-
Články
Top novinky
Reklama- Vzdělávání
- Časopisy
Top články
Nové číslo
- Témata
Top novinky
Reklama- Videa
- Podcasty
Nové podcasty
Reklama- Kariéra
Doporučené pozice
Reklama- Praxe
Top novinky
ReklamaInterferon-Induced Protects Mice from Lethal VSV Neuropathogenesis
Interferon protects mice from vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV) infection and pathogenesis; however, it is not known which of the numerous interferon-stimulated genes (ISG) mediate the antiviral effect. A prominent family of ISGs is the interferon-induced with tetratricopeptide repeats (Ifit) genes comprising three members in mice, Ifit1/ISG56, Ifit2/ISG54 and Ifit3/ISG49. Intranasal infection with a low dose of VSV is not lethal to wild-type mice and all three Ifit genes are induced in the central nervous system of the infected mice. We tested their potential contributions to the observed protection of wild-type mice from VSV pathogenesis, by taking advantage of the newly generated knockout mice lacking either Ifit2 or Ifit1. We observed that in Ifit2 knockout (Ifit2−/−) mice, intranasal VSV infection was uniformly lethal and death was preceded by neurological signs, such as ataxia and hind limb paralysis. In contrast, wild-type and Ifit1−/− mice were highly protected and survived without developing such disease. However, when VSV was injected intracranially, virus replication and survival were not significantly different between wild-type and Ifit2−/− mice. When administered intranasally, VSV entered the central nervous system through the olfactory bulbs, where it replicated equivalently in wild-type and Ifit2−/− mice and induced interferon-β. However, as the infection spread to other regions of the brain, VSV titers rose several hundred folds higher in Ifit2−/− mice as compared to wild-type mice. This was not caused by a broadened cell tropism in the brains of Ifit2−/− mice, where VSV still replicated selectively in neurons. Surprisingly, this advantage for VSV replication in the brains of Ifit2−/− mice was not observed in other organs, such as lung and liver. Pathogenesis by another neurotropic RNA virus, encephalomyocarditis virus, was not enhanced in the brains of Ifit2−/− mice. Our study provides a clear demonstration of tissue-, virus - and ISG-specific antiviral action of interferon.
Published in the journal: . PLoS Pathog 8(5): e32767. doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1002712
Category: Research Article
doi: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1002712Summary
Interferon protects mice from vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV) infection and pathogenesis; however, it is not known which of the numerous interferon-stimulated genes (ISG) mediate the antiviral effect. A prominent family of ISGs is the interferon-induced with tetratricopeptide repeats (Ifit) genes comprising three members in mice, Ifit1/ISG56, Ifit2/ISG54 and Ifit3/ISG49. Intranasal infection with a low dose of VSV is not lethal to wild-type mice and all three Ifit genes are induced in the central nervous system of the infected mice. We tested their potential contributions to the observed protection of wild-type mice from VSV pathogenesis, by taking advantage of the newly generated knockout mice lacking either Ifit2 or Ifit1. We observed that in Ifit2 knockout (Ifit2−/−) mice, intranasal VSV infection was uniformly lethal and death was preceded by neurological signs, such as ataxia and hind limb paralysis. In contrast, wild-type and Ifit1−/− mice were highly protected and survived without developing such disease. However, when VSV was injected intracranially, virus replication and survival were not significantly different between wild-type and Ifit2−/− mice. When administered intranasally, VSV entered the central nervous system through the olfactory bulbs, where it replicated equivalently in wild-type and Ifit2−/− mice and induced interferon-β. However, as the infection spread to other regions of the brain, VSV titers rose several hundred folds higher in Ifit2−/− mice as compared to wild-type mice. This was not caused by a broadened cell tropism in the brains of Ifit2−/− mice, where VSV still replicated selectively in neurons. Surprisingly, this advantage for VSV replication in the brains of Ifit2−/− mice was not observed in other organs, such as lung and liver. Pathogenesis by another neurotropic RNA virus, encephalomyocarditis virus, was not enhanced in the brains of Ifit2−/− mice. Our study provides a clear demonstration of tissue-, virus - and ISG-specific antiviral action of interferon.
Introduction
Virus infection of mammals induces the synthesis of type I interferons (IFN), which, in turn, inhibit virus replication. The high susceptibility of type I IFN receptor knockout (IFNAR−/−) mice to infection by a variety of viruses [1]–[3] provides strong evidence for the major role of the IFN system in protecting from viral pathogenesis. In these mice, although IFN is induced by virus infection, it cannot act on target cells. Similarly, in genetically altered mice that are defective in IFN production due to the absence of specific pathogen-associated pattern recognition receptors, signaling proteins or specific transcription factors, viral pathogenesis is enhanced [4]–[6]. Although the critical importance of the IFN system in regulating viral pathogenesis is now well established, in many cases it is still unclear how IFN inhibits the replication and spread of a specific virus in vivo. In this context, activation of different components of the immune system plays a major role in controlling viral diseases that are relatively slow to develop [7]–[9]. In contrast, in acute infection by viruses that cause severe pathogenesis and death within a few days after infection, protection is primarily provided by the intrinsic antiviral actions of IFN-induced proteins encoded by the hundreds of IFN-stimulated genes (ISGs) [10]–[12], several of which often contribute to the overall effect of IFN against a given virus. Our knowledge of the antiviral and the biochemical properties of individual ISG products is mostly limited to a few intensively studied examples such as PKR, OAS/RNase L or Mx [13]. However, recent systematic investigation of the antiviral functions of the entire family of ISGs has started producing exciting new information [14].
In the above context, we have been investigating the biochemical and biological functions of the members of the Ifit family of ISGs, which are very strongly induced by IFN. There are three members of this family of genes in mice: Ifit1/ISG56, Ifit2/ISG54 and Ifit3/ISG49; all of the encoded proteins contain multiple tetratricopeptide repeats (TPR), which mediate protein-protein and protein-RNA interactions [15]. In vitro, P56 and P54, the products of Ifit1 and Ifit2, respectively, bind to the translation initiation factor eIF3 and inhibit protein synthesis [16]. The third member, P49, the product of Ifit3, does not share this property [17]. Recently, it has been reported that Ifit proteins form a multi-protein complex that can bind to the triphosphorylated 5′ end of RNAs, an RNA-species produced during the replication of some, but not all, viruses [18]. In vivo, these genes are strongly induced in brains of mice infected with West Nile virus (WNV) or Lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus (LCMV); surprisingly, different Ifit genes are differentially induced in different regions of the brain, suggesting non-redundant functions [19]. To further explore the antiviral properties of the Ifit proteins, we generated Ifit1 knockout (Ifit1−/−) mice and challenged them with different viruses. We observed that Ifit1−/− mice were particularly susceptible to a WNV mutant that is defective in its mRNA cap 2′-O methylation; the mutant virus killed Ifit1−/− mice but not the wild-type (wt) mice [20].
Here, we report on the antiviral properties of the newly generated Ifit2−/− mice; these mice, but not Ifit1−/− mice, were highly susceptible to neuropathogenesis after intranasal infection with vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV), a negative sense, single-stranded RNA rhabdovirus. VSV replication is highly sensitive to the inhibitory action of IFN and is routinely used to assay the antiviral activity of IFN in vitro [21]. As expected, IFNAR−/− mice are highly susceptible to VSV pathogenesis and the same is true for mice that specifically lack expression of IFNAR on the cells of their central nervous system (CNS) [1]. In spite of these observations, little is known about how IFN inhibits VSV replication in vivo. Our new results indicate that in the brain, but not in other organs, Ifit2 is a major mediator of IFN's protective effect against VSV. In contrast, Ifit2 could not protect mice from neuropathogenesis caused by encephalomyocarditis virus (EMCV), a picornavirus. Thus, we have uncovered a virus-specific, tissue-specific and ISG-specific antiviral effect of the IFN system.
Results
Generation of Ifit2/ISG54 and Ifit1/ISG56 knockout mice
Ifit2 gene knockout (Ifit2−/−) mice were generated by deleting the entire protein-encoding region of the gene, which was achieved by flanking exons 2 and 3 with frt recombinase sites in C57BL/6 embryonic stem cells and excising the flanked region with Flp recombinase (Figure 1A). Ifit2−/− mice were bred to homozygosity (Figure 1B), and deficiency for induced expression of Ifit2 protein was confirmed in lysates of IFN-β-treated primary murine embryonic fibroblasts (MEF) (Figure 1C). Mice deficient for Ifit1 (Ifit1−/−) were derived from C57BL/6 embryonic stem cells lacking the entire Ifit1 coding region (Figure 1A). Genotypic homozygosity of the Ifit1−/− mice and deficiency for Ifit1 protein induction were confirmed (Figure 1B and 1C). Both knockout mouse lines were healthy and fertile. Moreover, deletion of one gene within the Ifit locus did not alter the pattern of induction of other adjacent gene family members, as compared to wild-type (wt) mice (Figure 1C).
