-
Články
Top novinky
Reklama- Vzdělávání
- Časopisy
Top články
Nové číslo
- Témata
Top novinky
Reklama- Videa
- Podcasty
Nové podcasty
Reklama- Kariéra
Doporučené pozice
Reklama- Praxe
Top novinky
ReklamaTobacco Company Efforts to Influence the Food and Drug Administration-Commissioned Institute of Medicine Report An Analysis of Documents Released through Litigation
Background:
Spurred by the creation of potential modified risk tobacco products, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) commissioned the Institute of Medicine (IOM) to assess the science base for tobacco “harm reduction,” leading to the 2001 IOM report Clearing the Smoke. The objective of this study was to determine how the tobacco industry organized to try to influence the IOM committee that prepared the report.Methods and Findings:
We analyzed previously secret tobacco industry documents in the University of California, San Francisco Legacy Tobacco Documents Library, and IOM public access files. (A limitation of this method includes the fact that the tobacco companies have withheld some possibly relevant documents.) Tobacco companies considered the IOM report to have high-stakes regulatory implications. They developed and implemented strategies with consulting and legal firms to access the IOM proceedings. When the IOM study staff invited the companies to provide information on exposure and disease markers, clinical trial design for safety and efficacy, and implications for initiation and cessation, tobacco company lawyers, consultants, and in-house regulatory staff shaped presentations from company scientists. Although the available evidence does not permit drawing cause-and-effect conclusions, and the IOM may have come to the same conclusions without the influence of the tobacco industry, the companies were pleased with the final report, particularly the recommendations for a tiered claims system (with separate tiers for exposure and risk, which they believed would ease the process of qualifying for a claim) and license to sell products comparable to existing conventional cigarettes (“substantial equivalence”) without prior regulatory approval. Some principles from the IOM report, including elements of the substantial equivalence recommendation, appear in the 2009 Family Smoking Prevention and Tobacco Control Act.Conclusions:
Tobacco companies strategically interacted with the IOM to win several favored scientific and regulatory recommendations.
Please see later in the article for the Editors' Summary
Published in the journal: . PLoS Med 10(5): e32767. doi:10.1371/journal.pmed.1001450
Category: Research Article
doi: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1001450Summary
Background:
Spurred by the creation of potential modified risk tobacco products, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) commissioned the Institute of Medicine (IOM) to assess the science base for tobacco “harm reduction,” leading to the 2001 IOM report Clearing the Smoke. The objective of this study was to determine how the tobacco industry organized to try to influence the IOM committee that prepared the report.Methods and Findings:
We analyzed previously secret tobacco industry documents in the University of California, San Francisco Legacy Tobacco Documents Library, and IOM public access files. (A limitation of this method includes the fact that the tobacco companies have withheld some possibly relevant documents.) Tobacco companies considered the IOM report to have high-stakes regulatory implications. They developed and implemented strategies with consulting and legal firms to access the IOM proceedings. When the IOM study staff invited the companies to provide information on exposure and disease markers, clinical trial design for safety and efficacy, and implications for initiation and cessation, tobacco company lawyers, consultants, and in-house regulatory staff shaped presentations from company scientists. Although the available evidence does not permit drawing cause-and-effect conclusions, and the IOM may have come to the same conclusions without the influence of the tobacco industry, the companies were pleased with the final report, particularly the recommendations for a tiered claims system (with separate tiers for exposure and risk, which they believed would ease the process of qualifying for a claim) and license to sell products comparable to existing conventional cigarettes (“substantial equivalence”) without prior regulatory approval. Some principles from the IOM report, including elements of the substantial equivalence recommendation, appear in the 2009 Family Smoking Prevention and Tobacco Control Act.Conclusions:
Tobacco companies strategically interacted with the IOM to win several favored scientific and regulatory recommendations.
Please see later in the article for the Editors' SummaryIntroduction
Because cigarettes and other tobacco products deliver a wide range of toxic chemicals along with nicotine, the addictive drug in tobacco, the cigarette companies mounted efforts dating back to at least the 1950s [1] to develop a “safe” cigarette. These efforts waned in the 1980s as a result of technical failures combined with industry lawyers' concerns that success in creating a “safer” cigarette would create liabilities for other “less safe” brands.
One idea that attracted wide public and scientific acceptance beginning in the 1960s was the idea that cigarettes that produced lower tar and nicotine yields (based on machine-smoking tests) would be less toxic. This assumption led to their widespread use but ultimately provided no benefit to the public health [2],[3],[4],[5]. Health authorities later learned that machine smoking tests translate poorly to how smokers actually smoke and the dose of toxins they receive. Low-yield cigarettes performed better in machine tests because cigarette companies modified the filters with ventilation holes to dilute the smoke with air, lowering the machine-measured yields. In contrast, smokers covered these holes with their fingers or lips and inhaled the unvented smoke or smoked more intensively, a process that the industry called “smoker compensation,” to maintain or even increase nicotine delivery and exposure to smoke toxins. For many years, low-yield cigarettes were perceived as “safer” products, and the tobacco industry used direct marketing claims and later, implied claims, to encourage people to initiate smoking or delay quitting [1],[2],[4].
The issue of new tobacco products that were designed to deliver nicotine accompanied with lower levels of other toxins reemerged as a public health issue in 1988 when R.J. Reynolds Tobacco (RJR) introduced its new “Premier” product, which worked by delivering a heated aerosol of nicotine rather than by burning tobacco [6].
The question of how to assess the relative harm of different tobacco products gained further currency in 1996, when the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) asserted jurisdiction over tobacco products. To inform its regulatory efforts in 1999 the FDA commissioned the Institute of Medicine (IOM) to formulate scientific methods and standards to assess tobacco products that could potentially reduce exposure to toxicants. The IOM is part of the National Academies (which consists of the National Academy of Sciences, The National Academy of Engineering, the Institute of Medicine, and the National Research Council), elite self-selected professional organizations whose purpose is to provide scholarly advice to policy makers. Originally chartered by Congress in 1863 as the National Academy of Science, the National Academies describe their role as “produc[ing] groundbreaking reports that have helped shape sound policies, inform public opinion, and advance the pursuit of science, engineering, and medicine” [7]. The National Academies describe their reports as influential because, “Over many decades, the National Academy of Sciences (NAS), National Academy of Engineering (NAE), Institute of Medicine (IOM), and National Research Council have earned a solid reputation as the nation's premier source of independent, expert advice on scientific, engineering, and medical issues” [8]. Thus, while not a regulatory body per se, the IOM's advice carries much weight with policy makers and regulatory bodies, including the FDA.
FDA's charge to the IOM was to consider four questions about harm-reduction tobacco products in general [3]:
- 1
Does use of the product decrease exposure to the harmful substances in tobacco?
- 2
Is this decreased exposure associated with decreased harm to health?
- 3
Are there surrogate indicators of this effect on health that could be measured in a time frame sufficient for product evaluation?
- 4
What are the public health implications of tobacco harm-reduction products?
In response, the IOM formed its Committee to Assess the Science Base for Tobacco Harm Reduction, composed of 12 experts in fields ranging from toxicology to epidemiology from inside and outside tobacco control [3], supported by IOM staff, nonvoting liaisons from other IOM boards, and nonvoting consultants. The committee gathered information from scientists and advocates representing public health and academia and compiled a draft report, which was submitted to peer reviewers selected by the study staff before being released to the public.
The final report, Clearing the Smoke: Assessing the Science Base for Tobacco Harm Reduction [3] was issued in 2001 and set the tone for future development and regulation of tobacco products, particularly products claiming to be less dangerous than conventional cigarettes. The report, which included a set of Regulatory Principles (Box 1) in addition to a review of the science base, generated controversy within the tobacco control community because some believed the recommendations did not adequately protect public health [9].
Box 1. IOM Clearing the Smoke Regulatory Principles [3]
-
Manufacturers of tobacco products, whether conventional or modified, should be required to obtain quantitative analytical data on the ingredients of each of their products and to disclose such information to the regulatory agency.
-
All tobacco products should be assessed for yields of nicotine and other tobacco toxicants according to a method that reflects actual circumstances of human consumption; when necessary to support claims, human exposure to various tobacco smoke constituents should be assessed using appropriate biomarkers. Accurate information regarding yield range and human exposure should be communicated to consumers in terms that are understandable and not misleading.
-
Manufacturers of all PREPs should be required to conduct appropriate toxicological testing in preclinical laboratory and animal models as well as appropriate clinical testing in humans to support the health-related claims associated with each product and to disclose the results of such testing to the regulatory agency.
-
Manufacturers should be permitted to market tobacco related products with exposure-reduction or risk-reduction claims only after prior agency approval based on scientific evidence (a) that the product substantially reduces exposure to one or more tobacco toxicants and (b) if a risk reduction claim is made, that the product can reasonably be expected to reduce the risk of one or more specific diseases or other adverse health effects, as compared with whatever benchmark product the agency requires to be stated in the labeling. The “substantial reduction” in exposure should be sufficiently large that measurable reduction in morbidity and/or mortality (in subsequent clinical or epidemiological studies) would be anticipated, as judged by independent scientific experts.
-
The labeling, advertising, and promotion of all tobacco related products with exposure-reduction or risk-reduction claims must be carefully regulated under a “not false or misleading” standard with the burden of proof on the manufacturer, not the government. The agency should have the authority and resources to conduct its own surveys of consumer perceptions relating to these claims.
-
The regulatory agency should be empowered to require manufacturers of all products marketed with claims of reduced risk of tobacco-related disease to conduct post-marketing surveillance and epidemiological studies as necessary to determine the short-term behavioral and long-term health consequences of using their products and to permit continuing review of the accuracy of their claims.
-
In the absence of any claim of reduced exposure or reduced risk, manufacturers of tobacco products should be permitted to market new products or modify existing products without prior approval of the regulatory agency after informing the agency of the composition of the product and certifying that the product could not reasonably be expected to increase the risk of cancer, heart disease, pulmonary disease, adverse reproductive effects or other adverse health effects, compared to similar conventional tobacco products, as judged on the basis of the most current toxicological and epidemiological information.
-
All added ingredients in tobacco products, including those already on the market, should be reported to the agency and subject to a comprehensive toxicological review.
-
The regulatory agency should be empowered to set performance standards (e.g., maximum levels of contaminants; definitions of terms such as “low tar”) for all tobacco products, whether conventional or modified, or for classes of products.
-
The regulatory agency should have enforcement powers commensurate with its mission, including power to issue subpoenas.
-
Exposure reduction and risk reduction claims for drugs that are supported by appropriate scientific and clinical evidence should be allowed by the FDA.
The tobacco companies have a long history of working to shape scientific discussions and agendas [1],[4],[5], including producing research results designed to “create controversy” about the dangers of smoking and secondhand smoke [1],[10],[11],[12] and influencing scientific standards of how research is conducted or interpreted [13],[14],[15]. The cigarette companies used this experience as the basis for their efforts to influence the IOM. They worked with consultants and lawyers to gain access and involvement with the IOM process and to contribute scientific information to the IOM committee that was largely produced by industry insiders and consultants and carefully vetted by lawyers. While available evidence does not permit cause-and-effect conclusions, and the IOM may have come to the same conclusions without the influence of the tobacco industry, in the end, the companies were pleased with the report and sought ways to use it to advance their business and regulatory agendas.
Methods
Between May 2011 and February 2012, we searched the UCSF Legacy Tobacco Documents Library (LTDL, http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu) for documents outlining how the tobacco companies tried to influence the IOM committee. We used standard snowball techniques [16], starting with terms including “Institute of Medicine,” “IOM committee,” “Clearing the Smoke,” and “Assessing the Science Base for Tobacco Harm Reduction.” We identified key persons, concepts, and events and viewed documents with adjacent Bates numbers.
Initial keyword and snowball searches yielded several thousand documents pertaining to the IOM project. Searches were narrowed to documents from specific years, namely 1999 and beyond. For documents that were exact duplicates, only one copy was included in the analysis. If the same document appeared with minor changes (i.e., handwritten notes or tracked changes in a word editing program), both versions were included.
The tobacco industry documents were analyzed for relevance, novel information, and internal consistency. Documents that were irrelevant (i.e., misclassified with metadata attributed to the wrong year, author, or topic) were excluded from the analysis. Documents that did not provide novel information (i.e., providing information that was already corroborated by other documents) were considered in the analysis for internal consistency (see below) but may not have been quoted in the final paper and do not appear in the reference list.
The remaining tobacco industry documents (about 1,000 documents) were analyzed for internal consistency. This was conducted by placing the documents in chronological order and quoting or summarizing each document to create an extensive timeline of events. The timeline was verified for content and internal consistency by authors CET and SAG. In cases where content of documents was ambiguous, additional searches for related documents were run to provide context and clarify meaning; if no supporting documents could be identified, the document was excluded from the analysis. No major conflicts arose within the documents or between the documents and known events.
