-
Články
Top novinky
Reklama- Vzdělávání
- Časopisy
Top články
Nové číslo
- Témata
Top novinky
Reklama- Videa
- Podcasty
Nové podcasty
Reklama- Kariéra
Doporučené pozice
Reklama- Praxe
Top novinky
ReklamaThe Dirty War Index: A Public Health and Human Rights Tool for Examining and
Monitoring Armed Conflict Outcomes
article has not abstract
Published in the journal: . PLoS Med 5(12): e243. doi:10.1371/journal.pmed.0050243
Category: Policy Forum
doi: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.0050243Summary
article has not abstract
Documentation, analysis, and prevention of the harmful effects of armed conflict on populations are established public health priorities [1–5]. Although public health research on war is increasingly framed in human rights terms [6–13], general public health methods are typically applied without direct links to laws of war. Laws of war are international humanitarian laws and customary standards regarding the treatment of civilians and combatants, mainly described in the four Geneva Conventions of 1949 and their Additional Protocols I and II regarding international and civil conflicts [14]. With notable exceptions [11,15–17], absolute numbers are usually reported (e.g., number of persons killed), without systematic description of the proportional effects of armed conflict, thereby limiting the utility of findings and scope of interpretation.
In this paper, we introduce the “Dirty War Index” (DWI): a data-driven public health tool based on laws of war that systematically identifies rates of particularly undesirable or prohibited, i.e., “dirty,” war outcomes inflicted on populations during armed conflict (e.g., civilian death, child injury, or torture). DWIs are explicitly linked to international humanitarian law to make public health outcomes directly relevant to prevention, monitoring, and humanitarian intervention for the moderation of war's effects. After choosing the particular outcome to be measured, a DWI is calculated as:
Summary Points
-
War, a major public health problem, is a situation where the interests of public health, human rights, and humanitarian law intersect.
-
The DWI is a data-driven public health tool that identifies rates of particularly undesirable or prohibited, i.e., “dirty,” outcomes inflicted on populations during war (e.g., civilian death, child injury, or torture).
-
A DWI is calculated as: (Number of “dirty,” i.e., undesirable or prohibited cases/Total number of cases) × 100.
-
DWIs are designed for direct, easy translation of war's public health outcomes into the human rights, policy, and interdisciplinary work needed to address war's practice.
-
DWIs support monitoring, deterrence, and humanitarian intervention by explicit links to international humanitarian laws and by exposing rates of unacceptable combat outcomes (DWI values) from different weapons or combatant groups.
For example: In Table 1, we measure the DWI ratio of “Number of civilians killed/Total number of civilians and opponent combatants killed” using a casualty dataset for Colombia's civil conflict [18]. Table 2 links this DWI to relevant laws of war. DWI values of 99 for illegal paramilitaries, 46 for guerrillas, and 45 for government forces show that paramilitaries are “dirtiest” in terms of proportion of civilians constituting their victims of unopposed attacks (chi-square = 5,010, degree of freedom [df] = 2, p < 0.001). 99% of paramilitary victims were civilians and only 1% were military opponents. This finding, combined with the paramilitaries' methods (execution by close-range gunfire in massacres), suggests intentional targeting of civilians that requires recognition in Colombia's paramilitary demobilization, disarmament, and reintegration process [19].