Fig. 1. Generation of Ifit2/ISG54 and Ifit1/ISG56 knockout mice. 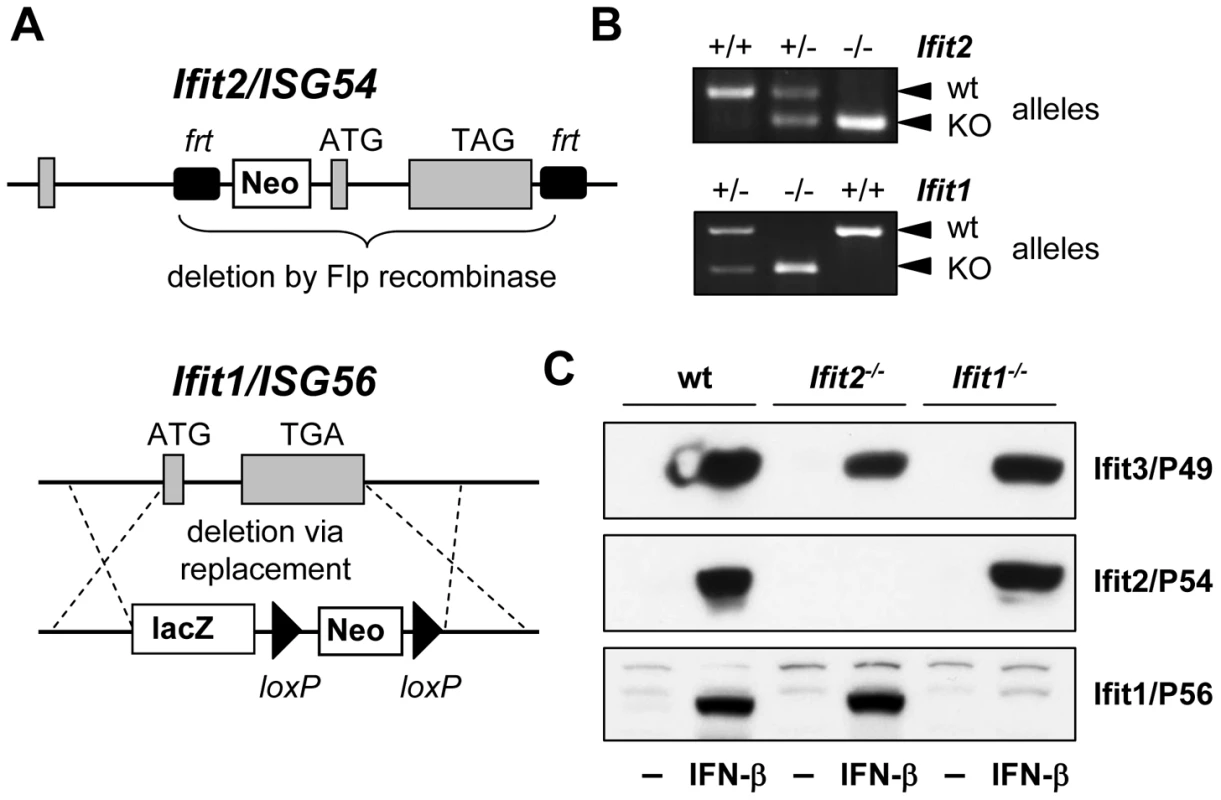
A, gene targeting strategy for genomic deletion of complete protein-encoding regions of Ifit2 = ISG54 or Ifit1 = ISG56 in embryonic stem cells; TAG/TGA, stop codons; grey boxes = exons. B, genotyping of deficiency for Ifit2 or Ifit1 by PCR on mouse tail DNA. C, IFN-β-induced protein expression of Ifit2/P54, Ifit1/P56 and Ifit3/P49 in Ifit2−/− or Ifit1−/− primary MEFs. Ifit2 protects mice from lethal intranasal VSV infection
To determine the impact of Ifit2 on the outcome of viral infections in vivo, we compared susceptibilities of Ifit2−/− and wt mice to VSV infection, using IFNAR−/− mice as positive controls of enhanced susceptibility. Virus was administered at a low dose [4×102 plaque forming units (pfu)], intranasally, reflecting a natural route of infection for VSV [22]. As seen previously, 100% of IFNAR−/− mice rapidly succumbed to VSV infection within 2 days (Figure 2A, and [1]), after suffering symptoms of lethargy. On the other hand, 79% of wt mice survived, the remaining 21% succumbed to VSV, and this occurred later, at 7–10 days post infection (d.p.i.). In contrast, 100% of Ifit2−/− mice died by 7 d.p.i. (Figure 2A), with most succumbing by 6 d.p.i.; thus, we observed uniform and more rapidly occurring death of Ifit2−/− compared to wt mice after VSV infection. Within 24 h before death, both wt and Ifit2−/− mice developed neurological signs including ataxia, hind limb paralysis, and hyper-excitability. Ifit2+/− mice displayed an intermediate survival curve, demonstrating a gene dosage effect (Figure 2B). Next, the role of a related gene, Ifit1, in VSV pathogenesis was evaluated by infecting Ifit1−/− mice. Unlike the results observed with Ifit2−/− mice, no statistically significant increase in mortality was observed in Ifit1−/− mice (Figure 2B, 21% death for wt versus 36% for Ifit1−/−, respectively; p>0.25). Consistent with this, survival kinetics of Ifit1−/− and wt mice were similar. Increasing the virus dose by 10,000-fold (to 4×106 pfu) did not appreciably change the survival curves of wt, Ifit1−/−, or Ifit2−/− mice (Figure 2C). These results demonstrate functional differences between the two closely related proteins encoded by Ifit1 and Ifit2. The virus-specificity of the antiviral action of Ifit2 was evaluated by infecting Ifit2−/− mice with EMCV, an unrelated neurovirulent positive-strand RNA virus of the picornavirus family (Figure 2D). IFNAR−/− mice were highly susceptible to EMCV infection with all mice succumbing within 2 d.p.i.; in contrast, wt mice died with a slower kinetics and at a rate of only 80%. Notably, Ifit2−/− mice behaved similarly to the wt mice, without enhanced or accelerated mortality (Figure 2D). The same conclusion was true for a lower dose of EMCV (Figure S1). The survival pattern of EMCV-infected Ifit1−/− mice also was similar to that of the wt mice (Figure 2D). Mice of all genotypes either succumbed after developing neurological symptoms, mainly hind limb paralysis, or survived without symptoms. These results demonstrate that the antiviral action of Ifit2 is both virus - and Ifit-specific.
Fig. 2. Ifit2 protects mice from lethal intranasal VSV infection. 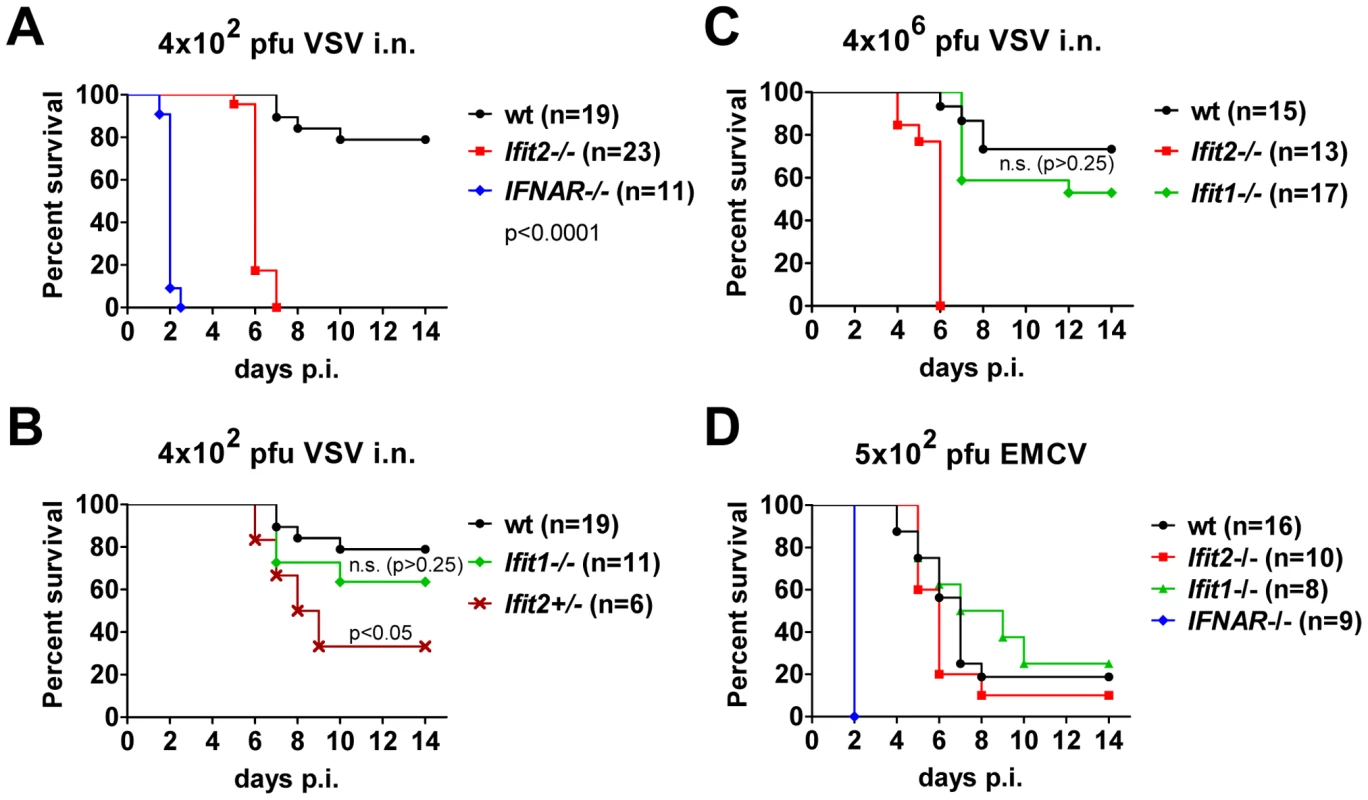
A, survival of Ifit2−/−, IFNAR−/− and wt mice after intranasal infection with 4×102 pfu of VSV Indiana. B, survival of Ifit1−/− and Ifit2-heterozygous (Ifit2+/−) mice after infection with 4×102 pfu of VSV; experiments in A and B shared wt mice (n = number of animals used). C, survival of Ifit2−/−, Ifit1−/− and wt mice after intranasal infection with a higher dose of VSV (4×106 pfu). D, survival of Ifit2−/−, Ifit1−/−, IFNAR−/− and wt mice after infection with 5×102 pfu of EMCV. In A–D, data are cumulative from at least two independent experiments (exceptions: Figure 2B, Ifit2+/− mice and Figure 2D, Ifit1−/− mice infected in a single experiment). Statistical significance of survival differences relative to wt mice is indicated by p-values; n.s., not significant; i.n., intranasal. Ifit2 does not inhibit VSV entry and replication in olfactory bulbs