In addition, documents were obtained via a public records access request to the NAS for documents associated with the IOM Committee to Assess the Science Base for Tobacco Harm Reduction. The Public Access Records Office (PARO) provided a master list of 268 documents meeting these criteria. We requested all 268 files; PARO provided 16 hard-copy documents and 64 digital files. The remaining items were papers, books, government documents, and media reports that were publicly available and not explicitly generated for or by the IOM committee. The 80 files we obtained contained all known written interactions between the tobacco companies and IOM. The timeline of events developed from the tobacco industry documents and supplemented and confirmed by the IOM documents naturally coalesced into thematically united sections; that is, documents from a particular period tended to address the same topic. Examples include: information gathering about IOM, lawyers editing presentations of industry scientists, and executives discussing the report after release. The final paper was written based on these thematically united segments.
Results
Phillip Morris Engages the IOM Committee
In 1999, when the FDA commissioned the IOM to prepare the report, the tobacco industry and FDA were engaged in a protracted legal contest over authority to regulate tobacco products ([3], p. 127–128; [17]). Despite their outward resistance, tobacco companies were internally acknowledging and preparing for regulation [17],[18]. A 1999 internal presentation at Philip Morris (PM) titled “Potential for Worldwide Product Regulation” described not only the IOM committee but also tracked the progress of several other tobacco regulatory efforts in Canada, the European Union, and the World Health Organization (WHO). This presentation identified harm reduction as a “critical regulatory issue” and suggested an approach by which, “in situations where significant questions remain, such as identifying important smoke components, obtaining meaningful exposure information and developing measures of harm reduction, it would be desirable to work with regulators to jointly address and answer these questions [emphasis added]” [18].
In October 1999, the IOM announced the creation and goals of the committee [19]. PM recognized an opportunity to influence the scientific evaluation and regulation of reduced-harm products. Through its Worldwide Regulatory Affairs (WRA) and Worldwide Scientific Affairs (WSA) divisions, PM began working with lawyers and consultants to collect information and plan ways to become involved. Established in 1993, WRA was a central resource to develop strategies and provide resources for PM Corporate Affairs staff to address smoking restrictions globally. WRA guided WSA to “develop scientific resources and contributions to the scientific debate” [20], initially on secondhand smoke and later on a wider range of scientific domains, including reduced-harm products.
In mid-November 1999 Arnold & Porter (A&P), a law firm representing PM, wrote Mark Berlind, Senior Assistant General Counsel of WRA, and Rick Solana and Bruce Davies, respectively Vice President and Manager of WSA, describing a telephone conversation A&P had had with Dr. Kathleen Stratton, the IOM study director. A&P reported that Stratton explained the committee structure, funding source (the FDA), staff, membership, and schedule [21]. A&P also gathered information about the degree to which industry representatives could be involved at every stage; A&P's memo to PM indicated that although IOM committees typically did not permit industry participation given potential conflict of interest situations, Stratton had anticipated that industry (both pharmaceutical and tobacco companies) would be encouraged to present information to the committee, either through testimony or submissions (including reference to relevant documents). A&P also indicated that, because peer reviewers on the draft committee are not subject to conflict of interest rules, it would be possible for members of industry to serve as peer reviewers. (The IOM used a lawyer from the Covington & Burling law firm, which represents the tobacco industry, as a peer reviewer.)
PM hired Multinational Business Services, Inc. (MBS), a lobbying and consulting firm founded by former Reagan White House Office of Management and Budget deputy administrator Jim Tozzi that specializes in regulatory issues and has a long history of working for the tobacco industry [13],[14] to provide options for PM to “enter the IOM process” [22]. To overcome the IOM's closely guarded decision-making process, MBS suggested two ways PM could approach the IOM:
-
Option 1: Efforts could be made to work with a nationally renown [sic] scientific organization to establish a panel which could undertake a course of inquiry parallel to that of the IOM committee. This new panel would work in concert with Philip Morris scientists in conducting its research. At a suitable time, the panel, in the course of its interactions with the IOM committee, could bring Philip Morris officials into the dialogue.
Option 2: Philip Morris and MBS could jointly approach the IOM Committee through our established contacts. [22]
PM's Solana began coordinating efforts to contact the IOM committee along with other members of WSA who would become key players: Richard Carchman, vice president of WSA; Wolf Reininghaus, head of Institut für Biologische Forschung (INBIFO, PM's biological research lab in Germany [23], renamed Philip Morris Research Laboratories GmbH in 2002 [24]); PM principal scientist George Patskan; PM scientific affairs manager Bruce Davies; and WSA group director Edward Sanders. Their initial plan was to critique the committee's “limited” range of expertise [25],[26],[27],[28],[29]. Davies recommended additional or alternate committee members, all of whom were affiliated with the tobacco industry: Bill (William) Rickert, who had been chair and editor of the 1996 and 1998 reports of Canada's Expert Committees on Cigarette Modifications and Cigarette Toxicity Reduction [30],[31] and owner of Labstat Corporation, which within the next year would sign a two-year US$950,000 contract with PM “to provide services relating to the testing and chemical analysis of tobacco, cigarettes, and cigarette smoke for constituents of interest” [32]; PM's Richard Carchman; and Oak Ridge National Laboratory's Roger Jenkins, a scientist who had a history of producing research that supported the industry's positions, particularly on secondhand smoke [33],[34].
Shortly after WSA's discussion of the IOM committee, MBS's Tozzi wrote PM that “the next step would be to raise the possibility of … data sharing with the IOM Committee” [35]. Using the information and recommendations from A&P and MBS, Solana and his WSA colleagues addressed a letter to the IOM committee on behalf of PM:
-
You have posted invitation for public comment on the committee for “Assessing the Science Base for Tobacco Harm Reduction” …
…[I]t is not clear that you have scientists with an in depth knowledge of cigarettes and cigarette smoke. I understand that industry scientists are not allowed to be on the committee. We are, therefore, available to you to share our knowledge, experience and expertise in product design and product performance, biological and chemical evaluation of cigarettes, and capability of different tests for use in toxicological evaluation. Attached is a reference list of some of our applicable publications and presentations. [36]
Solana's letter also followed MBS's advice [22] to cite the example of Canada's Expert Committees on Cigarette Modifications (1996) and Cigarette Toxicity Reduction (1998), which were Canada's attempts to establish priorities in tobacco harm reduction [36]. The Canadian committees had a strong tobacco industry presence; they included industry scientists J. Donald Bethizy (RJR), Patrick Dunn (Imperial Tobacco), and David Townsend (RJR) on the 1996 10-member committee; Bethizy and Hoffman again as well as Richard Carchman (PM) and Stewart Massey (British American Tobacco, Imperial Tobacco) on the 1998 11-member committee; non-disclosed industry consultant Roger Jenkins; and chair Bill Rickert. The Canadian reports included pro-industry minority opinions in the main report, immediately underneath the majority conclusions [30],[31]. These minority opinions from the industry representatives challenged widely accepted facts, including what Rickert described in his preface as committee chair as “major disagreement” about whether nicotine was addictive [30].
MBS and A&P attended the first IOM committee meeting (open to the public) in December 1999 and provided PM with detailed reports on the charge to the committee, the questions asked by the committee members, and their reactions to the answers. A&P also prepared detailed personal reports on all the committee members that included publications and sponsors [37],[38], which PM supplemented with resumes [39],[40],[41],[42],[43],[44],[45],[46],[47],[48],[49],[50],[51],[52],[53],[54],[55],[56],[57],[58],[59].
Shortly after the first committee meeting, IOM study director Stratton responded to Solana's request stating:
-
I am currently working with some of the committee members to develop a strategy for engaging the pharmaceutical and tobacco industries in order to broaden the input to and the scientific base of our committee's deliberations. I am happy to know of your personal interest in our work and will take the liberty of contacting you directly once this working group plans its next steps. [emphasis added by PM] [60].
Solana forwarded the email to several PM scientists who would play key roles in the company's upcoming interactions with the IOM: Bruce Davies, Hans-Juergen Haussman, George Patskan, Wolf Reininghaus, Edward Sanders, and Roger Walk, as well as Jack Nelson, PM senior VP of Operations [61]. Though only Solana communicated directly with Stratton, he shared their communications with many PM scientists, executives, and lawyers who worked together to collectively formulate his responses.
IOM Invites Tobacco Companies to Share Information
In January 2000, Stratton sent identical letters to the scientific division leaders at PM [62], RJR [63], and Brown & Williamson (B&W) [64] inviting participation in an IOM meeting. The invitation advised that an IOM working group wished to “explore how you can best provide meaningful scientific information for the committee's consideration” and asked the companies for scientific articles and company documents made public under the Master Settlement Agreement or by congressional action. The letter further noted, “…The invitation to meet with the working group and solicitation of input is not an endorsement of the products of your company or positions you might take regarding the health effects of tobacco or nicotine” [62],[63],[64].
Solana responded to Stratton's request for materials and references [65] and sent several copies of Analytical Determination of Nicotine and Related Compounds and Their Metabolites [66], a 772-page monograph on nicotine analysis PM commissioned, sponsored, and primarily written by industry scientists, consultants, and grantees [67]. Though the monograph stated that PM paid some of the cost of the book and that some contributors were employees, affiliates, or consultants of tobacco companies, it did not disclose that PM scientists, lawyers, and management at PM and RJR actively revised chapters or that PM agreed to purchase a minimum of 500 copies to make production of the monograph profitable for the publisher [67].
PM selected six speakers to present to the IOM: Richard A. Carchman (VP of WSA), Hans-Juergen Haussman (Executive Manager, Bioresearch at INBIFO), George Patskan (Director of Product Integrity), Richard Solana, and Principal Scientists from both PM and PM International [68]. Their presentations were carefully vetted by the “Core Team” of WSA and INBIFO research scientists [69] as well as in-house lawyers (Senior Vice President and Associate General Counsel and Vice President of Litigation and Associate General Counsel) [70]. Another PM lawyer, Kevin Osborne, helped edit the presentations [71],[72],[73]. A list of scheduled planning sessions for the presentations also indicated that a 4-hour session would involve a review by PM Vice President of Operations Jack Nelson [69]. Thus, while the primary work was conducted by the science personnel, they operated under the guidance of PM's legal, regulatory, and executive arms.
Sanders presented research by British statistician Peter Lee on low tar cigarettes and argued that “direct epidemiological evidence suggest[s] some reduction in risk for lung cancer” while “indirect epidemiological evidence appears to suggest the reverse” and that this “require[s] further research” [74]. Lee, a longtime tobacco industry consultant, had written articles denying or minimizing the health effects of cigarette smoking on behalf of British American Tobacco, PM, the Tobacco Institute, and others ([4], p. 86; [1],[10],[75],[76],[77],[78]), and in this case wrote an article concluding that “the switch to low tar/filter cigarettes has led to a substantial reduction in risk of lung cancer” [79]. This statement directly contradicted the scientific consensus, developed over several decades, that low-yield products failed to reduce population-wide risks of smoking [2].
When the IOM working group asked PM for a copy of Lee's study, which PM stated had been submitted to British Medical Journal [80], PM did not comply. Sanders informed the PM staff member fulfilling the IOM data request that, “The reason for [the refusal] is, of course, that if the article is rejected, it may be changed considerably” [81]. BMJ subsequently rejected the manuscript, and it was eventually published [82],[83] in 2001 in Inhalation Toxicology, a journal whose editor-in-chief [84] was a paid RJR consultant [85],[86],[87],[88],[89],[90], after receiving a positive review by peer reviewer Chris Coggins, Senior VP of Science and Technology at RJR, who declared it a “fine piece of epidemiological research [that] is suitable for publication with very minor changes [emphasis in original]” [91].
Another presentation to the IOM was by PM Principal Scientist Patskan who delivered a presentation about the smoke chemistry and toxicity of electronically heated cigarettes, new devices that claimed to reduce the risk of smoking by heating rather than burning tobacco. Patskan requested that his research colleagues send him results from assays and inhalation studies on a “TPM [total particulate matter] delivery basis” [92]. Previously, in its “Project Mix,” PM used the tactic of normalizing smoke yields by TPM delivery in order to obscure increases in cigarette smoke toxicity that occurred when additives were put in test cigarettes [93].
Like PM, RJR delivered high-priority talking points to the IOM, one of which was that modified products must be as similar to conventional cigarettes as possible, because the “degree of trade-off strongly influences cigarette acceptability” [94]. RJR cited their own data collected from smokers participating in company-run trials of Eclipse, their then-new tobacco-heating “cigarette” that advertised simpler smoke chemistry and reduced biological activity. The data showed that smokers were “unwilling to accept large trade-offs” of the taste, ritual, or performance for a risk reduction, causing RJR to recommend that regulators not require drastic modifications of tobacco products that would make them unattractive to consumers [94].