Tab. 1. 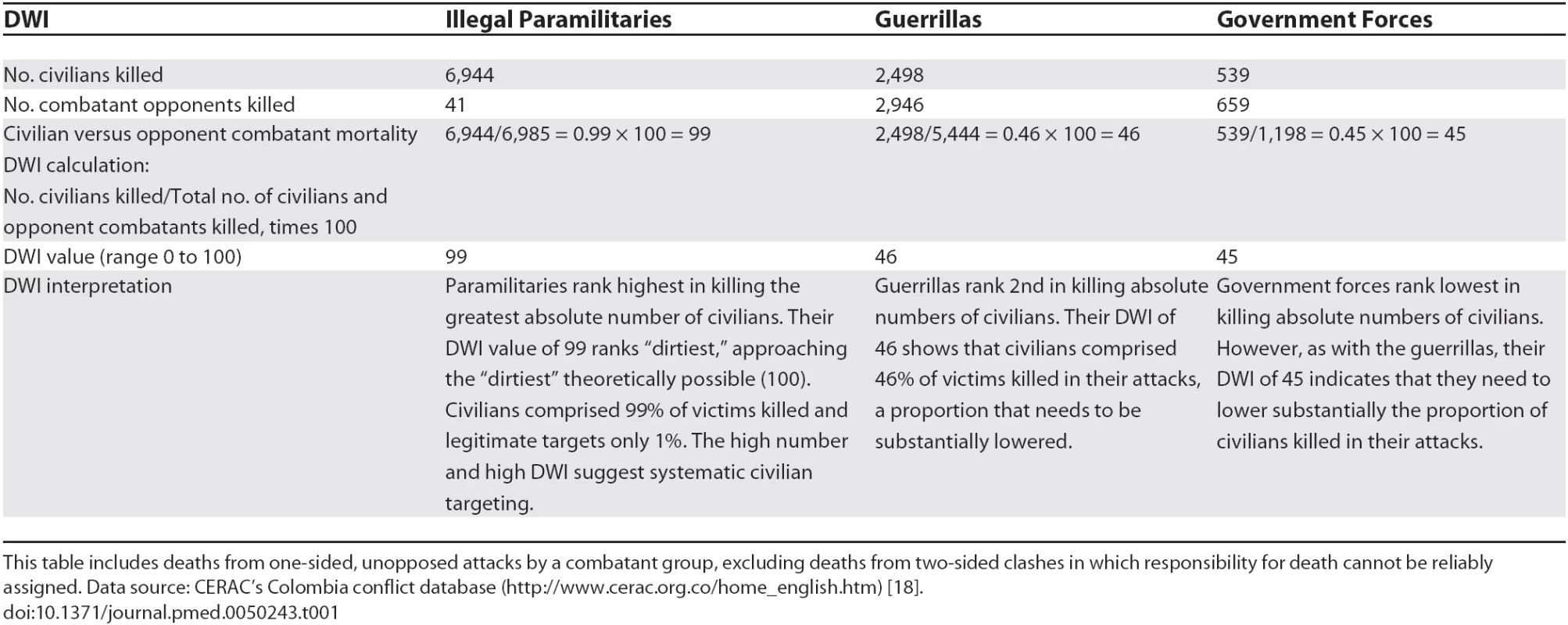
This table includes deaths from one-sided, unopposed attacks by a combatant group, excluding deaths from two-sided clashes in which responsibility for death cannot be reliably assigned. Data source: CERAC's Colombia conflict database (<a href="http://www.cerac.org.co/home_english.htm">http://www.cerac.org.co/home_english.htm</a>) [<em class="ref">18</em>]. Tab. 2. 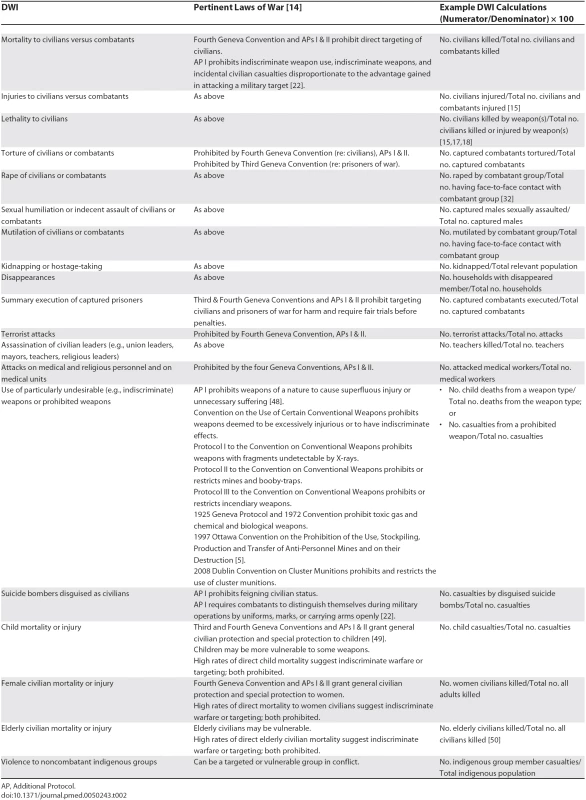
AP, Additional Protocol. As ratios, DWIs complement absolute numbers and lend themselves to comparisons over time, between wars, between weapons, and between warring combatant groups to identify better versus worse performers. Noncombatant wounded-to-killed ratios can provide evidence of war crimes [16]. Proportional “atrocity statistics” [20] from a Darfur survey substantiated US Secretary of State Colin Powell's declaration of genocide and the referral of Darfur's situation to the International Criminal Court [20,21]. By facilitating clear, systematic comparisons, DWIs can help analyze and expose how combatants engage in war and affect populations, thereby increasing the accountability of military and political leaders. This paper describes the theoretical basis and practical applications of the DWI, with brief examples from armed conflicts. More detailed DWI analyses of specific conflicts are planned for future papers.
Calculating and Using DWIs
A DWI can be easily used and understood, facilitating interdisciplinary communication and research on war's effects. DWIs can measure rates of undesirable outcomes from accepted methods (e.g., civilian casualties from aerial bombing of military targets). They can also measure rates of using prohibited, illegitimate methods (e.g., torture), and rates of applying illegitimate methods to especially vulnerable populations (e.g., torturing children) to describe rates of exceptional atrocity. However, the mere application of DWI analysis to a combatant group does not indicate that it is “dirty”: a DWI ratio simply identifies how often, if at all, the group is linked with the particular undesirable outcome being measured, facilitating comparisons. To illustrate, we draw on data from B'Tselem (http://www.btselem.org/english/statistics/Index.asp), a nongovernmental organization that monitors casualties from the Israeli-Palestinian conflict. We apply a “female mortality DWI” (Number of females killed/Total number killed) to conflict-related killings from September 29, 2000 to April 30, 2007: Israeli security forces killed 213 females among 4,057 Palestinians (DWI = 5). Palestinians killed 283 females among 705 Israeli civilians (DWI = 40). Palestinians killed 10 females among 317 Palestinians (DWI = 3). Comparison of actors' DWIs shows significantly higher discrimination of female from male targets by Israeli security forces and by Palestinian actors when targeting Palestinians, and lower discrimination of female from male targets when Palestinian actors target Israeli civilians (chi-square = 833, df = 2, p < 0.001).