The uniform penetrance of neuropathogenesis and lethality of VSV-infected Ifit2−/− mice, even at a low virus dose, prompted us to examine viral spread along its route from the nasal cavity into the CNS (Figure 3A). After intranasal administration, VSV infects the nasal epithelia including olfactory sensor neurons, which project to the outer layer of the olfactory bulbs (OB) [23]. This represents the entry step into the CNS, which we examined by immunostaining of OB sections. In wt mice, VSV P protein was detected exclusively within the glomeruli of the OB at 2 d.p.i. (Figure 3B, upper right panel and [1]), whereas in IFNAR−/− mice, VSV antigen had spread into deeper layers of the OB (Figure 3B, lower left panel). In Ifit2−/− mice OB, viral antigen was restricted to the glomeruli, as seen in wt mice (Figure 3B, lower right panel). This similar pattern of viral antigen expression between wt and Ifit2−/− mice was reflected in the equivalent levels of viral RNA in OB at 2 d.p.i. (Figure 3C). In contrast, ∼10 times more VSV RNA was present in OB of IFNAR−/− mice (Figure 3C, right panel, p<0.05). A comparison of the infectious viral burden between wt and Ifit2−/− mice in the OB confirmed these findings: at 2 d.p.i., ∼106 pfu/g of VSV was present in both wt and Ifit2−/− mice (Figure 3D, p = 1.0). However, later in the course of infection, by day 6, viral OB titers in Ifit2−/− mice were not significantly changed, whereas in wt mice average titers of infectious VSV as well as viral RNA levels had decreased by ∼10-fold (Figure 3C and D, both p<0.05). These results suggest that VSV initially enters and replicates with similar efficiency in both wt and Ifit2−/− OB before spreading into the rest of the brain.
Fig. 3. Ifit2 does not inhibit VSV entry and replication in olfactory bulbs. 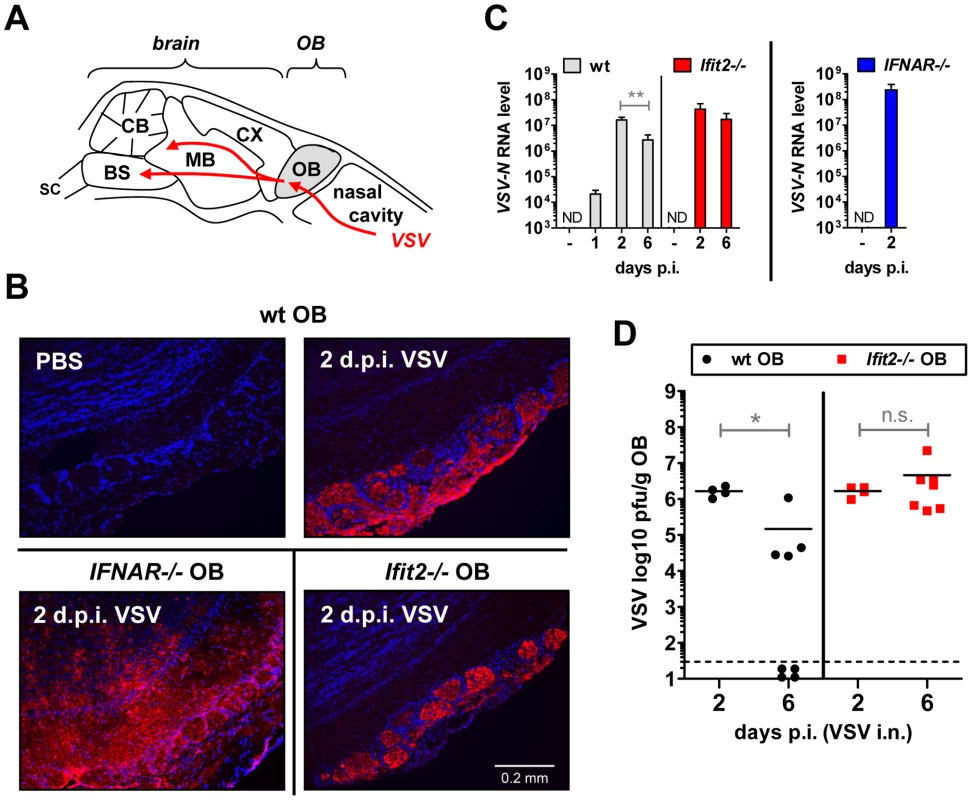
A, schematic entry route of VSV into the central nervous system of wt mice after intranasal infection, and VSV spread within brain, as reported in the literature. OB, olfactory bulbs; CX, cortex; MB, midbrain; CB, cerebellum; BS, brain stem; SC, spinal cord. B, VSV P protein in OB of VSV-infected wt, Ifit2−/− and IFNAR−/− mice at 2 d.p.i., detected by immunohistofluorescence. C, VSV RNA levels in OB of uninfected or VSV-infected wt, Ifit2−/− and IFNAR−/− mice at 1, 2 or 6 d.p.i., plotted as mean+SD on log scale; ND, none detected. D, infectious VSV titers in wt and Ifit2−/− OB at 2 and 6 d.p.i.; plotted as pfu/g with mean on log scale; dashed line depicts threshold of detection. In C and D, n = 4–8 mice per infected group accumulated from three independent experiments; in B, n = 2 mice from two independent experiments. All infections were 4×102 pfu of VSV administered intranasally. Asterisks indicate statistical significance: ** p = 0.006, * p<0.05; n.s.: not significant. Ifit2 suppresses replication of VSV in the brain after intranasal infection
The efficiency of VSV replication in the brain, excluding the OB, was examined by quantifying infectious VSV as well as viral RNA. Early after infection, at 2 d.p.i., virus titers in brains were low (∼104 to 105 pfu/g) and roughly equivalent in wt and Ifit2−/− mice (Figure 4A, p>0.25). Similarly, viral RNA levels at the same time were low and comparable between wt and Ifit2−/− (Figure 4B, p>0.25). However, at the same time, levels of VSV RNA (380-fold, p<0.05) were much higher in the brains of IFNAR−/− mice (Figure 4B, right panel). Later in the course of infection (6 d.p.i.), brains of wt mice accumulated only ∼5-fold more infectious VSV, with occasional clearance of the virus. In contrast, we detected markedly higher VSV titers in the brains of Ifit2−/− mice (∼350-fold higher compared to wt mice, p = 0.0009), reaching ∼108 pfu/g (Figure 4A); the high virus load likely caused the pronounced lethality. Differences in viral RNA levels in brains of wt and Ifit2−/− mice at 6 d.p.i. correlated well with levels of infectious VSV (Figure 4B). To determine whether Ifit2 selectively restricts replication of VSV in particular regions of the brain, we measured viral RNA levels in cortex, midbrain, cerebellum and brain stem at 6 d.p.i. In wt mice, VSV RNA was present prominently in the cortex, midbrain and brainstem, but not in the cerebellum (Figure 4C), which is consistent with published results [24]. However, in Ifit2−/− mice, viral RNA was 200-fold or more (p<0.05) abundant in all regions of the brain examined, including the cerebellum. The increase of VSV replication in Ifit2−/− brains was not due to a broadened cell tropism of the virus; immunostaining for viral P protein showed exclusive localization to neurons and not other cell types, such as astrocytes (Figure 4D). From the above observations, we conclude that after intranasal infection by VSV, Ifit2 protects mice from neuropathogenesis by suppressing replication or spread of the virus in brain neurons.