RJR also presented data showing that Eclipse produced less tar and other target compounds, such as carcinogenic polyaromatic hydrocarbons and tobacco-specific nitrosamines, than conventional low-yield cigarettes according to machine smoking and smoke composition tests [94]. After RJR's presentation to the IOM, the company's public relations department drafted a briefing sheet for media training about Eclipse (also sent to law firm Williams & Connolly to request suggested changes [95]) stating, “We have presented the science behind our claims to … the Institute of Medicine's committee on cigarette risk reduction, and to others in the scientific and public health communities” [96].
PM, RJR, and B&W all recommended similar test batteries for smoke chemistry and toxicology tests (the Ames test, neutral red uptake assay, sister chromatid exchange, chromosome aberration assay, 90-day subchronic inhalation studies in mice, and skin painting tests) as well as similar biomarkers for disease outcomes such as cardiovascular disease, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and cancer [94],[97],[98].
Following the presentations to the IOM working group, PM's Solana circulated an email to WSA [99] reporting on the meeting and expressing pleasure that “there was no animosity, and the working group was sincerely interested in our information and thoughts” [100], and that the committee inquired about the company's research collaborations, capabilities, and agenda as well as their opinion on the IOM's work and a regulatory framework for reduced-harm products. He described the “key messages” conveyed by PM, which included “us[ing] a balanced spectrum of assays for pre-market hazard characterization” such as machine smoking, “a useful tool [that] should use a validated, standard method,” and “confirm[ing] harm reduction determination with after-market epidemiology.” Solana reported that he told the working group that “PM will be glad to provide support to, and receive support from, this IOM committee” [101]. Finally, Solana mentioned that the IOM committee would be sending a list of further questions to be answered by the companies.
IOM Sends Twelve Questions to the Tobacco Companies
Six weeks after the company presentations, the IOM sent 12 questions on tobacco products and testing standards to PM, RJR, B&W, and Lorillard (Table 1) [102],[103],[104],[105]. Their responses were collaborative efforts within each company, with input from scientists, lawyers, and regulatory advisors to create carefully crafted responses [106],[107],[108],[109].
Tab. 1. IOM's Twelve Questions to the Tobacco Companies, Their Responses, and the Conclusions in Clearing the Smoke. 
Unless otherwise indicated, emphasis is the authors'. PM, Philip Morris; RJR, R.J. Reynolds Tobacco. The lawyers' influence is evident in PM's answer to a question about collaboration between industry, academia, and government, which was edited by Kevin Osborne, the in-house lawyer who reviewed PM's presentations to the IOM. The lawyers helped distinguish situations in which PM should openly disclose information to boost its credibility from situations in which such disclosure would reveal weaknesses or problems with the company's position. For example, in response to the IOM question about the “best mechanism to foster collaborative studies between tobacco industry, university, and other scientists” [102], PM wrote, “Philip Morris has already set up an ambitious program directed toward the development of harm-reduced products … [that] would involve Philip Morris support of external scientists through an independent funding mechanism” [110]. Osborne commented, “The ‘funding mechanism’ [the PM External Research Program] isn't independent; rather, the contemplated arrangement allows for the funding of independent research” [110]. The final version submitted to the IOM had no mention of PM's then-planned External Research Program.
In response to the question about criteria for determining harm, PM recommended a tiered testing system that proposed as many as 20 years of surveillance to either confirm or invalidate a reduced harm claim (Figure 1). PM recommended that the validation process be divided between the premarket phase, with standard toxicology tests “to insure that a new product design change does not increase overall smoke chemistry or measured biological activity” [97] (called “acceptability,” referring to a specific level of acceptable harm and not to be confused with “consumer acceptability,” referring to consumer tastes and preferences), and post-market surveillance. The primary assessment of new products would take place largely in the post-market phase, because “due to the need for large numbers of smokers who currently use a product as their brand, it would be best to conduct the study in an after-market environment” [111]. Adopters of products with potential reduced-harms claims would serve as the test population and tobacco companies would benefit from rapid introduction of their products into the market.
Fig. 1. 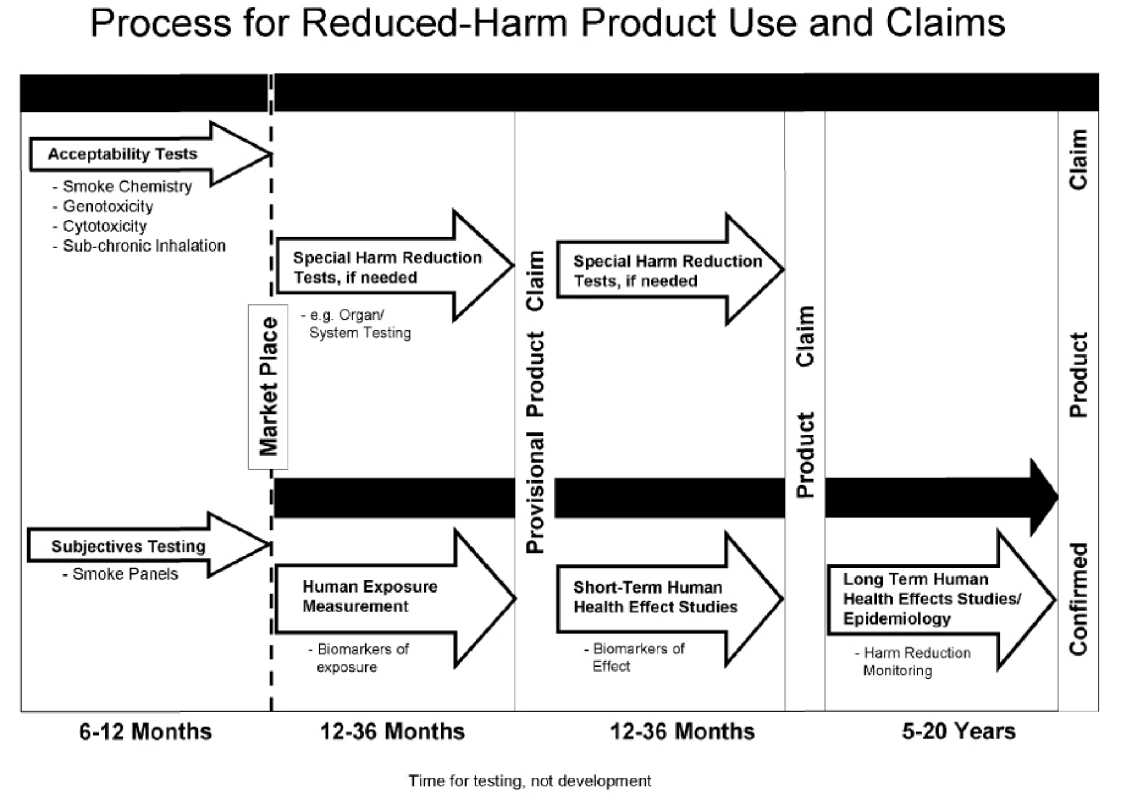
PM proposed timeline for assessment of reduced-harm products <em class="ref">[219]</em>. Although the wording was changed slightly, Regulatory Principle 4 of the IOM report was similar to the tiered testing system PM recommended to the working group. Indeed, an internal draft statement prepared by PM WSA noted that IOM had accepted PM's model in all but name [112]. The WSA scientists proposed this schematic, and after a similar version was published in the IOM report, conducted a post hoc analysis that it would allow PM to make early health claims soon after smoke chemistry, toxicity, and the first round of human biomarker testing, prior to marketing [112],[113], and continue after-market testing among consumers for several years [101].
The IOM took a much firmer stance than the original PM proposal, setting high preliminary testing hurdles. Nevertheless, PM was pleased by the IOM's overall approach and continued to promote this tiered system to other organizations, including the WHO Scientific Advisory Committee on Tobacco Product Regulation later that year [114].
Among members of the academic and public health communities that were invited to present to the committee as independent experts, John Slade, a physician specializing in addiction and tobacco control, specifically tried to counter the influence of the tobacco companies on the IOM. In a presentation about the history of light and filtered cigarettes [115], Slade explained how tobacco companies and PM in particular generated controversy to confuse the public about the dangers of smoking. Since all documents presented to the IOM, including copies of presentations and written submissions, were publicly available, Slade obtained the submissions by the tobacco companies and sent letters to the committee reminding them that tobacco companies had a history of bad behavior and presented a point-by-point rebuttal to the companies' responses to the 12 questions [116],[117],[118]. Slade was also suspicious of RJR's claims for Eclipse and the industry's willing participation in establishing standards for risk reduced products, stating, “All three of the major cigarette manufacturers are eager to have reduced risk products on the market in their own terms, terms which guarantee the continuation of the public health fraud they have perpetuated for decades by promoting poisonous and addictive products to consumers of all ages” [117].
Inviting IOM Committee Members to Apply for Funding from the Philip Morris External Research Program
A few months before the release of the IOM report, PM prepared to launch its new PM External Research Program (PMERP), nominally to fund independent research on harm reduction to aid product development [119],[120]. Solana sent identical letters to nine IOM committee members inviting them to apply for funding. Committee member, pathologist Adi Gazdar, planned to submit a research funding application. Prior to serving on the IOM committee, Gazdar had applied for and been refused money from the industry's Council for Tobacco Research [121],[122],[123],[124],[125],[126],[127],[128],[129],[130],[131],[132]. Kern Wildenthal, president of Gazdar's institution, University of Texas Southwestern at Dallas, prevented him from submitting the application. He described his reservations in a letter to Gazdar:
-
[A]lthough Philip Morris intends to make use of peer review and to exert no control over publications after grants are awarded, they make it clear that peer review is only part of the picture and that the grant program is, in fact, for the benefit of the company and under the company's control.
Specifically, they state that “the purpose” of the program is to support “research that…enables Philip Morris to continue its pursuit of product modification(s) or new product design(s) that might reduce the health risk of smoking.” They also state that after peer review, Philip Morris has “final approval,” and that the company must be provided “assurances” that all studies they fund “serve relevant business needs” of the company. [emphasis original] [133]
Wildenthal was correct to express reservations about PMERP. An independent retrospective analysis of the first round of funding of PMERP concluded that “the ostensible purpose of the programme is to help develop cigarette designs ‘that might reduce the health risk of smoking.’ Internal company documents also indicate that Philip Morris urgently seeks to restore its scientific ‘credibility,’ as part of a ‘new openness’ in relation to the external community” [120]. Gazdar's interest in PMERP nevertheless persisted. In 2003 he served as a member of PMERP's Scientific Advisory Board [134],[135],[136]. He also gave the keynote speech at the 2007 PMERP symposium, which showcased the work of scientists funded by the program [137].
Consistent with their desire to gain greater credibility in the scientific community, PM scientists shared information with or on behalf of committee members Henderson and Hatsukami at least once more after completion of the IOM report. Henderson invited the industry scientists to speak in a symposium she was organizing at a Society of Toxicology national meeting, on the “scientific basis of reducing harm from cigarette smoking” [138]. Hatsukami communicated with PM's Solana and Walk to obtain an overview of the company's research on biomarkers to assess reduced risk and exposure [139].
The IOM Report Is Released
On February 22, 2001, the IOM released Clearing the Smoke: Assessing the Science Base for Tobacco Harm Reduction [3]. As part of the press event accompanying the report's release, Committee Chair Stuart Bondurant stated:
-
The committee … concluded that the only way to ensure that the health claims made about these products are true, that the public is fully and accurately informed, and that the impact on the general population is positive is to use the potential capability of oversight, or regulation. We recommend that—in tandem with new surveillance and research efforts—regulatory principles [Box 1] be adopted to assure that the public is accurately informed about the health effects of new products, to prevent cigarettes with greater toxicity than those sold today from entering the market, and to gather complete information about new products…
We believe that manufacturers should have the necessary incentive to develop and market these products. What I mean by this is that there be a regulatory framework that is not so burdensome that manufacturers are not able to get these products to market but strict enough that they do in fact qualify as harm reduction products. [140]
The report also concluded that harm reduction was feasible despite the fact that there had never been a potential reduced exposure product (PREP) that had been evaluated comprehensively enough to conclude that it actually reduced or would very likely reduce harm compared to conventional tobacco use. IOM recommended a research agenda that included describing the dose–response relationship between tobacco smoke/constituent exposure and health outcomes, surrogate markers of disease, preclinical research (describing but not specifically recommending the test battery proposed by PM, RJR, and B&W), and short - and long-term epidemiology and surveillance [3].