The best possible DWI value is 0, indicating that the objectionable outcome is identified in no measured cases. The worst possible DWI value is 100, indicating that the objectionable outcome is identified in 100% of measured cases. Any rate above 0 for prohibited actions or war crimes is unacceptable, and eliminating violations is imperative. DWIs for undesirable outcomes are less straightforward. The highly undesirable outcome of civilian harm is not prohibited by laws of war if combatants do everything feasible to distinguish between civilians and military targets (the principle of distinction), if they attempt to minimize incidental harm to civilians, and if they intend to avoid harming civilians in excess of anticipated military goals (the principle of proportionality) [1,22,23]. Civilian harm is also balanced against the “military necessity” of objectives [24]. Though what is feasible, proportional, or necessary is highly subjective [22–24], clearly the lowest possible rates should be sought for undesirable outcomes such as “incidental” civilian death. High DWI values for undesirable outcomes indicate extreme destruction, signal the need for close scrutiny, and may suggest war crimes.
Tables 2 and 3 list specific DWIs, their pertinent laws of war, and example calculations. Table 2 lists DWIs for undesirable or prohibited aggression in armed conflict. DWIs can be analyzed by demographic subgroup for indiscriminate warfare, disproportionate effects of targeting, or particular vulnerability to weapons. For example, with “casualties” defined as injuries or deaths, a “child casualty DWI” (Number of child casualties/ Total number of casualties) applied to weapons-casualty data from Chechnya [25] gives the following child casualty ratios for different explosive devices: antitank landmines (34/223, DWI = 15), antipersonnel landmines (223/1,004, DWI = 22), booby traps (65/214, DWI = 30), and other unexploded ordnance (UXO) (255/892, DWI = 29). DWIs indicate that in Chechnya, UXO and booby traps are more dangerous to children than landmines and significantly “dirtier” in this respect (chi-square = 25.0, df = 3, p < 0.001).
Tab. 3. 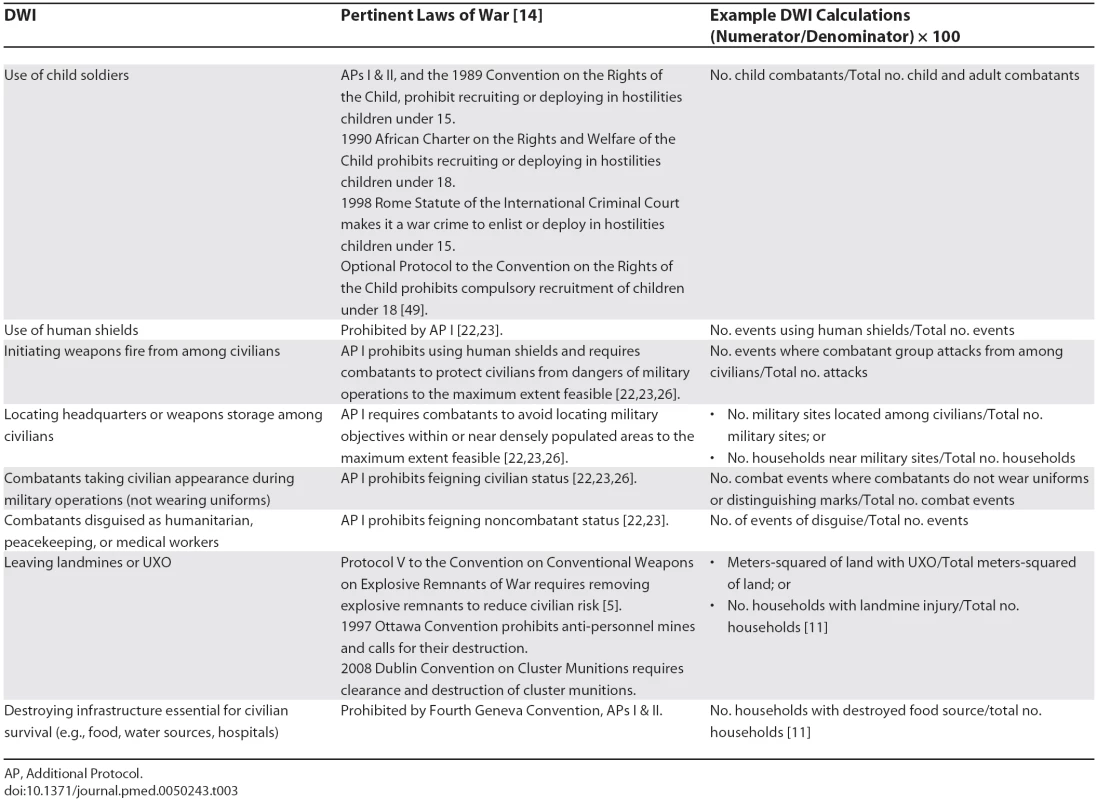
AP, Additional Protocol. Table 3 lists DWIs for unacceptable endangerment in armed conflict [14,23,24]. To illustrate, we apply the last DWI listed, “Destroying infrastructure essential for civilian survival (food, water, hospitals),” to survey data from eastern Burma where the Burmese military junta is in conflict with ethnic minority groups. The Burmese military regime destroyed or stole food from 472 of 1,813 surveyed households [11]. The Burmese military's DWI of 26 indicates a 26% rate of committing the humanitarian violation of destroying civilian food sources, associated in the study with significantly greater odds of household landmine injury (perhaps due to foraging for food), child malnutrition, and death [11].