Fig. 4. Ifit2 suppresses VSV replication in the brain after intranasal infection. 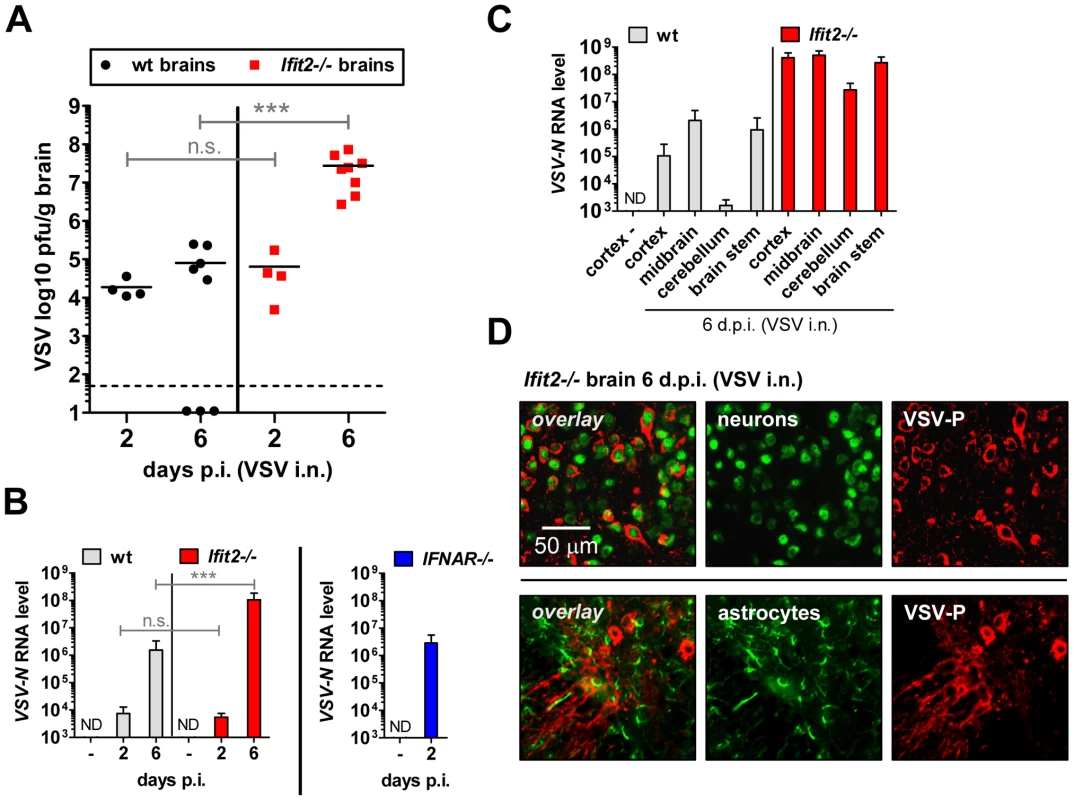
A, infectious VSV titers in wt and Ifit2−/− brains at 2 and 6 days after intranasal infection, plotted as pfu/g with mean on log scale; dashed line depicts threshold of detection. B, VSV RNA levels in brains of uninfected or VSV-infected wt, Ifit2−/− and IFNAR−/− mice at 2 or 6 d.p.i., plotted as mean+SD on log scale. C, VSV RNA levels in different regions of the brains of uninfected or VSV-infected wt and Ifit2−/− mice at 6 d.p.i., plotted as mean+SD on log scale. D, VSV P protein in midbrain neurons of Ifit2−/− mice at 6 d.p.i.; detection by immunohistofluorescence-labeling of VSV-P (red) and neuron (NeuN) or astrocyte (GFAP) markers (green); in A and B: n = 4–8 mice per infected group accumulated from three independent experiments; in C: n = 4 mice per infected group; in D: n = 2 mice per infected group; all infections in A–D were intranasal with 4×102 pfu of VSV. ND, none detected. Brains in A and B were separated from OBs assayed in Figure 3D and 3C, respectively. Asterisks indicate statistical significance: *** p≤0.0009; n.s.: not significant. Ifit2 and Ifit1 are induced in VSV-infected regions of OB and brain
The protective effect of type I IFN signaling and in particular, Ifit2, against VSV neuropathogenesis prompted us to confirm its expression in OB and brain of wt mice, and whether it was induced in a type I IFN-dependent manner. In wt OB, Ifit2, Ifit1, and IFN-β mRNA was induced strongly by 2 d.p.i., and Ifit2 and Ifit1 RNA remained abundant until day 6 d.p.i. (Figure 5A). The induction of these genes was dependent on type I IFN receptor in OB as well as in brain (Figure 5B and 5E, and data not shown). Furthermore, expression of Ifit2 mRNA in wt OB coincided with the presence of detectable levels of the encoded Ifit2 protein ( = P54) at 2 d.p.i. and 6 d.p.i., as seen by immunohistochemistry (Figure 5C, and data not shown). Ifit2 protein staining was observed in VSV-infected cells within OB glomeruli as well as in surrounding and distant viral antigen-free cells, consistent with a remote IFN-dependent induction of Ifit2 expression (Figure 5C, arrowheads in magnified images of right panel). Ifit1 and IFN-β mRNAs were induced as strongly in OB of Ifit2−/− as in wt mice, which correlated well with similar abundance of VSV RNA in wt and Ifit2−/− OB (Figure 5A compared to Figure 3C). In brains, at 6 d.p.i., in contrast to OB, induction of Ifit1 and IFN-β mRNAs was considerably stronger in Ifit2−/− mice compared to wt mice (Figure 5D, 5-fold and 27-fold, respectively, both p<0.005). The enhanced gene induction in VSV-infected Ifit2−/− mice was not restricted to specific regions of the brain (Figure S2). Enhanced cellular gene expression also was observed for several virus-induced cytokine and chemokine genes, as measured by quantitative RT-PCR (Figure S3A). Gene expression profiling of brain tissue at day 6 d.p.i., using microarray analysis, revealed that many other genes, including ISGs, were also more strongly induced (Table S1). These results demonstrated that enhanced virus replication in the brains of Ifit2−/− mice led to enhanced type I IFN, other cytokines and ISG induction, which nevertheless failed to restrict VSV replication in the absence of Ifit2.
Fig. 5. Ifit2 and Ifit1 are induced in VSV-infected regions of OB and brain. 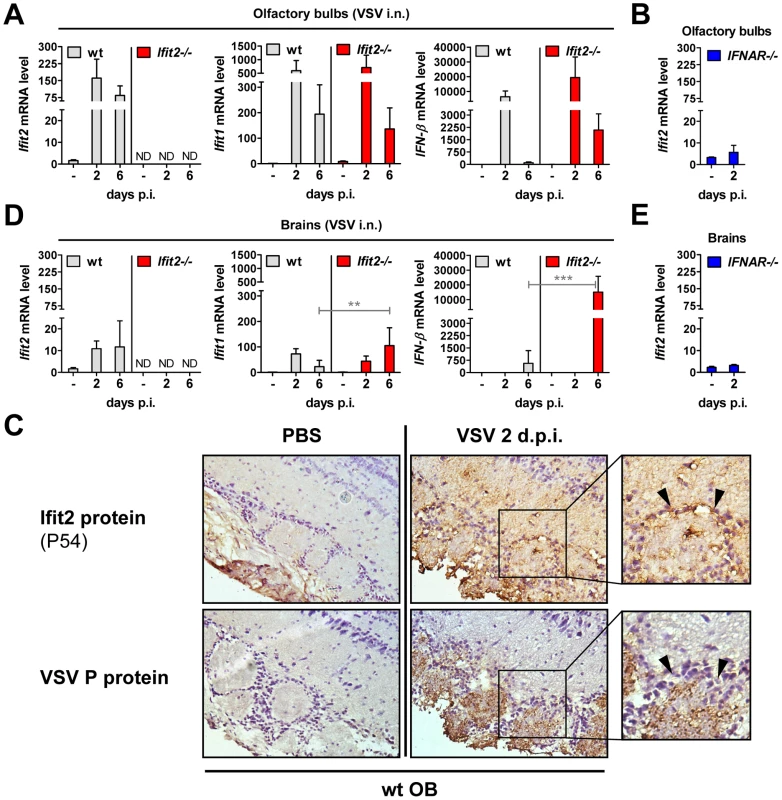
A/B, D/E, Ifit2, Ifit1 and IFN-β mRNA levels in OB (A, B) and separated brains (D, E) of uninfected or intranasally VSV-infected wt, Ifit2−/− and IFNAR−/− mice at 2 or 6 d.p.i., plotted as mean+SD. The same OB and brains were also assayed in Figure 3C and 4B for VSV RNA levels. In A/B/D/E: n = 4–8 mice per infected group accumulated from three independent experiments; ND, none detected. C, Ifit2 ( = P54) protein in wt OB sections, uninfected or 2 d.p.i., with parallel detection of VSV P protein in adjacent sections, detected by immunohistochemistry; arrowheads indicate Ifit2-positive, VSV-negative cells surrounding the glomeruli; n = 2 mice. All infections were intranasal with 4×102 pfu of VSV. Asterisks indicate statistical significance: ** p<0.005, *** p<0.0005; n.s.: not significant. Wt mice are as susceptible as Ifit2−/− mice to intracranial VSV infection
Our results from intranasal VSV infection indicated that Ifit2 induction in the brain was mediated by type I IFN that was, in all likelihood, produced by infected cells in the OB (Figure 5A). Virus replication and resultant IFN induction at 2 d.p.i. were similar in the OBs of wt and Ifit2−/− mice (Figs. 3C, 3D and 5A); presumably, the newly produced IFN diffused into the rest of the brain and induced local Ifit2 expression in the wt mouse brains, prior to the arrival of the infectious virus. If this were the case, one would anticipate that direct infection of the brain, without prior action of IFN produced in infected OB, would minimize the difference between the phenotypes of wt and Ifit2−/− mice. To test this idea, we injected a very low dose (10 pfu) of VSV intracranially. As hypothesized, wt and Ifit2−/− mice were now equally susceptible; almost all mice died by 3 d.p.i. even at this low dose (Figure 6A) and there were equally high virus titers and viral RNA levels in the brains of mice of both genotypes (Figure 6B and 6C). Concomitant with virus replication, there was similar induction of Ifit1 and IFN-β (Figure 6C) and other cytokines and chemokines (Figure S3B). These results indicate that in the absence of prior induction of Ifit2 by IFN, brain neurons are highly susceptible to VSV infection.