Internal PM emails among scientists, executives, and public relations staff reflected pleasure with the outcome [141],[142],[143],[144]. Ellen Merlo, Senior Vice President of Corporate Affairs, wrote, “If this is it, this is very good. Obviously, we agree and that's why we are working with public health officials and encouraging FDA regulation of the product… Very good positioning for us” [144]. Vice President of Federal Government Affairs John Scruggs agreed, “My initial view is that we should respond to the regulatory principles stated in the report because they appear to track so well with our position [emphasis added]” [145].
Mark Berlind, PM associate general counsel, emailed key company executives, communications staff, corporate affairs, and legal personnel to circulate a policy-oriented draft statement (it is unclear whether this was ever released to the public) reacting to the IOM report's 11 Regulatory Principles, noting that “there does seem to me to be … ways in which we could leverage them in both the FDA and WHO contexts”; both were organizations responsible for potential upcoming regulation [146].
PM gave a copy of the WRA draft statement to A&P to “see if anything in it is troubling as it relate[s] to legal/regulatory issues” [147]. Some copies of the draft statement are concealed behind attorney–client privilege claims [148],[149], but accessible versions permit comparisons. Earlier drafts contained more opinion and editorializing. For example, PM initially wrote that they considered the IOM's Regulatory Principles as an opportunity “in the spirit of continuing, constructive dialogue on these matters and in the hope of bringing diverse stakeholders together to find the common ground” [150], but removed this language from later drafts. Early drafts discussed how the Regulatory Principles could be applied to or whether they already existed in proposals for FDA regulatory legislation, WHO regulation, and the WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control; this discussion was also edited out for unspecified reasons. Finally, when addressing individual Regulatory Principles, PM initially accepted “nearly all” of them but opposed Principle 9, which stated that a regulatory agency should be empowered to set minimum performance standards for all tobacco products. Later drafts show that PM “accepted” all Regulatory Principles, including Principle 9 [150],[151],[152].
WSA began drafting an internal scientific response to support the statement being assembled by the lawyers and WRA. They identified statements and recommendations in the report and especially in the regulatory principles that supported PM's research priorities and positions on scientific issues. One WSA scientist wrote that Regulatory Principle 4 “seems to suggest that provided that the exposure reduction is shown to be large enough, exposure-reduction and risk-reduction claims can be made before clinical and epidemiological data are available [emphasis in original]” [113].
Lawyers also helped identify statements in the report that supported PM's research and business priorities. For example, PM lawyers Kevin Osborne and Paula Desel and A&P lawyer Rob Connelly discussed directions for evaluating the IOM report from scientific and policy standpoints with WSA's Solana [153].
PM's scientists considered Regulatory Principle 7, which said that manufacturers should be allowed to market conventional products (those without reduced exposure or reduced risk claims) without regulatory approval provided that they did not increase disease risk. The WSA's interpretation of the statement was that “We believe that our acceptability evaluations do this [prove that risk does not increase] for any new proposed product design changes” [112], meaning that no changes would occur in the evaluation of conventional tobacco products, despite the well-established evidence of their toxicity. The WSA's review of the IOM report was ultimately merged with the legal/regulatory statement written by the WRA [154], though it is unclear whether the final document was publicly released.
Discussion
The tobacco industry has a history of producing and promoting misleading research to serve its business needs [1],[4],[5],[10],[11],[12],[13],[14],[15]. Consistent with this history, the tobacco companies used their legal and regulatory staff to access the IOM information-sharing process and used this access to deliver specific, carefully formulated messages to serve their business interests. They were satisfied with the results of the IOM report and devised ways to use the report's Regulatory Principles to accomplish their scientific and regulatory goals, some of which have continuing policy implications today.
The tobacco companies individually strategically organized to influence the IOM committee to win their favored scientific and regulatory recommendations. Using the advice of lawyers and consultants, PM initiated contact with the IOM committee by citing the precedent set by Canada's Expert Committees, which included industry scientists and stressed the importance of involving all stakeholders, as a reason why they should be asked to contribute their expertise to the IOM committee. Motivated to gather input from all stakeholders, the IOM committee invited PM and other tobacco companies to share information. This stance positioned the “health establishment” and the “tobacco industry” as two legitimate but polarized positions that needed to be skillfully mediated, a dynamic encouraged by the industry [155].
PM and RJR presentations [94],[97] (obtained from IOM public records) show that the companies denied the evidence that low-yield products harmed public health, stressed that they should be permitted to manufacture harm-reducing products that consumers would accept and buy [156], presented data from industry research which made cigarettes appear safer [93], and tried to secure protection to sell conventional cigarettes without additional restrictions [74],[111]. Limited scientific rationales for these positions were presented or, in the latter two cases, were nonexistent.
In contrast to the presumptions about openness, honesty, ethics, and neutrality, which are expected in scientific and academic discourse, the tobacco companies viewed their interactions with governing and regulatory bodies not as scientific and academic discourse but as an adversarial relationship to defend commercial interests. The presentations of the industry scientists were closely supervised by executives, regulatory specialists (PM's WRA), internal and external lawyers (A&P), and consultants (MBS' Jim Tozzi). (Many of the documents from PM, RJR, and B&W pertaining to the IOM are not accessible because the companies withheld them claiming attorney–client privilege [157],[158],[159],[160],[161],[162],[163],[164],[165],[166],[167],[168],[169],[170],[171],[172],[173],[174],[175],[176],[177],[178],[179],[180],[181],[182],[183],[184],[185],[186],[187],[188],[189],[190],[191],[192],[193]).
The involvement of lawyers in managing the tobacco industry's positions on scientific issues is longstanding, dating back over half a century [1]. In 2006, in response to a case brought by the US Department of Justice against the major cigarette companies [194], their lobbying arm (the Tobacco Institute), and their extramural research arms (including the Council for Tobacco Research) under the Racketeer-Influenced and Corrupt Organizations (RICO) Act, federal judge Gladys Kessler found that the tobacco companies had formed an illegal “enterprise” that engaged in “a massive 50-year scheme to defraud the public, including consumers of cigarettes, in violation of [the Racketeer Influenced and Corrupt Organizations (RICO) Act],” and that such behavior was continuing and likely to continue in the future [4]. Judge Kessler specifically highlighted the role of the lawyers in managing the tobacco industry's scientific efforts:
-
At every stage, lawyers played an absolutely central role in the creation and perpetuation of the [racketeering] Enterprise and the implementation of its fraudulent schemes. They devised and coordinated both national and international strategy; they directed scientists as to what research they should and should not undertake; they vetted scientific research papers and reports as well as public relations materials to ensure that the interests of the Enterprise would be protected; they identified “friendly” scientific witnesses, subsidized them with grants from the Center for Tobacco Research and the Center for Indoor Air Research, paid them enormous fees, and often hid the relationship between those witnesses and the industry; and they devised and carried out document destruction policies and took shelter behind baseless assertions of the attorney client privilege. [4]
The Regulatory Principles in Action
Philip Morris used the IOM report's Regulatory Principles in its efforts to shape scientific standards and tobacco regulatory policy by quoting, and at times misinterpreting, these Regulatory Principles.
Regulatory Principles 4 and 6: Substantial reduction in exposure/risk and post-market epidemiological surveillance
Regulatory Principles 4 and 6 (Box 1) allowed manufacturers to market tobacco products with exposure or risk reduction claims, provided that the products “substantially reduced” exposure as judged by independent scientific experts, and empowered a hypothetical regulatory agency to require manufacturers to conduct post-marketing surveillance and epidemiological studies to determine behavioral and health consequences of their products. Nominally following IOM regulatory Principle 4, PM contracted with the “independent” Life Sciences Research Office (LSRO) to develop criteria and a surveillance plan called the “Reduced Risk Review” that PM could then apply to its products. Far from being “independent,” PM was involved in selecting members of LSRO committees [195],[196]; 44% of the committee members assembled for the Reduced Risk Review had documented financial ties to the tobacco industry, with several working for tobacco companies PM, RJR, Liggett, Lorillard, Star Scientific, or Japan Tobacco ([196]; Table 1 identifies committee members with documented ties to the tobacco industry).
A year and a half after the IOM report was released and at the beginning of the LSRO project, Ed Carmines, a PM associate principal scientist, emailed Robin Philips, a PM business planning R&D engineer, to explain how PM was going to use LSRO in the context of the Regulatory Principles. With respect to Regulatory Principle number 4:
-
LSRO is envisioned to represent PM's independent scientific experts to support the claims. The IOM did not identify what would be required only that it should undergo an independent review. After LSRO develops the criteria, we plan to ask them to review our data to see if it meets the criteria…
The second relevant principle is number 6: It says the [sic] there should be a surveillance plan before the product is marketed to permit continuing review of the marketing claims. We want LSRO to identify what would be necessary in a surveillance plan and then to determine if our plans meet the pre-established criteria. [emphasis added] [197].
LSRO assembled a committee for “Evaluating the Scientific Evidence for Potential Reduced-Risk Tobacco Products” that ultimately produced four monographs on scientific methods, biological effects assessment, exposure assessment, and differentiating the health risks of categories of tobacco products [198],[199],[200],[201]. The monographs recommended the same testing battery, analyses, and biomarkers, reference cigarettes, and machine testing protocols that PM and the other tobacco companies recommended to the IOM and that the IOM described in its report ([3], p. 292–293; [97],[111]).
It is important to emphasize that the second sentence in Regulatory Principle 4 states, “The ‘substantial reduction’ in exposure should be sufficiently large that measurable reduction in morbidity and/or mortality (in subsequent clinical or epidemiological studies) would be anticipated as judged by independent scientific experts [emphasis added]” in order to preclude perhaps biologically irrelevant reductions in toxin exposures to form the basis for marketing claims to the public.
Regulatory Principle 5: Claims must not be false or misleading
In 2001, as PM closely followed Congress's efforts to grant FDA jurisdiction over tobacco [202], key lawyers and executives at PM maintained a spreadsheet comparing elements of each proposed bill to standards in the IOM report [203],[204]. An undated position paper from the office of PM Vice President of Federal Government Affairs John Scruggs titled “Reduced Risk Tobacco Products: Full Disclosure vs. Government Suppression of Truthful and Non-Misleading Information” argued that the proposed bills, specifically one by Senator Ted Kennedy (D, MA), “appear[ed] to grant FDA authority to suppress information about reduced-risk or reduced-exposure tobacco products even if FDA has verified that these products, as a matter of science, genuinely have the potential to present reduced risks to individual consumers” [205]. The actual criteria set forth by the Kennedy Bill required that reduced risk products must not only reduce harm to individuals but also be otherwise appropriate to protect public health on a population level. PM did not agree with the latter criteria for withholding information about reduced risk claims and constructed a legal argument based on the First Amendment as well as statements made in the IOM report to argue that FDA should not have discretion to withhold information about verified claims:
-
Proposals to give FDA regulatory authority over tobacco products take different approaches to so-called “reduced-risk” products. But once FDA makes a scientific determination about a particular product, neither the agency nor any other government body is Constitutionally permitted to suppress truthful and non-misleading information about the product [referring to Clearing the Smoke Regulatory Principle #5]. [emphasis in original] [205].
The memo then quoted the IOM report, saying, “IOM added that the ‘regulatory process should not discourage or impede scientifically grounded claims of reduced exposure, so long as steps are taken to ensure that consumers are not misled…’ [emphasis added by PM author]” [205]. In short, PM considered using the IOM's regulatory principles (together with other legal arguments) to try to shape legislation that would maximize the company's ability to market FDA-recognized claims of reduced risk products using low standards.
While PM did not issue any statements publicly opposing the Kennedy bill using these legal arguments, what they did do was vigorously support a competing bill that was soundly opposed by the health groups. In 2001, PM supported alternative bills for tobacco regulation proposed by Representative Thomas M. Davis III (R-11th) and Senator Bill Frist (R-Tennessee) [17]. According to an independent analysis of tobacco documents related to regulation, PM's support of this legislation was based on the notion that “government regulation was part of PM USA's larger plan to be regarded as a normal, legitimate corporation, thereby ending its isolation and assuring its continued success” [17]. Public health groups were critical of the Davis and Frist bills. The Davis bill was declared to be “written on behalf of tobacco giant Philip Morris” in a position paper by the American Cancer Society, American Heart Association, American Lung Association, and Tobacco-Free Kids:
-
In many critical sections, the bill changes the standard under which FDA normally operates from one that places concern for public health as the top priority to one that protects tobacco industry interests. Virtually every important section has a loophole or a standard that would prevent FDA from protecting public health. [206].
Later that year, out of concern for the Davis and Frist bills “spinning out of control,” PM's Scruggs “concluded that Democratic Senator Edward Kennedy of Massachusetts was the key to success, and recommended negotiating with him to try to reach a compromise bill” [17], thus explaining why PM did not appear to publicly oppose the Kennedy bill.