In Table 4 we analyze the Northern Ireland conflict for two complementary DWIs: aggressive acts (killing civilians) and endangerment to civilians (by not wearing uniforms). Combatants who blur distinctions between themselves and civilians transfer their risk onto civilians [23,24]. Endangerment of noncombatants can be a byproduct of a method, as when guerrilla forces hide “among the people,” taking the battlefield to civilians [23,24,26]. Endangerment can also be a direct goal. As described by Viet Cong leaders [27] and American soldiers [23] in the Vietnam War, Viet Cong forces trained children to throw grenades at South Vietnamese and American soldiers, partly to provoke opponents to shoot children and bring shame to themselves and their force. Child soldiers are more often killed or injured than adult soldiers, being deployed at the front line, to lay or clear mines, or as suicide bombers because they provoke less suspicion [3,28,29]. To illustrate the issue of variable access to valid data for DWI applications, precise data for calculating child solider DWIs (Table 3) may be difficult to obtain for some conflicts. However, DWIs for using child soldier suicide bombers (Tables 2 and 3) could be highly accurate due to extensive media coverage of suicide attacks.
Tab. 4. 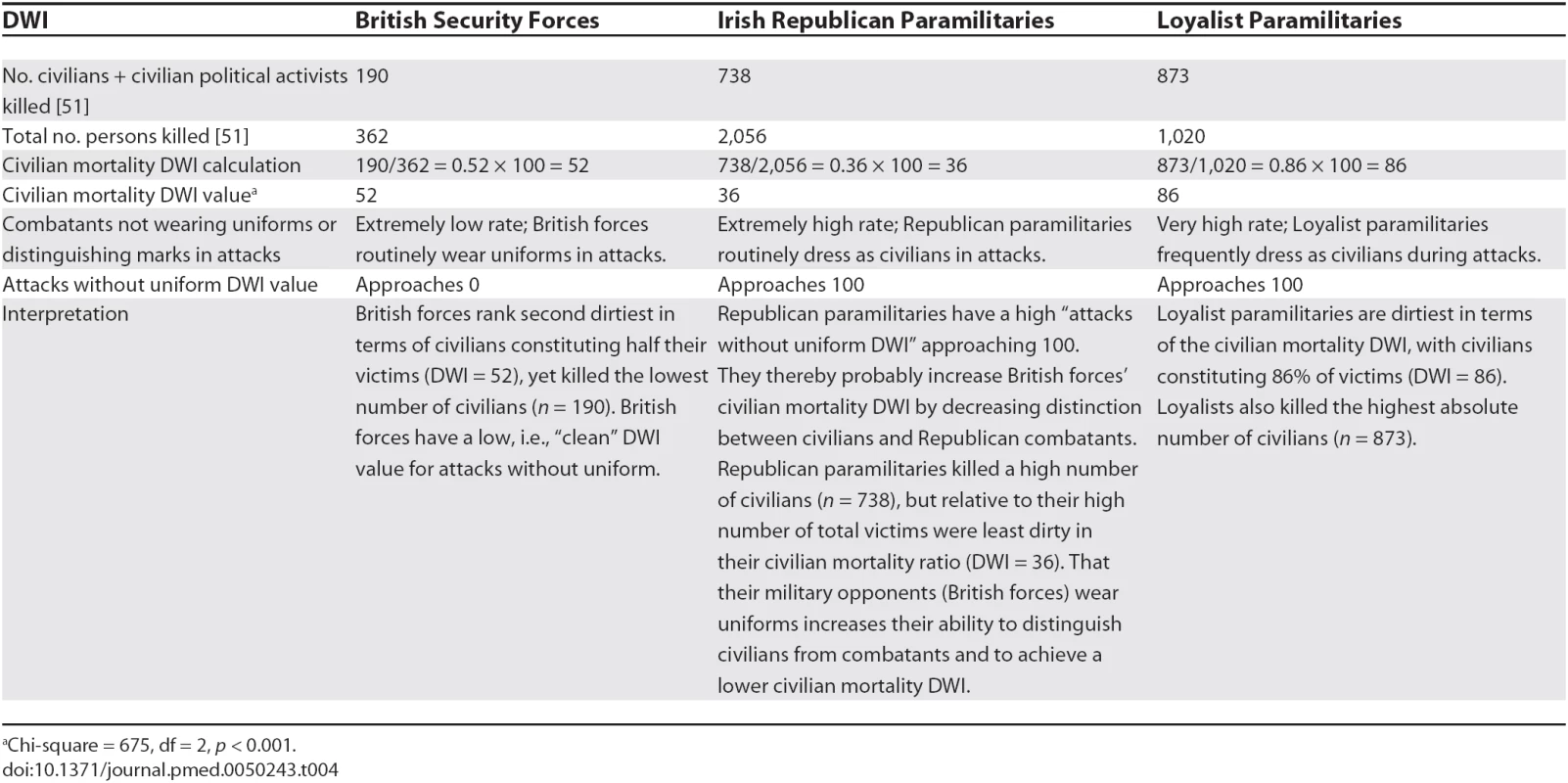
<sup>a</sup>Chi-square = 675, df = 2,<i>p</i> < 0.001. DWI analysis can use any data source (media reports, epidemiological surveys, coroners' reports) as long as the data are adequately valid, accurate, and comprehensive. DWI analysis can be applied to event-based data or to aggregated data covering, for example, a year, a phase, or a whole conflict. Analysis of all DWIs supported by good data provides fuller description of a conflict and combatant behavior. A qualitative understanding of a conflict's nature and context is necessary for DWI application and interpretation. When possible, analysis should recognize when combatants avoid inflicting dirty outcomes, i.e., “clean” combat. DWIs suggest valuable data for prospective inclusion in conflict monitoring.
Considerations
When DWIs are used to compare combatant groups or methods, it should not be assumed that those with the highest values are simply the dirtiest. Nor should it be assumed that lower DWI values “don't count.” A group may have a low DWI for recorded civilian mortality, but high DWIs for assassinating civilian leaders and disappearances. Another group may have low DWIs generally, and a very low DWI for torturing prisoners, but torture breaches the precepts of humanity utterly so that to have a measurable rate at all is deplorable.