Fig. 6. Wt mice are as susceptible as Ifit2−/− mice to intracranial VSV infection. 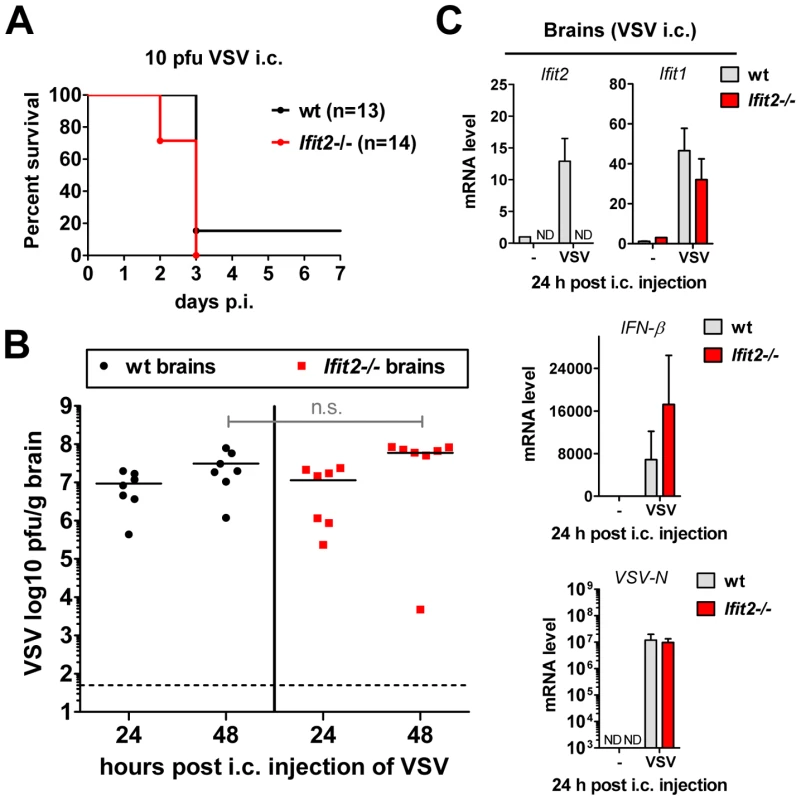
A, survival of wt and Ifit2−/− mice after intracranial injection of 10 pfu of VSV; cumulative data from three independent experiments. B, infectious VSV titers in wt and Ifit2−/− brains at 24 and 48 hours after intracranial injection of 10 pfu of VSV; plotted as pfu/g with mean on log scale; dashed line depicts threshold of detection; n = 7 mice per infected group from two independent experiments; n.s.: not significant. C, Ifit2, Ifit1, IFN-β and VSV-N RNA levels in brains of intracranially VSV-infected or PBS-injected wt and Ifit2−/− mice at 24 hours p.i., plotted as mean+SD, VSV RNA levels plotted on log scale; n = 3 mice per infected group; ND, none detected. Unlike the brain, other organs of Ifit2−/− mice are not more susceptible to intranasal VSV infection
IFNAR−/− mice succumbed within two days after VSV infection without accumulating very high VSV RNA levels in the brain (Figure 4B). These mice did not develop CNS-related signs of disease, but showed severe lethargy before death, suggesting that death was due to efficient replication of the virus in peripheral organs, due to the absence of an otherwise effective type I IFN-mediated antiviral protection of the same organs in wt mice. To test this, we assessed the kinetics of VSV accumulation in brains, livers and lungs of wt, IFNAR−/− and Ifit2−/− mice (Figure 7). At 2 d.p.i., VSV titers were very high in the liver of IFNAR−/− mice, reaching 109 pfu/g (Figure 7A). In contrast, no or little infectious virus was detected in the liver of wt mice at 2 or 6 d.p.i., indicating efficient IFN-dependent suppression of VSV replication; intriguingly, this was also observed in Ifit2−/− mice, demonstrating that Ifit2 did not mediate the anti-VSV effects of type I IFN in the liver. In lungs, which directly received a part of the virus inoculum from intranasal inhalation of VSV, the virus also replicated efficiently in IFNAR−/− mice, reaching 108 pfu/g before death (Figure 7B). In comparison, lungs of wt and Ifit2−/− mice exhibited much lower levels of VSV at 2 and 4 d.p.i. (3,000 to 10,000-fold lower for wt and Ifit2−/− compared to IFNAR−/− mice, all p<0.05). By days 5 and 6 d.p.i., the virus was cleared from the lungs of a subset of wt and Ifit2−/− mice. In contrast, in brains from the same animals, 10 to 100-fold higher average titers (p<0.05) of VSV accumulated in Ifit2−/− compared to wt mice at all time points between 2 and 6 d.p.i. (Figure 7C). As expected, in wt mice, both Ifit1 and Ifit2 were induced not only in brains (Figure 5D), but also in livers (Figure 7D) and lungs (Figure 7E); IFN-β was also induced in lungs, but not livers. Ifit1, Ifit2 and IFN-β mRNAs were also induced in the brains of EMCV-infected wt mice (Figure S3C). These findings demonstrate an unexpected brain-restricted and virus-restricted function of Ifit2 in the context of the type I IFN-mediated antiviral response to VSV infection. They also indicate that in Ifit2−/− mice, other ISGs, which presumably protect the peripheral organs of VSV-infected wt mice, are either not induced in neurons or insufficient to protect them.
Fig. 7. Unlike the brain, other organs of Ifit2−/− mice are not more susceptible to intranasal VSV infection. 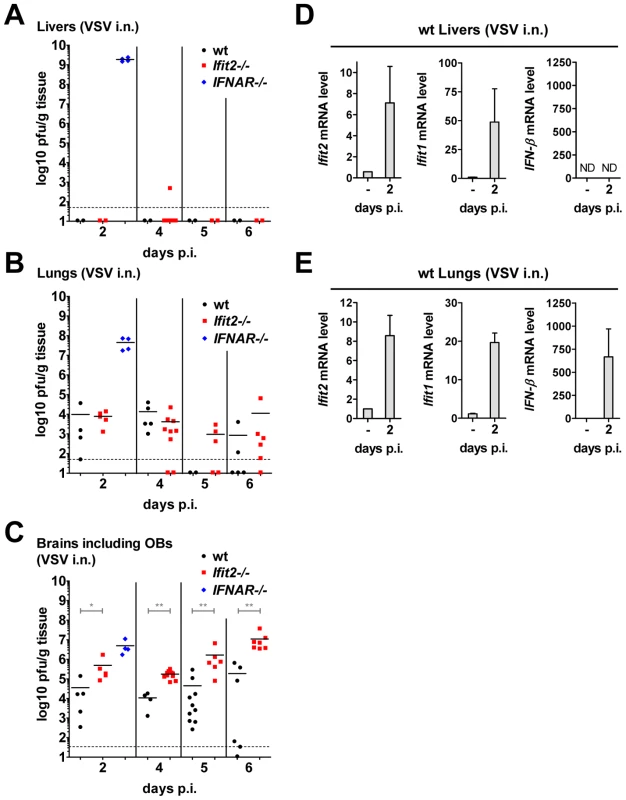
A–C, infectious VSV titers in organs of wt, Ifit2−/− or IFNAR−/− mice (n = 4–10 mice per group accumulated from three independent experiments) at 2, 4, 5 and 6 days after intranasal infection; livers (A), lungs (B) and brains (C, incl. OB) of the same mice were assayed and plotted as pfu/g with mean; not all available livers were titered. Dashed line depicts threshold of detection. D/E, Ifit2, Ifit1, IFN-β mRNA levels in livers (D) and lungs (E) of uninfected or VSV-infected wt mice at 2 d.p.i., plotted as mean+SD; n = 4 mice per infected group; ND, none detected. All infections were intranasal with 4×102 pfu of VSV. Asterisks indicate statistical significance: * p<0.05, ** p<0.005. Discussion
IFNs are defined by their antiviral activities. They inhibit the replication of many, if not all, viruses mostly by direct inhibition of replication in the infected cells but also by promoting the ability of immune cells to recognize and eliminate the virus-infected cells [25]. The direct effects are mediated by ISGs, which number in the hundreds, and different ISGs are thought to have more potent antiviral activities toward different families of viruses [13]. However, in most cases, it is not known which ISG inhibits the replication of a given virus; the rare exception is the Mx-mediated inhibition of influenza viruses, the underlying effect which allowed for the discovery of IFNs [26]. The task of connecting a specific IFN-induced protein to a specific antiviral action is compounded by the fact that often several IFN-induced proteins act in concert to inhibit the same virus at different stages of its life cycle. Moreover, a specific IFN-induced protein may be more relevant for inhibiting a virus in one specific cell-type than another. Recent systematic investigation of the specific antiviral effects of different ISGs has started providing significant insight into this problem [14]. Such findings are complemented by the analyses of the spectra of the antiviral effects of a specific ISG or a family of ISGs [27]. We have undertaken an investigation of the Ifit family of mouse ISGs. The corresponding human proteins are known to have antiviral activities against human papillomavirus (HPV) and hepatitis C virus (HCV), neither of which replicate in mouse cells. The anti-HPV activity of human IFIT1 ( = P56) has been attributed to its ability to bind HPV E1 protein and to inhibit its helicase activity, which is essential for HPV DNA replication [28], [29]. The antiviral effect on HCV, on the other hand, is manifested at the level of inhibiting viral protein synthesis as a consequence of the ability of IFIT1 to bind the translation initiation factor eIF3 and inhibit its various actions in translation initiation [30]. It has been reported recently that the IFIT1 protein can form a complex and bind to RNAs with triphosphorylated 5′ ends, presumably providing another means to inhibit specific viruses that produce such RNAs [18].