Regulatory Principle 7: Approval of products that do not claim to reduce risk or exposure
In their presentations and letters to the IOM, PM described a criterion of “acceptability,” defined as a product characteristic by which chemical or biological activity is no higher than “standard” [97],[111]. This “standard” was not defined but was implied to be conventional cigarettes currently on the market. For example, PM's response to the IOM's question about criteria to assert that a specific form of tobacco or tobacco product is less harmful than others stated, “We believe that as long as a new product does not increase the hazard of smoking, it should be allowed into commercial sales” [111]. The IOM report's Regulatory Principle 7 appeared to embody PM's principle of “acceptability”:
-
In the absence of any claim of reduced exposure or reduced risk, manufacturers of tobacco products should be permitted to market new products or modify existing products without prior approval of the regulatory agency after informing the agency of the composition of the product and certifying that the product could not reasonably be expected to increase the risk of cancer, heart disease, pulmonary disease, adverse reproductive effects, or other adverse health effects, compared to similar conventional tobacco products, as judged on the basis of the most current toxicological and epidemiological information. ([3], p. 10).
The 2009 Family Smoking Prevention and Tobacco Control Act (FSPTCA) [207] partially implemented Regulatory Principle 7's approach to new products by allowing manufacturers until March 22, 2011 to submit a report to the FDA if such products were “substantially equivalent” to products on the market on or before February 15, 2007, which would allow these products to be marketed unless the FDA acts to prohibit their sale (placing the burden on the FDA to disprove substantial equivalence) [208]. After March 22, 2011, products for which substantial equivalence is claimed may not be marketed until the agency acts. As of June 22, 2012, tobacco companies had submitted 3,303 applications for substantially equivalent products, 10 for modified risk tobacco products, and none for new tobacco products [209]; as of November 5, 2012, the FDA had not acted on any of these applications.
The Need for Explicit Skepticism of Industry Scientific Claims
The extent of the industry's deception of the public and the scientific community and the role of industry lawyers in managing its scientific enterprise [1],[210],[211],[212] has become more apparent in the years since Clearing the Smoke was released. In addition to Judge Kessler's 2006 ruling that the major cigarette companies had formed a continuing illegal “enterprise” that was likely to continue in the future [4], the companies' manipulative behavior was also recognized in Article 5.3 of the WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (FCTC), a treaty ratified by 176 parties as of July 2012, which requires that, “In setting and implementing their public health policies with respect to tobacco control, Parties shall act to protect these policies from commercial and other vested interests of the tobacco industry in accordance with national law” [213]. (The US has signed but not ratified the FCTC.)
In 2012, the IOM issued another FDA-commissioned report on regulation of tobacco products, Scientific Standards for Studies on Modified Risk Tobacco Products [214], which recommended minimum standards for scientific studies to support the marketing of modified-risk tobacco products and for postmarket studies of approved products. Similar to Clearing the Smoke, tobacco companies were permitted to make presentations to the new committee on study standards and study design and promoted similar ideas as in 2001, including the tiered testing system and consumer acceptability. The 2012 IOM report contextualized these industry contributions with an extensive discussion of the history of industry-funded research, the findings of the RICO lawsuit, and the danger posed to the FDA's reputation if it were to accept tobacco company–based research. In contrast to Clearing the Smoke, which only briefly mentioned but did not specifically recommend a minimal battery of tests, the new report conducted a thorough assessment of scientific studies including those mentioned in Clearing the Smoke in 2001 as well as the advances since then. In some ways, Scientific Standards for Studies on Modified Risk Tobacco Products improved on Clearing the Smoke by acknowledging that the tobacco industry has a well-documented record of scientific deception. However, even the IOM committee that prepared the 2011 report seemed to fail to take its own advice by permitting tobacco company scientists to present information to them. Any information submitted by tobacco interests should be treated with a high degree of skepticism in light of their history of deception documented by, among other things, the federal courts. While the US has not yet ratified the FCTC, and the FSPTCA requires nonvoting representatives on the FDA's Tobacco Products Scientific Advisory Committee [215], the FDA and advisory bodies such as the IOM should implement the guidelines for Article 5.3 “to protect [public health] policies from commercial and other vested interests of the tobacco industry in accordance with national law” [213]. While it may not be possible to exclude tobacco interests from presenting information to independent and government scientific and regulatory decision-making bodies, these bodies should be mindful of Principle 1 of the Guiding Principles for implementation of Article 5.3 of the FCTC which states, “There is a fundamental and irreconcilable conflict between the tobacco industry's interests and public health policy interests” [216].
Policy Implications
Many tobacco company ideas appeared in the final IOM report, and some have policy implications that were continuing to reverberate in 2012. The main ideas promoted by the tobacco industry to the IOM, as described in the Results section, were: (1) ability to market and sell potential reduced exposure products that pass initial acceptability tests, and to continue selling them for years in order to conduct epidemiological surveillance for health effects (a tiered testing system) [97],[101],[111],[112], (2) that harm reduction should be considered relative to conventional cigarettes, as opposed to absolute harm from baseline [97],[111],[112], (3) a mechanism to sell “substantially equivalent” products that were not more harmful (but not necessarily less harmful) than existing products [97],[111], and (4) the notion that reduced-harm products must appeal to consumers in order to be marketable and effective [94],[97].
An inherent limitation in the whole process that led to Clearing the Smoke was that the FDA was looking for assistance as to standards it should apply to tobacco company applications to market cigarette-like products (like RJR's Eclipse) that would be less harmful than cigarettes. The FDA's and IOM's assumption was that there might indeed be such products and that allowing companies to market them with proper restrictions might improve the public's health. Hence, ideas like making PREPs unattractive to consumers or banning them if they were more dangerous than not smoking at all were simply off the table.
The IOM's stance on consumer acceptability—which was consistent with the tobacco companies' imperative to sell their products—overlooks the regulatory option of reducing tobacco use by requiring that products be less “acceptable” by prohibiting the use of additives (such as menthol [155],[217]) that make the cigarettes less harsh and easier to smoke. In a well-regulated market that imposes high barriers on products that aim to please the consumer, less-acceptable products could be effective at reducing smoking-related disease.
The major regulatory goal that the industry aimed for but did not achieve was to restrict the evaluation of risk or exposure reduction to the individual level only. An analysis of the tobacco industry documents by McDaniel and Malone found that, “PM want[ed] reduced risk tobacco products to be regulated by the FDA, but it did not support applying a public health standard to such products. A public health standard would require the FDA to withhold approval from reduced risk cigarettes if they led to an increase in the incidence of smoking among the population by causing fewer people to quit or causing quitters to resume smoking. Instead, PM preferred a standard that focused on the benefits of reduced risk products for individual adult smokers” [17]. Consistent with this position, both PM and RJR answered the IOM's questions about population-level studies with nonspecific, vague responses (Table 1). Later PM objected to the proposed Kennedy bill for tobacco regulation, because it required a public health standard as well as an individual standard of harm reduction and empowered the FDA to withhold information about tobacco products if they did not meet both criteria. Despite the industry's urging, the IOM concluded that reduced-harm products must protect at both the individual and population levels and devoted a chapter of the report to population-based surveillance. Attention to population-level effects is important, because it is possible that a product that represented lower risk to an individual (such as smokeless tobacco compared to smoking cigarettes) could still increase population-level harm if the net effect was to reduce cessation of all tobacco use and promote initiation (even of the lower risk product) or dual use of the new product and cigarettes by the same people [218]. (Indeed, after the major US cigarette companies purchased smokeless tobacco companies they started promoting dual use of co-branded snus (oral, smokeless tobacco) and cigarettes with snus used in smoke-free environments such as bars and airplanes, and cigarettes at other times [218].) The FSPTCA also includes a provision requiring that modified-risk tobacco products can only be defined as such if they reduce harm for individuals and the population.
Limitations
As a result of the 1998 Minnesota settlement, the 1998 Master Settlement Agreement, and the federal RICO ruling, tobacco companies are required to make internal documents produced in discovery in smoking and health litigation publicly available. As a result, the Legacy Tobacco Documents Library provides important insights into the tobacco industry's approach to the IOM Committee to Assess the Science Base for Tobacco Harm Reduction, but some key documents remain withheld by tobacco companies (under privilege and confidentiality claims that apply to documents being used in anticipation of litigation or related to trade secrets and personal information) including drafts of presentations from PM, RJR, and B&W to the IOM working group [157],[158],[159],[160],[161],[162],[163],[164],[165],[166],[167],[168],[169],[170],[171],[172],[173],[174],[175],[176],[177],[178],[179],[180],[181],[182],[183],[184],[185],[186],[187],[188],[190],[191],[192] and drafts of PM's reaction to the report [148],[149],[189],[193]. Despite this limitation, the available documents reveal extensive coordination among industry scientists, lawyers, executives, and regulatory staff in the presentation of information to the IOM toward the fulfillment of the industry's scientific, regulatory, and business goals.
The written record alone in the form of available industry and IOM documents does not provide sufficient evidence to claim cause and effect, i.e. that the scientific information presented by the companies yielded a particular outcome. However, the evidence does show that the industry had certain goals they wanted to accomplish and were generally pleased with and able to leverage the Clearing the Smoke report to promote their business agendas.
Conclusion
The IOM report Clearing the Smoke was an early attempt to grapple with the complex scientific and regulatory issues surrounding the possibility of reduced-harm tobacco products. The relative lack of information in the field at the time created a void that the tobacco industry sought to fill with its own data and ideas about how reduced-harm products should be evaluated, regulated, and sold. The IOM committee's mandate was predicated on the belief of some in the public health community that lives could be saved if such a consumer-acceptable reduced-harm tobacco product was available. At the same time, it was understood then—and understood even better now—that many safeguards would be necessary to make sure that the product was not misrepresented as being safe when it was not (like filtered cigarettes and “low tar” cigarettes) and that it did not cause more harm by persuading people that it was safe to start or not to quit. While Clearing the Smoke states, “The committee believes that harm reduction is feasible and justified public health policy—but only if it is implemented carefully” and that “The effect of PREPS could be to increase or decrease tobacco-related disease in the population” [3], others in the public health community are very skeptical about such products. Readers should not be left with the impression that the fact that this skeptical point of view did not prevail is necessarily suggestive of tobacco industry influence. Rather, they should be aware of the complex strategies that tobacco companies have been using to attempt to influence regulatory policy and the urgent need to protect future endeavors.
There was a lack of clear policy on tobacco industry engagement by the IOM which, combined with the general presumption of honesty upon which all scientific discourse is based, created an opportunity for the tobacco companies to advocate positions that supported their interests. The industry took advantage of this situation and, in the end, some of the industry recommendations were reflected in Clearing the Smoke and the subsequent legislation assigning the FDA regulatory authority over tobacco products. The presence of tobacco industry representatives on the FDA's Tobacco Products Scientific Advisory Committee [215], combined with the FDA's official consideration of the tobacco industry as a “stakeholder,” increase the likelihood that the tobacco companies will continue to successfully manipulate the scientific discourse around tobacco product regulation, to the companies' benefit and to the detriment of public health. To prevent such an outcome, the FDA and counterpart organizations in other countries need to remain cognizant of the guidelines for implementing FCTC Article 5.3 [213] and that they are dealing with companies with a history of more than 50 years of intentionally misleading the public and who were found by two federal courts to have participated in “a pattern of racketeering activity” in violation of the RICO Act [4] when assessing the role of the tobacco companies and the information they present as part of the regulatory process.
Supporting Information
Zdroje
1. Glantz S, Slade J, Bero LA, Hanauer P, Barnes DE (1996) The Cigarette Papers. Berkeley and Los Angeles, California: University of California Press.
2. National Cancer Institute (2001) Monograph 13: Risks Associated with Smoking Cigarettes with Low Tar Machine-Measured Yields of Tar and Nicotine. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Public Health Service, National Institutes of Health, National Cancer Institute.
3. Stratton K, Shetty P, Wallace R, Bondurant S (2001) Clearing the Smoke: Assessing the Science Base for Tobacco Harm Reduction. Washington, D.C.: National Academy Press.
4. (2006) United States of America, et al. v. Philip Morris USA Inc., et al, 449 F. Supp 2d 1 (D.C. D. C. 2006), aff'd as to the tobacco companies except for certain remedies, 566 F.3d 1095 (D.C. Cir. 2009), cert. den. 130 S. Ct. 3501 (June 28, 2010) (also vacating judgment against the Tobacco Institute and Center for Tobacco Research as moot because the organizations “no longer exist”).
5. Proctor R (2011) Golden Holocaust: Origins of the Cigarette Catastrophe and the Case for Abolition. Berkeley and Los Angeles, CA: University of California Press.