DWIs reflect, in part, local conditions. For example, the lethality of civilian injuries reflects local treatment technology and access. It may therefore seem incorrect to compare DWIs for civilian lethality when health services differ. Similarly, it may seem unfair to compare child mortality DWIs between a conflict where children comprise a large proportion of the population and so are more likely to be killed and a conflict where children are few. However, researchers should not adjust for such factors when comparing DWIs across settings. This is because actors in armed conflict know, or are morally obliged to know, local resources and demographics and their implications for civilian harm. Combatants are obliged to take proportionately more care not to kill children when waging war in a child-dense population. Responsibility for dirty outcomes is not ameliorated by local conditions.
As for any conflict analysis [2,3,30], DWI selection, application, and interpretation must recognize the potential, varied biases of data sources and of particular DWIs. Conflicts are highly politicized, and combatants, supporters, and detractors have always tried to manipulate reports of war outcomes. Combatants may attempt to construct more favorable DWIs not only by decreasing dirty combat, but by concealing dirty outcomes, or by misrepresenting or provoking opponents' dirty outcomes. For example, a group might attempt to raise an opponent's child mortality DWI by using child soldiers or children as human shields.
Some DWI outcomes, such as injuries, may tend to be under-reported [16]. War-associated rape may be difficult to measure due to stigma and under-reporting, though substantial reports exist [21,24,31,32]. Although bias can affect DWI values, as ratios DWIs are relatively less affected by under - or over-counting than absolute numbers. For example, if a population generally under-reports war-related rape by 40%, this does not bias comparing rates between different combatant groups.
DWIs, complemented by absolute numbers, can suggest strategic aspects of actors' methods. For example, systematic civilian targeting is suggested by combined findings of: many events killing or injuring civilians; high ratios of civilian versus combatant mortality; frequent use of methods causing high civilian casualties; frequent use of methods causing high civilian lethality; and high rates of civilian harm from methods that are inherently “targeted” (handguns, machetes). Such proportional and numerical findings on civilian casualties have been used as evidence in International Criminal Court trials to establish systematic patterns indicating war crimes [33].
DWIs Measure Outcomes, Not Justifications or Intentions
DWIs focus on whether the practice of war is just (jus in bello) and ignore whether the reason for war is just (jus ad bellum), separating two logically distinct moral issues in war [23]. We focus on practical outcomes because justifications for war are contested, are used to legitimize dirty combat, and can bias examination of war's impact [24,27,34–36]. Combatants and their supporters may believe or describe methods as just, whether the method is suicide bombing [24,37,38] or the World War II targeting of civilians by Germany and by the Allies with carpet bombing, fire-bombing, and atomic bombs directed at cities [23,24,26,27].