The Ifit genes are clustered at a single locus in both human and mouse. In the latter species, two alleles of Ifit3 genes are flanked on two sides by one allele of Ifit2 and one allele of Ifit1 [15]. To identify their physiological functions, we have separately deleted the entire coding regions of Ifit1 or Ifit2 genes. The Ifit1−/− mice exhibited an interesting phenotype in allowing the replication of and resultant pathogenesis by a WNV mutant, which failed to replicate in wt mice [20]. Because this mutant is defective in 2′-O methylation of the cap structure of viral mRNAs, its rescue in the Ifit1−/− mouse indicates that this antiviral protein recognizes the 5′ ends of mRNAs, a conclusion that is consistent with the observation that, in vitro, it can bind to RNAs having specific structures at the 5′ ends [18]. It remains to be seen whether the proposed property of Ifit proteins to recognize 5′ ends of RNA is connected in any way to their ability to inhibit the functions of eIF3 [16], which participates in several steps of translation initiation taking place at or near the 5′ ends of mRNAs.
Replication of VSV is highly sensitive to the antiviral activity of IFNs, and VSV is widely used to determine the specific activities of IFN preparations quantitatively [21]. In spite of this strong connection, it is unclear how IFN inhibits VSV replication. An early report indicated that viral primary transcription is inhibited by IFN, but it is not known which IFN-induced protein mediates this inhibition [31]. The observed sensitivity of VSV replication in vitro is reflected in vivo. IFNAR−/− mice are extremely susceptible to VSV infection; they rapidly die within 2 days after infection and the virus replicates to very high titers in many organs of the infected mice. The extreme sensitivity of IFNAR−/− mice to VSV infection suggests that type I IFN provides the majority, if not all, of the protective innate immune defense. Eventually, protection may be facilitated by immune cell-mediated antiviral actions, but this is a slow process that does not appear to function before 6–10 days post-infection [32], [33]. Thus, it is likely that one or more ISGs directly inhibit VSV replication in vivo. In this context, it has been reported that mice lacking PKR, a well-studied ISG, display higher susceptibility to VSV pathogenesis [34]. However, detailed investigation of the underlying mechanism revealed that PKR did not execute IFN's antiviral action; rather, it was required for efficient induction of IFN-α/β in the infected mice [35]. In vivo VSV-infection induces IFN synthesis in many cell types, using either the cytoplasmic RIG-I pathway or the endosomal TLR7 pathway [4], [36]; however, it is unclear how PKR aids this process.
Our results show that Ifit2−/− mice are highly susceptible to intranasal VSV infection and the effect is gene dosage-dependent: Ifit2+/− mice had an intermediate susceptibility phenotype. Infected Ifit2−/− mice displayed symptoms of severe neuropathogenesis late after VSV infection accompanied by efficient replication of the virus in many regions of the brain. However, virus replication was restricted to neurons and did not spread to other types of cells in the brain, such as astrocytes. Our results are consistent with the hypothesis that prior, IFN-induced, Ifit2 expression in the brain restricts VSV replication. Supporting genetic evidence for the requirement of IFN action is provided by the high susceptibility of the IFNAR−/− mice, which possess the functional Ifit2 gene but Ifit2 is not induced by VSV infection because these mice cannot respond to type I IFN. Additional evidence comes from a previous study using brain-specific IFNAR−/− mice, which displayed a pattern of susceptibility to intranasal VSV infection similar to that of our Ifit2−/− mice [1]. In our experimental system, the source of the IFN production was most likely the OBs; abundant IFN was induced there early (2 d.p.i.) after infection (Figure 5A) causing the induction of Ifit2 in wt mice (Figure 5C). Ifit2 was also induced at this time in the rest of the brain, without any induction of IFN mRNA (Figure 5D) suggesting that the source of IFN was the OB. In accord with the well-established concept of IFN action, pre-induction of Ifit2 in neurons, before the onset of infection, was essential for the antiviral effect. In comparison, induction of IFN and Ifit2 that was concomitant with VSV infection failed to have an appreciable antiviral effect, as manifested by robust virus replication at directly infected sites, such as the OBs of wt mice infected intranasally (Figure 3D) or the brain of wt mice infected intracranially (Figure 6B). High mortality of the infected mice correlated with high virus titers in the brains of intranasally infected Ifit2−/− mice or intracranially infected wt and Ifit2−/− mice. In the intranasally infected Ifit2−/− mice, death was not preceded by widespread apoptosis in the brain (Figure S4). However, as expected with high viral loads, IFN and other cytokines and chemokines were strongly induced (Figures 5D, S2 and S3A); consequently, many ISGs, except Ifit2, were also induced (Table S1).
Pre-induced Ifit2 prevents efficient VSV replication in the brain, most probably by blocking one or more essential step of the viral life cycle including viral entry, uncoating, primary transcription, viral protein synthesis, RNA replication, virion assembly or egress. It also might block trans-synaptic spread of the virus, although unlike another rhabdovirus, rabies virus, VSV is not known to depend on transit from neuron to neuron. In this context, it is important to note the observations made by Iannacone et al. [37] using a footpad VSV infection model. They concluded that type I IFN, produced by infected macrophages and plasmacytoid dendritic cells in infected mice, blocked infection of peripheral neurons resulting in lowered infection of the CNS and prevention of neuropathogenesis. It is worth noting that in our studies, the absence of Ifit2 did not affect IFN induction by VSV (Figures 5A and 6C). Further investigation of the biochemical mechanism behind the observed in vivo effect of Ifit2−/− is hampered by the absence of a suitable cell culture model of the phenomenon. For example, Ifit2 was not required for mediating the anti-VSV effect of IFN in mouse embryonic fibroblasts (Figure S5), in primary fetal neurons or in Ifit2-ablated neuroblastoma cells (data not shown), results that are not surprising given the strong tissue-specificity of Ifit2 action observed in vivo (Figure 7). Specific RNA-binding properties of Ifit proteins have been recently reported [18]. Following this lead, we examined the RNA-binding properties of recombinant murine Ifit1 and Ifit2 using VSV leader RNA as the probe in an electrophoretic mobility shift assay: Ifit1 bound RNA with a 5′-ppp end but not with a 5′-OH end; however, Ifit2 bound neither (Figure S6). To obtain meaningful leads, future investigation of this kind may require using brain extracts from infected mice to detect protein-viral RNA complexes that may contain Ifit2 along with adult neuron-specific proteins.
Our results revealed several layers of specificity of IFN action, some of which were not anticipated. First, compared to Ifit2−/− mice, Ifit1−/− mice were much less susceptible to intranasal VSV infection; this was true for both low and high doses of virus. This finding was surprising in view of a recent report on VSV susceptibility of Ifit1−/− mice [18] and the observation that Ifit1, but not Ifit2, could bind VSV leader RNA in vitro (Figure S6). The above results demonstrate that different Ifit proteins have non-redundant functions in vivo. The second layer of specificity was directed toward the nature of the infecting virus. Although both VSV and EMCV caused neuroinvasive disease, induced IFN-β, Ifit1 and Ifit2 in the brain and type I IFN action was required for protection against both viruses, Ifit2 was critical only for protection against VSV; the absence of either Ifit1 or Ifit2 did not exacerbate susceptibility to EMCV. The third layer of specificity was revealed by the organ-specific action of Ifit2. In the complete absence of type I IFN action in the IFNAR−/− mice, intranasally infected VSV replicated vigorously not only in brains, but also in livers and lungs (Figure 7A–C). In contrast, in Ifit2−/− mice, efficient VSV replication was restricted to the brain suggesting that Ifit2 does not act as an anti-VSV ISG in the liver or the lung because its absence did not impact virus titers, even though Ifit2 was induced in these organs of infected wt mice (Figure 7D and 7E). The efficient VSV replication in livers and lungs of IFNAR−/− mice, but not wt and Ifit2−/− mice, indicates that other ISGs must have anti-VSV effects in those organs. Further investigation is needed to determine the basis of neuronal specificity of Ifit2 action and the identities of other ISGs that inhibit VSV replication in other organs.
Materials and Methods
Ethics statement
All animal experiments were performed in strict accordance with all provisions of the Animal Welfare Act, the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals, and the PHS Policy on Humane Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. The protocol was approved by the Cleveland Clinic Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC), PHS Assurance number A3047-01. All experimental manipulations or intranasal instillations of mice were performed under anesthesia induced by pentobarbital sodium or isofluorane, respectively, and all efforts were made to minimize suffering.