6. Parker-Pope T. Safer Cigarettes: A History. Nova Oct. 2, 2001 http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/nova/body/safer-cigarettes-history.html. (Accessed Nov. 3, 2012)
7. The National Academies: Who We Are. http://www.nas.edu/about/whoweare/index.html. (Accessed October 22, 2012)
8. The National Academies: Our Reputation. http://www.nationalacademies.org/about/reputation/index.html. (Accessed October 22, 2012)
9. BatesC (2001) Clearing the smoke or muddying the water? Tob Control 10 : 87–88.
10. HongMK, BeroLA (2002) How the tobacco industry responded to an influential study of the health effects of secondhand smoke. BMJ 325 : 1413–1416.
11. OngEK, GlantzSA (2000) Tobacco industry efforts subverting International Agency for Research on Cancer's second-hand smoke study. Lancet 355 : 1253–1259.
12. BeroLA (2005) Tobacco industry manipulation of research. Public Health Rep 120 : 200–208.
13. OngEK, GlantzSA (2001) Constructing “sound science” and “good epidemiology”: tobacco, lawyers, and public relations firms. Am J Public Health 91 : 1749–1757.
14. BabaA, CookDM, McGarityTO, BeroLA (2005) Legislating “sound science”: the role of the tobacco industry. Am J Public Health 95 Suppl 1: S20–27.
15. CookDM, TongEK, GlantzSA, BeroLA (2005) The power of paperwork: how Philip Morris neutralized the medical code for secondhand smoke. Health Aff (Millwood) 24 : 994–1004.
16. MaloneRE, BalbachED (2000) Tobacco industry documents: treasure trove or quagmire? Tob Control 9 : 334–338.
17. McDanielPA, MaloneRE (2005) Understanding Philip Morris's pursuit of US government regulation of tobacco. Tob Control 14 : 193–200.
18. Philip Morris. Potential for Worldwide Product Regulation. 03 Sep 1999. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/yky97d00.
19. Philip Morris. Reducing Exposure to Harmful Substances in Tobacco: The Science Base. Oct 1999. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/gul90b00.
20. Philip Morris. Worldwide Regulatory Affairs Five Year Plan 1995–1999 ETS Strategy. Mar 1995. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/lrc74a00.
21. Levine A, Richman J. Arnold & Porter. Institute of Medicine Study on “Reducing Exposure to Harmful Substances in Tobacco: The Science Base”. 15 Nov 1999. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/syf42c00.
22. Multinational Business Services. Information Sharing with the IOM Committee on “Reducing Exposure to Harmful Substances in Tobacco”. 01 Oct 1999. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/fje25c00.
23. DiethelmPA, RielleJC, McKeeM (2005) The whole truth and nothing but the truth? The research that Philip Morris did not want you to see. Lancet 366 : 86–92.
24. Geffe J. Philip Morris Research Laboratories GmbH. New Company Name. 26 Nov 2002. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/rzq34a00.
25. McAlpin L. Philip Morris. Institute of Medicine. 29 Nov 1999. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/kzj50b00.
26. Carchman R. Philip Morris. Given the project scope and its membership I have the following preliminary comments. Dec 1999. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/fcl70b00.
27. Hough JD. Philip Morris. Institute of Medicine. 01 Dec 1999. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/itg70b00.
28. Patskan GJ. Philip Morris. IOM. 01 Dec 1999. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/mok19c00.
29. Davies B. Philip Morris. Comments on IOM Document. Dec 1999. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/otm11b00.
30. Rickert WS (1996) Report of Canada's Expert Committee on Cigarette Modifications. Toronto, Ontario, Canada: Health Canada.
31. Rickert WS (1998) Report of Canada's Expert Committee on Cigarette Toxicity Reduction. Toronto, Ontario, Canada: Health Canada.
32. Cox RH, Rickert WS. Agreement for Independent Contractor Services between Labstat International Inc. and Philip Morris Incorporated. 15 Sep 2000. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/zrd34a00.
33. BarnesRL, HammondSK, GlantzSA (2006) The tobacco industry's role in the 16 Cities Study of secondhand tobacco smoke: do the data support the stated conclusions? Environ Health Perspect 114 : 1890–1897.
34. Tobacco Documents Online Profiles: Jenkins, Roger Allen, Ph.D. http://tobaccodocuments.org/profiles/jenkins_roger.html. (Accessed April 12, 2012)
35. Tozzi J. Multinational Business Services. Data Sharing with the IOM Committee. 06 Dec 1999. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/wpg95c00.
36. Solana RP. Philip Morris. You have posted invitation for public comment on the committee for “Assessing the Science Base for Tobacco Harm Reduction”. 12 Dec 1999. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/vyd69h00.
37. Arnold & Porter. Profile of Dorothy Hatsukami. 21 Dec 1999. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/qxl34a00.
38. Arnold & Porter. Profile of Garrett A. Fitzgerald. Dec 1999. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/dhz95c00.
39. Bondurant Bibliography (in Philip Morris Collection). Dec 1999. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/xjl66c00.
40. Crout Bibliography (in Philip Morris Collection). Dec 1999. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/odd92g00.
41. Fitzgerald Bibliography (in Philip Morris Collection). Dec 1999. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/rdd92g00.
42. Gazdar Bibliography (in Philip Morris Collection). Dec 1999. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/lhm80g00.
43. Giovino Bibliography (in Philip Morris Collection). Dec 1999. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/wdd92g00.
44. Henderson Bibliography (in Philip Morris Collection). Dec 1999. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/ded92g00.
45. Reuter Bibliography (in Philip Morris Collection). Dec 1999. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/jed92g00.
46. Riley Bibliography (in Philip Morris Collection). Dec 1999. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/ned92g00.
47. Shields Bibliography (in Philip Morris Collection). Dec 1999. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/qvd92g00.
48. Wallace Bibliography (in Philip Morris Collection). Dec 1999. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/hwd92g00.
49. Willerson Bibliography (in Philip Morris Collection). Dec 1999. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/jwd92g00.
50. Philip Morris. Stuart Bondurant (Confidential Document). 1996. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/yoy31h00.
51. John Richard Crout Resume (in Phlilip Morris Collection). 1998. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/tnq81g00.
52. Garret Adare Fitzgerald Resume (in Philip Morris Collection). 1998. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/zoy31h00.
53. Henderson Rogene F. PhD Dabt 1998 Resume (in Philip Morris Collection). 01 Dec 1999. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/woy31h00.
54. Rogene Faulkner-Henderson Resume (in Philip Morris Collection). 00 1998. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/xoy31h00.
55. Barbara Hulka, MD Resume (in Philip Morris collection). 01 Dec 1999. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/xnq81g00.
56. Barbara Sorenson Hulka Resume (in Philip Morris Collection). 1998. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/mbz70g00.
57. David J. Riley, M.D Resume (in Philip Morris collection). 01 Dec 1999. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/ybc79h00.
58. Dr. Peter Reuter, Ph.D Resume (in Philip Morris collection). 01 Dec 1999. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/zbc79h00.
59. Adi F. Gazdar, MD Resume (in Philip Morris collection). 01 Dec 1999. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/elc79h00.
60. Stratton K. Institute of Medicine. Re: “Assessing the Science Base for Tobacco Harm Reduction” Meetings (email to Rick Solana). 13 Jan 2000. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/aha49c00.
61. Solana RP. Fw: Re: “Assessing the Science Base for Tobacco Harm Reduction” Meetings. 13 Jan 2000. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/zga49c00.
62. Stratton K. The Institute of Medicine Has Convened the Committee to Assess the Science Base for Tobacco Harm Reduction in Response to a Request by the Food and Drug Administration. 28 Jan 2000. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/erg95c00.
63. Stratton K. The Institute of Medicine Has Convened the Committee to Assess the Science Base for Tobacco Harm Reduction in Response to a Request by the Food and Drug Administration. 28 Jan 2000. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/keg70d00.
64. Stratton K. Letter from Kathleen Stratton to Rufus H Honeycutt regarding harmful substances in tobacco. 01 Feb 2000. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/jvy92a99.
65. Solana RP. I look forward to meeting you on March 1. 02 Feb 2000. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/epg80b00.
66. Gorrod JW, Jacob III P, editors(1999) Analytical Determination of Nicotine and Related Compound and their Metabolites. Amsterdam, The Netherlands: Elsevier Science B.V.
67. HongMK, BeroLA (2006) Tobacco industry sponsorship of a book and conflict of interest. Addiction 101 : 1202–1211.
68. Philip Morris. CVs of Presenters Scheduled for 3-2001 Presentation. 24 Feb 2000. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/tiw50b00.
69. Philip Morris. Prep Sessions. Mar 2000. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/xra49c00.
70. McAlpin L. IOM Information. 11 Feb 2000. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/hkn47c00.
71. King V. Philip Morris Worldwide Scientific Affairs. Facsimile transmitting draft of Don Leydens' presentation. 29 Feb 2000. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/ivk45c00.
72. Philip Morris. Draft materials for IOM presentations. Mar 2000. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/evk45c00.
73. Philip Morris. How Does the Uptake of Gas Phase and Particulate Phase Smoke Constituents Relate to Cigarette Design? The Total Exposure Project. 17 Feb 2000. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/nlm92g00.
74. Philip Morris. Low Yield Cigarettes 01 Mar 2000. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/kvk45c00.
75. YanoE (2005) Japanese spousal smoking study revisited: how a tobacco industry funded paper reached erroneous conclusions. Tob Control 14 : 227–233; discussion 233–225.
76. ChapmanS (2005) Research from tobacco industry affiliated authors: need for particular vigilance. Tob Control 14 : 217–219.
77. Sourcewatch: Peter N. Lee. http://www.sourcewatch.org/index.php?title=Peter_N._Lee. (Accessed April 19, 2012)
78. Wertz M, Kyriss T, Paranjape S, Glantz SA. Response to Comments from Michael J. Oldham Ph.D., Associate Principal Scientist, and Willie J. McKinney Jr., Ph.D., D.A.B.T., Director, Product Integrity, Altria Client Services, March 5, 2012, re: Wertz et al. 2011 “The Toxic Effects of Cigarette Additives. Philip Morris' Project Mix Reconsidered: An Analysis of Documents Released through Litigation”, PLoS Medicine, December 2011, Vol 8(12). http://www.plosmedicine.org/annotation/listThread.action?root=13441. (Accessed Apr. 24, 2012)
79. Baker R. Fax to Dr. Scott Appleton Re: Peter Lee. 16 Jun 2000. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/gcz92a99.
80. Lee PN. Letter submitting “Lung cancer and type of cigarette smoked” to BMJ. 03 Mar 2000. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/quk45c00.
81. Sanders E. Re: Peter Lee Manuscript for IOM. 10 Mar 2000. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/muk45c00.
82. LeePN (2001) Lung cancer and type of cigarette smoked. Inhal Toxicol 13 : 951–976.
83. Gardner DE, Inhalation Toxicology. THANK YOU FOR THE REVISION OF YOUR MANUSCRIPT NUMBER 0-01-571 ENTITLED “LUNG CANCER AND TYPE OF CIGARETTE SMOKED”. 14 May 2001. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/ijg50d00.
84. Gardner DE. Donald E. Gardner, Ph.D., Fellow: Ats. Inhalation Toxicology Associates, Inc. Consultants. 00 1999. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/yob90d00.
85. Burger GT, Lyalls TM. Accounts Payable Voucher. Dr. Gardner Provided Professional Consulting Services to R.J. Reynolds Tobacco at the Request of Dr. Gary T. Burger from January 17 through February 4, 2000 (20000117–20000204). 15 Feb 2000. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/iod50b00.
86. Burger GT, Lyalls TM. Accounts Payable Voucher. At the Request of R.J. Reynolds Tobacco, Dr. Gardner Attended an Eclipse Expert Panel Meeting in Philadelphia on March 23 and 24, 2000 (20000323–20000324). 31 Mar 2000. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/jod50b00.
87. Burger GT, Lyalls TM. Accounts Payable Voucher. Dr Gardner Was Invited by R.J. Reynolds Tobacco to Participate on an Expert Panel to Review Research on Eclipse. 26 Feb 1999. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/hod50b00.
88. Burger GT, Lyalls TM. Accounts Payable Voucher. Honorarium—Dr. Donald E. Gardner Served on an Expert Panel to Review Research on Eclipse at the Invitation of R.J. Reynolds Tobacco. 26 Feb 1999. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/god50b00.
89. Gardner DE, Burger GT. Enclosed for Your Review and Approval Is an Invoice for Consultant Service on Eclipse Carbon Monoxide Study Group That Met in Winston-Salem, North Carolina. 13 Nov 1996. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/eod50b00.
90. Townsend DE, Lyalls TM. Accounts Payable Voucher. At the Request of R.J. Reynolds Tobacco, Dr. Gardner Attended an Eclipse Expert Panel Meeting in San Francisco, CA on March 30 & 31, 2001 (20010330–20010331). 11 Apr 2001. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/end50b00.