Although intentions affect combat outcomes, such as civilian mortality rates [16,27,34,35], we separate DWIs from intentionality for the following reasons. Intentions are contested, obscured, and distorted [3,35]. Dirty outcomes can result from malicious intent, beneficent intent, or recklessness (lack of intent to take due care). Frequently, combatant violence that appears wanton, sadistic, or vengeful (e.g., rape, mutilation) is mobilized by political actors for hidden strategic aims [24,27,35,39,40]. Combatants' intended effects may be disrupted by targets or adversaries [41]. Individual combatant behavior reflects overriding goals and sociocultural aspects of larger groups [34,35,38].
Accommodating intentions or justifications in DWIs would imply that good intentions or a “just war” attenuate responsibility for bad outcomes; an implication that is morally and legally refuted [36]. DWIs therefore only recognize the crucial matter of outcomes: the killing, injury, or abuse of individuals and populations who should be protected from war.
Potential Deterrent Effect of the Dirty War Index
We choose the term “Dirty War Index” for three reasons. First, it unites moral, humanitarian, and scientific values inherent to most armed conflict research. Second, it avoids euphemisms that sanitize descriptions of war-induced public harm [12,13,27,42]. Third, emotional and cultural implications of “dirty” versus “clean” may heighten the sensitivity of combatant groups to the index, increasing its potential deterrent effect. No nation or combatant group wants to be considered “dirty” or described as dirtier than others.
Increased accountability can have a deterrent effect in armed conflict and encourages adherence to international humanitarian law; an important element in preventing violence towards noncombatants [1,24]. DWIs increase scrutiny and accountability specifically for dirty war methods. DWIs are analogous to corruption and bribery indices used by nongovernmental organizations and the World Bank to improve international governance through public monitoring and ranking governments by corruption [43,44]. In Better: A Surgeon's Notes on Performance [45], Atul Gawande describes how systematic analysis of war casualties reveals problems and suggests solutions, and how identifying exemplary performers can improve general performance. The DWI is developed for systematic, data-driven identification of relatively good versus bad performance, heightening its potential to stimulate positive change.
Military and political leaders not only want to win wars. They also seek superior moral authority [23]. Moral authority has social currency, creating better access to material resources, support, and security within local and international communities. To improve behavior in combatants and politicians insufficiently motivated by altruism, harnessing such self-interest is crucial. Exposure of atrocities through DWIs can put reputation, legitimacy, future resources, threat of retaliation, or power itself at stake [24].
As comparative rates, DWIs evoke the potential for change. The possibility of becoming “cleaner” may appeal to some offenders [24]. Actors may compete for better outcomes relative to military opponents, relative to in-group political competitors, or relative to themselves over time. A DWI's potency can be increased by engagement with social, cultural, and religious values of actors and their communities: honor versus dishonor [24], gaining versus losing “face,” shame versus pride, dignity versus humiliation [37,46], sacred versus profane [37], and valuing mercy and the lives of innocents [47]. Terms other than “Dirty War Index,” e.g., the “Dishonorable War Index,” could be used to greater effect in different contexts.
War and its destruction trigger emotions and self-interests that can obscure analysis by threatening us so that we revert to familiar prejudices, reactions, and cognitive frameworks. Through a public health approach using valid, precise proportional rates as outcomes, DWIs can help us and our audiences to detach from political biases and break through psychological denial when considering actors or methods in war. DWIs can present conflict data from a new perspective, thereby encouraging actors in war to reassess their combat methods, accountability, and interests.
Linked Perspectives
This Policy Forum is further discussed in two PLoS Medicine Perspectives:
Taback N (2008) The Dirty War Index: Statistical issues, feasibility, and interpretation. PLoS Med 5(12): e248. doi:10.1371/journal.pmed.0050248
Sondorp E (2008) A new tool for measuring the brutality of war. PLoS Med 5(12): e249. doi:10.1371/journal.pmed.0050249
Zdroje
1. Krug
EG
Dahlberg
LL
Mercy
JA
Zwi
AB
Lozano
R
editors
2002
World report on violence and health. World Health
Organization.
Available: http://www.who.int/violence_injury_prevention/violence/world_report/en/.
Accessed 4 November 2008
2. Murray
CJL
King
G
Lopez
AD
Tomijima
N
Krug
EG
2002
Armed conflict as a public health problem.
BMJ
324
346
349
3. Mack
A
editor
2008
Human Security Brief 2007. Human Security Report Project.
Available: http://www.humansecuritybrief.info/access.html. Accessed 4 November
2008
4. Coupland
R
2007
Security, insecurity and health.
Bull World Health Organ
85
181
184
5. Cobey
JC
Raymond
NA
2001
Antipersonnel land minds: A vector for human suffering.
Ann Intern Med
134
421
422
6. Annas
GJ
1998
Human rights and health—The Universal Declaration of Human Rights
at 50.
N Engl J Med
339
1778
1781
7. Flanagin
A
2000
Human rights in the biomedical literature: The social responsibility of
medical journals.
JAMA
284
618
619
8. Levy
BS
Sidel
VW
editors
2008
War and public health
2nd edition
New York
Oxford University Press
486
9. van Ommeren
M
Sharma
B
Prasain
D
Poudyal
BN
2002
Addressing human rights violations: A public mental health perspective on
helping torture survivors in Nepal.
