of Living Primates
- Roles of the Espin Actin-Bundling Proteins in the Morphogenesis and Stabilization of Hair Cell Stereocilia Revealed in CBA/CaJ Congenic Jerker Mice
- A Cholinergic-Regulated Circuit Coordinates the Maintenance and Bi-Stable States of a Sensory-Motor Behavior during Male Copulation
- PLOS Genetics
- Archiv čísel
- Aktuální číslo
- Informace o časopisu
Nejčtenější v tomto čísle- Whole-Exome Re-Sequencing in a Family Quartet Identifies Mutations As the Cause of a Novel Skeletal Dysplasia
- Origin-Dependent Inverted-Repeat Amplification: A Replication-Based Model for Generating Palindromic Amplicons
- FUS Transgenic Rats Develop the Phenotypes of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis and Frontotemporal Lobar Degeneration
- Limited dCTP Availability Accounts for Mitochondrial DNA Depletion in Mitochondrial Neurogastrointestinal Encephalomyopathy (MNGIE)
Kurzy
Zvyšte si kvalifikaci online z pohodlí domova
Současné možnosti léčby obezity
nový kurzAutoři: MUDr. Martin Hrubý
Všechny kurzyPřihlášení#ADS_BOTTOM_SCRIPTS#Zapomenuté hesloZadejte e-mailovou adresu, se kterou jste vytvářel(a) účet, budou Vám na ni zaslány informace k nastavení nového hesla.
- Vzdělávání