Mice
All mice used were of C57BL/6 background and of both sexes; Ifit2−/− mice were custom-generated by Taconic Farms, Inc. by flanking exons 2 and 3 of Ifit2, encompassing the complete protein-encoding region, with frt sites in C57BL/6 embryonic stem (ES) cells, and deleting the flanked region by transfection of Flp recombinase. ES cell clones were injected into BL/6 blastocysts, and heterozygous offspring mice were crossed to homozygosity. Ifit1−/− mice were generated from C57BL/6 ES cells lacking the whole coding region of Ifit1 (20); ES cells were obtained from the NIH Knockout mouse project (KOMP, allele Ifit1tm1(KOMP)Vlcg). The same ES cell line was independently used to generate mice in another study [18]. IFNAR−/− mice (lacking Ifnar1) were a gift of Murali-Krishna Kaja (Emory University, Atlanta, GA). Congenic wild-type mice were obtained from Taconic Farms.
Viruses and infections
Vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV) Indiana was a gift from Amiya K. Banerjee, Lerner Research Institute, Cleveland, Ohio. For intranasal infections, between 4×102 and 4×106 pfu of VSV in 35 µl of endotoxin-free PBS were inhaled by isofluorane-anesthetized 8–12 week-old mice, with PBS-only as control. For intracranial infections, 10 pfu of VSV in 30 µl of endotoxin-free PBS were injected into the brains of 6–7 week-old mice, with PBS-only as control. Thereafter, mice were monitored daily (twice daily after i.c. injection) for weight loss and symptoms of disease. Encephalomyocarditis virus (EMCV) K strain was a gift from Robert H. Silverman, Lerner Research Institute, Cleveland, Ohio. For intraperitoneal infections, between 25 and 5×102 pfu of EMCV in 500 µl of PBS were injected into the peritoneal cavity of mice. Mice were monitored daily for weight loss and symptoms of disease.
Immunohistochemistry and TUNEL assay
Mice were anesthetized with pentobarbital (150 mg/kg) and blood was removed from organs by cardiac perfusion with 10 ml of PBS, followed by perfusion with 10 ml of 4% paraformaldehyde/PBS for fixation. Brains were placed in 4% paraformaldehyde overnight for complete fixation, submerged in 30% sucrose/PBS overnight for cryoprotection, and frozen in O.C.T. compound (Sakura Finetek USA, Torrance, CA, USA). 10 µm sagittal sections were cut at −20°C in a Leica CM1900 cryostat, mounted on coated slides (Superfrost Plus, Fisherbrand, Fisher Scientific); membranes were permeabilized by 0.2% Triton X-100/PBS treatment for 15 min. For immunohistochemistry, the Envision+ DAB kit (Dako, Carpinteria, CA) was used with anti-mouse Ifit2/P54 [38] or anti-VSV-P protein (a gift from Amiya K. Banerjee, Lerner Research Institute, Cleveland, Ohio) as primary antibodies. For immunohistofluorescence, anti-VSV-P or anti-NeuN (Chemicon Intl./Millipore, Billerica, MA) or anti-GFAP (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO) were used; labeled brain sections were stained with AlexaFluor-594 secondary antibody (Invitrogen/Molecular Probes, Carlsbad, CA). For detection of apoptotic cells in brain sections, the DeadEnd fluorometric TUNEL system (Promega) was used according to manufacturer's instructions. All objects were then mounted with VectaShield (with DAPI, Vector Labs, Burlingame, CA), and examined with a Leica DRM fluorescence microscope.
Quantitative RT-PCR and microarray analysis
Mice were anesthetized with pentobarbital (150 mg/kg) and blood was removed from organs after cardiac perfusion with 10 ml of PBS. Brains were separated into olfactory bulbs and the remainder of the brain, snap-frozen in liquid nitrogen (as well as livers and lungs) and RNA was extracted using TRIzol reagent (Invitrogen). DNase I treatment (DNAfree, Applied Biosystems/Ambion) and reverse transcription with random hexamers (ImProm-II, Promega) were performed according to manufacturer's instructions. 0.5 ng of RNA was used in 384 well-format realtime PCRs in a Roche LightCycler 480 II using Applied Biosystem's SYBR Green PCR core reagents. PCR primers for murine ISG49/Ifit3, ISG54/Ifit2, ISG56/Ifit1 and 18S rRNA have been published previously [17]; primers targeting murine Ifnb1 [5′-CTTCTCCGTCATCTCCATAGGG-3′ [39], with the alternative reverse primer: 5′-CACAGCCCTCTCCATCAACT-3′], VSV N RNA [40] or EMCV 3D polymerase genomic region [41] were described previously. Primers for Ccl2, Il1b, Il6, Tnf, Il12b and Nos2 have been described previously [42], [43]. Average expression levels, relative to 18S rRNA and normalized by use of calibrator samples, were graphed with Prism 5.02 software. For analysis of different regions of the brain, brains without OB of perfused mice were separated into cortex, cerebellum, brain stem and remaining “midbrain”, and tissue was submerged into RNAlater stabilizing reagent (Qiagen) overnight and frozen. RNA was then extracted via TRIzol and further processed and assayed by realtime RT-PCR as described above. For microarray analysis, TRIzol-extracted and DNase I-treated RNA was additionally purified using spin columns (RNeasy Mini kit, Qiagen) before subjection to mRNA expression microarray analysis via Illumina Mouse Ref-8 V2 beadchip and GenomeStudio software V2010.2 (Illumina, Inc.); RNA hybridization to chips was performed by the Lerner Research Institute Genomics Core at the Cleveland Clinic. Microarray raw data were deposited in the NCBI Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO), accession number GSE33678.
Virus quantification
For quantification of infectious VSV in organs, mice were anesthetized with pentobarbital (150 mg/kg) and blood was removed from organs by cardiac perfusion with 10 ml of PBS. Organs were snap-frozen in liquid nitrogen, weighed, pestle/tube-homogenized (Kimble/Kontes) in 1 ml of PBS per brain or peripheral organ or 0.1 ml per pair of olfactory bulbs, and virus was titered in 10-fold serial dilutions on Vero cells by plaque assay. Results are expressed as plaque-forming units (pfu) per gram of tissue. For quantification of infectious VSV yields in MEF, cells (−/+IFN-β pretreatment as indicated) were infected with VSV inoculum for 1 h, and after another 12 h, cells were freeze/thawed, and cleared supernatants of lysates were assayed for VSV by plaque assay on Vero cells.
Immunoblot
Primary murine embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) were stimulated with 1000 U/ml murine IFN-β (PBL, Inc., Piscataway, NJ) for 16 h and lysed in lysis buffer [50 mM Tris pH 7.6, 150 mM NaCl, 0.5% Triton X-100, 1 mM sodium orthovanadate, 10 mM sodium fluoride, 5 mM sodium pyrophosphate, 10 mM β-glycerophosphate and 1× complete EDTA-free protease inhibitor (Roche, Indianapolis, IN)]. 10 µg of whole cell extract were separated via 10% SDS-PAGE, transferred to PVDF membranes, blocked with 5% dry milk in Tris-buffered saline/0.05% Tween-20 overnight and labeled with anti-Ifit3/P49, anti-Ifit2/P54 or anti-Ifit1/P56 polyclonal rabbit sera [17], [38].
Electrophoretic mobility shift assay
Single-stranded VSV leader RNA (nucleotides 1–18) was T7 polymerase-transcribed in presence of [α-32P]-CTP, yielding radiolabeled 5′-triphosphorylated (ppp-) RNA, followed by alkaline phosphatase treatment for generation of 5′-hydroxyl (HO-) RNA. ppp-RNA or HO-RNA were added to bacterially expressed and purified 6xHis-tagged Ifit1 or Ifit2 protein in reaction buffer (50 mM Tris pH 8.0, 100 mM NaCl, 1 mM EDTA, 2 mM DTT, 0.05% Triton X-100, 10% glycerol) and incubated for 30 min on ice. Reaction products were separated by 6% native polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis followed by exposure to film.
Statistical analysis
Statistical significance of mouse survival differences was calculated by Mantel-Cox log rank test. To assess significance of differences in gene expressions or virus titers, the two-tailed Mann-Whitney test was used. All calculations were performed using GraphPad Prism 5.02 software.
Gene accession numbers
Previously published transcript sequences in the NCBI Entrez Nucleotide database: Ifit2, NM_008332; Ifit1, NM_008331; Ifit3, NM_010501; Ifnb1, NM_010510; Ifnar1, NM_010508.