In
de Jong
J
editor
Trauma, war, and violence: Public mental health in socio-cultural context
New York
Kluwer Academic
259
281
10. Thoms
ONT
Ron
J
2007
Public health, conflict and human rights: Toward a collaborative research
agenda.
Confl Health
1
11
11. Mullany
LC
Richards
AK
Lee
CI
Suwanvanichkij
V
Maung
C
2007
Population-based survey methods to quantify associations between human
rights violations and health outcomes among internally displaced persons in eastern
Burma.
J Epidemiol Community Health
61
908
914
12. McDonnell
SM
Bolton
P
Sunderland
N
Bellows
B
White
M
2004
The role of the applied epidemiologist in armed conflict.
Emerg Themes Epidemiol
1
4
13. Nathanson
V
2000
Preventing and limiting suffering should conflict break out: The role of
the medical profession.
International Review of the Red Cross
839
601
615
Available: http://www.icrc.org/Web/Eng/siteeng0.nsf/html/57JQQ5. Accessed 4 November
2008
14. International Committee of the Red Cross
2008
International humanitarian law.
Available: http://www.icrc.org/Web/Eng/siteeng0.nsf/htmlall/ihl?OpenDocument.
Accessed 4 November 2008
15. Coupland
RM
2001
Armed violence.
Med Glob Surviv
7
33
37
16. Coupland
RM
Meddings
DM
1999
Mortality associated with use of weapons in armed conflicts, wartime
atrocities, and civilian mass shootings: Literature review.
BMJ
319
407
410
17. Taback
N
Coupland
R
2005
Towards collation and modeling of the global cost of armed violence on
civilians.
Med Confl Surviv
21
19
27
18. Restrepo
J
Spagat
M
Vargas
JF
2004
The dynamics of the Colombian civil conflict: A new data
set.
Homo Oeconomicus
21
396
428
19. Spagat
M
2006
Colombia's paramilitary DDR: Quiet and tentative success.
Available: http://www.cerac.org.co/pdf/UNDP_DDR_V1.pdf. Accessed 4 November
2008
20. Straus
S
2006
‘Atrocity statistics' and other lessons from
Darfur.
In
Totten
S
Markusen
E
editors
Genocide in Darfur: Investigating the atrocities in the Sudan
New York
Routledge
189
195
21. Totten
S
Markusen
E
editors
2006
Genocide in Darfur: Investigating the atrocities in the Sudan
New York
Routledge
284
22. Schmitt
MN
2005
Precision attack and international humanitarian law.
International Review of the Red Cross
87
445
466
23. Walzer
M
1977
Just and unjust wars: A moral argument with historical illustrations
New York
Basic Books
361
24. Slim
H
2007
Killing civilians: Method, madness and morality in war
London
Hurst & Company
319
25. Bilukha
OO
Tsitsaev
Z
Ibragimov
R
Anderson
M
Brennan
M
2006
Epidemiology of injuries and deaths from landmines and unexploded ordnance
in Chechnya, 1994 through 2005.
JAMA
296
516
518
26. Smith
R
2005
The utility of force: The art of war in the modern world
London
Allen Lane, Penguin Group
428
27. Grossman
D
1995
On killing: The psychological cost of learning to kill in war and society
New York
Back Bay Books/Little, Brown and Company
366
28. Coalition to Stop the Use of Child Soldiers
2008
Child soldiers.
Available: http://www.child-soldiers.org/childsoldiers. Accessed 4 November
2008
29. McKay
S
2005
Girls as “weapons of terror” in Northern Uganda and
Sierra Leonean rebel fighting forces.
Studies in Conflict & Terrorism
28
385
397
30. Romeu
JL
2008
Statistical thinking and data analysis: Enhancing human rights
work.
In
Asher
J
Banks
D
Scheuren
FJ
editors
Statistical methods for human rights
New York
Springer
65
85
31. Kolbe
AR
Hutson
RA
2006
Human rights abuse and other criminal violations in Port-au-Prince, Haiti:
A random survey of households.
Lancet
368
864
873
32. Physicians for Human Rights
2002
War-related sexual violence in Sierra Leone: A population-based
assessment.
Available: http://physiciansforhumanrights.org/library/report-sierraleone-2000.html.
Accessed 4 November 2008
33. Spirer
HF
Seltzer
W
2008
Obtaining evidence for the International Criminal Court using data and
quantitative analysis.
In
Asher
J
Banks
D
Scheuren
FJ
editors
Statistical methods for human rights
New York
Springer
195
226
34. Appy
CG
2006
Vietnam: The definitive oral history told from all sides
London
Ebury Press
574
35. Kalyvas
SN
2006
The logic of violence in civil war
New York
Cambridge University Press
485
36. Bugnion
F
2002
Just wars, wars of aggression and international humanitarian
law.
International Review of the Red Cross
84
523
546
37. Atran
S
2006
The moral logic and growth of suicide terrorism.
Wash Q
29
127
147
38. Bloom
A
2006
Dying to kill: Motivations for suicide terrorism.