91. Coggins C. Ms 01-571: Lung Cancer and Type of Cigarette Smoked. Lee, P.N. 30 Mar 2001. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/ync43c00.
92. Patskan GJ. Re: Your IOM Presentation. 14 Feb 2000. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/bsa49c00.
93. WertzMS, KyrissT, ParanjapeS, GlantzSA (2011) The toxic effects of cigarette additives. Philip Morris' project mix reconsidered: an analysis of documents released through litigation. PLoS Med 8: e1001145.
94. Reynolds Tobacco R.J. (2000) A Scientific Strategy for Assessing Tobacco Product Harm Reduction Potential. Presentation to the IOM Industry Working Group to Assess the Science Base for Tobacco Harm Reduction. Washington, D.C. IOM Public Access File.
95. Rucker TJ. Attached is a Page from a Briefing Paper Draft by Seth Moskowitz to be Given to Dave, Brice, Etc., for Media Training Next Week. 17 Mar 2000. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/drq31d00.
96. Moskowitz SW. Regulation/Policy. 13 Mar 2000. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/erq31d00.
97. Philip Morris Tobacco (2000) Presentation to the IOM Industry Working Group to Assess the Science Base for Tobacco Harm Reduction. Washington, D.C. IOM Public Access File.
98. Brown & Williamson Tobacco (2000) Assessment Strategies for Reduced Risk Cigarettes. Presentation to the IOM Industry Working Group to Assess the Science Base for Tobacco Harm Reduction. Washington, D.C. IOM Public Access File.
99. Solana RP. IOM Meeting - FYI. 02 Mar 2000. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/sre95c00.
100. Solana R. On March 1, the following Philip Morris scientists and I participated in a meeting with an Institute of Medicine working group of the Committee to Assess the Science Base for Tobacco Harm Reduction. Apr 2000. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/spg95c00.
101. Philip Morris. Our Understanding of IOM Committee Task. 01 Mar 2000. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/upg95c00.
102. Stratton K. Letter to RP Solana (Philip Morris) with follow-up questions from the Institute of Medicine Committee to Assess the Science Base for Harm Reduction from Tobacco. 17 Apr 2000. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/jmv95c00.
103. Stratton K. Letter to JD DeBethizy (RJR) regarding follow-up questions from the Institute of Medicine Committee to Access the Science Base for Harm Reduction from Tobacco. 17 Apr 2000. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/qrs81b00.
104. Stratton K. Letter to C Coggins (Lorrilard) transmititng follow-up questions from the Institute of Medicine Committee to Access the Science Base for Harm Reduction from Tobacco. 17 Apr 2000. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/sau64d00.
105. Stratton K. Letter from Kathleen Stratton to Scott Appleton (Brown and Williamson) regarding questions from the Institute of Medicine Committee. 17 Apr 2000. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/bsa14a99.
106. Philip Morris. Draft responses to IOM questions. 2000. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/ney08c00.
107. Bugg JJ, Osborne KB. IOM - Reread. 05 May 2000. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/vnv46c00.
108. Osborne K. Re: IOM - Reread. 07 May 2000. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/xnv46c00.
109. Philip Morris. Privileged+Confidential KBO Comments to draft responses to IOM questions. May 2000. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/sey08c00.
110. Bugg JJ. Q 10 Rewrite. 04 May 2000. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/pey08c00.
111. Solana R (2000) “In response to your follow-up question date April 17…”. Washington, D.C. IOM Public Access File.
112. WSA Scientific Review of the 2001 IOM Report “Clearing the Smoke”. 09 Apr 2001. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/guz81c00.
113. Lau RW. Re: Rick's Questions. 18 Mar 2001. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/ynk92c00.
114. Philip Morris. Harm Reduction Evaluation Process Process for Reduced-Harm Product Use and Claims. 13 Oct 2000. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/frv46c00.
115. Slade J (2000) Filtered & Light Cigarettes. Presentation to the IOM Committee to Assess the Science Base for Tobacco Harm Reduction: March 2, 2000–March 3, 2000. Washington, DC: IOM Public Access File.
116. Slade J (2000) Letter from John Slade to the Committee with supporting materials. Mar. 29, 2000. Washington, DC: IOM Public Access File.
117. Slade J (2000) Letter from John Slade to the Committee with supporting materials. May 8, 2000. Washington, DC: IOM Public Access File.
118. Slade J (2000) Letter from John Slade to the Committee. Aug. 13, 2000. Washington, DC: IOM Public Access File.
119. HirschhornN, BialousSA, ShatensteinS (2006) The Philip Morris External Research Program: results from the first round of projects. Tob Control 15 : 267–269.
120. HirschhornN, BialousSA, ShatensteinS (2001) Philip Morris' new scientific initiative: an analysis. Tob Control 10 : 247–252.
121. Letter from Adi F. Gazdar M.D re: preliminary application for research support, entitled “A comparison of bronchial epithelial changes in smokers and nonsmokers”. 14 Jan 1993. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/hhq72b00.
122. McAllister H. Council for Tobacco Research. Letter to A Gazdar regarding recent inquiry concerning support by Council for Tobacco Research. 22 Feb 1993. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/ihq72b00.
123. Research CfT. Request for peer review of New Application No. 3950 Adi F. Gazdar, Ph.D., University of Texas, Dallas, Texas Genes Involved in Lung Cancer Progression and Metastasis. 17 Jan 1994. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/zdg06d00.
124. Pierce. Council for Tobacco Research. Review of “Genes Involved in Lung Cancer Progression and Metastasis”. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/yrf06d00.
125. Lynch HT. Council for Tobacco Research. Review of ADI F. GAZDAR, M.D. #3950 “Genes Involved in Lung Cancer Progression and Metastasis”. 17 Feb 1994. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/zrf06d00.
126. Glenn J. Council for Tobacco Research. Letter to A. Gadzar declining funding of Application No. 3950. 25 Apr 1994. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/ctf06d00.
127. Gill GN. CTR Grant 3514 Nicotine Receptors in Human Lung Cancer. 24 Aug 1992. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/auf00d00.
128. Adams P, Minna J. Competing Renewal Application Genetic Lesions in Lung Cancer. 31 May 1996. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/xbo98d00.
129. Biographical Sketch Adi F. Gazdar, M.D. 11 Dec 1995. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/bco98d00.
130. Vogt P. Council for Tobacco Research. Review of Grant Application Grant Application #: 3514a. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/vbo98d00.
131. Joklik WK. Council for Tobacco Research. Review of “John D. Minna Genetic Lesions in Lung Cancer”. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/ubo98d00.
132. Glenn J. Council for Tobacco Research. Letter to JD Minna declining funding for Application No. 3514a. 17 Oct 1996. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/tbo98d00.
133. Wildenthal K. Letter to AF Gadzar explaining decision to decline approval to submit grant to PMERP. 15 Nov 2000. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/qwj20i00.
134. WSA Contracts. 17 Sep 2002. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/yop20i00.
135. Sourcewatch: Adi F. Gazdar. http://www.sourcewatch.org/index.php?title=Adi_F._Gazdar. (Accessed April 20, 2012)
136. Solana RP. Request for Applications 2003 Research Focus. Philip Morris External Research Program. 2003. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/gcs80g00.
137. Regulatory Circuitry. Philip Morris External Research Program Symposium 20071209–20071211. 09 Dec 2007. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/vos94g00.
138. Henderson R, IRRI. Symposium at SOT. 22 Mar 2001. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/xso20d00.
139. Walk RA. Fw: Walk, Letter to D. Hatsukami, 2003-10-30. 15 Apr 2005. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/zmt81g00.
140. Bondurant S. Clearing the Smoke: Assessing the Science Base for Tobacco Harm Reduction Opening Statement. 22 Feb 2001. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/lif31c00.
141. Solana RP. IOM. 22 Feb 2001. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/mif31c00.
142. Merlo E. Re: IOM. 22 Feb 2001. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/nif31c00.
143. Pfeil ME. Re: IOM. 22 Feb 2001. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/oif31c00.
144. Merlo E. Re: IOM. 22 Feb 2001. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/qif31c00.
145. Scruggs J. Re: President's Commission - Preliminary Draft Comments. 23 Feb 2001. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/dhf31c00.
146. Berlind M. IOM's 11 Principles. 25 Feb 2001. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/xtz81c00.
147. Desel P. Re: IOM's 11 Principles. 13 Mar 2001. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/ztz81c00.
148. Desel P. Email from Philip Morris in-House Counsel to Philip Morris in-House Counsel Memorializing a Discussion with Philip Morris Outside Litigation Counsel (Conley) Regarding Responding to the Institute of Medicine's Report on the Eleven Tobacco Regulatory Principles. 27 Mar 2001. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/ofv42b00.
149. Osborne K. IOM Report - Initial Observation. 23 Mar 2001. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/orz30i00.
150. Philip Morris USA and Philip Morris International Perspective on the Institute of Medicine's Eleven Regulatory Principles. 25 Feb 2001. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/fqh77a00.
151. Philip Morris USA and Philip Morris International Perspective on the Institute of Medicine's Eleven Regulatory Principles. 04 Apr 2001. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/kxd51b00.
152. Philip Morris USA and Philip Morris International Perspective on the Institute of Medicine's Eleven Regulatory Principles. 23 Apr 2001. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/jxd51b00.
153. Bugg JJ. RE: IOM Report - initial observation. 28 Mar 2001. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/kyw95g00.
154. Desel P. Fw: Draft WSA Review of IOM Report. 03 Apr 2001. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/uiy08c00.
155. McDanielPA, SmithEA, MaloneRE (2006) Philip Morris's Project Sunrise: weakening tobacco control by working with it. Tob Control 15 : 215–223.
156. Burger GT (2000) “We at the R.J. Reynolds Tobacco Company appreciate the opportunity to respond…”. Washington DC: IOM Public Access File.
157. Wells J. Confidential Handwritten Notes of B&W in-House Counsel Reflecting Counsel's Legal Advice Regarding B&W's Draft Comment to National Academy of Sciences Institute of Medicine Concerning Assessment Strategies for Reduced Risk Cigarettes. 01 Mar 2000. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/sse51i00.
158. Assessment Strategies for Reduced Risk Cigarettes; Comments by Brown & Williamson Tobacco Corporation; Presented to National Academy of Sciences Institute of Medicine Committee to Assess the Science Base for Tobacco Harm Reduction. 01 Mar 2000. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/xti21c00.
159. An Effective Scientific Strategy for Assessing Harm Reduction Potential in Cigarettes (Confidential). 04 May 2000. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/nyu06h00.
160. An Effective Scientific Strategy for Assessing Harm Reduction Potential in Cigarettes. 04 May 2000. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/nxx43h00.
161. An Effective Scientific Strategy for Assessing Harm Reduction Potential in Cigarettes. 05 May 2000. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/snt56h00.
162. An Effective Scientific Strategy for Assessing Harm Reduction Potential in Cigarettes. 29 Feb 2000. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/kao53h00.
163. An Effective Scientific Strategy for Assessing Harm Reduction Potential in Cigarettes. 05 May 2000. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/smt56h00.
164. An Effective Scientific Strategy for Assessing Harm Reduction Potential in Cigarettes. 04 May 2000. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/tnx43h00.
165. An Effective Scientific Strategy for Assessing Harm Reduction Potential in Cigarettes. 27 Feb 2000. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/ysv95h00.
166. Debethizy JD. Overview of Scientific Strategy. An Effective Scientific Strategy for Assessing Harm Reduction Potential in Cigarettes. 16 Mar 2000. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/sae34h00.
167. Debethizy JD. An Effective Scientific Strategy for Assessing Harm Reduction Potential in Cigarettes. 28 Feb 2000. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/qdv95h00.
168. An Effective Scientific Strategy for Assessing Harm Reduction Potential in Cigarettes. 07 Feb 2000. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/fzc93h00.
169. An Effective Scientific Strategy for Assessing Harm Reduction Potential in Cigarettes. 00 1999. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/krj94h00.
170. Debethizy JD, Doolittle DJ, Mosberg AT, Robinson JH. An Effective Scientific Strategy for Assessing Harm Reduction Potential in Cigarettes. 04 May 2000. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/wzw45h00.
171. An Effective Scientific Strategy for Assessing Harm Reduction Potential in Cigarettes. 04 May 2000. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/dlq05h00.
172. An Effective Scientific Strategy for Assessing Harm Reduction Potential in Cigarettes. 10 May 2000. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/gkf47h00.
173. Archived Email 1994–2000 (Box 11); an Effective Scientific Strategy for Assessing Harm Reduction Potential in Cigarettes. 28 Feb 2000. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/ysi01i00.