Supporting Information
Zdroje
1. DetjeCNMeyerTSchmidtHKreuzDRoseJK 2009 Local type I IFN receptor signaling protects against virus spread within the central nervous system. J Immunol 182 2297 2304
2. MullerUSteinhoffUReisLFHemmiSPavlovicJ 1994 Functional role of type I and type II interferons in antiviral defense. Science 264 1918 1921
3. HwangSYHertzogPJHollandKASumarsonoSHTymmsMJ 1995 A null mutation in the gene encoding a type I interferon receptor component eliminates antiproliferative and antiviral responses to interferons alpha and beta and alters macrophage responses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 92 11284 11288
4. KatoHTakeuchiOSatoSYoneyamaMYamamotoM 2006 Differential roles of MDA5 and RIG-I helicases in the recognition of RNA viruses. Nature 441 101 105
5. SatoMSuemoriHHataNAsagiriMOgasawaraK 2000 Distinct and essential roles of transcription factors IRF-3 and IRF-7 in response to viruses for IFN-alpha/beta gene induction. Immunity 13 539 548
6. KumarHKawaiTKatoHSatoSTakahashiK 2006 Essential role of IPS-1 in innate immune responses against RNA viruses. J Exp Med 203 1795 1803
7. LoewendorfABenedictCA 2010 Modulation of host innate and adaptive immune defenses by cytomegalovirus: timing is everything. J Intern Med 267 483 501
8. AltfeldMFaddaLFrletaDBhardwajN 2011 DCs and NK cells: critical effectors in the immune response to HIV-1. Nat Rev Immunol 11 176 186
9. BenderSJWeissSR 2010 Pathogenesis of murine coronavirus in the central nervous system. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol 5 336 354
10. DurbinJEHackenmillerRSimonMCLevyDE 1996 Targeted disruption of the mouse Stat1 gene results in compromised innate immunity to viral disease. Cell 84 443 450
11. MerazMAWhiteJMSheehanKCBachEARodigSJ 1996 Targeted disruption of the Stat1 gene in mice reveals unexpected physiologic specificity in the JAK-STAT signaling pathway. Cell 84 431 442
12. DerSDZhouAWilliamsBRSilvermanRH 1998 Identification of genes differentially regulated by interferon alpha, beta, or gamma using oligonucleotide arrays. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95 15623 15628
13. SadlerAJWilliamsBR 2008 Interferon-inducible antiviral effectors. Nat Rev Immunol 8 559 568
14. SchogginsJWWilsonSJPanisMMurphyMYJonesCT 2011 A diverse range of gene products are effectors of the type I interferon antiviral response. Nature 472 481 485
15. FensterlVSenGC 2011 The ISG56/IFIT1 gene family. J Interferon Cytokine Res 31 71 78
16. TerenziFPalSSenGC 2005 Induction and mode of action of the viral stress-inducible murine proteins, P56 and P54. Virology 340 116 124
17. FensterlVWhiteCLYamashitaMSenGC 2008 Novel characteristics of the function and induction of murine p56 family proteins. J Virol 82 11045 11053
18. PichlmairALassnigCEberleCAGornaMWBaumannCL 2011 IFIT1 is an antiviral protein that recognizes 5′-triphosphate RNA. Nat Immunol 12 624 630
19. WacherCMullerMHoferMJGettsDRZabarasR 2007 Coordinated regulation and widespread cellular expression of interferon-stimulated genes (ISG) ISG-49, ISG-54, and ISG-56 in the central nervous system after infection with distinct viruses. J Virol 81 860 871
20. DaffisSSzretterKJSchriewerJLiJYounS 2010 2′-O methylation of the viral mRNA cap evades host restriction by IFIT family members. Nature 468 452 456
21. RubinsteinSFamillettiPCPestkaS 1981 Convenient assay for interferons. J Virol 37 755 758
22. LetchworthGJRodriguezLLDel C. BarreraJ 1999 Vesicular stomatitis. Vet J 157 239 260
23. PlakhovIVArlundEEAokiCReissCS 1995 The earliest events in vesicular stomatitis virus infection of the murine olfactory neuroepithelium and entry of the central nervous system. Virology 209 257 262
24. HuneycuttBSPlakhovIVShustermanZBartidoSMHuangA 1994 Distribution of vesicular stomatitis virus proteins in the brains of BALB/c mice following intranasal inoculation: an immunohistochemical analysis. Brain Res 635 81 95
25. BironCA 2001 Interferons alpha and beta as immune regulators–a new look. Immunity 14 661 664
26. HallerOKochsG 2011 Human MxA protein: an interferon-induced dynamin-like GTPase with broad antiviral activity. J Interferon Cytokine Res 31 79 87
27. LenschowDJLaiCFrias-StaheliNGiannakopoulosNVLutzA 2007 IFN-stimulated gene 15 functions as a critical antiviral molecule against influenza, herpes, and Sindbis viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104 1371 1376
28. SaikiaPFensterlVSenGC 2010 The inhibitory action of P56 on select functions of E1 mediates interferon's effect on human papillomavirus DNA replication. J Virol 84 13036 13039
29. TerenziFSaikiaPSenGC 2008 Interferon-inducible protein, P56, inhibits HPV DNA replication by binding to the viral protein E1. EMBO J 27 3311 3321
30. WangCPflugheberJSumpterRJrSodoraDLHuiD 2003 Alpha interferon induces distinct translational control programs to suppress hepatitis C virus RNA replication. J Virol 77 3898 3912
31. BelkowskiLSSenGC 1987 Inhibition of vesicular stomatitis viral mRNA synthesis by interferons. J Virol 61 653 660
32. ChristianAYBarnaMBiZReissCS 1996 Host immune response to vesicular stomatitis virus infection of the central nervous system in C57BL/6 mice. Viral Immunol 9 195 205
33. BiZBarnaMKomatsuTReissCS 1995 Vesicular stomatitis virus infection of the central nervous system activates both innate and acquired immunity. J Virol 69 6466 6472
34. BalachandranSRobertsPCBrownLETruongHPattnaikAK 2000 Essential role for the dsRNA-dependent protein kinase PKR in innate immunity to viral infection. Immunity 13 129 141
35. SchulzOPichlmairARehwinkelJRogersNCScheunerD 2010 Protein kinase R contributes to immunity against specific viruses by regulating interferon mRNA integrity. Cell Host Microbe 7 354 361
36. LeeHKLundJMRamanathanBMizushimaNIwasakiA 2007 Autophagy-dependent viral recognition by plasmacytoid dendritic cells. Science 315 1398 1401
37. IannaconeMMosemanEATontiEBosurgiLJuntT 2010 Subcapsular sinus macrophages prevent CNS invasion on peripheral infection with a neurotropic virus. Nature 465 1079 1083
38. TerenziFWhiteCPalSWilliamsBRSenGC 2007 Tissue-specific and inducer-specific differential induction of ISG56 and ISG54 in mice. J Virol 81 8656 8665
39. DaffisSSamuelMAKellerBCGaleMJrDiamondMS 2007 Cell-specific IRF-3 responses protect against West Nile virus infection by interferon-dependent and -independent mechanisms. PLoS Pathog 3 e106
40. SimonIDPublicoverJRoseJK 2007 Replication and propagation of attenuated vesicular stomatitis virus vectors in vivo: vector spread correlates with induction of immune responses and persistence of genomic RNA. J Virol 81 2078 2082
41. VanderhallenHKoenenF 1997 Rapid diagnosis of encephalomyocarditis virus infections in pigs using a reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction. J Virol Methods 66 83 89
42. KapilPAtkinsonRRamakrishnaCCuaDJBergmannCC 2009 Interleukin-12 (IL-12), but not IL-23, deficiency ameliorates viral encephalitis without affecting viral control. J Virol 83 5978 5986
43. PharesTWMarquesCPStohlmanSAHintonDRBergmannCC 2011 Factors supporting intrathecal humoral responses following viral encephalomyelitis. J Virol 85 2589 2598
Štítky
Hygiena a epidemiologie Infekční lékařství Laboratoř
Článek vyšel v časopisePLOS Pathogens
Nejčtenější tento týden
2012 Číslo 5- Jak souvisí postcovidový syndrom s poškozením mozku?
- Měli bychom postcovidový syndrom léčit antidepresivy?
- Farmakovigilanční studie perorálních antivirotik indikovaných v léčbě COVID-19
- 10 bodů k očkování proti COVID-19: stanovisko České společnosti alergologie a klinické imunologie ČLS JEP
-
Všechny články tohoto čísla
- Five Questions on Prion Diseases
- Type III Secretion in : Injectisome or Not?
- In Vitro and In Vivo Isolation and Characterization of Duvenhage Virus
- CD200 Receptor Controls Sex-Specific TLR7 Responses to Viral Infection
- From Molecular Genetics to Phylodynamics: Evolutionary Relevance of Mutation Rates Across Viruses
- Evolution of an Eurasian Avian-like Influenza Virus in Naïve and Vaccinated Pigs
- Vitamin D Inhibits Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 and Infection in Macrophages through the Induction of Autophagy
- Influence of Microbiota on Viral Infections
- Hydrophobins—Unique Fungal Proteins
- Interferon-Induced Protects Mice from Lethal VSV Neuropathogenesis
- A New Evolutionary Model for Hepatitis C Virus Chronic Infection
- The [Het-s] Prion, an Amyloid Fold as a Cell Death Activation Trigger
- PLOS Pathogens
- Archiv čísel
- Aktuální číslo
- Informace o časopisu
Nejčtenější v tomto čísle- Type III Secretion in : Injectisome or Not?
- Hydrophobins—Unique Fungal Proteins
- In Vitro and In Vivo Isolation and Characterization of Duvenhage Virus
- The [Het-s] Prion, an Amyloid Fold as a Cell Death Activation Trigger
Kurzy
Zvyšte si kvalifikaci online z pohodlí domova
Současné možnosti léčby obezity
nový kurzAutoři: MUDr. Martin Hrubý
Všechny kurzyPřihlášení#ADS_BOTTOM_SCRIPTS#Zapomenuté hesloZadejte e-mailovou adresu, se kterou jste vytvářel(a) účet, budou Vám na ni zaslány informace k nastavení nového hesla.
- Vzdělávání