In
Pedahzur
A
editor
Root causes of suicide terrorism: The globalization of martyrdom
London
Routledge
25
53
39. Richards
P
2004
Fighting for the rain forest: War, youth & resources in Sierra
Leone
Portsmouth (NH)
Heinemann
198
40. Leites
N
Wolf
C
Jr
1970
Rebellion and authority: An analytic essay on insurgent conflicts
Chicago
Markham
174
41. Harrison
M
2006
Bombers and bystanders in suicide attacks in Israel,
2000–2003.
Studies in Conflict & Terrorism
29
187
206
42. Zwi
AB
2004
How should the health community respond to violent political
conflict.
PLoS Med
1
e14
doi:10.1371/journal.pmed.0010014
43. Transparency International
2008
About Transparency International.
Available: http://www.transparency.org/about_us. Accessed 4 November 2008
44. World Bank
2007
Governance matters 2007: Worldwide governance indicators,
1996–2006.
Available: http://info.worldbank.org/governance/wgi/index.asp. Accessed 4 November
2008
45. Gawande
A
2007
Better: A surgeon's notes on performance
London
Profile Books
273
46. Lindner
E
2006
Making enemies: Humiliation and international conflict
Westport (CT)
Praeger Publishers
224
47. al-Oadah
S
2007
A Ramadan letter to Osama bin Laden.
Available: http://www.islamtoday.com/printmenice.cfm?cat_id=29&sub_cat_id=1521.
Accessed 4 November 2008
48. Coupland
RM
2005
Ballistic trauma, armed violence and international law.
In
Mahoney
PF
Ryan
JM
Brooks
AJ
Schwab
CW
editors
Ballistic trauma: A practical guide
2nd edition
London
Springer-Verlag
122
134
49. International Committee of the Red Cross
2003
Children in war: Summary table of IHL provisions specifically applicable to
children.
Available: http://www.icrc.org/web/eng/siteeng0.nsf/html/5fflj5/$file/ang03_04a_tableaudih_total_logo.pdf?openelement.
Accessed 4 November 2008
50. Spiegel
PB
Salama
P
2000
War and mortality in Kosovo, 1998–99: An epidemiological
testimony.
Lancet
355
2204
2209
51. Sutton
M
2002
An index of deaths from the conflict in Ireland. CAIN Web
Service.
Available: http://cain.ulst.ac.uk/sutton/index.html. Accessed 6 November
2008
Štítky
Interní lékařství
Článek vyšel v časopisePLOS Medicine
Nejčtenější tento týden
2008 Číslo 12- Berberin: přírodní hypolipidemikum se slibnými výsledky
- Léčba bolesti u seniorů
- Příznivý vliv Armolipidu Plus na hladinu cholesterolu a zánětlivé parametry u pacientů s chronickým subklinickým zánětem
- Jak postupovat při výběru betablokátoru − doporučení z kardiologické praxe
- Červená fermentovaná rýže účinně snižuje hladinu LDL cholesterolu jako vhodná alternativa ke statinové terapii
-
Všechny články tohoto čísla
- The Prevalence of Mental Disorders among the Homeless in Western Countries: Systematic Review and Meta-Regression Analysis
- Health and Human Rights Concerns of Drug Users in Detention in Guangxi Province, China
- African AIDS Vaccine Programme for a Coordinated and Collaborative Vaccine Development Effort on the Continent
- Mental Disorders among Homeless People in Western Countries
- The Disconnect between China's Public Health and Public Security Responses to Injection Drug Use, and the Consequences for Human Rights
- What Is the Future for Global Case Management Guidelines for Common Childhood Diseases?
- The Dirty War Index: A Public Health and Human Rights Tool for Examining and Monitoring Armed Conflict Outcomes
- Poverty and Cataract—A Deeper Look at a Complex Issue
- The Dirty War Index: Statistical Issues, Feasibility, and Interpretation
- A New Tool for Measuring the Brutality of War
- Accessing Maternal Health Services in Eastern Burma
- “Efforts to Reprioritise the Agenda” in China: British American Tobacco's Efforts to Influence Public Policy on Secondhand Smoke in China
- Homelessness Is Not Just a Housing Problem
- PLOS Medicine
- Archiv čísel
- Aktuální číslo
- Informace o časopisu
Nejčtenější v tomto čísle- Homelessness Is Not Just a Housing Problem
- The Dirty War Index: A Public Health and Human Rights Tool for Examining and Monitoring Armed Conflict Outcomes
- Accessing Maternal Health Services in Eastern Burma
- Poverty and Cataract—A Deeper Look at a Complex Issue
Kurzy
Zvyšte si kvalifikaci online z pohodlí domova
Současné možnosti léčby obezity
nový kurzAutoři: MUDr. Martin Hrubý
Všechny kurzyPřihlášení#ADS_BOTTOM_SCRIPTS#Zapomenuté hesloZadejte e-mailovou adresu, se kterou jste vytvářel(a) účet, budou Vám na ni zaslány informace k nastavení nového hesla.
- Vzdělávání