174. An Effective Scientific Strategy for Assessing Harm Reduction Potential in Cigarettes. 05 May 2000. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/axw45h00.
175. An Effective Scientific Strategy for Assessing Harm Reduction Potential in Cigarettes. 04 May 2000. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/yzx43h00.
176. An Effective Scientific Strategy for Assessing Harm Reduction Potential in Cigarettes. 05 May 2000. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/zio53h00.
177. An Effective Scientific Strategy for Assessing Harm Reduction Potential in Cigarettes. 04 May 2000. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/sox43h00.
178. Debethizy JD, Borgerding MF, Doolittle DJ, Mosberg AT. An Effective Scientific Strategy for Assessing Harm Reduction Potential in Cigarettes. 09 May 2000. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/akf47h00.
179. An Effective Scientific Strategy for Assessing Harm Reduction Potential in Cigarettes. 01 May 2000. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/gvg16h00.
180. An Effective Scientific Strategy for Assessing Harm Reduction Potential in Cigarettes. 04 May 2000. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/lgk72h00.
181. An Effective Scientific Strategy for Assessing Harm Reduction Potential in Cigarettes. 27 Feb 2000. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/ulq43h00.
182. An Effective Scientific Strategy for Assessing Harm Reduction Potential in Cigarettes. 04 May 2000. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/okf47h00.
183. An Effective Scientific Strategy for Assessing Harm Reduction Potential in Cigarettes. 04 May 2000. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/ktp15h00.
184. An Effective Scientific Strategy for Assessing Harm Reduction Potential in Cigarettes. 04 May 2000. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/ekf47h00.
185. An Effective Scientific Strategy for Assessing Harm Reduction Potential in Cigarettes. 04 May 2000. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/bcy43h00.
186. An Effective Scientific Strategy for Assessing Harm Reduction Potential in Cigarettes. 1993. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/fga82h00.
187. An Effective Scientific Strategy for Assessing Harm Reduction Potential in Cigarettes. 27 Feb 2000. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/vmq43h00.
188. An Effective Scientific Strategy for Assessing Harm Reduction Potential in Cigarettes. 16 Mar 2006. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/xyk36h00.
189. IOM Science Base for Tobacco Harm Reduction. Mar 2001. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/ylx41h00.
190. TES_exposure_characterization _Leyden_D 1 ._to_IOM_(Presentation)_2000-03-01.ppt ExcelWorkbook.xls. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/fzl32h00.
191. Surrogate_markers_suitable_for_testing _Haussmann_H 1 ._to_IOM_Committee_(Presentation)_2000-03-01.ppt ExcelWorkbook.xls. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/gau32h00.
192. Epidemiology_of_low_tar_products _Sanders_E 1 ._to_IOM_Committee_(Presentation)_2000-03-01.ppt. 29 Feb 2000. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/kpl32h00.
193. Frame work presentation IOM principles draft 3-6.ppt∧PowerPointPresentation.ppt. 12 Feb 2002. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/paa42h00.
194. Eubanks S, Glantz S (2012) Bad Acts: The Racketeering Case Against the Tobacco Industry. Washington, D.C.: American Public Health Association Press.
195. Project Description: Evaluating the Scientific Evidence for Potential Reduced-Risk Tobacco Products (“Reduced Risk Review”). LSRO http://www.lsro.org/rrrvw/rrrvw_project_description.pdf. (Accessed April 20, 2012)
196. SchickSF, GlantzSA (2007) Old ways, new means: tobacco industry funding of academic and private sector scientists since the Master Settlement Agreement. Tob Control 16 : 157–164.
197. Carmines EL. Fw: LSRO for Reduced Harm. 30 Nov 2004. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/noi91g00.
198. Brownawell AM (2007) The LSRO Report on Biological Effects Assessment in the Evaluation of Potential Reduced-Risk Tobacco Products. Bethesda, MA: Life Sciences Research Office.
199. Hilaire CLS (2007) The LSRO Report on Scientific Methods to Evaluate Potential Reduced-Risk Tobacco Products. Bethesda, MA: Life Sciences Research Office.
200. Lewis KD (2007) The LSRO Report on Exposure Assessment in the Evaluation of Potential Reduced-Risk Tobacco Products. Bethesda, MA: Life Sciences Research Office.
201. Lewis KD (2008) The LSRO Report on Differentiating the Health Risks of Categories of Tobacco Products. Bethesda, MA: Life Sciences Research Office.
202. PM Ongoing (and Completed) Legislative and Regulatory Projects for 20010000. 26 Apr 2001. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/arm10c00.
203. FDA Tobacco Jurisdiction Legislation in the 107th Congress House Bills. 20 Jun 2001. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/tth77a00.
204. FDA Tobacco Jurisdiction Legislation in the 107th Congress Side-by-Side Analysis. 19 Mar 2001. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/olz41b00.
205. Reduced-Risk Tobacco Products: Full Disclosure vs. Government Suppression of Truthful and Non-Misleading Information. Feb 2000. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/crx12c00.
206. Myers ML, Wheeler MC, Seffrin JR, Garrison JR. Letter to Congress States Bill “Would Do More to Protect the Tobacco Industry than to Protect the Public Health”. June 25, 2001 http://www.tobaccofreekids.org/press_releases/post/id_0372. (Accessed February 25)
207. S. 982–111th Congress: Family Smoking Prevention and Tobacco Control Act. (2009). In GovTrack.us (database of federal legislation). Retrieved June 19, 2012, from http://www.govtrack.us/congress/bills/111/s982.
208. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Overview Questions: Substantial Equivalence. http://www.fda.gov/TobaccoProducts/ResourcesforYou/ForIndustry/ucm237528.htm. (Accessed Nov. 5, 2012)
209. (2012) Letter to Gregory N. Connolly, Harvard School of Public Health. June 22, 2012.: US Food and Drug Administration Freedom of Information Office.
210. BarnoyaJ, GlantzS (2002) Tobacco industry success in preventing regulation of secondhand smoke in Latin America: the “Latin Project”. Tob Control 11 : 305–314.
211. BarnoyaJ, GlantzSA (2006) The tobacco industry's worldwide ETS consultants project: European and Asian components. Eur J Public Health 16 : 69–77.
212. LandmanA, CorteseDK, GlantzS (2008) Tobacco industry sociological programs to influence public beliefs about smoking. Soc Sci Med 66 : 970–981.
213. World Health Organization (2003) WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control. Geneva, Switzerland.
214. IOM (Institute of Medicine) (2012) Scientific Standards for Studies on Modified Risk Tobacco Products. Washington, DC.
215. GlantzSA, BarnesR, EubanksSY (2009) Compromise or capitulation? US Food and Drug Administration jurisdiction over tobacco products. PLoS Med 6: e1000118.
216. World Health Organization. Guidelines for implementation of Article 5.3 of the WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control. http://www.who.int/fctc/guidelines/article_5_3.pdf. (Accessed 20 Feb 2013)
217. LeeYO, GlantzSA (2011) Menthol: putting the pieces together. Tob Control 20 Suppl 2: ii1–7.
218. MejiaAB, LingPM, GlantzSA (2010) Quantifying the effects of promoting smokeless tobacco as a harm reduction strategy in the USA. Tob Control 19 : 297–305.
219. Philip Morris. Fig 1-Reduced_Risk Product Usage 41.Ppt. 20 Jan 2004. Available: http://legacy.library.ucsf.edu/tid/zie30i00.
Štítky
Interní lékařství
Článek vyšel v časopisePLOS Medicine
Nejčtenější tento týden
2013 Číslo 5- Berberin: přírodní hypolipidemikum se slibnými výsledky
- Léčba bolesti u seniorů
- Příznivý vliv Armolipidu Plus na hladinu cholesterolu a zánětlivé parametry u pacientů s chronickým subklinickým zánětem
- Jak postupovat při výběru betablokátoru − doporučení z kardiologické praxe
- Červená fermentovaná rýže účinně snižuje hladinu LDL cholesterolu jako vhodná alternativa ke statinové terapii
-
Všechny články tohoto čísla
- Measuring Coverage in MNCH: Challenges and Opportunities in the Selection of Coverage Indicators for Global Monitoring
- Measuring Coverage in MNCH: Tracking Progress in Health for Women and Children Using DHS and MICS Household Surveys
- Measuring Coverage in MNCH: Population HIV-Free Survival among Children under Two Years of Age in Four African Countries
- Tobacco Company Efforts to Influence the Food and Drug Administration-Commissioned Institute of Medicine Report An Analysis of Documents Released through Litigation
- Irreconcilable Conflict: The Tobacco Industry and the Public Health Challenge of Tobacco Use
- Providing Impetus, Tools, and Guidance to Strengthen National Capacity for Antimicrobial Stewardship in Viet Nam
- Measuring Coverage in MNCH: New Findings, New Strategies, and Recommendations for Action
- Grand Challenges: Integrating Maternal Mental Health into Maternal and Child Health Programmes
- Measuring Coverage in MNCH: Challenges in Monitoring the Proportion of Young Children with Pneumonia Who Receive Antibiotic Treatment
- Measuring Coverage in MNCH: Current Indicators for Measuring Coverage of Diarrhea Treatment Interventions and Opportunities for Improvement
- Measuring Coverage in MNCH: Evaluation of Community-Based Treatment of Childhood Illnesses through Household Surveys
- Measuring Coverage in MNCH: Accuracy of Measuring Diagnosis and Treatment of Childhood Malaria from Household Surveys in Zambia
- Grand Challenges: Integrating Mental Health Care into the Non-Communicable Disease Agenda
- Integrating Global and National Knowledge to Select Medicines for Children: The Ghana National Drugs Programme
- Grand Challenges: Integrating Mental Health Services into Priority Health Care Platforms
- Disability Transitions and Health Expectancies among Adults 45 Years and Older in Malawi: A Cohort-Based Model
- Comparative Efficacy of Seven Psychotherapeutic Interventions for Patients with Depression: A Network Meta-Analysis
- Measuring Coverage in MNCH: Design, Implementation, and Interpretation Challenges Associated with Tracking Vaccination Coverage Using Household Surveys
- Measuring Coverage in MNCH: A Prospective Validation Study in Pakistan and Bangladesh on Measuring Correct Treatment of Childhood Pneumonia
- Contribution of and Smoking Trends to US Incidence of Intestinal-Type Noncardia Gastric Adenocarcinoma: A Microsimulation Model
- Carriage of in the Upper Respiratory Tract of Symptomatic and Asymptomatic Children: An Observational Study
- Setting Research Priorities to Reduce Mortality and Morbidity of Childhood Diarrhoeal Disease in the Next 15 Years
- Grand Challenges: Improving HIV Treatment Outcomes by Integrating Interventions for Co-Morbid Mental Illness
- Gene Expression Classification of Colon Cancer into Molecular Subtypes: Characterization, Validation, and Prognostic Value
- Domestic Violence and Perinatal Mental Disorders: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- Intimate Partner Violence and Incident Depressive Symptoms and Suicide Attempts: A Systematic Review of Longitudinal Studies
- Effect of Facilitation of Local Maternal-and-Newborn Stakeholder Groups on Neonatal Mortality: Cluster-Randomized Controlled Trial
- Intimate Partner Violence and Population Mental Health: Why Poverty and Gender Inequities Matter
- Assessing Population Aging and Disability in Sub-Saharan Africa: Lessons from Malawi?
- The Paradox of Mental Health: Over-Treatment and Under-Recognition
- Measuring Coverage in MNCH: Determining and Interpreting Inequalities in Coverage of Maternal, Newborn, and Child Health Interventions
- Measuring Coverage in MNCH: Total Survey Error and the Interpretation of Intervention Coverage Estimates from Household Surveys
- Measuring Coverage in MNCH: Indicators for Global Tracking of Newborn Care
- PLOS Medicine
- Archiv čísel
- Aktuální číslo
- Informace o časopisu
Nejčtenější v tomto čísle- Gene Expression Classification of Colon Cancer into Molecular Subtypes: Characterization, Validation, and Prognostic Value
- Domestic Violence and Perinatal Mental Disorders: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- Intimate Partner Violence and Incident Depressive Symptoms and Suicide Attempts: A Systematic Review of Longitudinal Studies
- Measuring Coverage in MNCH: Challenges in Monitoring the Proportion of Young Children with Pneumonia Who Receive Antibiotic Treatment
Kurzy
Zvyšte si kvalifikaci online z pohodlí domova
Současné možnosti léčby obezity
nový kurzAutoři: MUDr. Martin Hrubý
Všechny kurzyPřihlášení#ADS_BOTTOM_SCRIPTS#Zapomenuté hesloZadejte e-mailovou adresu, se kterou jste vytvářel(a) účet, budou Vám na ni zaslány informace k nastavení nového hesla.
- Vzdělávání



